637
Leptin is the main hormone regulator of energy metabolism, part 1.
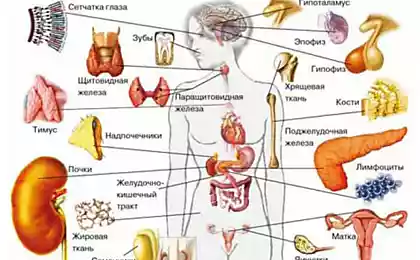
Leptin is the main regulator of energy metabolism: the mode of abundance. Leptin (from λεπτός — thin) is a key hormone regulating energy metabolism. The hormone is produced by adipose tissue and acts on the brain. That is why leptin is the most important regulator of the entire energy balance. That includes not only weight, but also the behavior and mood. No creature can not live or perform complex actions without energy.
Leptin is the main hormone regulator of energy metabolism to Draw your attention: it's not just about food, but also on motivation, mood and behavior, sexual activity, etc. Energy status is the common denominator of the action of the body. Of course, it was formed on the basis of dietary hormones, because it is a very ancient system of the body, and no food anywhere.
Mode of scarcity and abundance. The main threat to any organism is the hunger and lack of food. Very often come long hungry seasons that need to wait. In these cases, the body goes into deficit in order to slow down energy expenditure and through difficult times. It is known that many animals can and do hibernate.
The mode of deficit — an adaptation to the starving time. The body in the deficit regime tries by all means to slow down the calorie expenditure. This termination of siasimuna, slowing of physical activity, decreased motivation and efficiency, suppression of sexual and reproductive function. It's off the thyroid and ovaries. The deficit regime is to activate eating behavior on the search for high-calorie foods, disabling saturation and maximum fat gain. In the mode of deficiency the body is susceptible to any freebies.
When the body goes into deficit, his motto becomes "to survive at any cost". To do this, it slows down the metabolism and consumption of energy and becomes susceptible to any sources freestuff quick energy. Person resists the energy expenditure at all levels: from slowing down of metabolism to laziness and procrastination. He literally can't get up from the sofa, because his body is screaming: don't move, take care of every calorie you need to survive, do not smile, do not rejoice, I wait for the trick — because you live and survive. You do not need to accept the regime of the deficit as a bad thing: it is an ancient adaptive response that helps us survive. The trouble starts when this response is not working or activated the wrong signals. It's like body temperature: you do know that in disease the body temperature increases the body to better fight infection? Didn't you know?
How this system works OK? Normal — mode abundance. I want you to remember: in the experiments the weight is not depended on the food consumed, but only from the qualitative work of leptin and its receptors. Moreover, these changes are not quick: the transition from mode to mode takes three days. Full switch back to the mode of abundance is up to three weeks. Get the idea? The deficit can fall 2-3 days, and to go up to 3 weeks! If you are in deficit for a long time, then recovery may take 4 to 6 weeks. Normally, the content of leptin in the General circulation of the blood is subject to circadian rhythms with a nocturnal rise, and its secretion is of a pulsed nature. Morning leptin levels are low and we want to eat, and in the evening high – we don't want. Biorhythms and sleep play an important role in the secretion of leptin. Please note that some of these effects are not direct, but mediated through the brain.
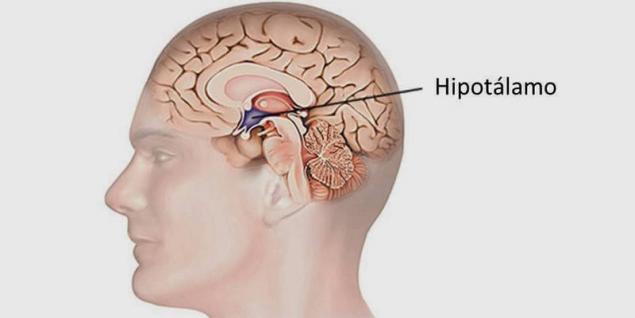
Gear lever mode — in the hypothalamus In normal leptin stands out fat cells and gives a signal to the brain, as there are available energy. And the brain decides how it will spend. Leptin-sensitive neurons in dorsomedial the hypothalamus are key regulators of body weight and energy expenditure.
