634
Attention! Oxalic acid and oxalates in foods and in your body
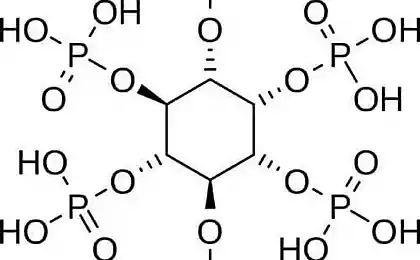
Oxalic acid – a substance that is found in some foods.This antinutrient that the plants generate to protect from being eaten. In small amounts it is harmless and is a byproduct of metabolism, which can easily be excreted along with the urine.But high doses inhibit calcium absorption and contribute to its accumulation. Sometimes, in some conditions, interferes with the normal excretion of salts of oxalic acid. As a consequence, kidney stones and bladder, problems with joints and systemic inflammation.We'll talk more about it:
Fifty one million twenty eight thousand nine hundred forty one
In principle, for a healthy person the use of oxalates safely. Scientists have determined a safe amount of salts and esters of oxalic acid (oxalate) per 100 grams of food in the amount of 50 mg. Healthy people can safely eat foods with oxalates in moderation, but people with kidney disease, gout, rheumatoid arthritis are advised to avoid food with lots of oxalates. Crystals of calcium oxalate, better known as kidney stone, kidney clog the ducts. It is believed that 80% of kidney stones formed from calcium oxalate.
The reasons for the high content of oxalates, as well as the difficulties encountered with their removal from the body can be very different. The most banal – excessive abuse of fruits and vegetables, however, the probability level of oxalates from one of food is extremely small. More often oxalates occur in the urine in the form of sediment in pyelonephritis, during diseases and in diabetes, or in cases of poisoning by ethylene glycol. Common signs oxaluria – severe fatigue, an increased amount of urine during urination, pain in the stomach. From time to time parents find in the General analysis of urine of their children increased content of calcium oxalate crystals. This immediately causes concern, because it is known that 75% of all kidney stones is the oxalate of calcium, and hyperoxaluria characteristic of urolithiasis (ICD).
The mechanisms of harmful action of the oxalatesOxaluria is urinary excretion of oxalates salts of oxalic acid in large quantities. The acid-alkaline balance is disturbed in the direction of acidification of the environment — acidosis. The appearance of acidosis associated with the presence in urine calcium associated with the oxalic acid, the most acid and its crystals. People with impaired metabolism of oxalic acid during the day it secretes about 1,000 mg. the person may experience unpleasant symptoms such as you describe above. It can be a pain in your side, lower abdomen, pain during urination, appearance of blood in the urine, and many others. This is due to irritating and traumatic effect of the crystals on the mucous membrane of the urethra and other urinary organs.
When such symptoms need to see a doctor, to pass all the necessary tests and complete examination. You will also need to adjust the diet and, if necessary, to take drugs.
Oxalic acid is not only formed in the body as a product of chemical reactions, it also comes from food. Consumption of foods rich in it can also lead to oxaluria and disorders of metabolism of this substance. In the gut also produces a small amount of this substance in the processing of carbohydrates by intestinal bacteria. Nervous excitement and strain stimulates the production of oxalic acid.
Fifty eight million eight hundred fifty six thousand one hundred seventy five
Its concentration in urine increases dramatically is called in medicine, this condition hyperoxaluria.In addition, oxalates and inflammation go hand in hand. Oxalate is the oxidants and the oxidants create oxidative stress. By oxidative stress molecules, which should not be linked, bind to each other.
The researchers found that 40% of all oxalates are the result of chemical processes occurring in the liver, 20% is the result of the metabolism of ascorbic acid, and 15% enters the body with food. Increase the amount of oxalates related to some diseases such as obesity, liver disease and diabetes.
