1181
How to teach your baby math: Incredible Doman method
The Institute advances the human potential of working with mothers and their children for the past 40 years. Research Center specialists dedicated a lot of time working with children who have damage to brain cells.
As a result of a thorough study of the problem revealed that children with disabilities go to school, talked and behaved as committed to health, and sometimes even have the intelligence level close to genius.
Why did healthy children, ceteris paribus not show better results than their peers who surgically removed the part of the brain cells? What's wrong?
Them
The problem is the level of development of the central nervous system.
A child with brain damage, a typical healthy child and a genius - it's not three different types of children, and exactly the same children with varying degrees of development and organization of the central nervous system. When a child learns to read, the level of development increases, and the more information a child receives, the faster it increases the level of intelligence. The brain - like a muscle, which improves their quality as training
. The book "How to teach your baby to read" was published in May 1964 and created a furor among parents. It was translated into fifteen languages and released a circulation of more than five million copies. The book contains a child's learning system to read from the cradle. If this kid can be taught to read, is it possible to teach him mathematics?
The book "How to teach your baby math" offers an effective training system, in which any child can easily count complicated examples in mind - to the delight of myself and my parents.
1. Why would a small child math?
Mothers and their children are an excellent team that is configured to receive the result. A small child is able to learn several languages, play the violin, to solve complex equations in his mind, to be physically fit. By teaching the child anything else, my mother not only increases the level of intelligence, but also forms a strong bond, permeated with love and respect.
Mathematics - a complex subject, but the brain of the child is able to understand it much easier and faster than us adults, it seems. The sooner the process of learning begins, the easier and easier to digest information. What is the secret?
Unlike adults, children are easier to memorize facts and not symbols denoting them. For example, the symbol of the "six" figure - a "6", and the fact - this is the actual number of items - six butterflies. Or note "before" images in music book, it is a symbol, but a fact - it's the sound that produces the note. Symbols child nothing is said. He wants the bare facts. If adults easily understand mathematical symbols, numbers from 1 to 1 000 000, the actual number of items, for example, more than twenty, is difficult to define the move. Children may also be a high degree of certainty as the number of items and the corresponding symbol, if you teach them at a young age.
eleven. The child wants to learn math
Children are curious by nature and at an early age absorb a huge amount of information. Adults mistakenly believe curiosity lack of concentration. For the first six years of a child learns, perhaps more than in the rest of his life. He learns a new language for him (any language in which the child begins to speak), and, most likely, after six years, he did not succeed quite so well in any other foreign language.
Unfortunately, many adults unconsciously limit the freedom of education. This can be avoided by encouraging the child's ability and willingness to learn. Children learn through all of their basic senses, without exception - they see, hear, feel, taste smell and taste. They follow the instincts. Adults also restrict their actions, trying to protect, and thus deprived of the opportunity to learn.
We buy them toys that can not be broken, for example, a bright rattle. The child spends exactly 90 seconds to study, and then loses interest. His attention shifts to a box of rattles, which is no less interesting. In contrast to the toy box can be broken and thus understand how it is arranged.
The sad truth is that adults invent such toys for himself, to get rid of the child, even if only temporarily. Children, in turn, will never create a toy, they create tools - a wooden stick, for example, can easily become a hammer, and the shell - plate
. We buy baby playpen for the game. We believe that protecting it. However, we protect ourselves from the need to constantly keep abreast of and responsibility for the child's safety. We do not give the baby to crawl, touch various objects, breaking them, limiting the learning process. And this at a time when the desire to learn from the child to the maximum level!
The child perceives the study as a game, the most fun in life, until, until it comes the realization that it is hard and unpleasant work. For some children this awareness does not come. We call them geniuses.

The basic rules of learning:
1. The process of learning begins at birth.
2. All the children an innate passion for learning.
3. Children will choose to study food.
4. Children will choose to study the game.
5. Children find their work growing up process.
6. Children want to grow this very second.
7. Children believe that training - it is a necessary survival skill
. 8. And they are definitely right.
9. The children want to know everything about everything and right now.
10. Mathematics - standing object for cognition
. 12. A child can learn math
All children - geniuses linguistics. In its first months, they learn a new, "foreign" for themselves, the language. And it is not we teach children first words. The child he remembers them, just by listening to our conversations. It is no secret that in a family where mom and dad are bilingual, the child can speak two languages, and it will not be something supernatural for him.
Speech and language ability - Built brain function. Understand the facts behind the mathematical symbols - also a built-in function of the brain
. The child learns the information at lightning speed if he is to provide clear, unambiguous facts. Unfortunately, adults tend to share the notion on concrete and abstract. Specific easily understand abstract - more difficult. To explain a child abstract concepts, we often give out the truth of our own opinion about this concept, rather than the bare fact. This is a big mistake. Give your child the facts, and he will understand the logic of their cooperation.
A good example on this subject have a wonderful children's writer Korney Chukovsky in his book "Between two and five».
All the family waited for the postman. He appeared at the very gates. Varya first noticed him.
- C o h m a n a n h a t a n to go! - Happily heralded it
. The girl usually well-learned education professions titles such as the milkman, the butcher, and so on. D., And has done with the use of it in practice. She just did not know about the exceptions to the rule.
13. WORTH child learn math
There are two very important reasons why young children should learn math:
Man - the only living creature on Earth that can solve mathematical problems, and this is one of the few things that he encounters daily
. The sooner the child will understand the essence of mathematical examples, the faster it will increase the overall level of intelligence.
Our brain - a wonderful thing. As the muscles in our body, it becomes more perfect if it often train. The brain contains as much information as we give him. Even the not so - the brain is able to store a much information as we can not give him my entire life
. Man of the animal has a number of abilities, which is responsible for the brain:
Getting around on two legs.