The hypothalamus is a small region of the intermediate brain, including a large number of groups of cells (more than 30 nuclei) that regulate neuroendocrine activity and homeostasis of the body. The hypothalamus is connected by nerve paths with almost all parts of the Central nervous system, including the cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, cerebellum, brain stem and spinal cord. Together with the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus forms the hypothalamic-pituitary system in which the hypothalamus controls the secretion of hormones of the pituitary gland and is the Central link between the nervous and endocrine systems. It secretes hormones and neuropeptides regulates functions such as the feeling of hunger and thirst, body temperature regulation, sexual behavior, sleep and wakefulness (the circadian rhythms). Recent studies show that the hypothalamus plays an important role in the regulation of higher functions such as memory and emotional state, and thereby participates in the formation of various aspects of behavior.
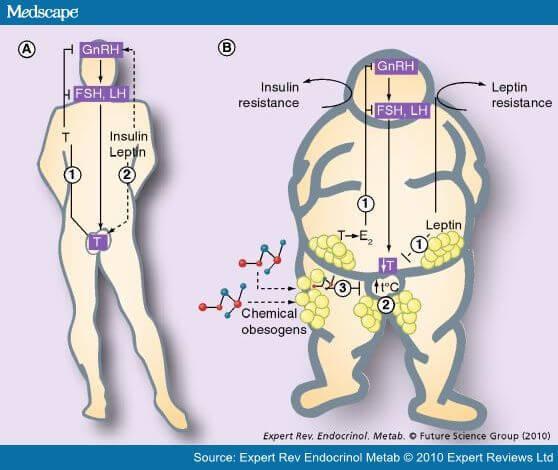
Negative energy balance caused by the restriction of food intake or starvation, leads to a decrease in concentrations of leptin, while positive, caused by overeating, increases its level. Glucocorticoids, insulin, estrogens, TNF - α, interleukin-1 (IL-1) stimulate the synthesis and secretion of leptin by adipocytes. High levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone, androgens, agonists of β-adrenergic receptors, growth hormone and the use of tiazolidindionov inhibit secretion of this mediator.
The model of the regulation of energy balance by leptin with the involvement of hypothalamic anabolic (neuropeptide Y) and catabolic (α-melanocytestimulating hormone and corticotropin-releasing hormone) pathways. Leptin serves as a "lipostat", which, through its receptors that inform the brain about the state of energy reserves in adipose tissue and alters efferent link energy homeostasis.
Negative energy balance increases the level of neuropeptide Y in arcuate and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus. Secretion of neuropeptide Y causes hyperphagia and hyperinsulinemia. Observed parallel activation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal system with increased release of blood corticosteroids. Hyperinsulinemia stimulates the accumulation of adipose tissue, and increased level of cortisol inhibits glucose utilization. The combination of hyperinsulinemia and hypercortisolemia increases the production of leptin by adipocytes, elevated levels of which causes an increase in levels monolinolein acid corticotropin-releasing hormone and proopiomelanocortin/α-melanocytestimulating hormone/melanocortin in arcuate nuclei of the hypothalamus. This in turn leads to decreased food intake and reduced body weight.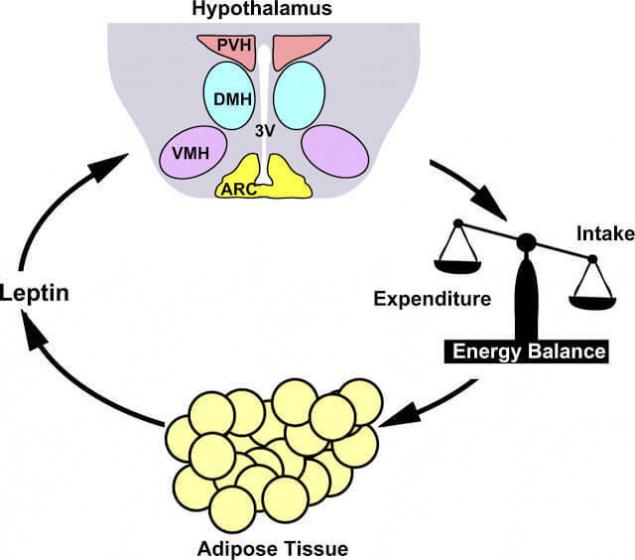
If energy excess, the brain gives the command to burn the excess fat. Therefore, in normal operation, the hormone can overeat and not gain weight. And if the brain decides that energy is low, the brain rebuilds the metabolism so that to save energy and to get as much energy from the environment the easiest mode (deficit). So, to understand how leptin works in the mode of abundance (when the brain knows what energy it is sufficient).