Approximately 80 — 1200 mg of oxalate daily enters the body with food in the average diet, but if diet vegetarian — 80 — 2000 mg per day. About 10% of the oxalate is absorbed. In addition, the intestinal absorption of oxalate is also formed endogenously, mainly from glyoxalases and ascorbic acid at about 1 mg/hour.
Nineteen million nine hundred twenty five thousand eight hundred twenty seven
The balance of oxalate is achieved through renal excretion — 15 — 40 mg/day. Oxalic acid blood serum can be divided into exogenous, which enters the body as a result of absorption from the gastrointestinal tract (30 %) and endogenous, which is a product of metabolism (70 %).
Endogenous oxalate is formed in two ways:
There are primary (genetic) defects and secondary. Secondary metabolic oxalic acid occur in selectronic (excess supply csalogany products, poor drinking regime, deficiency of magnesium, vitamins B2 and B6, the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract) and other reasons.
1. The formation of crystals (oxalate of calcium) in the urinary tract and other organs (lungs, joints, brain). Due to the nature of the physical structure of such crystals can cause damage to the tissues of the body accompanied by acute pain and the development of an inflammatory process.
2. Education stubborn complex compounds with heavy metals (mercury, lead, cadmium, etc.) similar to the action of chelates. The task of detoxification when concentration of oxalate is complicated problem.
3. The formation of oxalate salts with minerals such as calcium, magnesium, zinc, leads to chronic shortage of these important minerals in the body. The affinity of oxalate to divalent cations is reflected in the ability to form insoluble precipitation. So in the body oxalate joins with cations such as Ca2+, Fe2+ and Mg2+. Resulting accumulate crystals of the corresponding oxalates, which, because of its shape irritate the intestines and kidneys. Because oxalates bind essential elements such as calcium, long nutrition food containing much oxalates can cause health problems.
In addition to kidney stones, high amounts of oxalic acid in the diet and may cause other unpleasant symptoms, such as weakness, cramps in the stomach, indigestion, burning of the mucous membranes (oral cavity, throat and sinuses). In severe cases, makes itself felt difficulty breathing and disruption of the cardiovascular system. About kidney stones show severe pain in the back or abdomen, and groin.
Characteristic symptoms: change in color of urine and the pain when urinating. In some cases, possible nausea. Oxaluria main symptoms: abdominal pain, fatigue, frequent urination. How to determine the increase in oxalates? The complexes are precipitated in the form of crystals, and the laboratory and describes them in the microscopy of urine sediment.
Where a lot of oxalates?The following list includes products the most common food sources of oxalates. It should be remembered that in the leaves of plants contain more oxalate than in roots or stems. A dessert of figs and nuts and green smoothies can be wonderful, but they also should not consume in large quantities every day.
Among the natural sources of oxalic acid are quite a lot of vegetables and fruits. For example, in 100 g of beet contains from 500 to 675 mg of the substance, chard – to 645 mg, lemon rind and lime – from 83 to 110 mg, okra – 145 mg. Among the medicinal herbs are absolute favorite is lakonos – to 475 mg. of Fruits with oxalic acid: apples, raspberries and strawberries, gooseberries and blackberries, bananas, mango, black currants, pomegranates and oranges.
Vegetables with oxalates: purslane and leaf mustard, potatoes and sweet potatoes, celery, and asparagus, eggplant and pumpkin, beet greens and radishes, green and sweet peppers, chicory and tomatoes, parsnips, radishes and cauliflower, parsley and green onions.
Beans, nuts, and chocolate: In nuts, chocolate, beans and some cereals also have oxalic acid: 187 mg roasted peanut, 202 mg in the pecans, 120 mg, classic chocolate, 270 mg in wheat germ. Dry cocoa powder contains an impressive 625 mg per 100 g. Other products with oxalic acid: amaranth, corn, wheat bran, oats, soy beans, kidney beans and lentils. A lot of oxalate in buckwheat, almonds and cashews.
