439
How to avoid obesity in a child
Spoon for mom, spoon for dad? Where do fat children come from, whether your baby is overweight and how to avoid the “fat” question – we are advised by an endocrinologist, pediatrician, nutritionist and psychologist.

My son was born quite large – 4 kg. Especially for me, a meter with a cap. And throughout the first year, he confidently overcame all the averages in height and weight. The doctors, looking at him and then at his mother, asked with surprise: “You must have a big dad?”
Our hamster with cheeks on his chest even turned over and sat down later - the build did not allow. But as soon as my boy got up his legs and ran, everything took off with his hand. Walks, active games, a bicycle-scooter-rollers, sambo, jumping into the water - becoming, as a child should, a perpetual engine, he turned into a grasshopper and went into the category of petite. Although he looks thin, his weight is normal.
It would seem that all healthy children are not particularly persevering. So where do babies come from, for whom excess weight is a problem?
Obesity is a disease that signals that everything is not okay with the body. Of course, it happens that excess adipose tissue is associated with hereditary ailments. But when we talk about children, we mean, first of all, the acquired character of the disease. Doctors call the problem of excess fat tissue a non-infectious epidemic.
Elena Jonovna Medvedeva, pediatric endocrinologist, candidate of medical sciences:
In recent years, obesity has become very “younger”. More than 50% of overweight babies are diagnosed before the age of two, and by the age of 5, 90% of overweight children are diagnosed with this diagnosis. According to the Moscow Department of Health, at the beginning of 2013, the share of obesity in the structure of endocrine pathology in children exceeded 30%. In other words, every 3rd child turns to an endocrinologist about being overweight!
Russia takes "honorable" 5th place among the most “fat” countries in the world, the list of which is headed by Mexico, then the United States, New Zealand and Australia.
Living a “full” life: what threatens childhood obesity
In the period from 1 year to 3 years, the child wants and must move a lot - there is a process of active cognition of the surrounding world, to a greater extent - the world of objects. Excess weight creates physical inconvenience and limits the child’s capabilities. During walking and running, he is uncomfortable, he quickly gets tired, and not yet strong muscles can not cope with the required load.
Uncontrolled obesity, which began in childhood, does not pass by itself and persists in adulthood. Hence serious health problems: the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, diseases of the digestive system, mental disorders and pathology of the musculoskeletal system increases. In the future, such children expect not only illness, but also no less unpleasant and complex problems with relationships with others.
Victoria Igorevna Korpacheva, child clinical psychologist
The consequence of obesity at an early age can be: delayed mental and physical development, speech delay due to underdevelopment of large and small motor skills, impaired coordination of movements.
Full children are more teased, starting with kindergarten. Boys are more likely to experience complexes associated with physical weakness, because because of excess weight, strength and activity are poorly developed. Girls suffer more and experience because of appearance, there is an inferiority complex, isolation, shyness, increased touchiness and vindictiveness.
Such children in preschool and later in school age are characterized by a passive life position, the desire to avoid failure, increased sensitivity and emotionality. The surrounding children often show cruelty and do not hesitate in their expressions towards full children, thereby turning their lives into a constant stressful state that can lead to neurosis.”
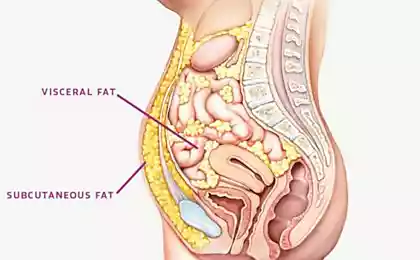
Overweight and obesity in children
Of course, at a very young age, a child rarely experiences complexes associated with his appearance, and many parents comfort themselves with thoughts that “puffy baby” is charming, and if he eats a lot – it means he is healthy. Health and excess weight are the opposite.
Over whom thickens “obesity”: causes of obesity

However, there remains a small percentage (2-3%) attributable to endocrine causes of obesity (syndromal, monogenic, obesity in neuroendocrine diseases, hypothalamic, iatrogenic).
To identify these rare forms of obesity, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist in time.
The “fat” question: overweight or obesity? In adults, to determine the norm of weight, calculate the body mass index (BMI). To do this, the body weight in kilograms is divided by the square of growth in meters.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), if a BMI of 25 to 29.9 kg / m2 is overweight. The diagnosis of obesity is made when the mass index is 30 kg / m2.
