867
Insulin: the hormone of health and longevity
Insulin is an important hormone for our health and longevity, but also for weight control and its structure (growth of muscle mass and decrease body fat mass). However, about insulin there are many myths that deceive the reader without scientific training. So I will try to tell you in detail and nuances.
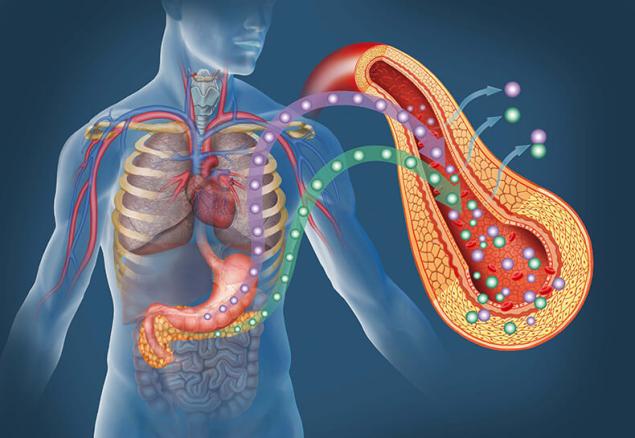
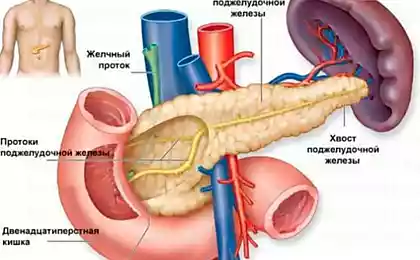
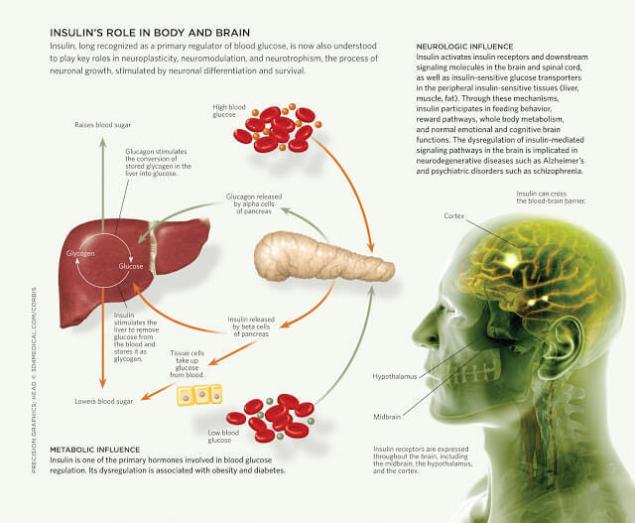
So we know that insulin is a pancreatic hormone that regulates glucose levels in the blood. After you ate something bad, carbohydrates from food are broken down into glucose (a sugar that cells use as fuel). Insulin helps to glucose hit the liver, muscle and fat cells. When the concentration of glucose decreases, and decreases insulin levels. As a rule, the level of insulin is lowered in the morning because the last meal was about eight hours.
Insulin is a prudent owner ("the house" — no matter what and where). So, if you have no room for calories, he puts them anywhere. It is therefore important to chronobiology of nutrition and physical activity.
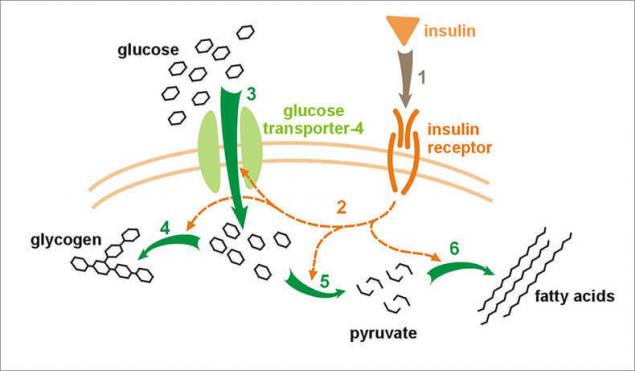
Insulin stimulates and inhibits at the same time.
