1009
High protein diet Raw foodists and flora

The network can easily meet the most different and sometimes unique formulation and explain the operation symbiontic intestinal microflora. This interesting conclusion that "to digest nuts need appropriate special microflora" and categorical assertion that "the only exclusively on syromonoednom diet may develop beneficial microflora symbiontic in all its power," and much more. Now let's see, what's wrong authors of such statements.

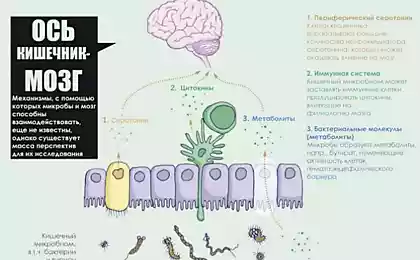
So, initially raw foodists need to know about the intestinal microflora that its main representatives are very diverse: Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and many others. The composition and properties of our useful intestinal microflora depend, primarily, from the culture medium in which these organisms live. Therefore, it is from the human diet will depend on what will be colonized by bacteria in large amounts, and which are oppressed, because of the lack of nutrients necessary for their development. According to the features of microorganisms, it is convenient to divide the microflora of the large intestine into two main groups:
The proteolytic bacteria (break down proteins): (Bacteroides, Proteus, etc.) are harmful to human pathogenic microflora. These micro-organisms are used as nutrient substrate protein and its decay products, causing putrefaction, end metabolites that are toxic to human substance - indole, skatole, cadaverine, putrescine, mercaptan, phenol, etc.
. Saccharolytic bacteria (cleave sugar): (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, etc.) is used as a food various carbohydrates and polysaccharides intestinal mucus. These representatives of the intestinal flora are useful in human, as they suppress the growth of pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms synthesize vitamins -. B1, B2, B3, B6, K, PP, etc., stimulate peristalsis, and also participate in the hydrolysis of cellulose, which is not digested by digestive juices and enzymes person.
Putrefaction and useful microflora are fighting each other for space and resources in the host organism. Thus, the dominance of one class of microorganisms inhibits and prevents the development of the other, and vice versa. The decisive factor in this is the percentage antagonism of carbohydrates and protein in the diet. In addition, in the gastrointestinal tract still exists regulation microbial biocenosis epithelial and immune cells, but it has a food substrate and determining the most pronounced effect on the composition of the intestinal microflora. Because of this feature of our microflora comes very simple consequence:
The more high-protein foods in the diet,
the more gut rot organisms (!!!)
It is important to understand that the development of putrefactive bacteria counts only the concentration of protein in the food substrate, and the nature of the protein molecules they are absolutely indifferent. After all, eight of the twenty amino acids becomes a source of decay in all proteins, whether they are of animal origin (meat, fish, cheese, eggs) or vegetable (seeds, nuts, grains, legumes). (I)
The advantage of the use of high-protein plant foods as compared to an animal is its low bioavailability of proteins. In the human stomach after chewing food in the remaining cells of animal membrane tissue easily dissolved by digestive juices. Therefore, their content is supplied free in the cavity of the gastrointestinal tract, where it is exposed to putrid microflora.
Quite a different situation is with the plant cells, which are surrounded by a thick cell wall of cellulose, resistant to digestive juices and enzymes of the human body. Plant cells into particles of food are not targeted by mechanical destruction during chewing retain part of its contents inside, and with it removed from the body, thereby reducing the bioavailability of nutrients in the food substrate, both human and for its intestinal microflora. Surely raw foodists who consume nuts, noticed after a visit to the toilet in their natural secretions of virtually the whole or pieces of poorly chewed maloizmenёnnye nuts, which are not able to digest in their gastrointestinal tract.
The low bioavailability of plant proteins is that at about the same percentage of protein in the diet from raw foodists as compared to traditional power supporter putrid microflora develops slowly. But do not entertain illusions those raw foodists who think that rotting food stops after switching to a raw food diet. This is not so! After all, even of the available protein and its decay products, which is available in the gut after eating raw nuts, legumes and grains, is quite enough for intensive growth of colonies of putrefactive microorganisms. What is clearly evidenced by an unpleasant smell (skatole, mercaptans and other decay products), which you can feel after a visit to the toilet on the high-protein diet.
And carnivore, and raw foodists, regularly consume plant foods with a high concentration of protein in the intestine always be actively undergo the processes of decay (!!!) A person can not oppose this anything other than a low-protein diet, since only a small concentration of the protein in food naturally limits the development of putrefactive bacteria. And this is not someone's invention, and an elementary consequence of the biological characteristics of proteolytic microorganisms commonly present within and around us.
The development of atrophic processes, increased load on the liver, vitamin deficiency, reduced resistance to infection - all the result of the presence in the body of pathogenic microflora. Under the influence of this negative factor, body balance between health and disease, which at the slightest further weakened immune forces (hypothermia, fatigue, stress, etc.) at risk to develop into any particular ailment.