302
Exercises in chest osteochondrosis

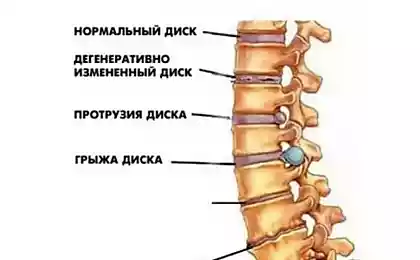
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine - it is characterized by degenerative and dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs of the thoracic region. For its treatment, special exercises for chest osteochondrosis are successfully used.
Features of the thoracic department and thoracic osteochondrosis
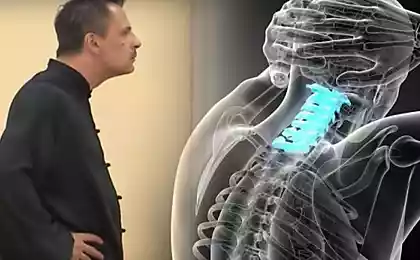
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is a less common disease than osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic regions. In many ways, this feature is associated with the structure of the thoracic department. The thoracic part of the spine has 20 vertebrae connected to the ribs through the joints. The front ribs are connected with each other by a sternum, this creates a rigid and durable frame, which consists of a spine and ribs with a sternum. All this protects the internal organs of the chest. The links of the thoracic spine differ from other vertebrae in that they have a small height and long spiny processes located as shingles above each other. The freedom of movement of this part of the spine is significantly limited due to this special structure.
Intervertebral discs are less injured in the thoracic region than the movable discs of the neck and lower back. Therefore, degenerative and dystrophic changes in the thoracic region occur more slowly and much less often. Due to the natural bulge of the spine back, i.e. kyphosis, in the thoracic region, the load is distributed properly, while the anterior and lateral sections receive greater tension. For this reason, it is the anterior and lateral sections of the spine that suffer from growing osteophytes. They are much less likely to form on their posterior surface due to the absence of nerve roots and the lining of the spinal cord.
The main reason why chest osteochondrosis develops is poor nutrition of the intervertebral discs, improperly distributed load, this leads to a violation of metabolic processes in the tissues and as a result, dystrophic pathologies develop. Most often, people turn to specialists who are forced by their profession to be in an uncomfortable position for a long time, sitting at a desk in the office or driving a car. At risk are also patients who have scoliosis, because it creates an uneven load on the vertebrae.
Pain in the thoracic spine is caused by a dystrophic process on the joints located between the vertebrae. The cause of pain may also be spondyloarthritis, osteoarthritis in the rib-vertebral joints and transverse rib joints. This process often causes narrowing of the holes between the vertebrae. In this case, compression of nerve fibers and roots occurs, as a result of which pain appears in the innervation area of the affected nerve. If it happens that the compression had on the sympathetic nerves responsible for the work of the internal organs, then various violations in their work may occur.
Symptoms and similarity with other diseases Breast osteochondrosis provokes pain in the shoulder blades or in the thoracic region along the spine. Pain may increase during movement or during exercise. But exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis must be performed so that the disease does not progress, and to restore your spine. With pinching of nerve fibers, pain in the heart, liver and other pathologies in the functioning of organs can occur.
Pain in the chest is divided into two types:
- Dorsalgia (or back pain) – prolonged pain in the affected discs. These sensations and discomfort are caused by low mobility of the cervical-thoracic region and the lumbo-thoracic region. Pain is mild.
- Dorsago – the pain can be described as acute and intense, can look like a sudden attack. There may be difficulty breathing and limited muscle ability to move.
Symptoms of chest osteochondrosis
- Pain between the shoulder blades and below. It is not uncommon to shoot through the intercostal nerves. The pain becomes stronger during active movements;
- A symptom that is similar to coronary heart disease is pain in the left half of the thoracic region. Therefore, it is important to undergo electrocardiography for osteochondrosis;
- In the thoracic region, mobility decreases. This is also characteristic of some diseases. Establishing a reliable cause of limited activity, an x-ray examination is carried out;
- Violation of sexual function;
- Numbness in the chest;
- Pain in the heart, stomach, liver;
- Shingles pain in the chest, becomes stronger under an hour of movement and breathing.
Intervertebral hernia Intercostal neuralgia Disc protrusion Vertebrogenic radiculopathy Vertebrogenic thoracalgia (chest pain) Vertebrogenic, noncoronagenic cardialgia In thoracic osteochondrosis there is a feature that it can easily be confused with the symptoms of completely other diseases. No wonder in medical circles it is called “chameleon disease”. It can be disguised as a heart attack, angina, pain of cardiovascular diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, appendicitis, cholecystitis, peptic ulcer, gastritis, etc. Experienced specialists in order to distinguish this disease from others should conduct a comprehensive diagnosis.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is aimed primarily at eliminating pain and further prevention of the acute form of the disease. An obligatory part of the process of recovery of the spine is physical therapy, that is, the performance of special physical exercises for chest osteochondrosis, which are described in this article. But it is unnecessary to choose exercises yourself, especially if you already have osteochondrosis and especially if it is started. Consultation with a specialist is required. You may also need to undergo treatment and remove the symptoms and causes of the disease.
What to do so that chest osteochondrosis does not threaten you?
- Do not do excessive physical exertion.
- Do not overcool, keep the back dry and warm.
- Strengthen the muscles of the back, exercise, move more, watch your posture.
- The main enemies of the spine are humidity and cold.