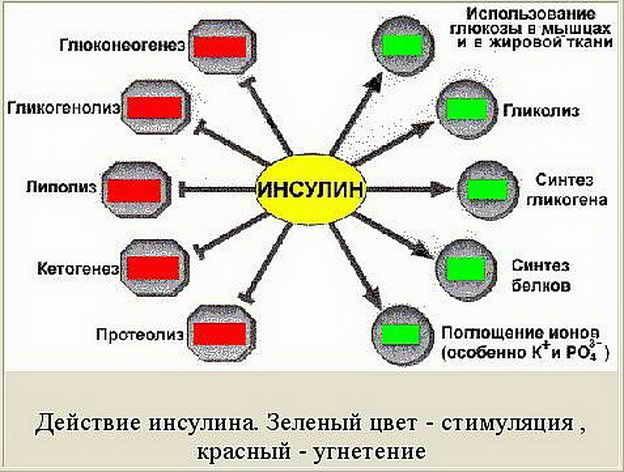
It is important to understand that insulin has two types of effects and its ability to inhibit some of the processes are as important as its stimulating effect. The inhibitory function of insulin is often much more important than it activates or stimulates the function. Thus, insulin is like a traffic controller or a traffic light at the intersection. It helps to slow and regulate traffic. No traffic lights or traffic controller would be a complete mess and a lot of accidents. That is, gluconeogenesis, glycolysis, proteolysis, synthesis of ketone bodies and lipolysis in the absence of insulin would pass at high speeds without any control. And all of this would end by hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis and death.
For example, high insulin:
1. Insulin helps muscle growth. Insulin stimulates protein synthesis by activating its production of ribosomes. In addition, insulin helps to move amino acids into the muscle fibers. Insulin actively transports certain amino acids into muscle cells. We are talking about BCAA's. Amino acid branched chain "personally" delivered by insulin in muscle cells. And it is very good if you are going to build muscle mass.
2. Insulin inhibits catabolism of proteins. Insulin prevents the breakdown of muscles. Although this may sound not very exciting, but the anti-catabolic nature of insulin is no less important than its anabolic properties.
Any person versed in Finance, will tell you that it's not important how much money you earn. It is also important how much money you spend. The same is true for the muscles. Every day our body synthesizes a number of proteins, and at the same time destroys the old. Will you be able over time to gain muscle mass, or not, depends on the "physiological arithmetic". To increase muscle, you must synthesize more protein than destroying it in the process of catabolism.
3. Insulin activates glycogen synthesis. Insulin increases the activity of enzymes (e.g., glikogensintetazy), which stimulate the formation of glycogen. This is very important because it helps to build up a reserve of glucose in muscle cells, thus improving their performance and recovery.
4. The rise of insulin helps the feeling of satiety and suppresses hunger. Insulin is one of the many hormones that play a role in the emergence of feelings of satiety. For example, a protein stimulating insulin, contributed to the decrease in appetite. In numerous studies it has been shown that insulin actually suppresses appetite.
Black side insulin (metabolism)
1. Insulin inhibits lipase hormonereceptor. Insulin blocks an enzyme called hormonereceptor lipase, which is responsible for the breakdown of fatty tissue. Obviously this is bad since if the body cannot break down stored fat (triglycerides) and turn it into a form that can be burned (free fatty acids), you will not lose weight.
2. Insulin reduces the use of fat. Insulin (high insulin levels) reduces the use of fat for energy. Instead, it promotes the burning of carbohydrates. Simply put, insulin is the "fat stores". Although this has a negative influence on the appearance of our body, this action makes sense if we remember that the primary function of insulin is to get rid of excess glucose in the blood.
3. Insulin increases synthesis of fatty acids. And FFA (free fatty acids) is a key cause of insulin resistance! Insulin increases fatty acid synthesis in the liver, which is the first step in the process of fat accumulation.
But it also depends on the availability of excess carbs — if their volume exceeds a certain level, they are either immediately burned or stored as glycogen. Without a doubt, the excessive insulin is the main cause of increased level in the body of triglycerides, fats that were previously considered relatively safe.
Acne, dandruff and seborrhea. Did not expect? The higher the insulin, the more intensive lipogenesis, lipogenesis the more intense, the higher the triglycerides in the blood, the higher the triglycerides in the blood — the more "fat" stands out through the sebaceous glands located throughout the body, especially on scalp and face. We are talking about hyperthyroidism and hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands under the influence of insulin.
People with a very naturally smooth skin, never had acne and pimples, this is a side effect of insulin may completely be absent. Patients with more or less oily skin, with tendency to form acne insulin can cause pronounced acne, hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands and enlargement of skin pores. Acne in women is often one of the signs of hyperandrogenism, which may be accompanied by hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia.
4. Insulin activates lipoproteinlipazou. Insulin activates the enzyme, known as lipoprotein lipase called. If you are familiar with the medical terminology, it may initially be perceived as a positive characteristic of insulin. Because lipase is an enzyme that breaks down fat, so why not increasing it?
Remember what we just discussed how insulin increases fatty acid synthesis in the liver. Once these extra fatty acids are converted to triglycerides, they are captured by lipoproteins (for example, proteins VLDL — very low density lipoproteins) and released into the blood, and are looking for a place for their storage.
So far, so good, because triglycerides cannot be absorbed by fat cells. So, although in your blood can be rather of triglycerides, you actually won't accumulate fat. until it is not known as lipoprotein lipase into.As soon as it is activated by insulin, known as lipoprotein lipase breaks down these triglycerides into absorbable fatty acids that are quickly and easily absorbed by fat cells, again converted there into triglycerides and remain in the fat cells.
