490
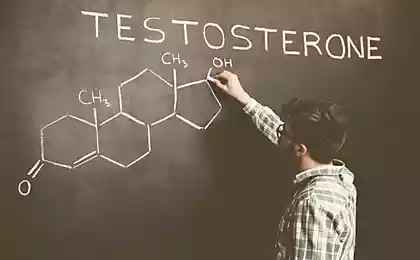
Zinc: High testosterone, a healthy prostate, nails without white spots
Zinc (Zn)
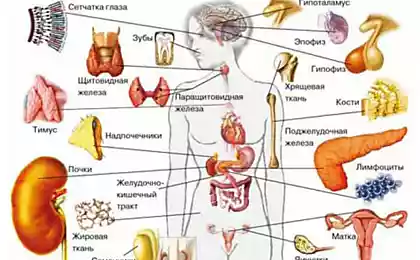
Zinc is a macronutrient that the human body participates in the synthesis of proteins, copying of genetic material, hematopoiesis, immune and endocrine systems, acts as a cofactor of several hundred zinc–dependent enzymes. Deficiency causes retarded growth, dwarfism, slowing of sexual maturation, skin lesions and mucous membranes (dermatitis, alopecia, parakeets), infertility, and increased growth of tumours, pathology of nails and hair.
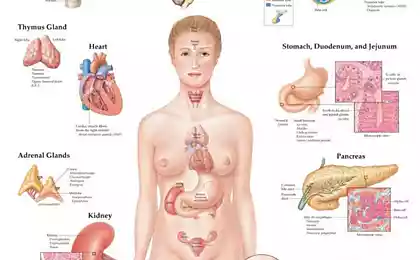
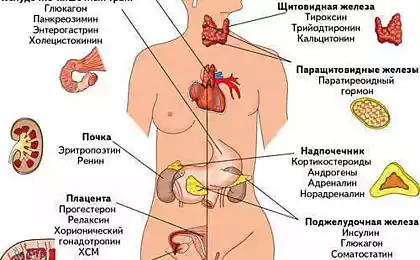
Zinc is involved not only in hematopoiesis, bone formation, immunity, but also in the activities of the endocrine glands (involved in the synthesis of male hormones, particularly testosterone and also insulin and growth hormone).

Zinc ensures normal functioning of the prostate and pancreas.
The daily needs of the male body in zinc more than women, and 15-25 mg. zinc Deficiency can develop with insufficient receipt it in an organism (1 mg/day or less).
Zinc essential for normal growth and development, so the need for zinc increases during pregnancy.
This need is generally small: about 100 mg for the entire period of pregnancy. It is possible to provide additional regular consumption of zinc in the dose of 0.6 mg/day throughout pregnancy.
It is especially important to provide the need for zinc fetus during the first 3 months of pregnancy. Placental development during this period requires a large mineral reserves. That's when a pregnant woman complains of changes in the perception of smell and taste.All this is the result of a lack of zinc in the taste the dermal papilla of the tongue or in the receptors of the nasal cavity.
Zinc deficiency in pregnant women can lead to atonic bleeding, premature birth, prolonged birth process.

In the initial period of puberty, when the sexual organs are formed, the boys also want high amounts of zinc. Body girls zinc during this period in smaller numbers only for the overall growth and development.
Adult men on the background of deficiency of zinc can reduce fertilizing capacity of sperm.
The total zinc content in adult body is about 1.5 g in women and 2.5–3 g – men.
Zinc is present in all organs, tissues, liquids, and secrets of the body. It is mainly concentrated in skin, hair and bone. More than 95% of zinc is present inside the cells. In biological systems zinc is always divalent ionic state. Certain depo zinc in the human body, so reduce consumption of zinc from food quickly leads to symptoms of deficiency.

Biological role: Zinc is essential for functioning of DNA– and RNA–polymerases that control the processes of transmission of hereditary information and protein biosynthesis, and thus the reparative processes in the body; as well as enzyme key reactions of biosynthesis of heme, which is part of hemoglobin, cytochromes of the respiratory chains of mitochondria, cytochrome P–450, catalase and myeloperoxidase. Zinc enters into the structure of a key antioxidant enzyme (Zn, Cu)–superoxide dismutase and induces the biosynthesis of protective proteins in cells of MT, in which zinc is an antioxidant of reparative action.
Zinc plays an important role in hormonal functions in the body. It directly affects the production and functioning of insulin, and thus the entire spectrum of insulin-dependent processes. In men, zinc is involved in the synthesis of testosterone and functioning of sex glands. Zinc is an essential factor for the female body, as part of the structure of the receptors for estrogen, thus regulating all estrogen-dependent processes.
Zinc is vital for the functioning of the thymus and the normal state of the immune system. Being, moreover, component latinaprincess protein,zinc together with vitamin a (and vitamin C) prevents immunodeficiencies, stimulating the synthesis of antibodies, and providing antiviral effect.
Zinc is essential for protein synthesis, including collagen, therefore, has a healing effect, the processes involved in perception of taste and smell, is essential for the functioning of the Central nervous system, including the processes of remembering.Zinc is required to maintain normal concentrations of vitamin E in the blood, it also increases the absorption of vitamin E.
Zinc regulates sebum secretion and helps prevent the development of acne, protects the liver from chemical damage and is vital for bone formation.