Oral and written to express their thoughts.
Read.
Listen and understand the language, which was created by the same person.
Tactile distinguish objects.
The more we improve one of these skills, the more improved and all the rest. The more we think, the more we raise the level of their intelligence. Mathematics - a great way to make a person think
. 2. Method
Doman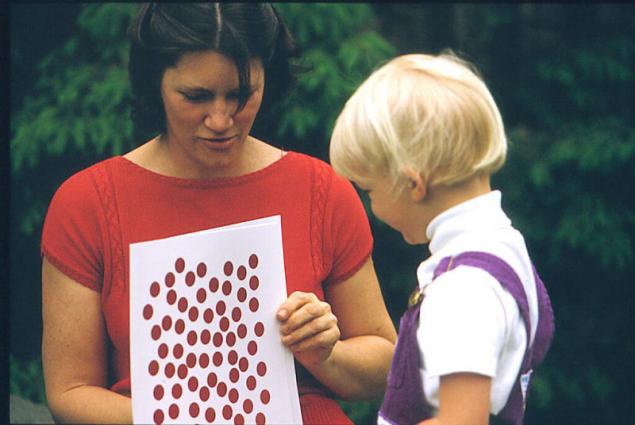
2.1. The secret method
The secret method is to acquaint the child with numbers and their true essence, showing him a picture with a particular number of red dots. Adult image "three" figures as a "3" or an image of three red dots - are one and the same. Method task - to teach the child to distinguish between them
. Adults can recognize up to twenty points in the image more or less confident. On the number of more than 20 can only guess. Children can easily cope with this task, if they are first taught the essence of numbers, rather than their characters.
If an adult to call a number, such as "six", he will soon introduce the figure six, and did not see the six subjects.
Not that he does not "see" it. He does not understand that this is a number of points in the figure. Adults need to manually count all the points. The child sees the correct answer just by looking at the picture.
The ability to distinguish "three" as "3" and "three" as the three red dots and will be an advantage to the older children. You will be able to teach a child math, even if you are not the master of the case. It's even easier than to teach him to read. And the whole process takes less than half an hour a day. Within a few weeks you will notice progress.
It is important to remember the following points:
1. Up to five years, the child can easily absorb a huge amount of information.
2. Up to five years, the child receives all the information.
3. The more information a child receives up to five years, the more of it remains.
4. Children under five years old have a huge amount of energy.
5. In children under five years a great desire to learn.
6. Children under five years of age can and want to learn to read.
7. All the little kids - brilliant linguists
. 8. Up to five years, they can learn a language or even several languages, if you help them in this.
Mathematics - is also a language that your child can easily explore
. 2.2. Fundamentals training
As a parent and a teacher, you must learn that study - the greatest adventure in the life of a child. This is the most interesting game of all. You should not forget that during the whole process. Someone said that we should not take the child's childhood, forcing him to learn. It speaks about a certain attitude toward learning. This does not work and is not a punishment. If you or your child do not enjoy the process, then you are doing something wrong.
The game should be enjoyable, and if the child or parent is tired or in a bad mood, it is necessary to delay the process for some time.
It is also important to remember that the submission of the information time should be as short as possible. For instance, it is possible to conduct such sessions are two-three times a day, but the duration of each should be not more than a few seconds. You have to stay until your child wants it himself.
Adults expect that the child will look at the educational material, concentrate on it and try to remember it. Babies do not need, they grasp the information on the fly. The rate of new material and the good mood of parents - is all you need
. You'd be surprised how hungry new information will have a child, when you begin training. Let it lead you. Do not let him get bored. There is nothing more boring than to memorize the same examples.
Be consistent - prepare all the study material in advance, and if it was necessary to postpone the session, then when the time comes to continue, not back to the already traversed. Continue to the point where finished. And never try to check the assimilation of the material are not tested their baby. All the tests are perceived as something unpleasant.
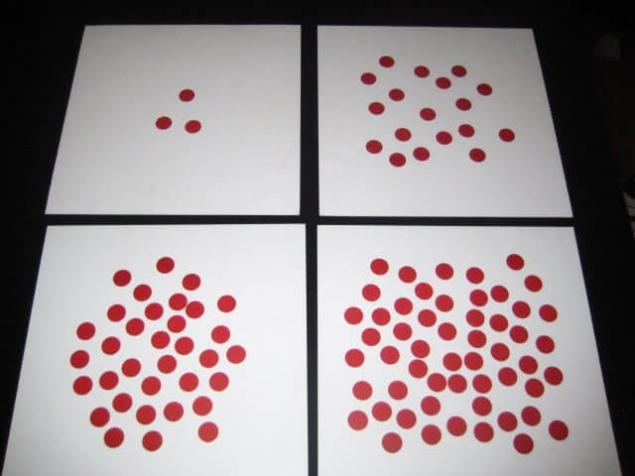
Training material is very simple:
1. White card format 30 x 30 cm. For the first time, you will need a minimum of 100 pieces, so it will be more convenient to buy ready-made and not waste valuable time cutting.
2. The red dots on adhesive paper with a diameter of about 2 cm. Red attracts kids.
3. The thick red marker, the thicker the better.
The preparation of the material will take time, but in general it is not difficult. There is a ready set of cards with points from one to one hundred designed by the publisher. But if it is not found, then here are some tips to simplify the task:
1. Start with the "hundred" card and continue in descending order. The greater the number of dots more difficult. As a rule, we are more focused and attentive in the beginning.