5. Insulin blocks the use of glycogen.
Black side insulin (like growth hormone)
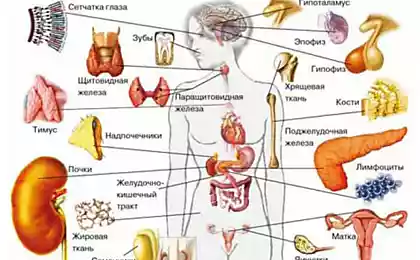
When chronically elevated level of insulin (insulin resistance) to the fore other black side of insulin. Excess insulin disrupts the normal working of other hormones, suppresses the growth hormone. Of course, insulin is one of the engines proper growth of children. But in adults its excess brings premature aging.
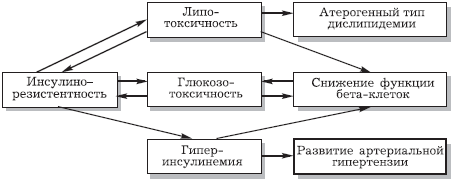
1. Excess insulin destroy arteries.
The excess insulin causes a clogging of the arteries, because it stimulates the growth of smooth muscle tissue around blood vessels. Such proliferation of cells plays a very important role in the development of atherosclerosis, when there is an accumulation of plaque, narrowing arteries and reducing blood flow. Additionally, insulin interferes with the operation of the system of dissolution of blood clots, raising the level of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Thus, it stimulated the formation of blood clots, which clog the artery.
2. Insulin increases blood pressure.
If you have high blood pressure, there is a 50% chance that you suffer from resistance of insulin and too much in your bloodstream. How insulin affects blood pressure is not precisely known. By itself, insulin has a direct vasodilator effect. In normal people, the introduction of physiological doses of insulin in the absence of hypoglycemia causes vasodilation, and does not increase blood pressure levels. However, in conditions of insulin resistance giperaktiwatia the sympathetic nervous system leads to arterial hypertension due to sympathetic stimulation of heart, vessels and kidneys.
3. Insulin stimulates the growth of cancerous tumors.
Insulin is a growth hormone, and an excess can lead to increased cell proliferation and tumors. Obese people produce more insulin, because the excess insulin causes obesity, so they more often than people with normal weight, develop cancer. In humans, high growth, insulin production is also increased (the higher the growth, the more insulin), so the risk of getting cancer is higher. Statistics and known facts.
Insulin is a growth hormone, and an excess can lead to increased cell proliferation and tumors. Obese people produce more insulin, because the excess insulin causes obesity, so they more often than people with normal weight, develop cancer. In humans, high growth, insulin production is also increased (the higher the growth, the more insulin), so the risk of getting cancer is higher. Statistics and known facts.
On the other hand, if you reduce insulin production in the body, the risk of developing cancer is also reduced. In animal experiments it was found that long-term regular breaks from food also reduce the risk of developing cancer, even if total calories in the diet of animals is not reduced, in other words, after these breaks, they have plenty. In these experiments it was found that the rare meals lead to a stable and permanent reduction in the level of insulin in the blood.
4. Hyperinsulinemia stimulates chronic inflammation.
Hyperinsulinemia stimulates the formation of arachidonic acid, which then turns into a stimulating inflammation in PG-E2 and the amount of inflammation in the body increases dramatically. Chronically high insulin levels or hyperinsulinemia also causes low adiponectin levels, and this is a problem as it increases insulin resistance and inflammation.
Adiponectin is a hormone of adipose tissue, which maintains normal sensitivity to insulin, prevents the development of diabetes and the risk of cardiovascular diseases is reduced. Adiponectin plays an important role in energy regulation as well as in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, reducing glucose and lipids, improving insulin sensitivity and having an anti-inflammatory effect. Fat people (particularly with abdominal obesity) the daily secretion of adiponectin, in the course of the day, was low.
Chronobiology of insulin.
For proper operation of insulin, you need to consider:
1. The basal level of insulin (depending on insulinchuvstvitelnyh)
2. Nutritional insulin (the amount and the insulin index of food).
3. The number of meals and the intervals between them.
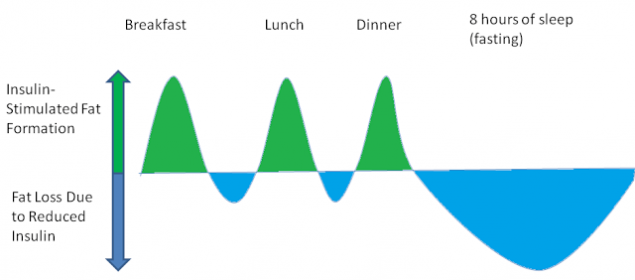
If you eat three times a day and observe the spaces between priemami food, lipogenesis and lipolysis balance each other. This is a very rough graph, where the green area represents the lipogenesis starting the meal. And the blue area shows the lipolysis that occurs between meals and during sleep.