For example, a man weighs 80 kg. Height - 1.80 m.
BMI = 80 kg: (1.80x1.80) = 24.7
Sedentary child: 6 disorders associated with insufficient activity
But this method is not suitable for children, so the WHO has developed separate criteria for them. Excess body weight and obesity in children aged 0 to 17 years are determined by the data of centile tables (conditional tables of physical development) or standard deviations of BMI (SDS-standard deviation score). They take into account not only the height, body weight, but also the sex and age of the child.
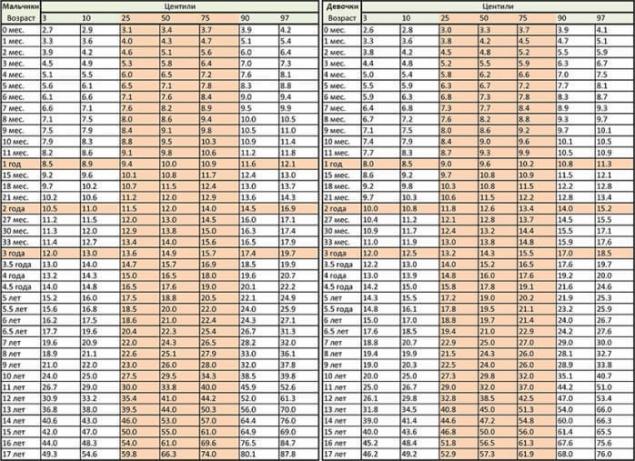
The "pink corridor" in the middle is the norm that most people represent. On the left are low rates. The right column is high. Extreme bars are 3-5% of the total number of children measured. When it comes to large deviations, a percentage of normal weight is applied.
Natalia Nikolaevna Antropova, pediatrician
Many mothers worry about the “eternal” question: Does the child have enough to eat? In order to make sure that the baby is developing normally, the pediatrician measures the weight and height of children at a preventive examination, and in babies up to 1 year old, the circumference of the chest and head is also observed. Up to a year, such inspections are carried out once a month. From 1 to 2 years - every 3 months. Then every six months and every year.
We are used to pitying the puffy cheeks and ass of our carapaces. Most of them do not go beyond the “corridor of norms”, but there are many children who exceed the average in terms of weight, height or both.
However, this is not always a pathology. Heredity is of great importance. After all, we do not believe that the growth of 160 cm or 195 cm in an adult is a pathology. Only a significant deviation from the norm in a child will be considered abnormal.
If mom and dad are big, then the baby probably won’t fit in. Conversely, when the parents are not very tall and slim enough, the baby’s weight and height are likely to be at the lower end of the norm or slightly lower.”
The big ones are seen from a distance: what to do?
Obesity in the initial stage, treatable, for quite a long time does not bother either parents or children. Doctors even joke: "1st degree causes envy, 2nd - surprise, 3rd - laughter, 4th - regret."
Suspecting or calculating for sure that your baby is more than well-fed, you need to determine the “scale of the disaster” and contact a pediatrician or endocrinologist. Although excess fat deposition is visible immediately.
Having examined and evaluated the physical development of the child, the specialist should exclude disorders in the endocrine system, i.e. endogenous obesity (the very 2-3% of rare forms). And also to establish the risk of complications.
For this purpose, a number of laboratory and instrumental examinations are appointed (general blood test, assessment of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, hormonal profile). In addition, ultrasound of the abdominal organs and ECG are performed. It may be necessary to consult other specialists (ophthalmologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, psychologist, etc.).
Having collected all the results, the doctor will select the right treatment and tactics. Especially carefully if one of the forms of endogenous obesity is confirmed.
How to avoid obesity in a child
In the event that a child’s obesity is due to the fact that “someone eats too much” and moves little (“fascinated” by inactivity), it is recommended to follow a diet and start physical activity. This form of obesity is called exogenous. By the way, among the uncomplicated, so it all depends on parents and other family members. Forget about “spoon for mom, spoon for dad!” – this is not a concern. Especially since drugs that affect weight loss are banned for children.

To prevent excess weight, you must first observe only 2 principles:
Healthy young children are very mobile. Therefore, parents, despite fatigue, employment and laziness, should in every possible way contribute to the active lifestyle of the baby, encourage and be an example, and not occupy him with various gadgets. And if you do not need to explain how to run, jump, skate, move, then we will dwell on the 2nd principle in more detail, since the main cause of obesity is overfeeding children.