Microflora and the gut
Intestinal hyperoxaluria often observed in patients with malabsorption syndrome, in which there is a malabsorption from the small intestine of nutrients. This syndrome develops in various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: inflammation, enzyme insufficiency, disorders of motility and blood supply, goiter, bypass anastomoses.
In the normal intestine, most of the oxalate binds with calcium and is excreted in the form of insoluble compounds. The increase in the intestinal lumen reabsorbiruetsa fatty acids (steatorrhea) leads to the fact that they bind calcium and are excreted in the form of calcium complexes. Thus, in these patients is not enough calcium to bind oxalate in the intestine and absorption of oxalate increases. Reducing the absorption of calcium causes hypocalcaemia, which leads to secondary hyperparathyroidism and hypercalciuria — the conditions for stone formation.
Seventy three million two hundred nine thousand three hundred twenty seven
Intestinal hyperoxaluria occurs as a result:
About it it is known that it feeds exclusively oxalates,this is her only source of energy, and that colonization of the gut Oxalobacter reduces the risk of stone formation and calcium oxalate 70%. According to the hypothesis, if the content of O. formigenes in the gastrointestinal tract is reduced, the greater the amount of oxalates in your diet, absorbed in the intestine and enters the bloodstream, and then into the urine, where they form crystals with calcium.
Studies have shown that most patients with oxaluria Oxalobacter formigenes in the gut is missing. One potential reason for this is the use of antibiotics. For example, a 2-week Helicobacter Pylori eradication demolish 63% of bacteria O. formigenes. And that's a violation of colonization persisted for up to six months.
Eighty four million three hundred fifty four thousand two hundred fifty six
Disorders of lipid metabolismIf you have a problem with bile and digestion of fats, it is best to limit the amount of fat. Healthy people are not affected. To reduce the absorption of oxalates in the intestinal pathology, it is recommended to limit fat intake, to provide the diet with foods adequate in calcium and magnesium.
When consuming large amount of fat with food fatty acids bind calcium. This causes an increased penetration of oxalic-acetic acids through the intestinal mucosa and increased its revenues through the kidneys into the urine. Normally, the oxalates contained in foods are associated with calcium in the intestinal lumen and excreted with the feces as insoluble calcium oxalate. Excessive absorption of oxalates in the intestine, which is associated with impaired fat digestion, is the most common cause of oxaluria (oxaluria). So if oxaluria associated with pathology of the digestive system, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of fat to prevent the enhanced absorption of salts of oxalic acid.
In diseases of the digestive tract accompanied by malabsorption syndrome, fats are not already in interaction with bile in enzymes come into interaction with calcium in the intestinal canal forming a soapy compound, which is clinically manifested by steatorrhea. One of the protective action of calcium is binding with an excess of oxalates the gut lumen and elimination from the body in the form of Davlekanovo of calcium.
But, since most of the Sa went on and interaction with fats, less binds to oxalate, leading to their accumulation in the intestinal lumen in a free form. The lack of calcium leaves open the intercellular space to the free penetration of excess oxalates into the bloodstream. Thus, we conclude that enteral limiting consumption of calcium does not affect the treatment of oxalate-calcium urolithiasis, and can even aggravate the condition of the cell wall of the intestine with the formation of the syndrome of "leaky gut".
Magnesium deficiencyTo a shortage of protective colloids results in inadequate dietary intake of vitamins A, b, D and especially vitamin B6 and magnesium (study of causes of ICD confirmed many times that Ox in the urine were detected mainly in residents of areas with natural deficiency of vitamin B6, lack of magnesium in drinking water and foods). Vitamin B6 promotes the transition of glycine to serine, which prevents the formation of aldehyde from which the human body is formed by the oxidation of oxalic acid (Ox).