High rise of insulin in food intake is good. This is good, because allows effectively to control the blood sugar level. Peaks of insulin ensure the normal course of important physiological processes.
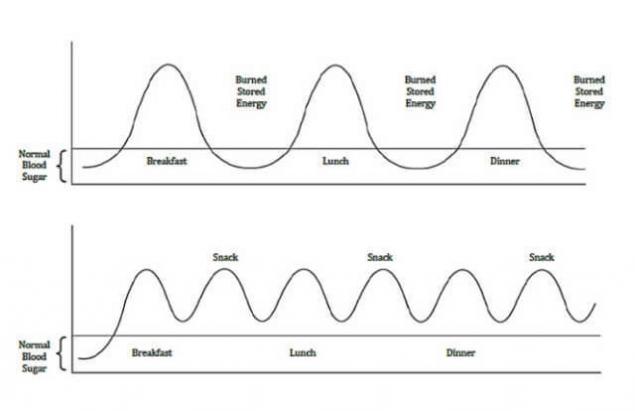
Snacking and weight loss
When eating, insulin secretion is biphasic. The first phase happens very quickly; in response to the increase of glucose concentration, for 1-2 minutes, the pancreas releases insulin. This rapid phase of insulin release is typically completed in approximately 10 minutes. It was revealed that this first phase is disrupted in people with impaired glucose tolerance (those people who have blood sugar after meal rises higher than expected in normal blood sugar fasting higher but diabetes is not). For example, an insulin response is correlated with the content of branched chain amino acids such as leucine, valine and isoleucine. For example, leucine stimulates the pancreas to produce insulin.
The first, fast phase is absent in the type II diabetes. And the second phase continues until the blood glucose is the stimulus. That is, the first releases of existing insulin, and produces additional (insulin secreted b-cell of the precursor (precursor) — proinsulin). The restoration of the rapid phase response of insulin improves the blood sugar regulation in diabetic patients: the rapid growth in the level of insulin in itself is not a bad thing.
Snacks and mesocyclone very negative effect on the regulation of insulin. In response to the snack, insulin takes off for 2-3 minutes and returns to normal in 30-40 minutes.
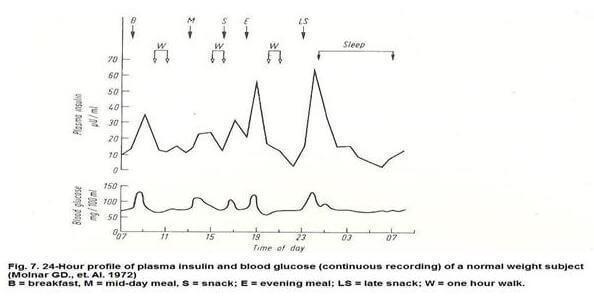
On the chart upper arrows mark the time you start eating or cutting. Daily fluctuations in insulin levels shown in the top graph, and the fluctuations of sugar on the bottom. As you can see, the wave of insulin after one cutting (S) reaches almost the same height as after a full lunch (M). But the wave of insulin after another cutting (LS) is so high that even above all others (evening-night snack!)
In experiments on mice it was found that if you feed them a day, they live longer and don't get sick. When the mice throughout their life 24 hours is not fed, and in the next 24 hours give them food to satiety, in comparison with mice fed daily 3 times a day, they, first, not lose weight, thedas when there is food, and second, never get sick, and third, live one and a half times longer than those mice that eat regularly 3 times every day. Due to this fact, the mice that eat less produce less insulin than those who eat frequently. Please note that there are less doesn't mean less, because the amount of calories there is no difference, the weight of both mice are the same.
Insulin and stress.
If there are substances that stimulate the release of insulin, then there are substances that inhibit this release. Such substances include kontrinsuljarnye hormones. One of the most powerful are the hormones of the medulla of the adrenal glands, which are neurotransmitters in the sympathetic nervous system – adrenaline and noradrenaline.
You know what these hormones? It is the hormone that saves us. They stand under acute stress, to mobilize the whole body. One of their properties – increase in blood sugar level, which is essential to the survival of the organism during times of stress.
This is due to stress hyperglycemia, which takes place after the disappearance of the threat to life. In this disease, as pheochromocytoma, is synthesized an excess of these hormones, which have a similar effect. So in this disease is often develop diabetes. To stress hormones also include the glucocorticoids – hormones of the adrenal cortex, the most famous representative of which is cortisol.
Insulin and aging.
Low concentration of insulin is associated with good health, but low insulin sensitivity is bad.
