614
Seizures - an important signal of the body about serious violations
Convulsions are convulsions (from English convulsions).
Tonic convulsions (as opposed to seizures of central and peripheral origin in lesions of the central nervous system) are sudden, involuntary, not amenable to controlled relaxation short-term contractions of muscles or a group of muscles, more often foot, perceived by a person as severe pain. They are familiar to almost all adults.
Seizures are quite dangerous if you are in a pond, mountains, driving. Particularly painful are convulsions of the muscles of the back, neck. But pain is not the worst thing in convulsions. Seizures are a signal of the body about serious trouble. Unfortunately, we do not always understand the “language” of the body and treat seizures as a simple trouble that complicates life, but no more.

Let’s understand in which cases the body gives us signals in the form of seizures.
Tonic convulsions occur with pathological excitation in a particular element of the motor unit:
Muscle structure
The mechanism of muscle fiber reduction is a long-studied phenomenon. In this publication, we will consider the work of cross-striped (skeletal) muscles, without affecting the principles of smooth muscle functioning.
Skeletal muscle consists of thousands of fibers, and each individual fiber, in turn, contains many myofibrils. Myofibrill in a simple light microscope is a strip in which tens and hundreds of muscle cells (myocytes) lined up in a row of nuclei are visible.
Each myocyte along the periphery has a special contractile apparatus oriented strictly parallel to the axis of the cell. The main functional unit of myofibrill, which has a contractile capacity, is the sarcomer (basic contractile unit of striated muscles, which is a complex of several proteins). Sarcomere consists of such proteins: actin (main), myosin, troponin and tropomyosin. Actin and myosin in shape resemble intertwined threads. With the participation of troponin, tropomyosin, calcium ions and ATP (a unit of energy produced in cells), there is a mutual convergence of actin and myosin threads, as a result of which the sarcomere is shortened, and accordingly the entire muscle fiber.
Mechanism of muscle contraction
The reduction of muscle fiber occurs in the following order:
The following factors lead to prolonged tonic contraction of muscle fiber:
1. Excessively frequent brain impulses.
2. Excess acetylcholine in the synaptic gap.
3. Lower myocyte excitability threshold.
4. Decreased ATP concentration.
5. Genetic defect of one of the contractile proteins.
Let’s take a closer look at each factor.
1. Excessively frequent brain impulses
The brain, namely its special department - the cerebellum, is responsible for maintaining a constant tone of each muscle of the body. Even during sleep, muscles do not cease to receive impulses from the brain, but are generated much less often than in the waking state.
Under certain circumstances, the brain begins to increase impulses, which the patient feels like a feeling of muscle stiffness. When a certain threshold is reached, the impulses become so frequent that they keep the muscle in a state of constant contraction.
Leg cramps due to increased brain impulses develop in the following diseases:
Eclampsia is preceded by preeclampsia, in which the pregnant woman has increased blood pressure, swelling appears and general well-being worsens. With high blood pressure numbers (on average from 140 mm Hg. column and above), the risk of placenta detachment increases due to narrowing of the blood vessels that feed it.

During seizures, sharp contractions and relaxation of the uterine muscles occur, leading to detachment of the fetal site and termination of fetal nutrition. In this situation, there is an urgent need for emergency delivery by cesarean section in order to save the life of the fetus and stop uterine bleeding in a pregnant woman.
Traumatic brain injuries can lead to leg cramps, but this happens quite rarely.
The remaining causes of seizures due to increased brain impulses will not be considered here.
2. Excess acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine is the main mediator involved in the transmission of impulse from the nerve to the muscle cell. Under certain conditions, an excess mediator can accumulate in the synaptic cleft, inevitably leading to more frequent and strong muscle contraction, up to the development of seizures, including the lower extremities.
The following conditions cause seizures by increasing the amount of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft:
Magnesium is one of the most important electrolytes in the body. One of its functions is to open the channels of the presynaptic membrane to reverse the entry of an unused mediator into the end of the axon (the central process of the nerve cell responsible for the transmission of an electrical impulse).
With a lack of magnesium, these channels remain closed, which leads to the accumulation of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. As a result, even light physical activity in a short time provokes the appearance of seizures.
Magnesium deficiency develops mainly:
With a long-term deep deficiency of magnesium, acute severe disorders are observed, mainly of the CNS; hemolytic anemia, cardiovascular diseases develop (angina pectoris, tachycardia, extrasystole, arrhythmias, thrombosis); cerebral disorders appear (headache, dizziness, fear, depression, memory impairment, confusion, hallucinations); abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, laryngeal spasms, bronchitis, weather, elevations in the body, fever, endemosis, and coldness;
With the aggravation of magnesium deficiency in the body, except for convulsions of the calf muscles, soles, feet, hands, convulsions of the occipital, spinal muscles, face can develop.
As you can see, serious attitude to the convulsions that have appeared and the elimination of such a cause of their occurrence as a long-term magnesium deficiency in the body can save you and your loved ones, especially children, from further serious disorders in the body.

How to identify magnesium deficiency in the body
Magnesium is mainly an intracellular element, so determining its level in the blood is not informative for detecting minor intracellular deficits, and intracellular diagnostics (except for scientific purposes) has not yet been developed. Low levels of magnesium in the blood is already a very deep deficiency of magnesium.