1. Body weight. Stimulates the preservation or reduction (in excess) of body weight. Promotes Ingenio mass of white fat. Increases the rate of lipolysis (breakdown of fat) and decrease the content of triglycerides in white adipose tissue. Leptin also induces weight loss independent of food intake, through the launch of thermogenesis.
2. The regulation of appetite. Suppresses appetite in the brain. Improve satiety, prevent overeating. It is believed that it acts on the hypothalamus, inhibiting the synthesis and release of neuropeptide Y, which causes the feeling of hunger. Interaction with specific leptin receptors located in hypothalamic region, activates the production of nerve impulses to parts of the brain responsible for appetite regulation.
4. Metabolism. Inhibits release of insulin. Normalizes and improves the functioning of the thyroid gland.
5. Enhances the breakdown of fat cells brown adipose tissue (turns fat into heat).
6. Stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. Moreover, leptin stimulates the sympathetic nervous system and thermogenesis by uncoupling of oxidation (cellular respiration) and phosphorylation (synthesis of ATP) in the mitochondria of white adipose tissue.
Leptin influence on the psyche and behavior.1. Increases motor activity and endurance. One of the possible mechanisms: increased hepatic glycogenolysis and the seizure of glucose by skeletal muscles.
2. Improves mood, has protivoleprosnami effect. The anxiety level of depression increases, usually when the body is lowered the content of leptin.
3. Increases stress, reduces anxiety. According to scientists, the reason for the above relationships is the ability of leptin to inhibit depressive behavior by stimulating the secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus, as well as provide anti-anxiety effect by inhibition of dopaminergic neurons of the mid brain structures. About dopamine and leptin we will write separately.
Other leptin influence on health. 1. A variety of health effect: the strengthening of bones, blood thinners, etc. the thyroid gland, liver etc. Will write more later.
2. Sex. Enhances libido, regulates menstrual cycle and reproductive function (ability to get pregnant). Leptin also controls the ability to conceive in women. If a woman is resistant to the leptin, it will be a big problem if she wants to get pregnant. Example: polycystic ovary syndrome, anorexia, exhaustion, problems with pregnancy with depression. In men affect testosterone levels. But appetite and metabolism, leptin also regulates the level of testosterone. In the journal Archives of Andrology presents the results of a survey of 77 men aged 20 to 60 years. The purpose of the experiment was to determine the factors affecting the suppression of the function of the production of testosterone. After careful analysis it was found that the suppression of testosterone is closely related to body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, insulin resistance and high leptin levels
3. Is associated with the development of metabolic syndrome: diabetes, hypertension, etc. Changes in sensitivity to leptin precede the development of insulin resistance.It is established that the link between leptin and cardiovascular disease is independent of other risk factors such as Smoking, high cholesterol and high blood pressure and due to the influence of leptin on arterial elasticity. In addition, high leptin levels creates a high probability of thrombosis: as a result of specific interactions between leptin and the receptors to it, located on the platelets responsible for blood clotting, stimulates thrombus formation.
Violations of leptin is not always associated with excess body weight. On the contrary, most studies show that it may be impaired even with normal and low body weight, i.e. in the mode of deficiency, you can go with a normal body weight. In addition, many people can be so-called"invisible stomach" is visceral fat, the excess of which is with a lack of muscle mass gives a normal body weight.
So, the researchers found that among the diseases provoked by low contents of leptin, is as serious as anorexia nervosa, functional hypothalamic amenorrhea, in which women stop menstruation, despite normal weight. Impaired concentration leptin affects mental health, and it can also be at a normal weight! A correlation analysis of leptin and Galina with the results of psychological testing showed the presence of a strong feedback between the concentration of leptin and the scores of the examinee in the HAM-D, HAM-A and PSS (scale of depression and anxiety). This correlation was independent of body mass index (BMI). Thus, the regime of scarcity and abundance is a universal work tool settings energy status regardless of body weight. published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © Join us at Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: beloveshkin.com/2015/07/leptin-glavnyj-gormon-i-regulyator-ehnergeticheskogo-obmena-chast-1.html

Leptin is the main hormone regulator of energy metabolism to Draw your attention: it's not just about food, but also on motivation, mood and behavior, sexual activity, etc. Energy status is the common denominator of the action of the body. Of course, it was formed on the basis of dietary hormones, because it is a very ancient system of the body, and no food anywhere.
Mode of scarcity and abundance. The main threat to any organism is the hunger and lack of food. Very often come long hungry seasons that need to wait. In these cases, the body goes into deficit in order to slow down energy expenditure and through difficult times. It is known that many animals can and do hibernate.