As recently stated: it seems paradoxical that attenuation of insulin/IGF‑1 prolongs life (low level of insulin in the blood), but the resistance (resistance) to insulin leads to diabetes of the 2nd type. A real paradox is why, in the case of mammals, low insulin levels associated with good health and a weakened response to insulin with the bad. The theory of quasi-programs that run TOR, gives the answer. Insulin and IGF‑1 activate TOR. Thus, attenuation of insulin/IGF‑1 reduces the activity of TOR and thereby slows the aging process.
Resistant to insulin is a manifestation of increased activity of TOR, as TOR over-active causing the resistant to insulin. So in both cases, to blame the increased activity of TOR is it the insulin or it manifests itself in the form of resistance to insulin.
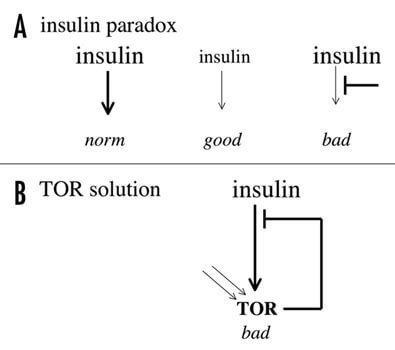
Low insulin is "good health", and weakened insulin signal is "bad for health". (C) subject to TOR no paradox there. Hyperactive TOR may be the result of the high content of insulin and decrease insulin signal could be the result of hyperactivity TOR. In both cases, hyperactivity TOR "harmful to health"
Insulin sensitivity.
The higher you have the amount of insulin in the blood (average), the more it stands out and the longer it lasts, the worse chuvstvitelnost to insulin. The concentration of receptors on the cell surface (which includes the receptors of insulin) depends, among other things, on the level of hormones in the blood. If this level is significantly and permanently increases the number of receptors relevant of the hormone is reduced, i.e. decreases the sensitivity of cells to the hormone circulating in the blood in excess. And Vice versa.
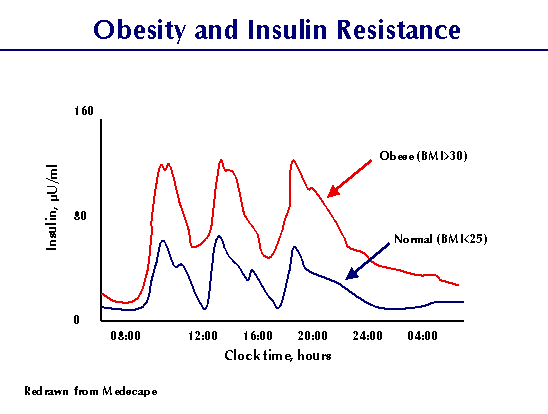
It is confirmed that the sensitivity of tissues to insulin is reduced by 40% in excess of body weight by 35-40% of normal. Insulin sensitivity, on the other hand, is very good. In this case, your cells — especially the muscle — a great react even on a small the secretion of insulin.
And, accordingly, need quite a bit of insulin to bring them in an anabolic state. So high insulin sensitivity is what we are looking for. It insulin sensitivity determines the ratio of fat to muscle in your body, especially when you are trying to gain or lose weight.
If weight you more sensitive to insulin, you will gain more muscle than fat. For example, with normal insulin sensitivity you will gain 0.5 kg of muscle for every pound of fat, that is, the ratio is 1:2. With increased sensitivity you will be able to gain 1 kg of muscle for every pound of fat. Or even better.
Physical activity is the most important factor in maintaining normal insulin sensitivity. A strong shock is applied to a sedentary lifestyle and lack of force activity.
Moral muscle: the adductor muscles of the thigh
Subcutaneous muscle of the neck: the secret to younger and healthy neck
Conclusion.
1. Our goal: low basal insulin levels and a good sensitivity to it.
2. This is achieved: 2-3 meals a day. Perfect – two. The absence of snacking and mesocyclone
3. Normalization of the stress level (remove non-food triggers insulin).
4. Do not eat high carbohydrate foods without the proper level of physical activity.
5. Compliance with at least the minimum of physical activity, reducing sedentary lifestyle up to 4-5 hours a day (not more). published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2015/09/insulin-edinstvo-i-borba-protivopolozhnostej.html

So we know that insulin is a pancreatic hormone that regulates glucose levels in the blood. After you ate something bad, carbohydrates from food are broken down into glucose (a sugar that cells use as fuel). Insulin helps to glucose hit the liver, muscle and fat cells. When the concentration of glucose decreases, and decreases insulin levels. As a rule, the level of insulin is lowered in the morning because the last meal was about eight hours.
Insulin is a prudent owner ("the house" — no matter what and where). So, if you have no room for calories, he puts them anywhere. It is therefore important to chronobiology of nutrition and physical activity.

Insulin stimulates and inhibits at the same time.