Synergists and antagonists of zinc: Functional antagonists of zinc are copper, cadmium, lead, especially against the background of protein deficiency.In the form of chelating compounds, the zinc can act as a synergist to chromium.
Increased intake of Filatov, phosphates, excess of calcium, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, steroids, antimetabolites, diuretics, alcohol, immunosuppressive drugs can cause zinc deficiency in the body.
Signs of insufficiency:
The zinc content is increased in the anemias, leukemia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, fatigue, stress.
The main manifestations of excess zinc:
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.pharmacognosy.com.ua/index.php/makro-i-mikro-chudesa/tsink-vysokij-testosteron-zdorovaya-prostata
Zinc is a macronutrient that the human body participates in the synthesis of proteins, copying of genetic material, hematopoiesis, immune and endocrine systems, acts as a cofactor of several hundred zinc–dependent enzymes. Deficiency causes retarded growth, dwarfism, slowing of sexual maturation, skin lesions and mucous membranes (dermatitis, alopecia, parakeets), infertility, and increased growth of tumours, pathology of nails and hair.
Zinc is involved not only in hematopoiesis, bone formation, immunity, but also in the activities of the endocrine glands (involved in the synthesis of male hormones, particularly testosterone and also insulin and growth hormone).

Zinc ensures normal functioning of the prostate and pancreas.
The daily needs of the male body in zinc more than women, and 15-25 mg. zinc Deficiency can develop with insufficient receipt it in an organism (1 mg/day or less).
Zinc essential for normal growth and development, so the need for zinc increases during pregnancy.
This need is generally small: about 100 mg for the entire period of pregnancy. It is possible to provide additional regular consumption of zinc in the dose of 0.6 mg/day throughout pregnancy.
It is especially important to provide the need for zinc fetus during the first 3 months of pregnancy. Placental development during this period requires a large mineral reserves. That's when a pregnant woman complains of changes in the perception of smell and taste.All this is the result of a lack of zinc in the taste the dermal papilla of the tongue or in the receptors of the nasal cavity.
Zinc deficiency in pregnant women can lead to atonic bleeding, premature birth, prolonged birth process.

In the initial period of puberty, when the sexual organs are formed, the boys also want high amounts of zinc. Body girls zinc during this period in smaller numbers only for the overall growth and development.
Adult men on the background of deficiency of zinc can reduce fertilizing capacity of sperm.
The total zinc content in adult body is about 1.5 g in women and 2.5–3 g – men.
Zinc is present in all organs, tissues, liquids, and secrets of the body. It is mainly concentrated in skin, hair and bone. More than 95% of zinc is present inside the cells. In biological systems zinc is always divalent ionic state. Certain depo zinc in the human body, so reduce consumption of zinc from food quickly leads to symptoms of deficiency.

Biological role: Zinc is essential for functioning of DNA– and RNA–polymerases that control the processes of transmission of hereditary information and protein biosynthesis, and thus the reparative processes in the body; as well as enzyme key reactions of biosynthesis of heme, which is part of hemoglobin, cytochromes of the respiratory chains of mitochondria, cytochrome P–450, catalase and myeloperoxidase. Zinc enters into the structure of a key antioxidant enzyme (Zn, Cu)–superoxide dismutase and induces the biosynthesis of protective proteins in cells of MT, in which zinc is an antioxidant of reparative action.
Zinc plays an important role in hormonal functions in the body. It directly affects the production and functioning of insulin, and thus the entire spectrum of insulin-dependent processes. In men, zinc is involved in the synthesis of testosterone and functioning of sex glands. Zinc is an essential factor for the female body, as part of the structure of the receptors for estrogen, thus regulating all estrogen-dependent processes.
Zinc is vital for the functioning of the thymus and the normal state of the immune system. Being, moreover, component latinaprincess protein,zinc together with vitamin a (and vitamin C) prevents immunodeficiencies, stimulating the synthesis of antibodies, and providing antiviral effect.
Zinc is essential for protein synthesis, including collagen, therefore, has a healing effect, the processes involved in perception of taste and smell, is essential for the functioning of the Central nervous system, including the processes of remembering.Zinc is required to maintain normal concentrations of vitamin E in the blood, it also increases the absorption of vitamin E.
Zinc regulates sebum secretion and helps prevent the development of acne, protects the liver from chemical damage and is vital for bone formation.

