11047
It is important to know: the Compatibility of vitamins and minerals
What vitamins and minerals are combined and not combined with each other?Our body is like a chemical factory, which is simultaneously many different processes. For all of these processes needs different items that we get from the outside - proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals.
To ensure that all these substances were absorbed and optimally used by the body, it is important to know what substances are combined with each other, and which are not. Some vitamins and minerals interfere with the absorption of each other and others, on the contrary, help. Moreover, some vitamins and minerals generally cannot be absorbed and used by the body separately.

Let's see how to combine between them the most common vitamins (A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, B12, C, D, E, K) and minerals (iron, magnesium, manganese, copper, calcium, silicon, selenium, phosphorus, zinc).
Good compatibility of vitamins and mineralsWhat vitamins and minerals together?
Simultaneous reception goes well between vitamins and minerals has the effect that exceeds the effect of taking them separately. Synergy is one of those times when 2+2=10, not 4.
The reasons may be different:

Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)Good compatibility with vitamins B3, B6, B9 and K and the mineral zinc.
Some combinations of vitamins and minerals can destroy each other or depressing influence on the properties of each other. Such vitamins and minerals should preferably be taken separately, with a break of 4-6 hours.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)Poor compatibility with vitamins B2, B3, B6 and B12 and minerals magnesium and calcium.
In addition to compatibility of various vitamins and minerals, it is advisable to consider the impact of products. Vitamin and mineral supplements are only a Supplement to Your main food, which also contains biologically active substances. It is not always a positive influence.
Here are the main factors that can significantly degrade the result vitaminov and minerals:
Some foods impair the absorption of vitamins and minerals or provoke their loss. It is caffeinated beverages (coffee, black and green tea), milk and dairy products. If possible, try to avoid the use of these products, or at least to reduce their number. At least, should not combine their use of vitamins and minerals, wait 4-6 hours, so the nutrients have time to be absorbed in the body. A necessary substances are produced by beneficial bacteria living in the gut. For optimal absorption and use of entering the body of vitamins and minerals need a healthy microflora. If You eat meat, eggs, dairy products, the most beneficial bacteria You replace putrefactive bacteria. To restore the microflora of kishechnika, reduce the amount of animal products and increase the share of fresh vegetable food is the foods beneficial bacteria. Also, harmful effects on the microflora have antibiotics. Stress also kills some beneficial bacteria (more precisely, the adrenaline entering the intestines due to the fact that under stress we don't use it — don't run, don't fight, and sit and experience). So after taking antibiotics or strong continuous stress, you should always drink a course of probiotics. Your vitamins and minerals you can eat... parasites. 90% of the population are infected with parasites. To avoid infection, almost unreal. Parasites have from time to time to get rid of the Paradox is that all of these factors are usually the primary reason why You receive less vitamins and minerals from food and are forced to take them in pill form. published
Author: Inna Doubson
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: //health4ever.org/vitaminy-i-mineraly/sovmestimost-vitaminov-i-mineralov
To ensure that all these substances were absorbed and optimally used by the body, it is important to know what substances are combined with each other, and which are not. Some vitamins and minerals interfere with the absorption of each other and others, on the contrary, help. Moreover, some vitamins and minerals generally cannot be absorbed and used by the body separately.

Let's see how to combine between them the most common vitamins (A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, B12, C, D, E, K) and minerals (iron, magnesium, manganese, copper, calcium, silicon, selenium, phosphorus, zinc).
Good compatibility of vitamins and mineralsWhat vitamins and minerals together?
Simultaneous reception goes well between vitamins and minerals has the effect that exceeds the effect of taking them separately. Synergy is one of those times when 2+2=10, not 4.
The reasons may be different:
- Vitamins and minerals can interact in storage or already in the stomach, helping the digestion of each other (pharmaceutical interaction).
- Vitamins and minerals can potentiate each other by participating in the same processes in the body (pharmacological interaction).
- Vitamins C and E protect vitamin a from oxidation.
- Vitamin E improves the absorption of vitamin A, but only in the case of vitamin E a bit. Large amounts of vitamin E, on the contrary, prevents the absorption of vitamin A.
- Zinc enhances the absorption of vitamin A, contributing to its transformation in the retina.
- Vitamin a improves iron absorption and allows you to use the stock iron in the liver.

Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)Good compatibility with vitamins B3, B6, B9 and K and the mineral zinc.
- The transition of the vitamins B3, B6, B9 and K to its active form takes place in the presence of vitamin B2.
- Vitamin B2 enhances the bioavailability of zinc.
- Copper and vitamin B6 enhances the absorption of vitamin B3.
- Vitamins B1 and B2 significantly enhances the absorption of vitamin B5.
- Vitamin B5 facilitates the absorption of vitamin B4, B9 and C.
- Vitamin B2 helps vitamin B6 to move into the active form, a magnesium improves its ability to penetrate into cells.
- Vitamin B6 reduces the loss of zinc by the body.
- Vitamin C protects vitamin B9 in the body tissues.
- Calcium helps the absorption of vitamin B12 in the body.
- The antioxidant action of vitamin C is enhanced by carotenoids, vitamin E and flavonoids.
- Vitamin C restores the activity of vitamin E.
- Vitamin C helps to preserve vitamin B9 in tissues.
- Vitamin C helps the absorption of calcium and chromium.
- Vitamin D improves the metabolism of phosphorus and calcium in the body.
- Selenium enhances the antioxidant effect of vitamin E.
- Vitamin C regenerates vitamin E in the oxidation.
- Vitamin K helps calcium to build bone in the body.
- Vitamin B2 is required for transport of vitamin K to its active form.
- This vitamin-mineral complex (calcium, magnesium, boron and vitamins B6, B12, D and K) provides the best absorption of calcium and reduces its loss by the body. Magnesium should not be in excess, otherwise the result will be the opposite.
- Copper and vitamins A and C improve the absorption of iron.
- Vitamin D improves the absorption of phosphorus.
- Copper in small quantities helps the body absorb iron.
- Magnesium promotes the absorption of vitamin B complex (except B1) and calcium.
- Zinc enhances the absorption of vitamin A, contributing to its transformation in the retina.
- Vitamin B2 enhances the bioavailability of zinc and vitamin B6 inhibits the loss of zinc by the body.
Some combinations of vitamins and minerals can destroy each other or depressing influence on the properties of each other. Such vitamins and minerals should preferably be taken separately, with a break of 4-6 hours.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)Poor compatibility with vitamins B2, B3, B6 and B12 and minerals magnesium and calcium.
- Excessive consumption of vitamin B1 is dangerous in and of itself, because of frequently encountered allergic reactions. The co-administration of vitamin B1 with vitamin B12 may intensify allergic reactions.
- Vitamins B2 and B3 completely destroy vitamin B1.
- Vitamin B6 inhibits the transition of vitamin B1 transition into a biologically active state.
- Magnesium and calcium interfere with the absorption of vitamin B1, znachitelno reducing its solubility in water.
- Iron and copper slow down the absorption of vitamin B2.
- Copper reduces the activity of vitamin B5.
- Vitamin B6 inhibits the transition of vitamin B1 to its active form.
- Vitamin B12 contributes to the destruction of vitamin B6.
- Zinc and folic acid (vitamin B9) together form an insoluble complex that impairs absorption of both.
- Under the action of iron, manganese and copper and vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, C and E vitamin B12 becomes inactive.
- When a person takes vitamin C, B12, copper, vitamin B1 in different tablets at different time — limit is reached a maximum in concentration in the blood which reduces the possibility of development of negative interaction.
- Overdose of vitamin C causes, among other troubles, to the leaching of copper from the body.
- To increase the absorption of vitamin E, it should be consumed separately from magnesium, zinc, copper and vitamin D.
- Vitamins E and A prevent the penetration of vitamin C into cells.
- A large amount of magnesium, iron, or phosphorus leads to calcium deficiency.
- Calcium, in turn, interferes with the absorption of these minerals.
- Zinc, magnesium, chromium and calcium interfere with the absorption of iron.
- Iron interferes with the absorption of vitamins E and B12, calcium, and manganese.
- The excess of magnesium and calcium leads to a deficiency of phosphorus in the body.
- The copper prevents the absorption of vitamins B2, B5, B12, C and E.
- Copper also interferes with the absorption of zinc.
- Large quantities of copper impairs the absorption of iron, though in small numbers, on the contrary, has a beneficial effect.
- Calcium and iron impair the absorption of manganese.
- Magnesium affects the absorption of vitamins B1 and E.
- Phosphorus and manganese reduces the absorption of magnesium in the body.
- High amounts of magnesium leads to a deficiency of calcium and phosphorus.
- Calcium, iron and copper inhibit the absorption of zinc by the body.
- Zinc and vitamin B9 together form an insoluble complex that reduces their absorption.
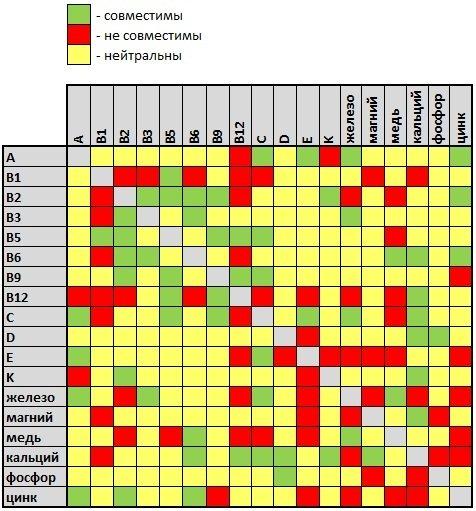
- Green is a good combination of vitamins and minerals that work well in the complex, helping the absorption of each other and/or reinforcing effect.
- Indicated in red are a bad combination that should be avoided. The effect of taking these vitamins and minerals together will be minimal or negative. They need to be taken separately, with an interval of 4-6 hours.
- Outlined in yellow and neutral combination. These vitamins and minerals can be used together or separately.