It is important to understand that insulin has two types of effects and its ability to inhibit some of the processes are as important as its stimulating effect. The inhibitory function of insulin is often much more important than it activates or stimulates the function. Thus, insulin is like a traffic controller or a traffic light at the intersection. It helps to slow and regulate traffic. No traffic lights or traffic controller would be a complete mess and a lot of accidents. That is, gluconeogenesis, glycolysis, proteolysis, synthesis of ketone bodies and lipolysis in the absence of insulin would pass at high speeds without any control. And all of this would end by hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis and death.
For example, high insulin:
- stimulates protein synthesis
- suppress fat breakdown
- stimulates fat accumulation
- inhibits the breakdown of glycogen

1. Insulin helps muscle growth. Insulin stimulates protein synthesis by activating its production of ribosomes. In addition, insulin helps to move amino acids into the muscle fibers. Insulin actively transports certain amino acids into muscle cells. We are talking about BCAA's. Amino acid branched chain "personally" delivered by insulin in muscle cells. And it is very good if you are going to build muscle mass.
2. Insulin inhibits catabolism of proteins. Insulin prevents the breakdown of muscles. Although this may sound not very exciting, but the anti-catabolic nature of insulin is no less important than its anabolic properties.
Any person versed in Finance, will tell you that it's not important how much money you earn. It is also important how much money you spend. The same is true for the muscles. Every day our body synthesizes a number of proteins, and at the same time destroys the old. Will you be able over time to gain muscle mass, or not, depends on the "physiological arithmetic". To increase muscle, you must synthesize more protein than destroying it in the process of catabolism.
3. Insulin activates glycogen synthesis. Insulin increases the activity of enzymes (e.g., glikogensintetazy), which stimulate the formation of glycogen. This is very important because it helps to build up a reserve of glucose in muscle cells, thus improving their performance and recovery.
4. The rise of insulin helps the feeling of satiety and suppresses hunger. Insulin is one of the many hormones that play a role in the emergence of feelings of satiety. For example, a protein stimulating insulin, contributed to the decrease in appetite. In numerous studies it has been shown that insulin actually suppresses appetite.
Black side insulin (metabolism)
1. Insulin inhibits lipase hormonereceptor. Insulin blocks an enzyme called hormonereceptor lipase, which is responsible for the breakdown of fatty tissue. Obviously this is bad since if the body cannot break down stored fat (triglycerides) and turn it into a form that can be burned (free fatty acids), you will not lose weight.
2. Insulin reduces the use of fat. Insulin (high insulin levels) reduces the use of fat for energy. Instead, it promotes the burning of carbohydrates. Simply put, insulin is the "fat stores". Although this has a negative influence on the appearance of our body, this action makes sense if we remember that the primary function of insulin is to get rid of excess glucose in the blood.
3. Insulin increases synthesis of fatty acids. And FFA (free fatty acids) is a key cause of insulin resistance! Insulin increases fatty acid synthesis in the liver, which is the first step in the process of fat accumulation.
But it also depends on the availability of excess carbs — if their volume exceeds a certain level, they are either immediately burned or stored as glycogen. Without a doubt, the excessive insulin is the main cause of increased level in the body of triglycerides, fats that were previously considered relatively safe.
Acne, dandruff and seborrhea. Did not expect? The higher the insulin, the more intensive lipogenesis, lipogenesis the more intense, the higher the triglycerides in the blood, the higher the triglycerides in the blood — the more "fat" stands out through the sebaceous glands located throughout the body, especially on scalp and face. We are talking about hyperthyroidism and hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands under the influence of insulin.
People with a very naturally smooth skin, never had acne and pimples, this is a side effect of insulin may completely be absent. Patients with more or less oily skin, with tendency to form acne insulin can cause pronounced acne, hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands and enlargement of skin pores. Acne in women is often one of the signs of hyperandrogenism, which may be accompanied by hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia.
4. Insulin activates lipoproteinlipazou. Insulin activates the enzyme, known as lipoprotein lipase called. If you are familiar with the medical terminology, it may initially be perceived as a positive characteristic of insulin. Because lipase is an enzyme that breaks down fat, so why not increasing it?
Remember what we just discussed how insulin increases fatty acid synthesis in the liver. Once these extra fatty acids are converted to triglycerides, they are captured by lipoproteins (for example, proteins VLDL — very low density lipoproteins) and released into the blood, and are looking for a place for their storage.
So far, so good, because triglycerides cannot be absorbed by fat cells. So, although in your blood can be rather of triglycerides, you actually won't accumulate fat. until it is not known as lipoprotein lipase into.As soon as it is activated by insulin, known as lipoprotein lipase breaks down these triglycerides into absorbable fatty acids that are quickly and easily absorbed by fat cells, again converted there into triglycerides and remain in the fat cells.