In a chemical reaction leading to the formation of crystals, only take part in ionized form kamneobrazuyuschih substances. Thus, the number of ionized calcium in the urine is 40 — 50 %. Under normal conditions, the magnesium ion binds 30 — 40% of oxalates in the urine, thus competing with calcium. In connection with the chemical antagonism of calcium and magnesium additional consumption of magnesium reduces the formation of calcium oxalate. Experimental, epidemiological and clinical data indicate that the lack of magnesium in the diet may contribute to the formation of oxalates, and the enrichment of the diet with magnesium helps in the excretion of oxalates
Twenty eight million eight hundred thirty nine thousand five hundred fourteen
Other tips for reducing the amount of oxalates1. Digestion (with emptying the water). Green leafy vegetables should have a little hold in boiling water before you cook it (drain the water) — this reduces the levels of oxalates. Heat treatment with draining of water boiling in two waters. Use fresh young leaves.
2. Add calcium rich foods. There are enough foods containing calcium, When calcium and the amount of oxalates in the diet is balanced, then the crystals formed in the gut and in the blood is not absorbed. If the balance is disturbed in favor of the oxalates, the formation of crystals occurs in the kidneys and urinary system. Large amount of calcium together with food containing oxalates leads to the loss of calcium oxalate in the digestive tract, reducing the income of oxalates in the body by 97 %.
3. Drink enough of water – mineral water.
4. The use of citrates. Add in drinks lemon juice (100 g per day, distribute to each drink). Often the doctor appoints to the patient of sodium citrate and potassium citrate that will reduce the formation of complexes of hard-soluble salts of calcium, reduced the concentration of its ions and form complexes with citrate. D
5. Stop taking complexes with vitamin C. Excess vitamin C increases the amount of oxalic acid. Increased production of oxalates in the body also causes excessive consumption of ascorbic acid, which is metabolized in the body to oxalic acid.
Conclusion :Increasing the level of oxalic acid and oxalate is an important basis for the development of several diseases. published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: //www.beloveshkin.com/2015/08/shhavelevaya-kislota-i-oksalaty-v-produktakh-pitaniya-i-v-vashem-tele.html
Fifty one million twenty eight thousand nine hundred forty one
In principle, for a healthy person the use of oxalates safely. Scientists have determined a safe amount of salts and esters of oxalic acid (oxalate) per 100 grams of food in the amount of 50 mg. Healthy people can safely eat foods with oxalates in moderation, but people with kidney disease, gout, rheumatoid arthritis are advised to avoid food with lots of oxalates. Crystals of calcium oxalate, better known as kidney stone, kidney clog the ducts. It is believed that 80% of kidney stones formed from calcium oxalate.
The reasons for the high content of oxalates, as well as the difficulties encountered with their removal from the body can be very different. The most banal – excessive abuse of fruits and vegetables, however, the probability level of oxalates from one of food is extremely small. More often oxalates occur in the urine in the form of sediment in pyelonephritis, during diseases and in diabetes, or in cases of poisoning by ethylene glycol. Common signs oxaluria – severe fatigue, an increased amount of urine during urination, pain in the stomach. From time to time parents find in the General analysis of urine of their children increased content of calcium oxalate crystals. This immediately causes concern, because it is known that 75% of all kidney stones is the oxalate of calcium, and hyperoxaluria characteristic of urolithiasis (ICD).
The mechanisms of harmful action of the oxalatesOxaluria is urinary excretion of oxalates salts of oxalic acid in large quantities. The acid-alkaline balance is disturbed in the direction of acidification of the environment — acidosis. The appearance of acidosis associated with the presence in urine calcium associated with the oxalic acid, the most acid and its crystals. People with impaired metabolism of oxalic acid during the day it secretes about 1,000 mg. the person may experience unpleasant symptoms such as you describe above. It can be a pain in your side, lower abdomen, pain during urination, appearance of blood in the urine, and many others. This is due to irritating and traumatic effect of the crystals on the mucous membrane of the urethra and other urinary organs.
When such symptoms need to see a doctor, to pass all the necessary tests and complete examination. You will also need to adjust the diet and, if necessary, to take drugs.