The mode of deficit — an adaptation to the starving time. The body in the deficit regime tries by all means to slow down the calorie expenditure. This termination of siasimuna, slowing of physical activity, decreased motivation and efficiency, suppression of sexual and reproductive function. It's off the thyroid and ovaries. The deficit regime is to activate eating behavior on the search for high-calorie foods, disabling saturation and maximum fat gain. In the mode of deficiency the body is susceptible to any freebies.
When the body goes into deficit, his motto becomes "to survive at any cost". To do this, it slows down the metabolism and consumption of energy and becomes susceptible to any sources freestuff quick energy. Person resists the energy expenditure at all levels: from slowing down of metabolism to laziness and procrastination. He literally can't get up from the sofa, because his body is screaming: don't move, take care of every calorie you need to survive, do not smile, do not rejoice, I wait for the trick — because you live and survive. You do not need to accept the regime of the deficit as a bad thing: it is an ancient adaptive response that helps us survive. The trouble starts when this response is not working or activated the wrong signals. It's like body temperature: you do know that in disease the body temperature increases the body to better fight infection? Didn't you know?
How this system works OK? Normal — mode abundance. I want you to remember: in the experiments the weight is not depended on the food consumed, but only from the qualitative work of leptin and its receptors. Moreover, these changes are not quick: the transition from mode to mode takes three days. Full switch back to the mode of abundance is up to three weeks. Get the idea? The deficit can fall 2-3 days, and to go up to 3 weeks! If you are in deficit for a long time, then recovery may take 4 to 6 weeks. Normally, the content of leptin in the General circulation of the blood is subject to circadian rhythms with a nocturnal rise, and its secretion is of a pulsed nature. Morning leptin levels are low and we want to eat, and in the evening high – we don't want. Biorhythms and sleep play an important role in the secretion of leptin. Please note that some of these effects are not direct, but mediated through the brain.

Gear lever mode — in the hypothalamus In normal leptin stands out fat cells and gives a signal to the brain, as there are available energy. And the brain decides how it will spend. Leptin-sensitive neurons in dorsomedial the hypothalamus are key regulators of body weight and energy expenditure.
The hypothalamus is a small region of the intermediate brain, including a large number of groups of cells (more than 30 nuclei) that regulate neuroendocrine activity and homeostasis of the body. The hypothalamus is connected by nerve paths with almost all parts of the Central nervous system, including the cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, cerebellum, brain stem and spinal cord. Together with the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus forms the hypothalamic-pituitary system in which the hypothalamus controls the secretion of hormones of the pituitary gland and is the Central link between the nervous and endocrine systems. It secretes hormones and neuropeptides regulates functions such as the feeling of hunger and thirst, body temperature regulation, sexual behavior, sleep and wakefulness (the circadian rhythms). Recent studies show that the hypothalamus plays an important role in the regulation of higher functions such as memory and emotional state, and thereby participates in the formation of various aspects of behavior.
Negative energy balance caused by the restriction of food intake or starvation, leads to a decrease in concentrations of leptin, while positive, caused by overeating, increases its level. Glucocorticoids, insulin, estrogens, TNF - α, interleukin-1 (IL-1) stimulate the synthesis and secretion of leptin by adipocytes. High levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone, androgens, agonists of β-adrenergic receptors, growth hormone and the use of tiazolidindionov inhibit secretion of this mediator.
The model of the regulation of energy balance by leptin with the involvement of hypothalamic anabolic (neuropeptide Y) and catabolic (α-melanocytestimulating hormone and corticotropin-releasing hormone) pathways. Leptin serves as a "lipostat", which, through its receptors that inform the brain about the state of energy reserves in adipose tissue and alters efferent link energy homeostasis.
Negative energy balance increases the level of neuropeptide Y in arcuate and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus. Secretion of neuropeptide Y causes hyperphagia and hyperinsulinemia. Observed parallel activation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal system with increased release of blood corticosteroids. Hyperinsulinemia stimulates the accumulation of adipose tissue, and increased level of cortisol inhibits glucose utilization. The combination of hyperinsulinemia and hypercortisolemia increases the production of leptin by adipocytes, elevated levels of which causes an increase in levels monolinolein acid corticotropin-releasing hormone and proopiomelanocortin/α-melanocytestimulating hormone/melanocortin in arcuate nuclei of the hypothalamus. This in turn leads to decreased food intake and reduced body weight.