2. Read the red dots before gluing them onto the card.
3. On the back of the cards at each corner put down the value before gluing points on the card.
4. Make sure that the pasted point not resembled any shape (eg, square or triangle).
5. Stick to card points so that they do not overlap.
6. Leave the field that your fingers do not block the point, when you hold the card.
2.3. Step 1: Identification number of
The first thing you need to start learning math - is to learn the essence of the denomination or digits. For the first classes will be enough cards with values from one to ten. a total of five cards needed for a single session. Wait until the baby in a good mood and nothing does not bother him. Select a place where the child will not have anything to distract. TV, radio - all you need to turn off
. Take the card with one point. Show it to your child and say loud and clear: "This one." Do not delay. Say the phrase exactly as long as it takes to say it. Then, remove the card from one point, remove the card with the two and say, "These are the two" - and so on until five. Watch carefully for the child. Do not ask the child to repeat the numbers. Hug and kiss him. Let him understand that you really like this collaborative process. This one session. Repeat it three times during the day.
The next day, show cards your child from six to ten. Also praise at the end of each session. Do not bribe him with sweets. Once you have shown cards in ascending order, combine them, and during the following sessions show the cards in random order. It is important not to procrastinate. Children memorize information at lightning speed.
Show your child the card from one to ten for five days, mixing them, and then add a couple of new cards (following the order), and remove as much of the old (one, two, three and so on. D.). It is important to remember the basic rule - the child should not be boring! If he got bored, you slowly showing cards.
It is enough to learn the cards from one to one hundred, so that the child can immediately see how many dots in the picture - twenty-eight or twenty-nine. Everything is so simple. Now he will not have to remember the unfortunate phrase "two write, one in mind." He will understand what is at stake. He will "see" the real number behind the figures. You will be tempted to check the already acquired knowledge. Do not do this. You can flush out the baby, and he'll lose interest in learning.
2.4. Step 2. Arithmetic
Perhaps even before your child will master the "hundreds", he will be ready for the next step -Just arithmetic operations. To take the training material ready cards and write on the back of a number of examples of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Start with adding. This is a simple example, because the child is already familiar with it. When you showed him the cards in ascending order, that is, in fact, you are added to each card unit.
Take three cards and put them on his lap, face down. Then, pronouncing the equation starts to show cards. For example, "one" (SHOW CARD 'one'), "plus two" (show the "two" card) "is equal to three" (show the "three" card). All say the phrase out loud and clear. At this stage you do not need to explain to a child the meaning of words "plus" and "equal". He himself will understand them as we go. It is important to use all the time the same terminology.
During one session show by three equations, you get a total of nine examples in the day. Do not repeat the examples. Learn addition in two weeks.
The same principle also for other arithmetic operations.
2.5. Step 3. Solution examples
As has been said, do not try to check their child. Children love to learn, but hate inspections. The learning process can either be delayed or stop altogether. Child suspect that you do not believe that it can solve a particular example, as he does not prove it to you. In fact, it is an attempt to find out what the child does not know, and you, in turn, you know.
Instead, you need to give your child a chance to show themselves. Suggest to him to solve the problem. Например, возьмите две карточки «тридцать восемь» и «двенадцать», покажите их ребенку и спросите: «Где тридцать восемь?» Пусть ребенок посмотрит на правильную карточку или дотронется до нее. Если ребенок сразу не отвечает, поднесите правильную карточку и спросите еще раз: «Вот же тридцать восемь, правда?»
Добавьте по одному такому примеру в каждый сеанс обучения. Так у вас будут чередоваться цифры, арифметические действия и решение примеров.
Чтобы увлечь ребенка, добавьте разнообразия в свои уравнения. К примеру, можно создать ряд примеров с похожим компонентом.
4 х 3 х 5 = 60
3 х 5 х 4 = 60
5 х 3 х 4 = 60
На данном этапе важно не смешивать сложение и вычитание с умножением и делением, во избежание ошибок. Добавляйте до четырех компонентов в пример, и вы будете удивлены, насколько быстро ваш малыш научится с ними справляться.
Более продвинутые родители могут продолжить обучать своего ребенка другим арифметическим функциям — арифметической и геометрической прогрессиям, «больше чем» или «меньше чем», неравенствам и простейшей алгебре.
2.6. Шаг 4. Распознавание цифр
Как только ребенок научился понимать количественную сущность, можно научить его распознавать и сами цифры, а именно графическое отображение цифр, как мы, взрослые, привыкли их видеть. Для этого нужно взять уже известные нам пустые карточки и черным маркером написать цифры от одного до ста. Будьте последовательны и внимательны. Цифры должны быть визуально одного размера, примерно 15 см в высоту и 8 см в ширину. Принцип обучения аналогичен первому шагу. Вам потребуется не более пятидесяти дней на изучение числительных. Можете добавить примеры числительных больше ста — 200, 300, 400 и т. д., а также не круглых числительных — 258, 369, 1256 и т. д.
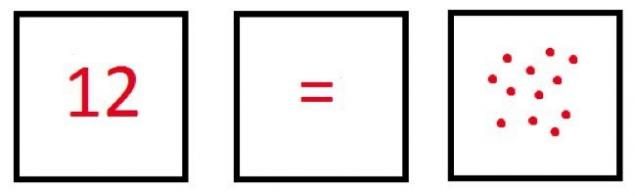
После того как ваш ребенок усвоил числительные, смешайте карточки с точками и цифрами и составьте свои уравнения. Покажите ему карточку с привычной нам цифрой, скажем, «двенадцать», громко произнесите ее вслух. Потом скажите «равно» и покажите карточку с двенадцатью красными точками, скажите «двенадцать».
Этот шаг, как правило, является самым легким для ребенка.
