149
The rules for choosing delicious persimmon
With the onset of the cold season, sweet or tart astringent persimmon (Latin Diospyros) appears on the shelves of stores. “Food of the gods”, as this name is translated from Latin, is really able to bring us true gastronomic pleasure.

We used to use it. persimmon fresh, but tart fruit is also widely used for making jams, jam, excellent salads and sauces, bright pastries, unusual pancakes, incredibly delicious desserts and drinks.

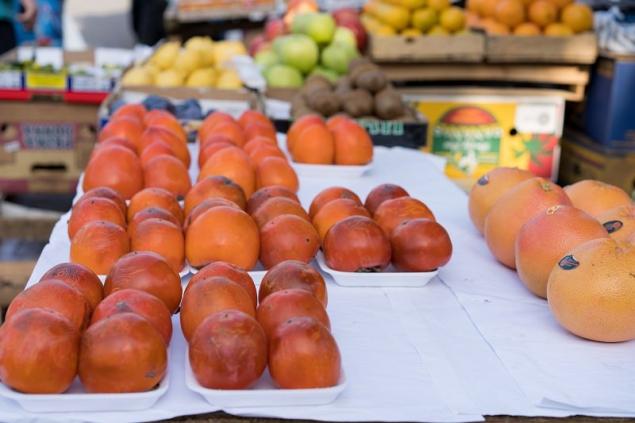
However, behind all the variety of persimmons on store shelves, we often get lost, not knowing what distinguishes the “charon” from the “king”, and how to choose sweet fruits that will not knit your mouth.
Experts divide all varieties of persimmon into two groups: variable and constant. With constant varieties, it is clear that they always have unchanged characteristics, and the properties of varying ones depend on the conditions in which they were formed.

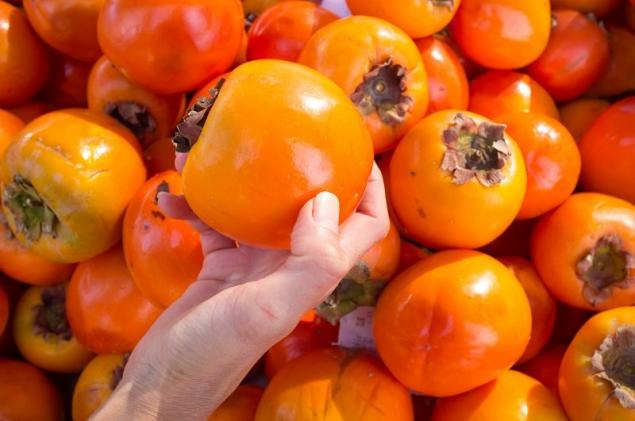
Fruits that are formed without fertilization and do not contain seeds do not change the color of the flesh upon maturation, and the tartness is lost only after final ripening in the refrigerator, when their flesh acquires a jelly-like consistency.
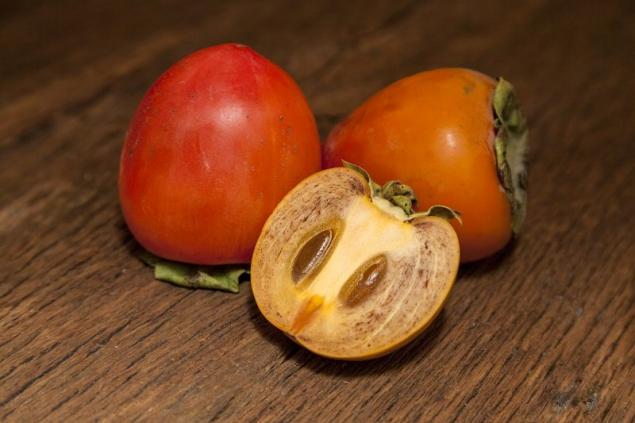
Fruits of the same varieties, but formed after pollination and having seeds, already on the tree have sweet flesh, a large number of bones, and the color of their flesh darkens, up to dark brown. This group includes a group of king or chocolate varieties such as hiakum and zenji maru.
To choose a mature persimmon, pay attention to its color. It should be bright orange to dark brown (depending on the variety) with dry brownish leaves. You should pay attention to the brown stripes on the skin of the fruit. The more stripes, the sweeter the fruit. The fruit should be semi-transparent.

Whichever variety of persimmon you choose, remember that it can bring your body considerable benefits. The main thing is to adhere to simple recommendations regarding the use of this gift of nature.
If there is a predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases, then without health consequences you can eat no more than one fruit per day. In addition, you should not drink persimmon with dairy products.

We used to use it. persimmon fresh, but tart fruit is also widely used for making jams, jam, excellent salads and sauces, bright pastries, unusual pancakes, incredibly delicious desserts and drinks.

However, behind all the variety of persimmons on store shelves, we often get lost, not knowing what distinguishes the “charon” from the “king”, and how to choose sweet fruits that will not knit your mouth.
Experts divide all varieties of persimmon into two groups: variable and constant. With constant varieties, it is clear that they always have unchanged characteristics, and the properties of varying ones depend on the conditions in which they were formed.