Oxalic acid is not only formed in the body as a product of chemical reactions, it also comes from food. Consumption of foods rich in it can also lead to oxaluria and disorders of metabolism of this substance. In the gut also produces a small amount of this substance in the processing of carbohydrates by intestinal bacteria. Nervous excitement and strain stimulates the production of oxalic acid.
Fifty eight million eight hundred fifty six thousand one hundred seventy five
Its concentration in urine increases dramatically is called in medicine, this condition hyperoxaluria.In addition, oxalates and inflammation go hand in hand. Oxalate is the oxidants and the oxidants create oxidative stress. By oxidative stress molecules, which should not be linked, bind to each other.
The researchers found that 40% of all oxalates are the result of chemical processes occurring in the liver, 20% is the result of the metabolism of ascorbic acid, and 15% enters the body with food. Increase the amount of oxalates related to some diseases such as obesity, liver disease and diabetes.
Approximately 80 — 1200 mg of oxalate daily enters the body with food in the average diet, but if diet vegetarian — 80 — 2000 mg per day. About 10% of the oxalate is absorbed. In addition, the intestinal absorption of oxalate is also formed endogenously, mainly from glyoxalases and ascorbic acid at about 1 mg/hour.
Nineteen million nine hundred twenty five thousand eight hundred twenty seven
The balance of oxalate is achieved through renal excretion — 15 — 40 mg/day. Oxalic acid blood serum can be divided into exogenous, which enters the body as a result of absorption from the gastrointestinal tract (30 %) and endogenous, which is a product of metabolism (70 %).
Endogenous oxalate is formed in two ways:
- As a result of the metabolism of ascorbic acid (30 %)
- As a result of the metabolism of glyoxalase acid (40 %)
There are primary (genetic) defects and secondary. Secondary metabolic oxalic acid occur in selectronic (excess supply csalogany products, poor drinking regime, deficiency of magnesium, vitamins B2 and B6, the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract) and other reasons.
1. The formation of crystals (oxalate of calcium) in the urinary tract and other organs (lungs, joints, brain). Due to the nature of the physical structure of such crystals can cause damage to the tissues of the body accompanied by acute pain and the development of an inflammatory process.
2. Education stubborn complex compounds with heavy metals (mercury, lead, cadmium, etc.) similar to the action of chelates. The task of detoxification when concentration of oxalate is complicated problem.
3. The formation of oxalate salts with minerals such as calcium, magnesium, zinc, leads to chronic shortage of these important minerals in the body. The affinity of oxalate to divalent cations is reflected in the ability to form insoluble precipitation. So in the body oxalate joins with cations such as Ca2+, Fe2+ and Mg2+. Resulting accumulate crystals of the corresponding oxalates, which, because of its shape irritate the intestines and kidneys. Because oxalates bind essential elements such as calcium, long nutrition food containing much oxalates can cause health problems.
In addition to kidney stones, high amounts of oxalic acid in the diet and may cause other unpleasant symptoms, such as weakness, cramps in the stomach, indigestion, burning of the mucous membranes (oral cavity, throat and sinuses). In severe cases, makes itself felt difficulty breathing and disruption of the cardiovascular system. About kidney stones show severe pain in the back or abdomen, and groin.
Characteristic symptoms: change in color of urine and the pain when urinating. In some cases, possible nausea. Oxaluria main symptoms: abdominal pain, fatigue, frequent urination. How to determine the increase in oxalates? The complexes are precipitated in the form of crystals, and the laboratory and describes them in the microscopy of urine sediment.
Where a lot of oxalates?The following list includes products the most common food sources of oxalates. It should be remembered that in the leaves of plants contain more oxalate than in roots or stems. A dessert of figs and nuts and green smoothies can be wonderful, but they also should not consume in large quantities every day.