2.7. Шаг 5. Уравнения с числительными
Этот шаг повторяет все предыдущие с одной лишь разницей. Теперь в уравнениях задействованы привычные нам цифры. Для уравнений с числительными вам понадобятся новые карточки прямоугольной формы длиной 45 см и шириной 10 см с меньшим шрифтом. Примерно такие:
25 + 5 = 30
Всегда держите правильный ответ под рукой. Ребенок не должен увидеть ваши сомнения в поиске правильного ответа.
Когда вы пройдете с вашим ребенком все шаги, можно считать, что вы открыли ему двери в волшебный мир математики, где он будет чувствовать себя как рыба в воде.
3. Идеальный возраст для обучения
Система обучения ясна, но как нам определить, когда наш ребенок готов к обучению?
3.1. С рождения до трех месяцев
Как только ребенок открывает глаза и видит этот мир, он начинает учиться. Это не значит, что он сразу может считать сложные уравнения в уме. В это время происходит развитие визуальных функций его головного мозга. Мы не можем начинать «шаг один» без предварительной подготовки. Назовем это «шаг ноль».
Это будет скорее не обучение математике, а стимуляция визуального восприятия. Ребенок не сразу начинает видеть детали предметов. Занятия с ребенком математикой по системе Домана стимулируют эту способность. Это легко и даже логично. Мы же разговариваем с ребенком с самого рождения, и даже в течение девяти месяцев до него.
«Шаг ноль» заключается в том, чтобы показывать ребенку карточки с красными точками от одного до семи. Сами карточки должны быть раза в полтора больше, чем обычные, и сами точки — тоже больше. Место для занятий должно быть хорошо освещено. Покажите ребенку карточку, громко и отчетливо произнесите цифру и подождите. В этот момент ребенок будет искать глазами карточку. Его внимание в этом возрасте хорошее, а вот зрение плохое. Однако не старайтесь поймать его внимание карточкой. Он отвлечется на движущийся объект и забудет про то, что вы ему сказали.
В первый день занятий ожидание его внимания к карточке займет секунд пятнадцать, но в каждый последующий раз все меньше и меньше. Начните с того, что вы покажете ему карточку с одной точкой до десяти раз в первый день.
Во второй день — карточку с двумя точками и т. д. Итак, скажем, в понедельник ребенок будет видеть карточку «один», в воскресенье — «семь». На следующей неделе повторите процесс.
И так три недели. Не забывайте, что ребенок должен быть в хорошем расположении духа. На четвертую неделю возьмите новые карточки от восьми до четырнадцати. Еще через три недели ваш ребенок будет готов перейти к «шагу один».
3.2. От трех до шести месяцев
В этом возрасте хорошо воспринимаются первые два шага. Сосредоточьтесь на них. Ребенок уже хорошо узнает детали и умеет на них концентрироваться. Он буквально заглатывает всю информацию, которую ему говорят громко и отчетливо. Сам он при этом общается с нами звуками. Как же можно заниматься с ребенком математикой, если он и говорить-то не умеет? Это и не нужно. Глаза и уши — основные в это время органы восприятия. Основные правила — показывайте карточки быстро и чаще обновляйте материал.
3.3. От семи до двенадцати месяцев
Частота сеансов и еще большая скорость показа карточек — то, что стоит запомнить на этом этапе. Большой объем новой информации обернется катастрофой. В этом возрасте ребенок начинает двигаться, потом ползать и, наконец, ходить, и огромная часть его внимания уходит на процесс движения. Это уже не трехмесячный ребенок, который сидит на одном месте и которому вы можете показывать все новые карточки. Сейчас крайне важно не отвлекать ребенка от важного занятия надолго. Он не сможет просмотреть пятьдесят карточек за раз. Пяти будет достаточно.
3.4. От двенадцати до восемнадцати месяцев
На этом этапе важно не забывать про краткость сеансов и необходимость остановиться до того, как ребенок сам этого захочет. Прислушивайтесь к своему малышу. В этом возрасте он готов легко воспринимать первый, второй и третий шаги программы. С другой стороны это время еще больших открытий. Он все больше ходит и бегает – и меньше сидит на месте. Именно поэтому все сеансы должны быть максимально короткими.
3.5. От восемнадцати до тридцати месяцев
В восемнадцать месяцев и старше ребенку становится все труднее запоминать новую информацию, поэтому, если вы начинаете программу обучения с этого этапа, то постарайтесь перейти к пятому шагу как можно быстрее. Первые этапы могут показаться ребенку слишком скучными. В этом возрасте пропадает непредвзятое отношение к новой информации. Теперь ему может что-то нравиться, а что-то нет. Ребенок начинает говорить, осознает, что его понимают, и формирует миллион требований. В данной ситуации стоит преподать материал таким образом, чтобы сначала заинтересовать его, а затем оставить немного «голодным».
3.6. Старше тридцати месяцев
Разница между новорожденным ребенком и ребенком в возрасте тридцати месяцев колоссальна. Это уже не ребенок, и ему гораздо сложнее освоить карточки с количеством. Вы все еще можете попробовать поработать с карточками с красными точками, но шанс их усвоения невысок. Однако это еще не конец света. Не вся математика состоит из умения мгновенно решать в уме сложные арифметические задачки. Сосредоточьтесь на карточках с цифрами и уравнениях.
Заключение

Метод, разработанный Гленном Доманом, удивительно прост и невероятно эффективен. Его цель —научить ребенка распознавать цифры и их суть. Мы начинаем с того, что с самого раннего возраста по несколько раз в день показываем ребенку карточки с точками. Это учит его связывать понятия абстрактных цифр и осязаемого количества. От точек мы переходим к карточкам с цифрами, арифметическим примерам и даже простейшей алгебре.