Fruits that are formed without fertilization and do not contain seeds do not change the color of the flesh upon maturation, and the tartness is lost only after final ripening in the refrigerator, when their flesh acquires a jelly-like consistency.
Fruits of the same varieties, but formed after pollination and having seeds, already on the tree have sweet flesh, a large number of bones, and the color of their flesh darkens, up to dark brown. This group includes a group of king or chocolate varieties such as hiakum and zenji maru.
- Persimmon
Classic, well-known persimmon usually has an astringent taste and fully matures only in the freezer.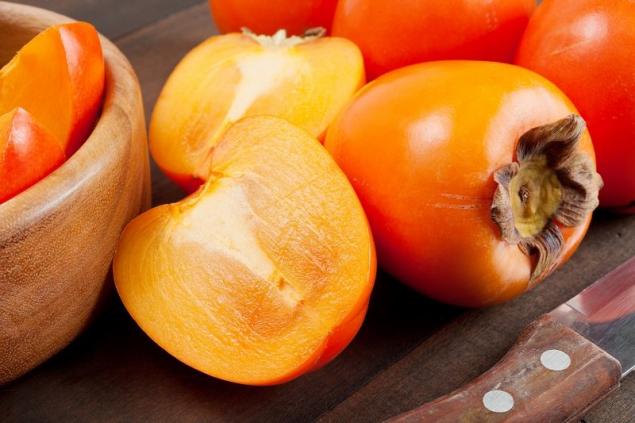
In shape, it is spherical, flat, and angular, and sometimes resemble an acorn. Yellow-orange shade distinguishes the usual persimmon from the "king" or "charon". - The King.
There is some confusion about the use of the term king. Usually, this term means a group of persimmon varieties of dark orange color with sweet and non-stringent brown flesh.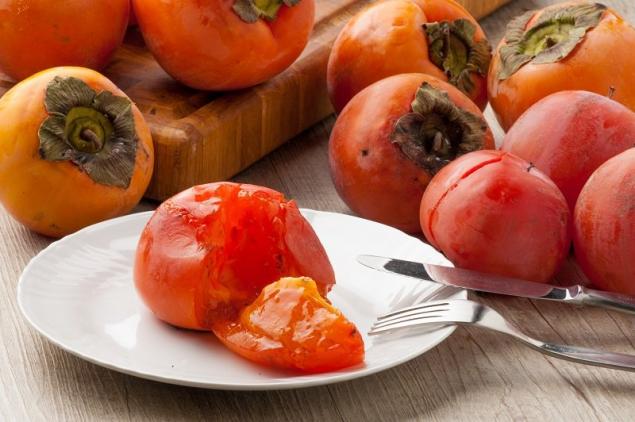
It should be noted that the more seeds in the king fruit - the more delicious they are. The most popular varieties of this group include “hiakum”, “zenji-Maru”, “gateley”.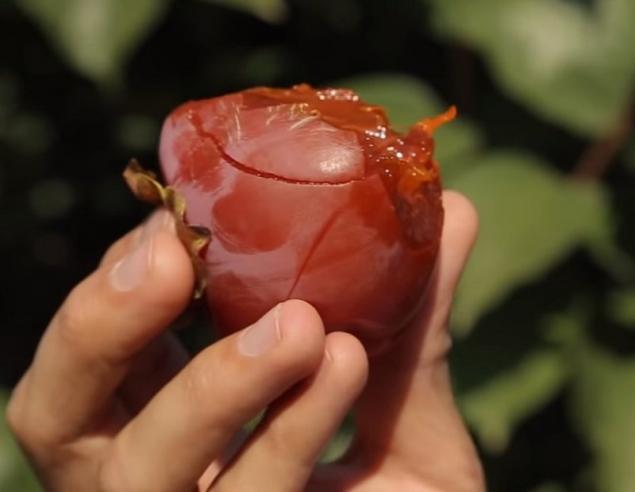
It has also been said that the common persimmon and the “king” are not two different varieties, but simply two different types of fruit that can sometimes be found on the same tree. According to this version, “king” is persimmon, which developed from a pollinated flower.
Properties of persimmon "kings" - sweetness, excellent taste, the presence of bones, dark flesh and external difference in the form of ring dark cracks on the top. She is valued for not knitting her mouth even when immature.
Thus, the unique taste of the “king” we owe to bees. If the mystery of pollination did not take place, a fruit develops, which can be called “just persimmon”. It has no bones and knits until it matures and becomes soft. - "Sharon."
Sharon persimmon is a hybrid produced by Israeli breeders and named after the Sharon Valley. Fruits in this variety have a fiery orange color, and their taste is similar to a mixture of quince, persimmon, apricot and apple.
The main difference between the "charon" is a slight tartness of the fruits even in an immature form. This variety has a refined and delicate taste, which has pleased many connoisseurs of this wonderful berry. Unlike other varieties, this one does not contain seeds.
Azerbaijani Sharon persimmon It has sharp tips, and the Spanish “charon” is smooth in shape with crushed crosses at the end.
To choose a mature persimmon, pay attention to its color. It should be bright orange to dark brown (depending on the variety) with dry brownish leaves. You should pay attention to the brown stripes on the skin of the fruit. The more stripes, the sweeter the fruit. The fruit should be semi-transparent.

Whichever variety of persimmon you choose, remember that it can bring your body considerable benefits. The main thing is to adhere to simple recommendations regarding the use of this gift of nature.
If there is a predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases, then without health consequences you can eat no more than one fruit per day. In addition, you should not drink persimmon with dairy products.