Excess magnesium in the blood can be a consequence of the loss of magnesium by cells during their destruction, so sometimes microelementologists consider not as an excess of magnesium inside cells, but as a loss of magnesium by cells and the release of magnesium into the blood.
Determining the level of magnesium in the hair is more informative, especially when magnesium deficiency is detected (found much more often than in the blood). If the level of magnesium in the blood is a momentary state, then its level in the hair is an accumulation in 2-3 months (1 cm of hair - 1 month if you cut the hair for analysis at the root, and not the tips of the hair).
There is no unequivocal analysis to determine the level of magnesium inside cells at the moment, so a competent specialist focuses not only on tests, but also on the symptoms of magnesium deficiency.
Magnesium is not normally retained in the body. With the normal intake of magnesium in the body through the kidneys, 30% of the magnesium received is excreted. Real excess magnesium in the body develops mainly in chronic renal failure and intravenous administration of magnesium.
To compensate for the deficiency of magnesium in cells, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of poor absorption of magnesium, its increased excretion and provide the body with magnesium with food and special preparations. According to the recommendations, magnesium should be taken together with calcium in a ratio of 1: 2 (calcium 2 times more), it is by this formula that most vitamin-mineral complexes and pharmaceuticals are created. However, with a deficiency of magnesium, the first stage of correction should provide the body with magnesium (Magne-B6, especially in drinking ampoules, Cholespazmin, Magnesium Plus, etc.). Taking drugs should be agreed with the doctor.
The daily rate of magnesium is 400 mg (in some diseases and conditions increases to 800 mg).
For food correction of magnesium deficiency with excess protein food in the diet include: green leafy vegetables, cocoa powder, almonds, watermelon, buckwheat kernel and wheat, hazelnuts, walnuts, dried apricots, raisins, prunes, Borodino bread, spirulina, chlorophyll, tomato paste without salt, sea salt instead of table salt.
To correct magnesium deficiency with a deficiency of protein food in the diet include: hard cheese, squid, meat and heart, sea fish, cod liver, seafood.
The following cause of excess acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft:
Overdose of drugs of cholinesterase blockers group
Cholinesterase is an enzyme that destroys acetylcholine. Thanks to cholinesterase, acetylcholine does not linger long in the synaptic cleft, which as a result leads to muscle relaxation and rest. Preparations of the cholinesterase blockers group: bind this enzyme, leading to an increase in the concentration of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft and an increase in the tone of the muscle cell.
Myorelaxation with depolarizing drugs
Myorelaxation is used in performing anesthesia before surgery and leads to better anesthesia.
3. Reduction of myocyte excitability threshold
The muscle cell, like any other cell in the body, has a certain threshold of excitability. Although this threshold is specific to each cell, it is not constant. It depends on the difference in the concentration of certain ions inside and outside the cells and the safe operation of cellular pumping systems.
The main causes of seizures due to a decrease in the threshold of myocyte excitability are:
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts an electric current due to “decay” into ions. The difference in the concentration of electrolytes creates a certain charge on the cell surface. In order for a cell to be excited, the impulse it receives must be equal to or greater in strength than the charge of the cell membrane. In other words, the impulse must overcome a certain threshold value in order to bring the cell into a state of excitation. This threshold is not stable, but depends on the concentration of electrolytes in the space surrounding the cell.
When the electrolyte balance in the body changes, the threshold of excitability decreases, and weaker impulses cause muscle contraction. The frequency of contractions also increases, which leads to a state of constant excitation of the muscle cell - seizures.
The four most famous electrolytes in the human body are sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium.
Calcium.The paradox of calcium is that its lack (as well as excess) increases the risk of seizures (this is the leading symptom of not only magnesium deficiency, but also calcium).
Calcium ions (Ca2+) are attached to negative charges on the outer surface of the cell membrane, thereby increasing the "plus" outside, therefore, increases the charge difference (voltage) between the "positive" external and "negative" internal environment of the cell. If the calcium is low, then this difference (membrane potential) decreases, as if we have already begun to excite the cell. In addition, the lack of calcium increases the sensitivity of sodium channels.
All physiological effects of calcium (including participation in muscle contraction) are carried out by its ionized form (Ca++). Free calcium accounts for 43% to 50% of total calcium. Its concentration varies throughout the day: a minimum concentration of 20 hours, a maximum of 2-4 hours in the morning (due to the leaching of calcium from the bone). At this time, night cramps are most often observed. Also at this time, the level of glucose in the blood (that is, ATP) decreases, which also creates conditions for seizures.
The level of ionized calcium is maintained by the hormones parathormone, calcitonin, the active form of vitamin D3. The production of these hormones, in turn, depends on the level of Ca++. Its concentration in the blood is influenced by many factors - proteins, magnesium (it is necessary to study the concentration of magnesium and vitamin D if hypocalcemia is detected).
The acid-base state is very important: alkalosis increases binding and reduces concentration, and acidosis, on the contrary, reduces binding and increases the concentration of ionized calcium in the blood. Determination of free calcium (calcium ionized and, at the same time, parathyroid hormone, the active form of vitamin D3 - 25-OH-Vitamin D) allows you to more accurately assess the state of calcium metabolism.