В основу метода Домана положены следующие принципы:
Мозг вашего малыша способен на то, о чем вы даже не догадываетесь. Дайте ему «чистый» материал, голые факты, тогда он сам додумается до правил, по которым эти факты работают. Ведь дети — это маленькие ученые, которые начинают учиться с чистого листа.
От возраста начала занятий будет зависеть формат учебного материала, скорость подачи материала и количество сеансов в день. Например, для новорожденного малыша стоит подготовить карточки большего размера и ограничиться цифрами от одного до семи. А когда ребенок начнет ползать и ходить, информацию нужно подавать быстрее и обновлять чаще, чтобы он не успевал заскучать. Всегда помните: нужно остановиться до того, как этого захотел ваш ученик.
Маленькие дети любопытны и голодны до новых знаний. Они предпочтут учебу игре или еде. Дайте им такую возможность, и чем раньше, тем лучше.
Когда вам захочется проверить, насколько малыш усвоил учебный материал, не тестируйте его, а обозначайте проблему и предлагайте ее решить.
Получение новых знаний — это самое веселое времяпрепровождение, о котором можно только мечтать. Никогда не начинайте занятия, если вы или ваш ребенок в плохом настроении или неважно себя чувствуете.
Математика научит ребенка логически мыслить, пополнит словарный запас и даже поможет быстрее начать говорить.
As a result of a thorough study of the problem revealed that children with disabilities go to school, talked and behaved as committed to health, and sometimes even have the intelligence level close to genius.
Why did healthy children, ceteris paribus not show better results than their peers who surgically removed the part of the brain cells? What's wrong?
Them

The problem is the level of development of the central nervous system.
A child with brain damage, a typical healthy child and a genius - it's not three different types of children, and exactly the same children with varying degrees of development and organization of the central nervous system. When a child learns to read, the level of development increases, and the more information a child receives, the faster it increases the level of intelligence. The brain - like a muscle, which improves their quality as training
. The book "How to teach your baby to read" was published in May 1964 and created a furor among parents. It was translated into fifteen languages and released a circulation of more than five million copies. The book contains a child's learning system to read from the cradle. If this kid can be taught to read, is it possible to teach him mathematics?
The book "How to teach your baby math" offers an effective training system, in which any child can easily count complicated examples in mind - to the delight of myself and my parents.
1. Why would a small child math?
Mothers and their children are an excellent team that is configured to receive the result. A small child is able to learn several languages, play the violin, to solve complex equations in his mind, to be physically fit. By teaching the child anything else, my mother not only increases the level of intelligence, but also forms a strong bond, permeated with love and respect.
Mathematics - a complex subject, but the brain of the child is able to understand it much easier and faster than us adults, it seems. The sooner the process of learning begins, the easier and easier to digest information. What is the secret?
Unlike adults, children are easier to memorize facts and not symbols denoting them. For example, the symbol of the "six" figure - a "6", and the fact - this is the actual number of items - six butterflies. Or note "before" images in music book, it is a symbol, but a fact - it's the sound that produces the note. Symbols child nothing is said. He wants the bare facts. If adults easily understand mathematical symbols, numbers from 1 to 1 000 000, the actual number of items, for example, more than twenty, is difficult to define the move. Children may also be a high degree of certainty as the number of items and the corresponding symbol, if you teach them at a young age.
eleven. The child wants to learn math
Children are curious by nature and at an early age absorb a huge amount of information. Adults mistakenly believe curiosity lack of concentration. For the first six years of a child learns, perhaps more than in the rest of his life. He learns a new language for him (any language in which the child begins to speak), and, most likely, after six years, he did not succeed quite so well in any other foreign language.
Unfortunately, many adults unconsciously limit the freedom of education. This can be avoided by encouraging the child's ability and willingness to learn. Children learn through all of their basic senses, without exception - they see, hear, feel, taste smell and taste. They follow the instincts. Adults also restrict their actions, trying to protect, and thus deprived of the opportunity to learn.
We buy them toys that can not be broken, for example, a bright rattle. The child spends exactly 90 seconds to study, and then loses interest. His attention shifts to a box of rattles, which is no less interesting. In contrast to the toy box can be broken and thus understand how it is arranged.
The sad truth is that adults invent such toys for himself, to get rid of the child, even if only temporarily. Children, in turn, will never create a toy, they create tools - a wooden stick, for example, can easily become a hammer, and the shell - plate
. We buy baby playpen for the game. We believe that protecting it. However, we protect ourselves from the need to constantly keep abreast of and responsibility for the child's safety. We do not give the baby to crawl, touch various objects, breaking them, limiting the learning process. And this at a time when the desire to learn from the child to the maximum level!
The child perceives the study as a game, the most fun in life, until, until it comes the realization that it is hard and unpleasant work. For some children this awareness does not come. We call them geniuses.

The basic rules of learning:
1. The process of learning begins at birth.
2. All the children an innate passion for learning.
3. Children will choose to study food.
4. Children will choose to study the game.
5. Children find their work growing up process.
6. Children want to grow this very second.
7. Children believe that training - it is a necessary survival skill
. 8. And they are definitely right.
9. The children want to know everything about everything and right now.
10. Mathematics - standing object for cognition
. 12. A child can learn math
All children - geniuses linguistics. In its first months, they learn a new, "foreign" for themselves, the language. And it is not we teach children first words. The child he remembers them, just by listening to our conversations. It is no secret that in a family where mom and dad are bilingual, the child can speak two languages, and it will not be something supernatural for him.
Speech and language ability - Built brain function. Understand the facts behind the mathematical symbols - also a built-in function of the brain
. The child learns the information at lightning speed if he is to provide clear, unambiguous facts. Unfortunately, adults tend to share the notion on concrete and abstract. Specific easily understand abstract - more difficult. To explain a child abstract concepts, we often give out the truth of our own opinion about this concept, rather than the bare fact. This is a big mistake. Give your child the facts, and he will understand the logic of their cooperation.