5. Insulin blocks the use of glycogen.
Black side insulin (like growth hormone)
When chronically elevated level of insulin (insulin resistance) to the fore other black side of insulin. Excess insulin disrupts the normal working of other hormones, suppresses the growth hormone. Of course, insulin is one of the engines proper growth of children. But in adults its excess brings premature aging.

1. Excess insulin destroy arteries.
The excess insulin causes a clogging of the arteries, because it stimulates the growth of smooth muscle tissue around blood vessels. Such proliferation of cells plays a very important role in the development of atherosclerosis, when there is an accumulation of plaque, narrowing arteries and reducing blood flow. Additionally, insulin interferes with the operation of the system of dissolution of blood clots, raising the level of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Thus, it stimulated the formation of blood clots, which clog the artery.
2. Insulin increases blood pressure.
If you have high blood pressure, there is a 50% chance that you suffer from resistance of insulin and too much in your bloodstream. How insulin affects blood pressure is not precisely known. By itself, insulin has a direct vasodilator effect. In normal people, the introduction of physiological doses of insulin in the absence of hypoglycemia causes vasodilation, and does not increase blood pressure levels. However, in conditions of insulin resistance giperaktiwatia the sympathetic nervous system leads to arterial hypertension due to sympathetic stimulation of heart, vessels and kidneys.
3. Insulin stimulates the growth of cancerous tumors.
Insulin is a growth hormone, and an excess can lead to increased cell proliferation and tumors. Obese people produce more insulin, because the excess insulin causes obesity, so they more often than people with normal weight, develop cancer. In humans, high growth, insulin production is also increased (the higher the growth, the more insulin), so the risk of getting cancer is higher. Statistics and known facts.
Insulin is a growth hormone, and an excess can lead to increased cell proliferation and tumors. Obese people produce more insulin, because the excess insulin causes obesity, so they more often than people with normal weight, develop cancer. In humans, high growth, insulin production is also increased (the higher the growth, the more insulin), so the risk of getting cancer is higher. Statistics and known facts.
On the other hand, if you reduce insulin production in the body, the risk of developing cancer is also reduced. In animal experiments it was found that long-term regular breaks from food also reduce the risk of developing cancer, even if total calories in the diet of animals is not reduced, in other words, after these breaks, they have plenty. In these experiments it was found that the rare meals lead to a stable and permanent reduction in the level of insulin in the blood.
4. Hyperinsulinemia stimulates chronic inflammation.
Hyperinsulinemia stimulates the formation of arachidonic acid, which then turns into a stimulating inflammation in PG-E2 and the amount of inflammation in the body increases dramatically. Chronically high insulin levels or hyperinsulinemia also causes low adiponectin levels, and this is a problem as it increases insulin resistance and inflammation.
Adiponectin is a hormone of adipose tissue, which maintains normal sensitivity to insulin, prevents the development of diabetes and the risk of cardiovascular diseases is reduced. Adiponectin plays an important role in energy regulation as well as in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, reducing glucose and lipids, improving insulin sensitivity and having an anti-inflammatory effect. Fat people (particularly with abdominal obesity) the daily secretion of adiponectin, in the course of the day, was low.
Chronobiology of insulin.
For proper operation of insulin, you need to consider:
1. The basal level of insulin (depending on insulinchuvstvitelnyh)
2. Nutritional insulin (the amount and the insulin index of food).
3. The number of meals and the intervals between them.

If you eat three times a day and observe the spaces between priemami food, lipogenesis and lipolysis balance each other. This is a very rough graph, where the green area represents the lipogenesis starting the meal. And the blue area shows the lipolysis that occurs between meals and during sleep.
High rise of insulin in food intake is good. This is good, because allows effectively to control the blood sugar level. Peaks of insulin ensure the normal course of important physiological processes.

Snacking and weight loss
When eating, insulin secretion is biphasic. The first phase happens very quickly; in response to the increase of glucose concentration, for 1-2 minutes, the pancreas releases insulin. This rapid phase of insulin release is typically completed in approximately 10 minutes. It was revealed that this first phase is disrupted in people with impaired glucose tolerance (those people who have blood sugar after meal rises higher than expected in normal blood sugar fasting higher but diabetes is not). For example, an insulin response is correlated with the content of branched chain amino acids such as leucine, valine and isoleucine. For example, leucine stimulates the pancreas to produce insulin.
The first, fast phase is absent in the type II diabetes. And the second phase continues until the blood glucose is the stimulus. That is, the first releases of existing insulin, and produces additional (insulin secreted b-cell of the precursor (precursor) — proinsulin). The restoration of the rapid phase response of insulin improves the blood sugar regulation in diabetic patients: the rapid growth in the level of insulin in itself is not a bad thing.
Snacks and mesocyclone very negative effect on the regulation of insulin. In response to the snack, insulin takes off for 2-3 minutes and returns to normal in 30-40 minutes.