Potassium.The main amount of potassium (98%) is found inside cells in the form of fragile compounds with proteins, carbohydrates and phosphorus. Part of potassium is contained in cells in ionized form and provides their membrane potential. In the extracellular environment, a small amount of potassium is mainly in ionized form. Usually, the release of potassium from cells depends on an increase in their biological activity, the breakdown of protein and glycogen, lack of oxygen. If the potassium inside the cell is low, it does not actively leave the cell along the concentration gradient, the resting potential decreases (as if we have already begun to excite the cell).
Sodium.Lack of sodium (Na+) in the extracellular environment leads to the fact that it becomes less concentrated than intracellular. By osmosis, water enters the cells. Water, entering the cells, dilutes intracellular potassium, i.e. its concentration inside the cell decreases. Consequently, it no longer leaves the cell so actively in the concentration gradient, the resting potential decreases (as if we had already begun to excite the cell).
The operation of the potassium-sodium pump is volatile. Therefore, with ATP deficiency, the electrolyte balance is disturbed, which increases the risk of seizures.
Lactic acid buildup.Osmotic edema of muscle cells in combination with a large concentration of lactic acid (lactate) with increased physical exertion disrupts the process of relaxation of the muscle cell (it is assumed that proteins that pump calcium from the cytoplasm into the EPS are denatured). Excess lactic acid occurs not only with increased physical exertion, but also completely without it in people with oxygen deficiency. In this situation, the body receives a significant part of the energy during anaerobic (oxygen-free) burning of glucose. In such people, muscle pain is present almost constantly, even without prior physical exertion.
Another reason for the high proportion of anaerobic glycolysis in the muscles ishypodynamia.
A blood test to determine the level of lactate in the blood in the absence of increased physical activity can be useful for detecting oxygen deficiency inside the cells.
Hypertensive dehydration (excess electrolytes with a shortage of water in the body) can also cause seizures, for example, in a situation where you have eaten very salty food and there is no opportunity to get drunk.
Excess water intake (both with and without electrolytes) in the body can also disrupt the water-electrolyte balance and cause seizures.
Hypovitaminosis
Vitamins play an extremely important role in the development of the body and maintaining its normal performance. They are part of enzymes and coenzymes that perform the function of maintaining the constancy of the internal environment of the body.
The contractile function of the muscles is more affected by the deficiency of vitamins A, B, D and E. At the same time, the integrity of cell membranes suffers and as a result, a decrease in the excitability threshold occurs, leading to seizures.
Vitamin D is involved in maintaining calcium and magnesium levels in the body.
4. Decrease in ATP concentration
ATP is the main chemical energy carrier in the body, synthesized by the mitochondria of cells. The allocated energy is spent on the operation of most systems that support the viability of the cell.
In the muscle cell, calcium ions normally lead to its reduction, and ATP is responsible for relaxation.
If we consider that a change in the concentration of calcium in the blood extremely rarely leads to seizures, since calcium is not consumed and is not formed during the work of the muscle, then a decrease in the concentration of ATP is a direct cause of seizures, since this resource is consumed.
It should be noted that seizures develop only in the case of extreme depletion of ATP, responsible for muscle relaxation. Restoring ATP concentration takes a certain amount of time, which corresponds to resting after hard work. Until the normal concentration of ATP is restored, the muscle does not relax. It is for this reason that the "overworked" muscle is hard to the touch and difficult to extend.
Diseases and conditions leading to a decrease in the concentration of ATP and the appearance of seizures:
5. Genetic defect of one of the contractile proteins
This category of diseases belongs to incurable. It is comforting that the incidence of the disease in the population is low and the probability of manifestation of the disease is 1: 200-300 million. This group includes various fermentopathies and diseases of abnormal proteins.
One of the diseases of this group, manifested by seizures, is Tourette syndrome (Gilles de la Tourette). Due to the mutation of specific genes in the seventh and eleventh pairs of chromosomes in the brain, abnormal connections are formed, leading to the appearance of involuntary movements (tics) and screams (more often, obscene). In the case when the tic affects the lower limb, it can manifest itself in the form of periodic seizures.
First aid for seizures
When the cause of seizures is not related to epilepsy, the following measures should be taken:
This manipulation leads to violent stretching of the muscle, which like a sponge draws blood rich in oxygen. In parallel, it is useful to produce a light massage of the limb, since it improves microcirculation and speeds up the recovery process.
Ticks and injections have a distracting effect and interrupt the reflex chain, closed with pain from muscle spasm.

The better to stretch and warm up the muscles before training, the less chance of trouble. Make lunges with a tilt, just bends - the stomach to the hips, the legs are bent. Remember that on exhalation, the elasticity of the muscles increases: bent and exhaled, while stretching.
There is an opinion that if your leg is reduced in water, you can drown. Don't believe it! In terms of physiology, even if you have cramped both legs, you can swim to shore in your arms. Drowning with a reduced leg is possible only if you give in to panic.
Many are frightened, begin to beat, inhale water from terror and go to the bottom out of stupidity. If you have reduced your foot in the sea or lake, the easiest way out is this: turned over on your back, breathe deeply and row to the shore with your hands. Feet dangling, relaxing or horribly hooking from a cramp – we continue to breathe and, without slowing down, swim.
If you are confident in the water, you can take the form of a “bomb” (hanging in the water with your legs bent upside down) and carefully knead your leg until it passes. But in this case, a person will occasionally dive under water, dive. And this method is suitable only for those who are friendly with water, calm as a tank and able to hold their breath.