- large (more than 1 g/kg) amount contained in cocoa beans, chocolate, celery, spinach, sorrel, parsley, rhubarb;
- moderate (from 0.3 to 1.0 g/kg) in carrots, beets, chicory, green beans, onions, tomatoes, tea;
- small (0,05 — 0,3 g/kg) of fresh cabbage, apricots, bananas, currants, Brussels sprouts, potatoes;
- the least amount of oxalic acid contain eggplant, cucumbers, squash, mushrooms, cauliflower, lettuce, peas.
Among the natural sources of oxalic acid are quite a lot of vegetables and fruits. For example, in 100 g of beet contains from 500 to 675 mg of the substance, chard – to 645 mg, lemon rind and lime – from 83 to 110 mg, okra – 145 mg. Among the medicinal herbs are absolute favorite is lakonos – to 475 mg. of Fruits with oxalic acid: apples, raspberries and strawberries, gooseberries and blackberries, bananas, mango, black currants, pomegranates and oranges.
Vegetables with oxalates: purslane and leaf mustard, potatoes and sweet potatoes, celery, and asparagus, eggplant and pumpkin, beet greens and radishes, green and sweet peppers, chicory and tomatoes, parsnips, radishes and cauliflower, parsley and green onions.
Beans, nuts, and chocolate: In nuts, chocolate, beans and some cereals also have oxalic acid: 187 mg roasted peanut, 202 mg in the pecans, 120 mg, classic chocolate, 270 mg in wheat germ. Dry cocoa powder contains an impressive 625 mg per 100 g. Other products with oxalic acid: amaranth, corn, wheat bran, oats, soy beans, kidney beans and lentils. A lot of oxalate in buckwheat, almonds and cashews.
Microflora and the gut
Intestinal hyperoxaluria often observed in patients with malabsorption syndrome, in which there is a malabsorption from the small intestine of nutrients. This syndrome develops in various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: inflammation, enzyme insufficiency, disorders of motility and blood supply, goiter, bypass anastomoses.
In the normal intestine, most of the oxalate binds with calcium and is excreted in the form of insoluble compounds. The increase in the intestinal lumen reabsorbiruetsa fatty acids (steatorrhea) leads to the fact that they bind calcium and are excreted in the form of calcium complexes. Thus, in these patients is not enough calcium to bind oxalate in the intestine and absorption of oxalate increases. Reducing the absorption of calcium causes hypocalcaemia, which leads to secondary hyperparathyroidism and hypercalciuria — the conditions for stone formation.
Seventy three million two hundred nine thousand three hundred twenty seven
Intestinal hyperoxaluria occurs as a result:
- failure of formation of calcium oxalate complexes in the gut as a result of low calcium content due to the lower consumption of dietary calcium or the formation of complexes of calcium + fatty acids in patients with gastrointestinal disorders;
- increase the absorption of oxalic acid for unknown reasons;
- consumption of very high doses of ascorbic acid;
- reduce the population of bacteria Oxalobacter formigenes.
About it it is known that it feeds exclusively oxalates,this is her only source of energy, and that colonization of the gut Oxalobacter reduces the risk of stone formation and calcium oxalate 70%. According to the hypothesis, if the content of O. formigenes in the gastrointestinal tract is reduced, the greater the amount of oxalates in your diet, absorbed in the intestine and enters the bloodstream, and then into the urine, where they form crystals with calcium.
Studies have shown that most patients with oxaluria Oxalobacter formigenes in the gut is missing. One potential reason for this is the use of antibiotics. For example, a 2-week Helicobacter Pylori eradication demolish 63% of bacteria O. formigenes. And that's a violation of colonization persisted for up to six months.
Eighty four million three hundred fifty four thousand two hundred fifty six
Disorders of lipid metabolismIf you have a problem with bile and digestion of fats, it is best to limit the amount of fat. Healthy people are not affected. To reduce the absorption of oxalates in the intestinal pathology, it is recommended to limit fat intake, to provide the diet with foods adequate in calcium and magnesium.