Synergists and antagonists of zinc: Functional antagonists of zinc are copper, cadmium, lead, especially against the background of protein deficiency.In the form of chelating compounds, the zinc can act as a synergist to chromium.
Increased intake of Filatov, phosphates, excess of calcium, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, steroids, antimetabolites, diuretics, alcohol, immunosuppressive drugs can cause zinc deficiency in the body.
Signs of insufficiency:
- loss of senses of taste and smell;
- brittleness, splitting nails, the formation of them white spots;
- acne; delayed puberty;
- fatigue;
- slowing growth,
- hair loss;
- high cholesterol;
- the weakening of the night vision;
- infertility, impotence, dysfunction of the prostate gland;
- increased susceptibility to infections;
- the weakening of the memory;
- the predisposition to diabetes;
- skin lesions and slow wound healing.
The zinc content is increased in the anemias, leukemia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, fatigue, stress.
The main manifestations of excess zinc:
- disorders of the immune system;
- autoimmune reactions;
- violation of a condition of the skin, hair and nails;
- painful sensibility of the stomach, nausea;
- the reduction of the body iron, copper, and cadmium;
- the weakening of the functions of the prostate gland;
- the weakening of the functions of the pancreas.
- the weakening of the liver.
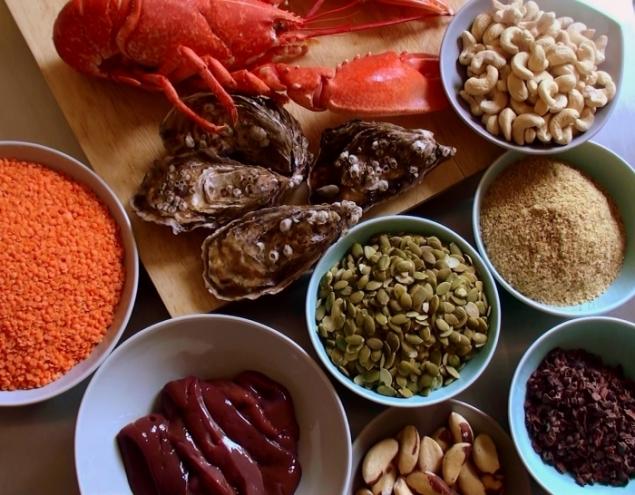
- oysters, fish (especially sardines) and other seafood (in particular – kelp (laminaria),
- liver, meat, ham;
- brewer's yeast;
- cereals and legumes: beans, peas, buckwheat, corn, alfalfa, oats, millet, soft wheat, durum wheat, unpolished rice, rice wild, rye, soybeans, beans, lentils, barley;
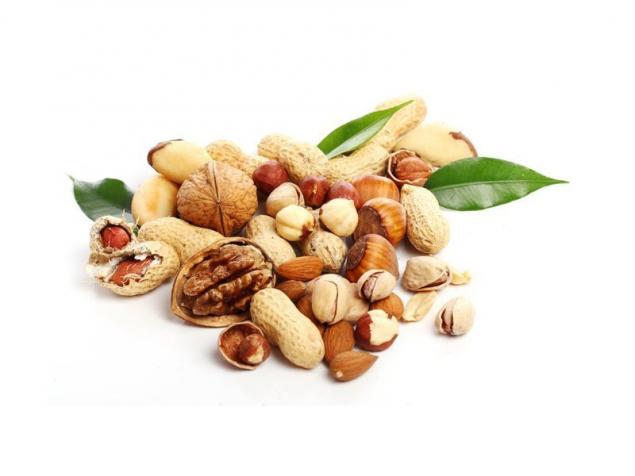
- whole grain; black pepper; nuts and seeds: peanuts, cashews, sesame seeds, poppy seeds, macadamia, almonds, Brazilian nuts, walnuts, pine nuts, sunflower seeds, pistachios, hazelnuts, and especially pumpkin seeds ("white seeds").
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.pharmacognosy.com.ua/index.php/makro-i-mikro-chudesa/tsink-vysokij-testosteron-zdorovaya-prostata