An attack of seizures should be stopped first of all, since it is a stressful state for the body. The causes that caused it are treated in the second place.
Treating seizures
For the treatment of seizures, it is necessary to find the causes of their occurrence and, if possible, eliminate them.
The most common causes of seizures are: iron deficiency and other anemia, hypothyroidism and excessive accumulation of glycosaminoglycans and water in the intercellular space (the effect of muscle compression, “clogged muscle”), magnesium and vitamin D deficiency (and subsequent deficiency of ionized calcium), irregular exercise and hypodynamia.
Convulsions due to a deficiency of vitamins and trace elements are especially common in pregnant women, since a pregnant woman needs to share with the child. It is especially important for them to get a norm of iron, iodine, magnesium, calcium, vitamins.
If it is impossible to eliminate the causes, the patient should receive constant pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment (drug treatment is prescribed only by a doctor), aimed at reducing the likelihood and severity of seizures.
For the prevention of seizures, it is important to take vitamin-mineral complexes that ensure the norm of magnesium, calcium, iodine, iron, vitamins of groups B, A, C, D, C and E.
More than 80% of pregnant women suffer from seizures. For them, regular intake of vitamins and trace elements in daily dosages is a salvation from seizures.
It is necessary to provide the body with full nutrition (in terms of quality and calorie content).
It is necessary to ensure the rate of intake of any fluid (not only plain water) in the body (about 30 mg of fluid per 1 kg of weight). The norm of fluid should be increased at elevated body temperature or ambient air. Dehydration at times increases the likelihood of seizures.
For the prevention of seizures, it is very important to constantly perform muscle stretching exercises. If the muscles are not stretched and seizures occur quite often, it is better to start with a deep, rather long course of connective tissue massage.
Avoid working in the cold (or not warm enough)
In diabetes, it is important to constantly monitor blood sugar levels.
With a tendency to seizures, you should avoid everything that can cause leg swelling: lack of sleep (sitting at a computer after 24-01 am and later), long flights, excess salt and liquid, taking drugs and products containing bromelain and papain (Wobenzym, Bromelain, pineapple raw, papaya raw, kiwi).
Pelvic Muscle Training – Super Exercises for Women
Psychosomatics of pancreatic diseases
Remember, convulsions are not only unpleasant pain, but also a signal from the body about serious violations! Listen to this signal and respond correctly.published
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Source: www.sethealth.ru/2016/12/17/%D1%8D%D1%82%D0%BE-%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%8C-%D0%B0%D0%B0%B6%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B0%B9-%D1%81%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%
Tonic convulsions (as opposed to seizures of central and peripheral origin in lesions of the central nervous system) are sudden, involuntary, not amenable to controlled relaxation short-term contractions of muscles or a group of muscles, more often foot, perceived by a person as severe pain. They are familiar to almost all adults.
Seizures are quite dangerous if you are in a pond, mountains, driving. Particularly painful are convulsions of the muscles of the back, neck. But pain is not the worst thing in convulsions. Seizures are a signal of the body about serious trouble. Unfortunately, we do not always understand the “language” of the body and treat seizures as a simple trouble that complicates life, but no more.

Let’s understand in which cases the body gives us signals in the form of seizures.
Tonic convulsions occur with pathological excitation in a particular element of the motor unit:
- neuron (nerve cell);
- its axon (a long cylindrical process of kener cell, through which nerve impulses go from the cell body to organs and other nerve cells);
- neuromuscular synapse (the place of contact between two neurons or between a neuron and the receiving cell),
- Or muscle fibers.
Muscle structure
The mechanism of muscle fiber reduction is a long-studied phenomenon. In this publication, we will consider the work of cross-striped (skeletal) muscles, without affecting the principles of smooth muscle functioning.
Skeletal muscle consists of thousands of fibers, and each individual fiber, in turn, contains many myofibrils. Myofibrill in a simple light microscope is a strip in which tens and hundreds of muscle cells (myocytes) lined up in a row of nuclei are visible.

Each myocyte along the periphery has a special contractile apparatus oriented strictly parallel to the axis of the cell. The main functional unit of myofibrill, which has a contractile capacity, is the sarcomer (basic contractile unit of striated muscles, which is a complex of several proteins). Sarcomere consists of such proteins: actin (main), myosin, troponin and tropomyosin. Actin and myosin in shape resemble intertwined threads. With the participation of troponin, tropomyosin, calcium ions and ATP (a unit of energy produced in cells), there is a mutual convergence of actin and myosin threads, as a result of which the sarcomere is shortened, and accordingly the entire muscle fiber.
Mechanism of muscle contraction
The reduction of muscle fiber occurs in the following order:
- A nerve impulse occurs in the brain and is transmitted along the nerve to the muscle fiber.
- Through the substance (mediator) produced in the body - acetylcholine, an electrical impulse is transmitted from the nerve to the surface of the muscle fiber.
- Propagation of the impulse throughout the muscle fiber and its penetration deep through special T-shaped tubules.
- Transition of excitation from T-tubes to tanks. Cisterns are called special cellular formations containing a large amount of calcium ions. As a result, calcium channels are opened and calcium is released into the intracellular space.