When consuming large amount of fat with food fatty acids bind calcium. This causes an increased penetration of oxalic-acetic acids through the intestinal mucosa and increased its revenues through the kidneys into the urine. Normally, the oxalates contained in foods are associated with calcium in the intestinal lumen and excreted with the feces as insoluble calcium oxalate. Excessive absorption of oxalates in the intestine, which is associated with impaired fat digestion, is the most common cause of oxaluria (oxaluria). So if oxaluria associated with pathology of the digestive system, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of fat to prevent the enhanced absorption of salts of oxalic acid.
In diseases of the digestive tract accompanied by malabsorption syndrome, fats are not already in interaction with bile in enzymes come into interaction with calcium in the intestinal canal forming a soapy compound, which is clinically manifested by steatorrhea. One of the protective action of calcium is binding with an excess of oxalates the gut lumen and elimination from the body in the form of Davlekanovo of calcium.
But, since most of the Sa went on and interaction with fats, less binds to oxalate, leading to their accumulation in the intestinal lumen in a free form. The lack of calcium leaves open the intercellular space to the free penetration of excess oxalates into the bloodstream. Thus, we conclude that enteral limiting consumption of calcium does not affect the treatment of oxalate-calcium urolithiasis, and can even aggravate the condition of the cell wall of the intestine with the formation of the syndrome of "leaky gut".
Magnesium deficiencyTo a shortage of protective colloids results in inadequate dietary intake of vitamins A, b, D and especially vitamin B6 and magnesium (study of causes of ICD confirmed many times that Ox in the urine were detected mainly in residents of areas with natural deficiency of vitamin B6, lack of magnesium in drinking water and foods). Vitamin B6 promotes the transition of glycine to serine, which prevents the formation of aldehyde from which the human body is formed by the oxidation of oxalic acid (Ox).
In a chemical reaction leading to the formation of crystals, only take part in ionized form kamneobrazuyuschih substances. Thus, the number of ionized calcium in the urine is 40 — 50 %. Under normal conditions, the magnesium ion binds 30 — 40% of oxalates in the urine, thus competing with calcium. In connection with the chemical antagonism of calcium and magnesium additional consumption of magnesium reduces the formation of calcium oxalate. Experimental, epidemiological and clinical data indicate that the lack of magnesium in the diet may contribute to the formation of oxalates, and the enrichment of the diet with magnesium helps in the excretion of oxalates
Twenty eight million eight hundred thirty nine thousand five hundred fourteen
Other tips for reducing the amount of oxalates1. Digestion (with emptying the water). Green leafy vegetables should have a little hold in boiling water before you cook it (drain the water) — this reduces the levels of oxalates. Heat treatment with draining of water boiling in two waters. Use fresh young leaves.
2. Add calcium rich foods. There are enough foods containing calcium, When calcium and the amount of oxalates in the diet is balanced, then the crystals formed in the gut and in the blood is not absorbed. If the balance is disturbed in favor of the oxalates, the formation of crystals occurs in the kidneys and urinary system. Large amount of calcium together with food containing oxalates leads to the loss of calcium oxalate in the digestive tract, reducing the income of oxalates in the body by 97 %.
3. Drink enough of water – mineral water.
4. The use of citrates. Add in drinks lemon juice (100 g per day, distribute to each drink). Often the doctor appoints to the patient of sodium citrate and potassium citrate that will reduce the formation of complexes of hard-soluble salts of calcium, reduced the concentration of its ions and form complexes with citrate. D
5. Stop taking complexes with vitamin C. Excess vitamin C increases the amount of oxalic acid. Increased production of oxalates in the body also causes excessive consumption of ascorbic acid, which is metabolized in the body to oxalic acid.
Conclusion :Increasing the level of oxalic acid and oxalate is an important basis for the development of several diseases. published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: //www.beloveshkin.com/2015/08/shhavelevaya-kislota-i-oksalaty-v-produktakh-pitaniya-i-v-vashem-tele.html