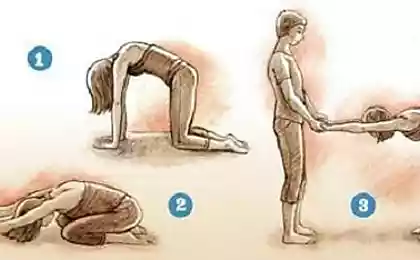
Exercises in thoracic osteochondrosisLFC - a set of physical exercises with proper breathing, which are aimed at prevention, restoration and treatment of organs, nervous system, musculoskeletal system, etc. The specialist will prescribe special exercises that correspond to the diseases and capabilities of the patient.
Before you learn and apply exercises for the thoracic department, try to eliminate the factors that favor the development of this disease. Learn to stand and sit properly.
If you have to stand for a long time, spread the weight on both legs evenly. The position of the shoulders is important, they should not move forward and slouch.
Sit right with a straight back. The buttocks should be located on the back of the seat. The lumbar is adjacent to the back of the chair, it is desirable that the back repeats the physiological bend of the back. The shoulders are relaxed and straight. Your feet should be completely on the floor.
To reduce the risk of pain in the chest, systematically perform specially designed exercises for chest osteochondrosis. It is advisable to perform them in the morning and evening and, if possible, during the day.
So, here are the exercises for the treatment and prevention of chest osteochondrosis and other back problems.
You need to stand up straight, your body should not be tense, relax it, the spine should be located on the same line. Straighten your legs and strain a little. The feet are parallel. Head straight, look forward. Hands hanging on the sides of the body.
Bend your hands at the elbows and raise your hands to the height of the shoulders, easily throw your hands back, exhale, at the same time put your chest forward. Return to the starting position on exhalation. Do 10-15 repetitions of the exercise, aligning them with the rhythm of breathing.
The starting position is identical to that of the previous exercise. Get behind your back clenched fists and start pressing them on the vertebrae. With the back of the hand, knuckles, press, massage and gradually move along the spine, treating as many vertebrae as possible.
Put your hands on the table (for example, written), the elbows are located under the rib arches, and the legs do not come off the floor. When tilting your body to the table, try to feel how the spine stretches. Tension hold 10 seconds, and the number of executions – 5 times.
You stand upright and your hands hang in a relaxed position. Rotate the hull sideways. Try to feel the tension of the back muscles.
The following exercise for chest osteochondrosis can be performed even without getting up from the chair. But the back of this chair should be the appropriate height, i.e. at the level of your shoulder blades. Put your hands behind your head and rot, leaning on the kick of the chair, this position will hold for a few seconds. Do 5-10 repetitions.
Stand up and clutch your hands behind your back into the lock, strain your hands. Change the position of your hands and repeat again. 5-10 replays.
Raise your shoulders in turn and then raise them at the same time. You can lift one shoulder up and the other pull down. The cervical and upper chest are well worked out. Once you’re done, you can start moving your shoulders. Put your shoulders forward and pull them back.
Mandatory, with cervical-thoracic osteochondrosis, rotation of the hands forward and backward. These movements work well (as well as the previous one) with the upper segment.
This exercise for thoracic osteochondrosis can perfectly involve the entire thoracic department. You have to do sideways tilts. In the first, easier version, you need to reach for the kneecap, making slopes sideways with your hands pressed to the body. So in the upper segments of the thoracic department, the volume of movements increases. A more difficult option is that the same movements are made, only the hands are raised above the head. With this option, you will work on the lower and upper segments.
Another exercise on the lower segments. You need to be flat, put your hands behind your back and connect them under the shoulder blades into the castle. Now bend backwards with all your might, and apply pressure with your hands in the opposite direction. Hold the effort for a few seconds, then return to the I.P., relax and repeat the exercise.
Get on the bed. Try to strain the legs, abdominal abs and shoulder girdle as much as possible. Hold the tension for a few seconds, then completely relax. Repeat the exercise to a feeling of slight fatigue, you should not overwork. Stop working if you feel pain.
This exercise is also done lying on the bed, the legs should be bent at the knees. When bending your torso, touch your knee to your nose. Take the I.P., then touch the nose with the other knee. If you change your knees several times, repeat the exercise. Movements should be smooth, avoiding sudden movements. If it is difficult for you, you can support your leg with your hand.
With osteochondrosis of any part of the spine, you need to carefully perform exercises, including those given in this become. Not all exercises are given, there are others. You can get acquainted with them in the article "Physical exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region", some of them will be repeated, or on other sites, video clips or with your doctor.
Sleeping on a fairly hard bed is a wonderful prevention of various problems associated with the spine. The spine in this case is restored overnight and in the morning the person feels more rested and full of strength.
Listen carefully to your feelings, your body. If some exercises cause pain, and it is given to you extremely hard, it may be excluded and replaced with another, or do it in a lower amplitude.
And yet, when you are affected by osteochondrosis several parts of the spine, it is better not to exercise for osteochondrosis yourself. Contact a qualified specialist. It will help you to make exercise therapy taking into account your characteristics, because not all exercises at first can suit you. After all, general recommendations can be used at the initial stage of the development of this ailment.
Be healthy, take care of yourself, live an active and fulfilling life.
Source: lubim-zhizn.ru/fizicheskaya-kultura/uprazhneniya-pri-grudnom-osteoxondroze-2.html
The eternal present: Kirill Kobrin of Baudelaire, Marx and revolution
Amazing walking trees of lake Baikal