Eating to live: proper nutrition of the child
The basics of the children's menu: balance, adaptation to a specific age and individual characteristics.
According to experts, if eating disorders occur in infancy, then the child’s problems will only grow like a snowball. And if you can say about a teenager that the child himself does not eat properly and harms himself, then in early childhood obesity is the mistake of only parents. Our experts believe that this problem is most often a consequence of hyperprotection. You can not constantly feed the baby without a special need and limit his activity, doing everything for him.
Children under one year should be breastfed (if this is not possible, the mixture should be selected specifically for your baby), and the introduction of complementary foods should be timely and correct.
For overweight children, it is recommended to start complementary foods with vegetable puree, for children with a weight deficit - with porridge. A pediatrician or nutritionist will definitely advise you on which dish to start introducing complementary foods to your child.
And doctors do not get tired of repeating: do not compare it with peers. Remember that all food standards are quite average and not suitable for everyone.
Natalia Nikolaevna Antropova, pediatrician:
“Children who are constantly moving will therefore eat more with appetite. And kids who prefer quiet games at the table (drawing, puzzles, sculpting) will eat in less volume. There is no need to force-feed children. Praise and swearing are not methods of education. Let the child eat a little, but quality food.
From a young age, a child should understand and see what food is useful and what will bring one harm. After all, in the future he will adhere to the family food habits and food culture.”
The calorie theme
Together with the most diverse and adapted diet, it is very important to observe the diet: when to eat. Baby food should be 4-5 a day: breakfast, lunch, afternoon and dinner. The interval between meals is at least 2 hours, but not more than 3.5-4 hours. A snack in the evening is desirable for the child no later than 1-1.5 hours before bedtime.
During the day, many children consume (mainly due to sweets) an adult number of calories - up to 2000. While a healthy child under 3 years old requires an average of 1500 calories. It is necessary to go through calories at least 1% a day - for a year the child may add a few extra pounds. Nutritionists advise to distribute calories as follows: breakfast should account for 25% of the daily norm, lunch - 40%, afternoon - 15% and 20% - for dinner. Approximately 1500-1600 grams per day.
Children on a diet
Large gaps between meals not only reduce the mental and physical abilities of the child, but also develop the habit of eating about the “stock”. If the baby eats, on the contrary, too often, his appetite worsens - he simply does not have time to walk it.
Svetlana Vladimirovna Makhina, specialist in the field of physical culture and sports, master in the field of adaptive physical culture, certified sports nutritionist
“It is important not only when and how much a child will eat, but also what will be on his plate. After all, his body must receive all useful substances. A common mistake of parents is “one-way” eating. For example, when too much fatty food or, conversely, the whole family eats only vegetables.
A child of 3 years, depending on weight, per day should eat: 30-50 g of protein, 35-60 g of fat and up to 200 g of carbohydrates.
The full menu of the preschooler includes, first of all, milk and dairy products (kefir, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt), which can be eaten during the day. They can be given to crumbs in natural form or bake a casserole, make a sandwich and add to dessert.
A good habit should include daily consumption of vegetables (200 g), fruits and natural beverages (juices, juices, compotes) - the main sources of vitamins.
Doctors do not advise the diet of a small “energyizer” to exclude meat, as well as bread, pasta (from hard varieties of wheat) and fats (vegetable or butter).
Children with strong will: what is important to know
What You Should Not Always Ask Your Child
Here are some tips for parents:
1. Deciding to take up the proper nutrition of the child, you should not excessively strictly and sharply limit it in food. You don’t want them to have troubles like bulimia or anorexia.
2. Instead of bans, let always be at hand healthy food (vegetables, fruits). Eat apples and carrots yourself. Kids are repeaters!
3. In no case, do not turn food into a reward by developing a conditioned reflex. It is better to encourage children with a new book, a useful walk or fun games – both at home and outdoors.