If energy excess, the brain gives the command to burn the excess fat. Therefore, in normal operation, the hormone can overeat and not gain weight. And if the brain decides that energy is low, the brain rebuilds the metabolism so that to save energy and to get as much energy from the environment the easiest mode (deficit). So, to understand how leptin works in the mode of abundance (when the brain knows what energy it is sufficient).
1. Body weight. Stimulates the preservation or reduction (in excess) of body weight. Promotes Ingenio mass of white fat. Increases the rate of lipolysis (breakdown of fat) and decrease the content of triglycerides in white adipose tissue. Leptin also induces weight loss independent of food intake, through the launch of thermogenesis.
2. The regulation of appetite. Suppresses appetite in the brain. Improve satiety, prevent overeating. It is believed that it acts on the hypothalamus, inhibiting the synthesis and release of neuropeptide Y, which causes the feeling of hunger. Interaction with specific leptin receptors located in hypothalamic region, activates the production of nerve impulses to parts of the brain responsible for appetite regulation.
4. Metabolism. Inhibits release of insulin. Normalizes and improves the functioning of the thyroid gland.
5. Enhances the breakdown of fat cells brown adipose tissue (turns fat into heat).
6. Stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. Moreover, leptin stimulates the sympathetic nervous system and thermogenesis by uncoupling of oxidation (cellular respiration) and phosphorylation (synthesis of ATP) in the mitochondria of white adipose tissue.
Leptin influence on the psyche and behavior.1. Increases motor activity and endurance. One of the possible mechanisms: increased hepatic glycogenolysis and the seizure of glucose by skeletal muscles.
2. Improves mood, has protivoleprosnami effect. The anxiety level of depression increases, usually when the body is lowered the content of leptin.
3. Increases stress, reduces anxiety. According to scientists, the reason for the above relationships is the ability of leptin to inhibit depressive behavior by stimulating the secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus, as well as provide anti-anxiety effect by inhibition of dopaminergic neurons of the mid brain structures. About dopamine and leptin we will write separately.
Other leptin influence on health. 1. A variety of health effect: the strengthening of bones, blood thinners, etc. the thyroid gland, liver etc. Will write more later.
2. Sex. Enhances libido, regulates menstrual cycle and reproductive function (ability to get pregnant). Leptin also controls the ability to conceive in women. If a woman is resistant to the leptin, it will be a big problem if she wants to get pregnant. Example: polycystic ovary syndrome, anorexia, exhaustion, problems with pregnancy with depression. In men affect testosterone levels. But appetite and metabolism, leptin also regulates the level of testosterone. In the journal Archives of Andrology presents the results of a survey of 77 men aged 20 to 60 years. The purpose of the experiment was to determine the factors affecting the suppression of the function of the production of testosterone. After careful analysis it was found that the suppression of testosterone is closely related to body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, insulin resistance and high leptin levels
3. Is associated with the development of metabolic syndrome: diabetes, hypertension, etc. Changes in sensitivity to leptin precede the development of insulin resistance.It is established that the link between leptin and cardiovascular disease is independent of other risk factors such as Smoking, high cholesterol and high blood pressure and due to the influence of leptin on arterial elasticity. In addition, high leptin levels creates a high probability of thrombosis: as a result of specific interactions between leptin and the receptors to it, located on the platelets responsible for blood clotting, stimulates thrombus formation.
Violations of leptin is not always associated with excess body weight. On the contrary, most studies show that it may be impaired even with normal and low body weight, i.e. in the mode of deficiency, you can go with a normal body weight. In addition, many people can be so-called"invisible stomach" is visceral fat, the excess of which is with a lack of muscle mass gives a normal body weight.
So, the researchers found that among the diseases provoked by low contents of leptin, is as serious as anorexia nervosa, functional hypothalamic amenorrhea, in which women stop menstruation, despite normal weight. Impaired concentration leptin affects mental health, and it can also be at a normal weight! A correlation analysis of leptin and Galina with the results of psychological testing showed the presence of a strong feedback between the concentration of leptin and the scores of the examinee in the HAM-D, HAM-A and PSS (scale of depression and anxiety). This correlation was independent of body mass index (BMI). Thus, the regime of scarcity and abundance is a universal work tool settings energy status regardless of body weight. published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © Join us at Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: beloveshkin.com/2015/07/leptin-glavnyj-gormon-i-regulyator-ehnergeticheskogo-obmena-chast-1.html