In addition to compatibility of various vitamins and minerals, it is advisable to consider the impact of products. Vitamin and mineral supplements are only a Supplement to Your main food, which also contains biologically active substances. It is not always a positive influence.
Here are the main factors that can significantly degrade the result vitaminov and minerals:
Some foods impair the absorption of vitamins and minerals or provoke their loss. It is caffeinated beverages (coffee, black and green tea), milk and dairy products. If possible, try to avoid the use of these products, or at least to reduce their number. At least, should not combine their use of vitamins and minerals, wait 4-6 hours, so the nutrients have time to be absorbed in the body. A necessary substances are produced by beneficial bacteria living in the gut. For optimal absorption and use of entering the body of vitamins and minerals need a healthy microflora. If You eat meat, eggs, dairy products, the most beneficial bacteria You replace putrefactive bacteria. To restore the microflora of kishechnika, reduce the amount of animal products and increase the share of fresh vegetable food is the foods beneficial bacteria. Also, harmful effects on the microflora have antibiotics. Stress also kills some beneficial bacteria (more precisely, the adrenaline entering the intestines due to the fact that under stress we don't use it — don't run, don't fight, and sit and experience). So after taking antibiotics or strong continuous stress, you should always drink a course of probiotics. Your vitamins and minerals you can eat... parasites. 90% of the population are infected with parasites. To avoid infection, almost unreal. Parasites have from time to time to get rid of the Paradox is that all of these factors are usually the primary reason why You receive less vitamins and minerals from food and are forced to take them in pill form. published
Author: Inna Doubson
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: //health4ever.org/vitaminy-i-mineraly/sovmestimost-vitaminov-i-mineralov