4. Do not self-medicate and do not diagnose your child “by eye”. Too fat or very thin is up to the doctors. published
Author: Elvira Sagalakova
Source: letidor.ru/article/pukhlyy-malysh-ili-tolstyy-reb_199375/?utm_source=letidorlj&utm_medium=social&_utma=1. 123570624.14626786.1471517318.1471517318.1&_utmb=1.10.10.1471517318&_utmc=1&_utmx=-&_utmz=1.1471517318.1.1.utmcsr=gutta-honey.livejourna

My son was born quite large – 4 kg. Especially for me, a meter with a cap. And throughout the first year, he confidently overcame all the averages in height and weight. The doctors, looking at him and then at his mother, asked with surprise: “You must have a big dad?”
Our hamster with cheeks on his chest even turned over and sat down later - the build did not allow. But as soon as my boy got up his legs and ran, everything took off with his hand. Walks, active games, a bicycle-scooter-rollers, sambo, jumping into the water - becoming, as a child should, a perpetual engine, he turned into a grasshopper and went into the category of petite. Although he looks thin, his weight is normal.
It would seem that all healthy children are not particularly persevering. So where do babies come from, for whom excess weight is a problem?
Obesity is a disease that signals that everything is not okay with the body. Of course, it happens that excess adipose tissue is associated with hereditary ailments. But when we talk about children, we mean, first of all, the acquired character of the disease. Doctors call the problem of excess fat tissue a non-infectious epidemic.
Elena Jonovna Medvedeva, pediatric endocrinologist, candidate of medical sciences:
In recent years, obesity has become very “younger”. More than 50% of overweight babies are diagnosed before the age of two, and by the age of 5, 90% of overweight children are diagnosed with this diagnosis. According to the Moscow Department of Health, at the beginning of 2013, the share of obesity in the structure of endocrine pathology in children exceeded 30%. In other words, every 3rd child turns to an endocrinologist about being overweight!
Russia takes "honorable" 5th place among the most “fat” countries in the world, the list of which is headed by Mexico, then the United States, New Zealand and Australia.
Living a “full” life: what threatens childhood obesity
In the period from 1 year to 3 years, the child wants and must move a lot - there is a process of active cognition of the surrounding world, to a greater extent - the world of objects. Excess weight creates physical inconvenience and limits the child’s capabilities. During walking and running, he is uncomfortable, he quickly gets tired, and not yet strong muscles can not cope with the required load.
Uncontrolled obesity, which began in childhood, does not pass by itself and persists in adulthood. Hence serious health problems: the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, diseases of the digestive system, mental disorders and pathology of the musculoskeletal system increases. In the future, such children expect not only illness, but also no less unpleasant and complex problems with relationships with others.
Victoria Igorevna Korpacheva, child clinical psychologist
The consequence of obesity at an early age can be: delayed mental and physical development, speech delay due to underdevelopment of large and small motor skills, impaired coordination of movements.
Full children are more teased, starting with kindergarten. Boys are more likely to experience complexes associated with physical weakness, because because of excess weight, strength and activity are poorly developed. Girls suffer more and experience because of appearance, there is an inferiority complex, isolation, shyness, increased touchiness and vindictiveness.
Such children in preschool and later in school age are characterized by a passive life position, the desire to avoid failure, increased sensitivity and emotionality. The surrounding children often show cruelty and do not hesitate in their expressions towards full children, thereby turning their lives into a constant stressful state that can lead to neurosis.”
Overweight and obesity in children
Of course, at a very young age, a child rarely experiences complexes associated with his appearance, and many parents comfort themselves with thoughts that “puffy baby” is charming, and if he eats a lot – it means he is healthy. Health and excess weight are the opposite.
Over whom thickens “obesity”: causes of obesity
- If a child consumes a lot of calories, but does not move much (up to 98% of children).
- If the child’s parents are also overweight (80%) or he grows up in an incomplete family (attempts of parents to “redeem” the guilt with sweets), a family with low financial income (not always have the opportunity to fully and diversely eat, and products are often of low quality) – 25%.
- If the child does not comply with the diet (skips breakfast, eats at dinner, eats little vegetables and fruits, abuses sweets, sodas and fast food).
- If the child does not sleep for a long time. Every extra hour of sleep significantly reduces the threat of obesity.
- If the child does not exercise in sports sections (40% of children) and lives far from the parks (20%)
- If your child has a TV in the room or watches more than 2 hours a day.
- If the mother smoked during pregnancy. Nicotine, an inhibitory saturation reflex, leads to overeating and, as a result, to obesity.