- Calcium initiates the process of mutual convergence of actin and myosin threads by activating and restructuring the active centers of troponin and tropomyosin.
- ATP is an integral component of the above process, as it supports the process of convergence of actin and myosin strands. ATP helps to detach the heads of myosin and release its active centers. In other words, without ATP, the muscle is not able to contract, as it can not relax before it.
- As the actin and myosin threads converge, the sarcomer shortens and the muscle fiber itself and the entire muscle contract.
The following factors lead to prolonged tonic contraction of muscle fiber:
1. Excessively frequent brain impulses.
2. Excess acetylcholine in the synaptic gap.
3. Lower myocyte excitability threshold.
4. Decreased ATP concentration.
5. Genetic defect of one of the contractile proteins.
Let’s take a closer look at each factor.
1. Excessively frequent brain impulses
The brain, namely its special department - the cerebellum, is responsible for maintaining a constant tone of each muscle of the body. Even during sleep, muscles do not cease to receive impulses from the brain, but are generated much less often than in the waking state.
Under certain circumstances, the brain begins to increase impulses, which the patient feels like a feeling of muscle stiffness. When a certain threshold is reached, the impulses become so frequent that they keep the muscle in a state of constant contraction.
Leg cramps due to increased brain impulses develop in the following diseases:
- epilepsy;
- Acute psychosis;
- eclampsia;
- traumatic brain injury;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- craniocerebral thromboembolism.
Eclampsia is preceded by preeclampsia, in which the pregnant woman has increased blood pressure, swelling appears and general well-being worsens. With high blood pressure numbers (on average from 140 mm Hg. column and above), the risk of placenta detachment increases due to narrowing of the blood vessels that feed it.

During seizures, sharp contractions and relaxation of the uterine muscles occur, leading to detachment of the fetal site and termination of fetal nutrition. In this situation, there is an urgent need for emergency delivery by cesarean section in order to save the life of the fetus and stop uterine bleeding in a pregnant woman.
Traumatic brain injuries can lead to leg cramps, but this happens quite rarely.
The remaining causes of seizures due to increased brain impulses will not be considered here.
2. Excess acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine is the main mediator involved in the transmission of impulse from the nerve to the muscle cell. Under certain conditions, an excess mediator can accumulate in the synaptic cleft, inevitably leading to more frequent and strong muscle contraction, up to the development of seizures, including the lower extremities.
The following conditions cause seizures by increasing the amount of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft:
- magnesium deficiency in the body;
- overdose of drugs of the cholinesterase blocker group;
- myorelaxation with depolarizing drugs.
Magnesium is one of the most important electrolytes in the body. One of its functions is to open the channels of the presynaptic membrane to reverse the entry of an unused mediator into the end of the axon (the central process of the nerve cell responsible for the transmission of an electrical impulse).
With a lack of magnesium, these channels remain closed, which leads to the accumulation of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. As a result, even light physical activity in a short time provokes the appearance of seizures.
Magnesium deficiency develops mainly:
- with reduced consumption (reduced content in “civilized” food, starvation);
- with reduced absorption of magnesium in the intestines (malabsorption syndrome, inflammatory enteropathies, a condition after intestinal resection, high calcium intake with food, eating foods too rich in proteins and fats);
- with increased need (intensive sports, chronic stress, growth period, pregnancy and breastfeeding, increased sweating, recovery period);
- with increased excretion (vomiting, prolonged diarrhea, frequent use of laxatives, diuretics, alcohol, strong coffee, tea, activated charcoal and other sorbents, some kidney diseases, diabetes, cancer treatment);
- with endocrine disorders: hyperthyroidism (excessive amount of thyroid hormones), hyperparathyroidism (excessive amount of parathyroid hormones), hyperaldosteronism (constantly elevated level of the adrenal hormone aldosterone).
- tingling in the feet and palms (paresthesia) - associated with overexcitation of sensitive endings;
- tremor, ataxia, nystagmus;
- autism;
- hearing loss;
- disorders of the emotional sphere, depression, degenerative diseases, chronic fatigue syndrome;
- migraine
- skin diseases, focal alopecia;
- Bronchospastic diseases, urolithiasis (oxalates), premenstrual syndrome, osteoporosis, fibromyalgia, arthritis and many others.
- hyperactivity – a person cannot stay in one place for a long time, constantly moves, even in a dream (the syndrome of “restless legs” is associated with increased excitability of skeletal muscles);
- diarrhea (“irritable” colon), sometimes constipation, abdominal pain,
- sensation of a lump in the throat (spasm in the throat), respiratory disorders - an increase in respiratory rhythm, a feeling of suffocation (under stress);
- disorders of urination: frequent urge, pain in the bladder;
- various sexual disorders more often of a neuro-mental nature (accelerated ejaculation and erectile dysfunction in men, decreased libido, anorgasmia or erased orgasm in women, etc.);
- pain in the back and lower back;
- Tetanya, deafness.
With a long-term deep deficiency of magnesium, acute severe disorders are observed, mainly of the CNS; hemolytic anemia, cardiovascular diseases develop (angina pectoris, tachycardia, extrasystole, arrhythmias, thrombosis); cerebral disorders appear (headache, dizziness, fear, depression, memory impairment, confusion, hallucinations); abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, laryngeal spasms, bronchitis, weather, elevations in the body, fever, endemosis, and coldness;
With the aggravation of magnesium deficiency in the body, except for convulsions of the calf muscles, soles, feet, hands, convulsions of the occipital, spinal muscles, face can develop.