A good example on this subject have a wonderful children's writer Korney Chukovsky in his book "Between two and five».
All the family waited for the postman. He appeared at the very gates. Varya first noticed him.
- C o h m a n a n h a t a n to go! - Happily heralded it
. The girl usually well-learned education professions titles such as the milkman, the butcher, and so on. D., And has done with the use of it in practice. She just did not know about the exceptions to the rule.
13. WORTH child learn math
There are two very important reasons why young children should learn math:
Man - the only living creature on Earth that can solve mathematical problems, and this is one of the few things that he encounters daily
. The sooner the child will understand the essence of mathematical examples, the faster it will increase the overall level of intelligence.
Our brain - a wonderful thing. As the muscles in our body, it becomes more perfect if it often train. The brain contains as much information as we give him. Even the not so - the brain is able to store a much information as we can not give him my entire life
. Man of the animal has a number of abilities, which is responsible for the brain:
Getting around on two legs.
Oral and written to express their thoughts.
Read.
Listen and understand the language, which was created by the same person.
Tactile distinguish objects.
The more we improve one of these skills, the more improved and all the rest. The more we think, the more we raise the level of their intelligence. Mathematics - a great way to make a person think
. 2. Method
Doman

2.1. The secret method
The secret method is to acquaint the child with numbers and their true essence, showing him a picture with a particular number of red dots. Adult image "three" figures as a "3" or an image of three red dots - are one and the same. Method task - to teach the child to distinguish between them
. Adults can recognize up to twenty points in the image more or less confident. On the number of more than 20 can only guess. Children can easily cope with this task, if they are first taught the essence of numbers, rather than their characters.
If an adult to call a number, such as "six", he will soon introduce the figure six, and did not see the six subjects.
Not that he does not "see" it. He does not understand that this is a number of points in the figure. Adults need to manually count all the points. The child sees the correct answer just by looking at the picture.
The ability to distinguish "three" as "3" and "three" as the three red dots and will be an advantage to the older children. You will be able to teach a child math, even if you are not the master of the case. It's even easier than to teach him to read. And the whole process takes less than half an hour a day. Within a few weeks you will notice progress.
It is important to remember the following points:
1. Up to five years, the child can easily absorb a huge amount of information.
2. Up to five years, the child receives all the information.
3. The more information a child receives up to five years, the more of it remains.
4. Children under five years old have a huge amount of energy.
5. In children under five years a great desire to learn.
6. Children under five years of age can and want to learn to read.
7. All the little kids - brilliant linguists
. 8. Up to five years, they can learn a language or even several languages, if you help them in this.
Mathematics - is also a language that your child can easily explore
. 2.2. Fundamentals training
As a parent and a teacher, you must learn that study - the greatest adventure in the life of a child. This is the most interesting game of all. You should not forget that during the whole process. Someone said that we should not take the child's childhood, forcing him to learn. It speaks about a certain attitude toward learning. This does not work and is not a punishment. If you or your child do not enjoy the process, then you are doing something wrong.
The game should be enjoyable, and if the child or parent is tired or in a bad mood, it is necessary to delay the process for some time.
It is also important to remember that the submission of the information time should be as short as possible. For instance, it is possible to conduct such sessions are two-three times a day, but the duration of each should be not more than a few seconds. You have to stay until your child wants it himself.
Adults expect that the child will look at the educational material, concentrate on it and try to remember it. Babies do not need, they grasp the information on the fly. The rate of new material and the good mood of parents - is all you need
. You'd be surprised how hungry new information will have a child, when you begin training. Let it lead you. Do not let him get bored. There is nothing more boring than to memorize the same examples.
Be consistent - prepare all the study material in advance, and if it was necessary to postpone the session, then when the time comes to continue, not back to the already traversed. Continue to the point where finished. And never try to check the assimilation of the material are not tested their baby. All the tests are perceived as something unpleasant.

Training material is very simple:
1. White card format 30 x 30 cm. For the first time, you will need a minimum of 100 pieces, so it will be more convenient to buy ready-made and not waste valuable time cutting.
2. The red dots on adhesive paper with a diameter of about 2 cm. Red attracts kids.
3. The thick red marker, the thicker the better.
The preparation of the material will take time, but in general it is not difficult. There is a ready set of cards with points from one to one hundred designed by the publisher. But if it is not found, then here are some tips to simplify the task:
1. Start with the "hundred" card and continue in descending order. The greater the number of dots more difficult. As a rule, we are more focused and attentive in the beginning.
2. Read the red dots before gluing them onto the card.
3. On the back of the cards at each corner put down the value before gluing points on the card.
4. Make sure that the pasted point not resembled any shape (eg, square or triangle).
5. Stick to card points so that they do not overlap.
6. Leave the field that your fingers do not block the point, when you hold the card.
2.3. Step 1: Identification number of
The first thing you need to start learning math - is to learn the essence of the denomination or digits. For the first classes will be enough cards with values from one to ten. a total of five cards needed for a single session. Wait until the baby in a good mood and nothing does not bother him. Select a place where the child will not have anything to distract. TV, radio - all you need to turn off
. Take the card with one point. Show it to your child and say loud and clear: "This one." Do not delay. Say the phrase exactly as long as it takes to say it. Then, remove the card from one point, remove the card with the two and say, "These are the two" - and so on until five. Watch carefully for the child. Do not ask the child to repeat the numbers. Hug and kiss him. Let him understand that you really like this collaborative process. This one session. Repeat it three times during the day.