On the chart upper arrows mark the time you start eating or cutting. Daily fluctuations in insulin levels shown in the top graph, and the fluctuations of sugar on the bottom. As you can see, the wave of insulin after one cutting (S) reaches almost the same height as after a full lunch (M). But the wave of insulin after another cutting (LS) is so high that even above all others (evening-night snack!)
In experiments on mice it was found that if you feed them a day, they live longer and don't get sick. When the mice throughout their life 24 hours is not fed, and in the next 24 hours give them food to satiety, in comparison with mice fed daily 3 times a day, they, first, not lose weight, thedas when there is food, and second, never get sick, and third, live one and a half times longer than those mice that eat regularly 3 times every day. Due to this fact, the mice that eat less produce less insulin than those who eat frequently. Please note that there are less doesn't mean less, because the amount of calories there is no difference, the weight of both mice are the same.
Insulin and stress.
If there are substances that stimulate the release of insulin, then there are substances that inhibit this release. Such substances include kontrinsuljarnye hormones. One of the most powerful are the hormones of the medulla of the adrenal glands, which are neurotransmitters in the sympathetic nervous system – adrenaline and noradrenaline.
You know what these hormones? It is the hormone that saves us. They stand under acute stress, to mobilize the whole body. One of their properties – increase in blood sugar level, which is essential to the survival of the organism during times of stress.
This is due to stress hyperglycemia, which takes place after the disappearance of the threat to life. In this disease, as pheochromocytoma, is synthesized an excess of these hormones, which have a similar effect. So in this disease is often develop diabetes. To stress hormones also include the glucocorticoids – hormones of the adrenal cortex, the most famous representative of which is cortisol.
Insulin and aging.
Low concentration of insulin is associated with good health, but low insulin sensitivity is bad.
As recently stated: it seems paradoxical that attenuation of insulin/IGF‑1 prolongs life (low level of insulin in the blood), but the resistance (resistance) to insulin leads to diabetes of the 2nd type. A real paradox is why, in the case of mammals, low insulin levels associated with good health and a weakened response to insulin with the bad. The theory of quasi-programs that run TOR, gives the answer. Insulin and IGF‑1 activate TOR. Thus, attenuation of insulin/IGF‑1 reduces the activity of TOR and thereby slows the aging process.
Resistant to insulin is a manifestation of increased activity of TOR, as TOR over-active causing the resistant to insulin. So in both cases, to blame the increased activity of TOR is it the insulin or it manifests itself in the form of resistance to insulin.

Low insulin is "good health", and weakened insulin signal is "bad for health". (C) subject to TOR no paradox there. Hyperactive TOR may be the result of the high content of insulin and decrease insulin signal could be the result of hyperactivity TOR. In both cases, hyperactivity TOR "harmful to health"

Insulin sensitivity.
The higher you have the amount of insulin in the blood (average), the more it stands out and the longer it lasts, the worse chuvstvitelnost to insulin. The concentration of receptors on the cell surface (which includes the receptors of insulin) depends, among other things, on the level of hormones in the blood. If this level is significantly and permanently increases the number of receptors relevant of the hormone is reduced, i.e. decreases the sensitivity of cells to the hormone circulating in the blood in excess. And Vice versa.

It is confirmed that the sensitivity of tissues to insulin is reduced by 40% in excess of body weight by 35-40% of normal. Insulin sensitivity, on the other hand, is very good. In this case, your cells — especially the muscle — a great react even on a small the secretion of insulin.
And, accordingly, need quite a bit of insulin to bring them in an anabolic state. So high insulin sensitivity is what we are looking for. It insulin sensitivity determines the ratio of fat to muscle in your body, especially when you are trying to gain or lose weight.
If weight you more sensitive to insulin, you will gain more muscle than fat. For example, with normal insulin sensitivity you will gain 0.5 kg of muscle for every pound of fat, that is, the ratio is 1:2. With increased sensitivity you will be able to gain 1 kg of muscle for every pound of fat. Or even better.
Physical activity is the most important factor in maintaining normal insulin sensitivity. A strong shock is applied to a sedentary lifestyle and lack of force activity.
Moral muscle: the adductor muscles of the thigh
Subcutaneous muscle of the neck: the secret to younger and healthy neck
Conclusion.
1. Our goal: low basal insulin levels and a good sensitivity to it.
2. This is achieved: 2-3 meals a day. Perfect – two. The absence of snacking and mesocyclone
3. Normalization of the stress level (remove non-food triggers insulin).
4. Do not eat high carbohydrate foods without the proper level of physical activity.
5. Compliance with at least the minimum of physical activity, reducing sedentary lifestyle up to 4-5 hours a day (not more). published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2015/09/insulin-edinstvo-i-borba-protivopolozhnostej.html
Step by step instructions masonry BBQ brick
Body care according to the biorhythms: choosing the optimal time