As you can see, serious attitude to the convulsions that have appeared and the elimination of such a cause of their occurrence as a long-term magnesium deficiency in the body can save you and your loved ones, especially children, from further serious disorders in the body.

How to identify magnesium deficiency in the body
Magnesium is mainly an intracellular element, so determining its level in the blood is not informative for detecting minor intracellular deficits, and intracellular diagnostics (except for scientific purposes) has not yet been developed. Low levels of magnesium in the blood is already a very deep deficiency of magnesium.
Excess magnesium in the blood can be a consequence of the loss of magnesium by cells during their destruction, so sometimes microelementologists consider not as an excess of magnesium inside cells, but as a loss of magnesium by cells and the release of magnesium into the blood.
Determining the level of magnesium in the hair is more informative, especially when magnesium deficiency is detected (found much more often than in the blood). If the level of magnesium in the blood is a momentary state, then its level in the hair is an accumulation in 2-3 months (1 cm of hair - 1 month if you cut the hair for analysis at the root, and not the tips of the hair).
There is no unequivocal analysis to determine the level of magnesium inside cells at the moment, so a competent specialist focuses not only on tests, but also on the symptoms of magnesium deficiency.
Magnesium is not normally retained in the body. With the normal intake of magnesium in the body through the kidneys, 30% of the magnesium received is excreted. Real excess magnesium in the body develops mainly in chronic renal failure and intravenous administration of magnesium.
To compensate for the deficiency of magnesium in cells, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of poor absorption of magnesium, its increased excretion and provide the body with magnesium with food and special preparations. According to the recommendations, magnesium should be taken together with calcium in a ratio of 1: 2 (calcium 2 times more), it is by this formula that most vitamin-mineral complexes and pharmaceuticals are created. However, with a deficiency of magnesium, the first stage of correction should provide the body with magnesium (Magne-B6, especially in drinking ampoules, Cholespazmin, Magnesium Plus, etc.). Taking drugs should be agreed with the doctor.
The daily rate of magnesium is 400 mg (in some diseases and conditions increases to 800 mg).
For food correction of magnesium deficiency with excess protein food in the diet include: green leafy vegetables, cocoa powder, almonds, watermelon, buckwheat kernel and wheat, hazelnuts, walnuts, dried apricots, raisins, prunes, Borodino bread, spirulina, chlorophyll, tomato paste without salt, sea salt instead of table salt.
To correct magnesium deficiency with a deficiency of protein food in the diet include: hard cheese, squid, meat and heart, sea fish, cod liver, seafood.
The following cause of excess acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft:
Overdose of drugs of cholinesterase blockers group
Cholinesterase is an enzyme that destroys acetylcholine. Thanks to cholinesterase, acetylcholine does not linger long in the synaptic cleft, which as a result leads to muscle relaxation and rest. Preparations of the cholinesterase blockers group: bind this enzyme, leading to an increase in the concentration of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft and an increase in the tone of the muscle cell.
Myorelaxation with depolarizing drugs
Myorelaxation is used in performing anesthesia before surgery and leads to better anesthesia.
3. Reduction of myocyte excitability threshold
The muscle cell, like any other cell in the body, has a certain threshold of excitability. Although this threshold is specific to each cell, it is not constant. It depends on the difference in the concentration of certain ions inside and outside the cells and the safe operation of cellular pumping systems.
The main causes of seizures due to a decrease in the threshold of myocyte excitability are:
- electrolyte imbalance;
- hypovitaminosis.
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts an electric current due to “decay” into ions. The difference in the concentration of electrolytes creates a certain charge on the cell surface. In order for a cell to be excited, the impulse it receives must be equal to or greater in strength than the charge of the cell membrane. In other words, the impulse must overcome a certain threshold value in order to bring the cell into a state of excitation. This threshold is not stable, but depends on the concentration of electrolytes in the space surrounding the cell.
When the electrolyte balance in the body changes, the threshold of excitability decreases, and weaker impulses cause muscle contraction. The frequency of contractions also increases, which leads to a state of constant excitation of the muscle cell - seizures.
The four most famous electrolytes in the human body are sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium.
Calcium.The paradox of calcium is that its lack (as well as excess) increases the risk of seizures (this is the leading symptom of not only magnesium deficiency, but also calcium).
Calcium ions (Ca2+) are attached to negative charges on the outer surface of the cell membrane, thereby increasing the "plus" outside, therefore, increases the charge difference (voltage) between the "positive" external and "negative" internal environment of the cell. If the calcium is low, then this difference (membrane potential) decreases, as if we have already begun to excite the cell. In addition, the lack of calcium increases the sensitivity of sodium channels.
All physiological effects of calcium (including participation in muscle contraction) are carried out by its ionized form (Ca++). Free calcium accounts for 43% to 50% of total calcium. Its concentration varies throughout the day: a minimum concentration of 20 hours, a maximum of 2-4 hours in the morning (due to the leaching of calcium from the bone). At this time, night cramps are most often observed. Also at this time, the level of glucose in the blood (that is, ATP) decreases, which also creates conditions for seizures.