However, there remains a small percentage (2-3%) attributable to endocrine causes of obesity (syndromal, monogenic, obesity in neuroendocrine diseases, hypothalamic, iatrogenic).
To identify these rare forms of obesity, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist in time.
The “fat” question: overweight or obesity? In adults, to determine the norm of weight, calculate the body mass index (BMI). To do this, the body weight in kilograms is divided by the square of growth in meters.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), if a BMI of 25 to 29.9 kg / m2 is overweight. The diagnosis of obesity is made when the mass index is 30 kg / m2.
For example, a man weighs 80 kg. Height - 1.80 m.
BMI = 80 kg: (1.80x1.80) = 24.7
Sedentary child: 6 disorders associated with insufficient activity
But this method is not suitable for children, so the WHO has developed separate criteria for them. Excess body weight and obesity in children aged 0 to 17 years are determined by the data of centile tables (conditional tables of physical development) or standard deviations of BMI (SDS-standard deviation score). They take into account not only the height, body weight, but also the sex and age of the child.

The "pink corridor" in the middle is the norm that most people represent. On the left are low rates. The right column is high. Extreme bars are 3-5% of the total number of children measured. When it comes to large deviations, a percentage of normal weight is applied.
- I degree of obesity - body weight exceeds the norm by 20-29%
- II article - excess of normal weight by 30-49%
- III article - excess by 50-99%
- IV - Body weight is more than normal by 100% or more
Natalia Nikolaevna Antropova, pediatrician
Many mothers worry about the “eternal” question: Does the child have enough to eat? In order to make sure that the baby is developing normally, the pediatrician measures the weight and height of children at a preventive examination, and in babies up to 1 year old, the circumference of the chest and head is also observed. Up to a year, such inspections are carried out once a month. From 1 to 2 years - every 3 months. Then every six months and every year.
We are used to pitying the puffy cheeks and ass of our carapaces. Most of them do not go beyond the “corridor of norms”, but there are many children who exceed the average in terms of weight, height or both.
However, this is not always a pathology. Heredity is of great importance. After all, we do not believe that the growth of 160 cm or 195 cm in an adult is a pathology. Only a significant deviation from the norm in a child will be considered abnormal.
If mom and dad are big, then the baby probably won’t fit in. Conversely, when the parents are not very tall and slim enough, the baby’s weight and height are likely to be at the lower end of the norm or slightly lower.”
The big ones are seen from a distance: what to do?
Obesity in the initial stage, treatable, for quite a long time does not bother either parents or children. Doctors even joke: "1st degree causes envy, 2nd - surprise, 3rd - laughter, 4th - regret."
Suspecting or calculating for sure that your baby is more than well-fed, you need to determine the “scale of the disaster” and contact a pediatrician or endocrinologist. Although excess fat deposition is visible immediately.
Having examined and evaluated the physical development of the child, the specialist should exclude disorders in the endocrine system, i.e. endogenous obesity (the very 2-3% of rare forms). And also to establish the risk of complications.
For this purpose, a number of laboratory and instrumental examinations are appointed (general blood test, assessment of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, hormonal profile). In addition, ultrasound of the abdominal organs and ECG are performed. It may be necessary to consult other specialists (ophthalmologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, psychologist, etc.).
Having collected all the results, the doctor will select the right treatment and tactics. Especially carefully if one of the forms of endogenous obesity is confirmed.
How to avoid obesity in a child
In the event that a child’s obesity is due to the fact that “someone eats too much” and moves little (“fascinated” by inactivity), it is recommended to follow a diet and start physical activity. This form of obesity is called exogenous. By the way, among the uncomplicated, so it all depends on parents and other family members. Forget about “spoon for mom, spoon for dad!” – this is not a concern. Especially since drugs that affect weight loss are banned for children.

To prevent excess weight, you must first observe only 2 principles:
- nutrition
- adequate physical activity
Healthy young children are very mobile. Therefore, parents, despite fatigue, employment and laziness, should in every possible way contribute to the active lifestyle of the baby, encourage and be an example, and not occupy him with various gadgets. And if you do not need to explain how to run, jump, skate, move, then we will dwell on the 2nd principle in more detail, since the main cause of obesity is overfeeding children.
Eating to live: proper nutrition of the child
The basics of the children's menu: balance, adaptation to a specific age and individual characteristics.