The next day, show cards your child from six to ten. Also praise at the end of each session. Do not bribe him with sweets. Once you have shown cards in ascending order, combine them, and during the following sessions show the cards in random order. It is important not to procrastinate. Children memorize information at lightning speed.
Show your child the card from one to ten for five days, mixing them, and then add a couple of new cards (following the order), and remove as much of the old (one, two, three and so on. D.). It is important to remember the basic rule - the child should not be boring! If he got bored, you slowly showing cards.
It is enough to learn the cards from one to one hundred, so that the child can immediately see how many dots in the picture - twenty-eight or twenty-nine. Everything is so simple. Now he will not have to remember the unfortunate phrase "two write, one in mind." He will understand what is at stake. He will "see" the real number behind the figures. You will be tempted to check the already acquired knowledge. Do not do this. You can flush out the baby, and he'll lose interest in learning.
2.4. Step 2. Arithmetic
Perhaps even before your child will master the "hundreds", he will be ready for the next step -Just arithmetic operations. To take the training material ready cards and write on the back of a number of examples of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Start with adding. This is a simple example, because the child is already familiar with it. When you showed him the cards in ascending order, that is, in fact, you are added to each card unit.
Take three cards and put them on his lap, face down. Then, pronouncing the equation starts to show cards. For example, "one" (SHOW CARD 'one'), "plus two" (show the "two" card) "is equal to three" (show the "three" card). All say the phrase out loud and clear. At this stage you do not need to explain to a child the meaning of words "plus" and "equal". He himself will understand them as we go. It is important to use all the time the same terminology.
During one session show by three equations, you get a total of nine examples in the day. Do not repeat the examples. Learn addition in two weeks.
The same principle also for other arithmetic operations.
2.5. Step 3. Solution examples
As has been said, do not try to check their child. Children love to learn, but hate inspections. The learning process can either be delayed or stop altogether. Child suspect that you do not believe that it can solve a particular example, as he does not prove it to you. In fact, it is an attempt to find out what the child does not know, and you, in turn, you know.
Instead, you need to give your child a chance to show themselves. Suggest to him to solve the problem. Например, возьмите две карточки «тридцать восемь» и «двенадцать», покажите их ребенку и спросите: «Где тридцать восемь?» Пусть ребенок посмотрит на правильную карточку или дотронется до нее. Если ребенок сразу не отвечает, поднесите правильную карточку и спросите еще раз: «Вот же тридцать восемь, правда?»
Добавьте по одному такому примеру в каждый сеанс обучения. Так у вас будут чередоваться цифры, арифметические действия и решение примеров.
Чтобы увлечь ребенка, добавьте разнообразия в свои уравнения. К примеру, можно создать ряд примеров с похожим компонентом.
4 х 3 х 5 = 60
3 х 5 х 4 = 60
5 х 3 х 4 = 60
На данном этапе важно не смешивать сложение и вычитание с умножением и делением, во избежание ошибок. Добавляйте до четырех компонентов в пример, и вы будете удивлены, насколько быстро ваш малыш научится с ними справляться.
Более продвинутые родители могут продолжить обучать своего ребенка другим арифметическим функциям — арифметической и геометрической прогрессиям, «больше чем» или «меньше чем», неравенствам и простейшей алгебре.
2.6. Шаг 4. Распознавание цифр
Как только ребенок научился понимать количественную сущность, можно научить его распознавать и сами цифры, а именно графическое отображение цифр, как мы, взрослые, привыкли их видеть. Для этого нужно взять уже известные нам пустые карточки и черным маркером написать цифры от одного до ста. Будьте последовательны и внимательны. Цифры должны быть визуально одного размера, примерно 15 см в высоту и 8 см в ширину. Принцип обучения аналогичен первому шагу. Вам потребуется не более пятидесяти дней на изучение числительных. Можете добавить примеры числительных больше ста — 200, 300, 400 и т. д., а также не круглых числительных — 258, 369, 1256 и т. д.
После того как ваш ребенок усвоил числительные, смешайте карточки с точками и цифрами и составьте свои уравнения. Покажите ему карточку с привычной нам цифрой, скажем, «двенадцать», громко произнесите ее вслух. Потом скажите «равно» и покажите карточку с двенадцатью красными точками, скажите «двенадцать».

Этот шаг, как правило, является самым легким для ребенка.
2.7. Шаг 5. Уравнения с числительными
Этот шаг повторяет все предыдущие с одной лишь разницей. Теперь в уравнениях задействованы привычные нам цифры. Для уравнений с числительными вам понадобятся новые карточки прямоугольной формы длиной 45 см и шириной 10 см с меньшим шрифтом. Примерно такие:
25 + 5 = 30
Всегда держите правильный ответ под рукой. Ребенок не должен увидеть ваши сомнения в поиске правильного ответа.
Когда вы пройдете с вашим ребенком все шаги, можно считать, что вы открыли ему двери в волшебный мир математики, где он будет чувствовать себя как рыба в воде.
3. Идеальный возраст для обучения
Система обучения ясна, но как нам определить, когда наш ребенок готов к обучению?
3.1. С рождения до трех месяцев
Как только ребенок открывает глаза и видит этот мир, он начинает учиться. Это не значит, что он сразу может считать сложные уравнения в уме. В это время происходит развитие визуальных функций его головного мозга. Мы не можем начинать «шаг один» без предварительной подготовки. Назовем это «шаг ноль».
Это будет скорее не обучение математике, а стимуляция визуального восприятия. Ребенок не сразу начинает видеть детали предметов. Занятия с ребенком математикой по системе Домана стимулируют эту способность. Это легко и даже логично. Мы же разговариваем с ребенком с самого рождения, и даже в течение девяти месяцев до него.