The level of ionized calcium is maintained by the hormones parathormone, calcitonin, the active form of vitamin D3. The production of these hormones, in turn, depends on the level of Ca++. Its concentration in the blood is influenced by many factors - proteins, magnesium (it is necessary to study the concentration of magnesium and vitamin D if hypocalcemia is detected).
The acid-base state is very important: alkalosis increases binding and reduces concentration, and acidosis, on the contrary, reduces binding and increases the concentration of ionized calcium in the blood. Determination of free calcium (calcium ionized and, at the same time, parathyroid hormone, the active form of vitamin D3 - 25-OH-Vitamin D) allows you to more accurately assess the state of calcium metabolism.
Potassium.The main amount of potassium (98%) is found inside cells in the form of fragile compounds with proteins, carbohydrates and phosphorus. Part of potassium is contained in cells in ionized form and provides their membrane potential. In the extracellular environment, a small amount of potassium is mainly in ionized form. Usually, the release of potassium from cells depends on an increase in their biological activity, the breakdown of protein and glycogen, lack of oxygen. If the potassium inside the cell is low, it does not actively leave the cell along the concentration gradient, the resting potential decreases (as if we have already begun to excite the cell).
Sodium.Lack of sodium (Na+) in the extracellular environment leads to the fact that it becomes less concentrated than intracellular. By osmosis, water enters the cells. Water, entering the cells, dilutes intracellular potassium, i.e. its concentration inside the cell decreases. Consequently, it no longer leaves the cell so actively in the concentration gradient, the resting potential decreases (as if we had already begun to excite the cell).
The operation of the potassium-sodium pump is volatile. Therefore, with ATP deficiency, the electrolyte balance is disturbed, which increases the risk of seizures.
Lactic acid buildup.Osmotic edema of muscle cells in combination with a large concentration of lactic acid (lactate) with increased physical exertion disrupts the process of relaxation of the muscle cell (it is assumed that proteins that pump calcium from the cytoplasm into the EPS are denatured). Excess lactic acid occurs not only with increased physical exertion, but also completely without it in people with oxygen deficiency. In this situation, the body receives a significant part of the energy during anaerobic (oxygen-free) burning of glucose. In such people, muscle pain is present almost constantly, even without prior physical exertion.
Another reason for the high proportion of anaerobic glycolysis in the muscles ishypodynamia.
A blood test to determine the level of lactate in the blood in the absence of increased physical activity can be useful for detecting oxygen deficiency inside the cells.
Hypertensive dehydration (excess electrolytes with a shortage of water in the body) can also cause seizures, for example, in a situation where you have eaten very salty food and there is no opportunity to get drunk.
Excess water intake (both with and without electrolytes) in the body can also disrupt the water-electrolyte balance and cause seizures.
Hypovitaminosis
Vitamins play an extremely important role in the development of the body and maintaining its normal performance. They are part of enzymes and coenzymes that perform the function of maintaining the constancy of the internal environment of the body.
The contractile function of the muscles is more affected by the deficiency of vitamins A, B, D and E. At the same time, the integrity of cell membranes suffers and as a result, a decrease in the excitability threshold occurs, leading to seizures.
Vitamin D is involved in maintaining calcium and magnesium levels in the body.
4. Decrease in ATP concentration
ATP is the main chemical energy carrier in the body, synthesized by the mitochondria of cells. The allocated energy is spent on the operation of most systems that support the viability of the cell.
In the muscle cell, calcium ions normally lead to its reduction, and ATP is responsible for relaxation.
If we consider that a change in the concentration of calcium in the blood extremely rarely leads to seizures, since calcium is not consumed and is not formed during the work of the muscle, then a decrease in the concentration of ATP is a direct cause of seizures, since this resource is consumed.
It should be noted that seizures develop only in the case of extreme depletion of ATP, responsible for muscle relaxation. Restoring ATP concentration takes a certain amount of time, which corresponds to resting after hard work. Until the normal concentration of ATP is restored, the muscle does not relax. It is for this reason that the "overworked" muscle is hard to the touch and difficult to extend.
Diseases and conditions leading to a decrease in the concentration of ATP and the appearance of seizures:
- oxygen deficiency: anemia (for any reason); lung and vascular diseases, adenoids, heart failure; altitude sickness; influenza;
- hypoglycemia (low blood sugar);
- deficiency of L-Carnitine (transfers fats to the mitochondria), coenzyme Q10 (especially when taking statins);
- deficiency of vitamins of group B (especially B1, B2, B5, B6);
- magnesium deficiency;
- hypothyroidism and excessive deposition of glycosaminoglycans in the intercellular space;
- diabetes mellitus;
- inferior vena cava syndrome;
- chronic heart failure;
- varicose veins;
- thrombophlebitis;
- obliterating matterosclerosis;
- early postoperative period;
- excessive physical exertion;
- Deficiency of substrates for energy production (hungry, low-calorie diets).
5. Genetic defect of one of the contractile proteins
This category of diseases belongs to incurable. It is comforting that the incidence of the disease in the population is low and the probability of manifestation of the disease is 1: 200-300 million. This group includes various fermentopathies and diseases of abnormal proteins.