According to experts, if eating disorders occur in infancy, then the child’s problems will only grow like a snowball. And if you can say about a teenager that the child himself does not eat properly and harms himself, then in early childhood obesity is the mistake of only parents. Our experts believe that this problem is most often a consequence of hyperprotection. You can not constantly feed the baby without a special need and limit his activity, doing everything for him.
Children under one year should be breastfed (if this is not possible, the mixture should be selected specifically for your baby), and the introduction of complementary foods should be timely and correct.
For overweight children, it is recommended to start complementary foods with vegetable puree, for children with a weight deficit - with porridge. A pediatrician or nutritionist will definitely advise you on which dish to start introducing complementary foods to your child.
And doctors do not get tired of repeating: do not compare it with peers. Remember that all food standards are quite average and not suitable for everyone.
Natalia Nikolaevna Antropova, pediatrician:
“Children who are constantly moving will therefore eat more with appetite. And kids who prefer quiet games at the table (drawing, puzzles, sculpting) will eat in less volume. There is no need to force-feed children. Praise and swearing are not methods of education. Let the child eat a little, but quality food.
From a young age, a child should understand and see what food is useful and what will bring one harm. After all, in the future he will adhere to the family food habits and food culture.”
The calorie theme
Together with the most diverse and adapted diet, it is very important to observe the diet: when to eat. Baby food should be 4-5 a day: breakfast, lunch, afternoon and dinner. The interval between meals is at least 2 hours, but not more than 3.5-4 hours. A snack in the evening is desirable for the child no later than 1-1.5 hours before bedtime.
During the day, many children consume (mainly due to sweets) an adult number of calories - up to 2000. While a healthy child under 3 years old requires an average of 1500 calories. It is necessary to go through calories at least 1% a day - for a year the child may add a few extra pounds. Nutritionists advise to distribute calories as follows: breakfast should account for 25% of the daily norm, lunch - 40%, afternoon - 15% and 20% - for dinner. Approximately 1500-1600 grams per day.
Children on a diet
Large gaps between meals not only reduce the mental and physical abilities of the child, but also develop the habit of eating about the “stock”. If the baby eats, on the contrary, too often, his appetite worsens - he simply does not have time to walk it.
Svetlana Vladimirovna Makhina, specialist in the field of physical culture and sports, master in the field of adaptive physical culture, certified sports nutritionist
“It is important not only when and how much a child will eat, but also what will be on his plate. After all, his body must receive all useful substances. A common mistake of parents is “one-way” eating. For example, when too much fatty food or, conversely, the whole family eats only vegetables.
A child of 3 years, depending on weight, per day should eat: 30-50 g of protein, 35-60 g of fat and up to 200 g of carbohydrates.
The full menu of the preschooler includes, first of all, milk and dairy products (kefir, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt), which can be eaten during the day. They can be given to crumbs in natural form or bake a casserole, make a sandwich and add to dessert.
A good habit should include daily consumption of vegetables (200 g), fruits and natural beverages (juices, juices, compotes) - the main sources of vitamins.
Doctors do not advise the diet of a small “energyizer” to exclude meat, as well as bread, pasta (from hard varieties of wheat) and fats (vegetable or butter).
Children with strong will: what is important to know
What You Should Not Always Ask Your Child
Here are some tips for parents:
1. Deciding to take up the proper nutrition of the child, you should not excessively strictly and sharply limit it in food. You don’t want them to have troubles like bulimia or anorexia.
2. Instead of bans, let always be at hand healthy food (vegetables, fruits). Eat apples and carrots yourself. Kids are repeaters!
3. In no case, do not turn food into a reward by developing a conditioned reflex. It is better to encourage children with a new book, a useful walk or fun games – both at home and outdoors.
4. Do not self-medicate and do not diagnose your child “by eye”. Too fat or very thin is up to the doctors. published
Author: Elvira Sagalakova
Source: letidor.ru/article/pukhlyy-malysh-ili-tolstyy-reb_199375/?utm_source=letidorlj&utm_medium=social&_utma=1. 123570624.14626786.1471517318.1471517318.1&_utmb=1.10.10.1471517318&_utmc=1&_utmx=-&_utmz=1.1471517318.1.1.utmcsr=gutta-honey.livejourna
A kitchen with a stove the unique design in the interior of your home
Simple Exercises to Improve the Endocrine System