«Шаг ноль» заключается в том, чтобы показывать ребенку карточки с красными точками от одного до семи. Сами карточки должны быть раза в полтора больше, чем обычные, и сами точки — тоже больше. Место для занятий должно быть хорошо освещено. Покажите ребенку карточку, громко и отчетливо произнесите цифру и подождите. В этот момент ребенок будет искать глазами карточку. Его внимание в этом возрасте хорошее, а вот зрение плохое. Однако не старайтесь поймать его внимание карточкой. Он отвлечется на движущийся объект и забудет про то, что вы ему сказали.
В первый день занятий ожидание его внимания к карточке займет секунд пятнадцать, но в каждый последующий раз все меньше и меньше. Начните с того, что вы покажете ему карточку с одной точкой до десяти раз в первый день.
Во второй день — карточку с двумя точками и т. д. Итак, скажем, в понедельник ребенок будет видеть карточку «один», в воскресенье — «семь». На следующей неделе повторите процесс.
И так три недели. Не забывайте, что ребенок должен быть в хорошем расположении духа. На четвертую неделю возьмите новые карточки от восьми до четырнадцати. Еще через три недели ваш ребенок будет готов перейти к «шагу один».
3.2. От трех до шести месяцев
В этом возрасте хорошо воспринимаются первые два шага. Сосредоточьтесь на них. Ребенок уже хорошо узнает детали и умеет на них концентрироваться. Он буквально заглатывает всю информацию, которую ему говорят громко и отчетливо. Сам он при этом общается с нами звуками. Как же можно заниматься с ребенком математикой, если он и говорить-то не умеет? Это и не нужно. Глаза и уши — основные в это время органы восприятия. Основные правила — показывайте карточки быстро и чаще обновляйте материал.
3.3. От семи до двенадцати месяцев
Частота сеансов и еще большая скорость показа карточек — то, что стоит запомнить на этом этапе. Большой объем новой информации обернется катастрофой. В этом возрасте ребенок начинает двигаться, потом ползать и, наконец, ходить, и огромная часть его внимания уходит на процесс движения. Это уже не трехмесячный ребенок, который сидит на одном месте и которому вы можете показывать все новые карточки. Сейчас крайне важно не отвлекать ребенка от важного занятия надолго. Он не сможет просмотреть пятьдесят карточек за раз. Пяти будет достаточно.
3.4. От двенадцати до восемнадцати месяцев
На этом этапе важно не забывать про краткость сеансов и необходимость остановиться до того, как ребенок сам этого захочет. Прислушивайтесь к своему малышу. В этом возрасте он готов легко воспринимать первый, второй и третий шаги программы. С другой стороны это время еще больших открытий. Он все больше ходит и бегает – и меньше сидит на месте. Именно поэтому все сеансы должны быть максимально короткими.
3.5. От восемнадцати до тридцати месяцев
В восемнадцать месяцев и старше ребенку становится все труднее запоминать новую информацию, поэтому, если вы начинаете программу обучения с этого этапа, то постарайтесь перейти к пятому шагу как можно быстрее. Первые этапы могут показаться ребенку слишком скучными. В этом возрасте пропадает непредвзятое отношение к новой информации. Теперь ему может что-то нравиться, а что-то нет. Ребенок начинает говорить, осознает, что его понимают, и формирует миллион требований. В данной ситуации стоит преподать материал таким образом, чтобы сначала заинтересовать его, а затем оставить немного «голодным».
3.6. Старше тридцати месяцев
Разница между новорожденным ребенком и ребенком в возрасте тридцати месяцев колоссальна. Это уже не ребенок, и ему гораздо сложнее освоить карточки с количеством. Вы все еще можете попробовать поработать с карточками с красными точками, но шанс их усвоения невысок. Однако это еще не конец света. Не вся математика состоит из умения мгновенно решать в уме сложные арифметические задачки. Сосредоточьтесь на карточках с цифрами и уравнениях.
Заключение

Метод, разработанный Гленном Доманом, удивительно прост и невероятно эффективен. Его цель —научить ребенка распознавать цифры и их суть. Мы начинаем с того, что с самого раннего возраста по несколько раз в день показываем ребенку карточки с точками. Это учит его связывать понятия абстрактных цифр и осязаемого количества. От точек мы переходим к карточкам с цифрами, арифметическим примерам и даже простейшей алгебре.
В основу метода Домана положены следующие принципы:
Мозг вашего малыша способен на то, о чем вы даже не догадываетесь. Дайте ему «чистый» материал, голые факты, тогда он сам додумается до правил, по которым эти факты работают. Ведь дети — это маленькие ученые, которые начинают учиться с чистого листа.
От возраста начала занятий будет зависеть формат учебного материала, скорость подачи материала и количество сеансов в день. Например, для новорожденного малыша стоит подготовить карточки большего размера и ограничиться цифрами от одного до семи. А когда ребенок начнет ползать и ходить, информацию нужно подавать быстрее и обновлять чаще, чтобы он не успевал заскучать. Всегда помните: нужно остановиться до того, как этого захотел ваш ученик.
Маленькие дети любопытны и голодны до новых знаний. Они предпочтут учебу игре или еде. Дайте им такую возможность, и чем раньше, тем лучше.
Когда вам захочется проверить, насколько малыш усвоил учебный материал, не тестируйте его, а обозначайте проблему и предлагайте ее решить.
Получение новых знаний — это самое веселое времяпрепровождение, о котором можно только мечтать. Никогда не начинайте занятия, если вы или ваш ребенок в плохом настроении или неважно себя чувствуете.
Математика научит ребенка логически мыслить, пополнит словарный запас и даже поможет быстрее начать говорить.
48-hour detox diet - fat melts at an incredible rate!
This man has improved every little thing one percent - and that's what came out of it