One of the diseases of this group, manifested by seizures, is Tourette syndrome (Gilles de la Tourette). Due to the mutation of specific genes in the seventh and eleventh pairs of chromosomes in the brain, abnormal connections are formed, leading to the appearance of involuntary movements (tics) and screams (more often, obscene). In the case when the tic affects the lower limb, it can manifest itself in the form of periodic seizures.
First aid for seizures
When the cause of seizures is not related to epilepsy, the following measures should be taken:
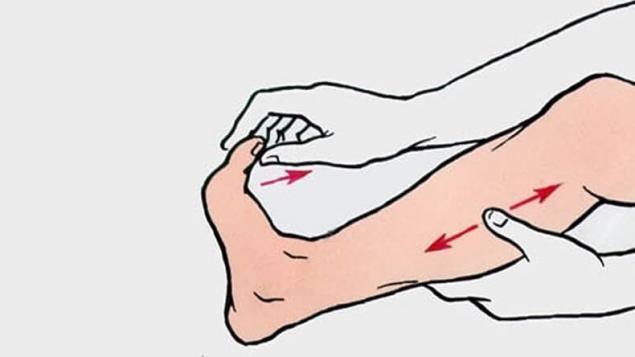
- First,You need to give the limbs an elevated position. This provides an improved outflow of blood and eliminates stagnation.
- Second,You should take the toes and make dorsal flexion of the foot (to the knee) in two stages - first half bend and release, and then again slowly bend as much as possible and hold in this position until the seizures stop.

This manipulation leads to violent stretching of the muscle, which like a sponge draws blood rich in oxygen. In parallel, it is useful to produce a light massage of the limb, since it improves microcirculation and speeds up the recovery process.
Ticks and injections have a distracting effect and interrupt the reflex chain, closed with pain from muscle spasm.
- ThereafterAfter a seizure, it is useful to do an intense massage, and, stretching exercises.

The better to stretch and warm up the muscles before training, the less chance of trouble. Make lunges with a tilt, just bends - the stomach to the hips, the legs are bent. Remember that on exhalation, the elasticity of the muscles increases: bent and exhaled, while stretching.
There is an opinion that if your leg is reduced in water, you can drown. Don't believe it! In terms of physiology, even if you have cramped both legs, you can swim to shore in your arms. Drowning with a reduced leg is possible only if you give in to panic.
Many are frightened, begin to beat, inhale water from terror and go to the bottom out of stupidity. If you have reduced your foot in the sea or lake, the easiest way out is this: turned over on your back, breathe deeply and row to the shore with your hands. Feet dangling, relaxing or horribly hooking from a cramp – we continue to breathe and, without slowing down, swim.
If you are confident in the water, you can take the form of a “bomb” (hanging in the water with your legs bent upside down) and carefully knead your leg until it passes. But in this case, a person will occasionally dive under water, dive. And this method is suitable only for those who are friendly with water, calm as a tank and able to hold their breath.
An attack of seizures should be stopped first of all, since it is a stressful state for the body. The causes that caused it are treated in the second place.
Treating seizures
For the treatment of seizures, it is necessary to find the causes of their occurrence and, if possible, eliminate them.
The most common causes of seizures are: iron deficiency and other anemia, hypothyroidism and excessive accumulation of glycosaminoglycans and water in the intercellular space (the effect of muscle compression, “clogged muscle”), magnesium and vitamin D deficiency (and subsequent deficiency of ionized calcium), irregular exercise and hypodynamia.
Convulsions due to a deficiency of vitamins and trace elements are especially common in pregnant women, since a pregnant woman needs to share with the child. It is especially important for them to get a norm of iron, iodine, magnesium, calcium, vitamins.
If it is impossible to eliminate the causes, the patient should receive constant pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment (drug treatment is prescribed only by a doctor), aimed at reducing the likelihood and severity of seizures.
For the prevention of seizures, it is important to take vitamin-mineral complexes that ensure the norm of magnesium, calcium, iodine, iron, vitamins of groups B, A, C, D, C and E.
More than 80% of pregnant women suffer from seizures. For them, regular intake of vitamins and trace elements in daily dosages is a salvation from seizures.
It is necessary to provide the body with full nutrition (in terms of quality and calorie content).
It is necessary to ensure the rate of intake of any fluid (not only plain water) in the body (about 30 mg of fluid per 1 kg of weight). The norm of fluid should be increased at elevated body temperature or ambient air. Dehydration at times increases the likelihood of seizures.
For the prevention of seizures, it is very important to constantly perform muscle stretching exercises. If the muscles are not stretched and seizures occur quite often, it is better to start with a deep, rather long course of connective tissue massage.
Avoid working in the cold (or not warm enough)
In diabetes, it is important to constantly monitor blood sugar levels.
With a tendency to seizures, you should avoid everything that can cause leg swelling: lack of sleep (sitting at a computer after 24-01 am and later), long flights, excess salt and liquid, taking drugs and products containing bromelain and papain (Wobenzym, Bromelain, pineapple raw, papaya raw, kiwi).
Pelvic Muscle Training – Super Exercises for Women
Psychosomatics of pancreatic diseases
Remember, convulsions are not only unpleasant pain, but also a signal from the body about serious violations! Listen to this signal and respond correctly.published
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Source: www.sethealth.ru/2016/12/17/%D1%8D%D1%82%D0%BE-%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%8C-%D0%B0%D0%B0%B6%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B0%B9-%D1%81%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%B0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%D0%