591
What are the risks of asymptomatic high uric acid levels
Uric acid increased: impact on health
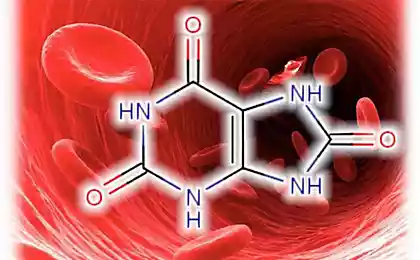
Asymptomatic high uric acid levels is a powerful risk factor for cardiovascular disease, obesity, atherosclerosis, senile dementia, impotence, etc. the Normal level of MK is 6.5–7 mg/DL in men and 6-6. 5 mg/DL in women. Concentration of 5.75 mg/DL and above for men and 4.8 mg/DL and above for women classified as "high normal", which means a certain impact on health. Uric acid is elevated if its level is more than 7.0 mg/DL and is associated with an increased risk of developing gout or kidney stones.
A new wave of interest to uric acid connected with understanding of the role of asymptomatic hyperuricemia (defined most often as the level of uric acid in the plasma of 7.0 mg/DL ) as a powerful, independent and modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality based on data from numerous epidemiological and prospective studies.
The most common causes that affect the level of uric acid are obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, arterial hypertension, use of diuretics and low dose acetylsalicylic acid, excessive use of alcohol, older age, renal failure. Among them, the leader of the metabolic syndrome and its components. Alcohol, impaired renal function and obesity are also associated with higher levels of uric acid.
Asymptomatic increases in uric acid.
According to the recommendations of the EULAR (European Antirheumatic League) hyperuricemia (Hu) is considered to increase uric acid (MK) serum above 360 µmol/L. it Often happens that you have elevated levels of uric acid, but it is not a disease, this condition happens according to some estimates, Belarus and the Russian Federation every fifth. According to more modest estimates, an asymptomatic increase in the level of MK have 5-8% of the population, of which, only 5-20% develop podagra the period from 1950 to 1980 in the population average level of MK in the serum increased from 5 to 6 mg/DL.
Currently proved the role of hyperuricemia as an independent predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with coronary heart disease, chronic and acute cardiac insufficiency, arterial hypertension and pre-hypertension and metabolic syndrome.
Currently all the more urgent becomes the question: how "harmless" asymptomatic increases in uric acid? Read about it below.
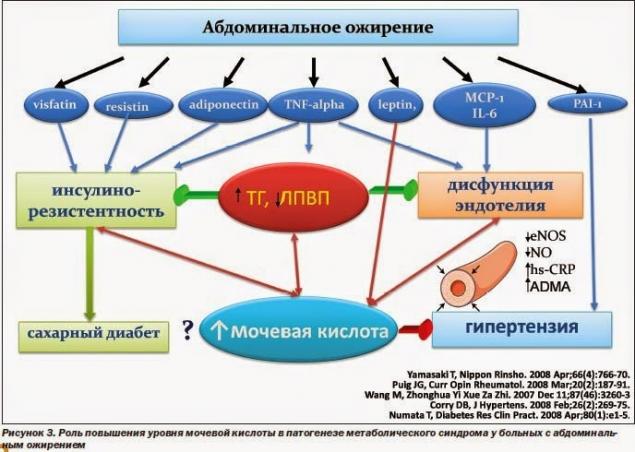
The relationship of increased level of uric acid in insulinorezistentnost and obesity Increase the amount of uric acid, together with increased low density lipoprotein, is considered part of the syndrome of insulin resistance which leads to cardiovascular morbidity. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia can reduce renal excretion of uric acid independently of obesity, and renal function. Probably, insulin increases tubular reabsorption of sodium is accompanied by increased reabsorption of uric acid. Binds insulin resistance, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia and hyperuricemia. However, urinary associated with triglycerides independently of insulin level fasting and obesity, showing that the mechanism underlying this connection is only partially relates to insulin resistance and obesity.
Selective insulin resistance are characteristic of patients with arterial hypertension, and insulin has a strong natriyureticeski effect, which is accompanied by decreased renal excretion of uric acid. Hyperinsulinemia also can increase the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which can contribute to uric acid in the blood. The view that hyperuricemia may be an indicator of insulin resistance, has recently confirmed an 8–year study proved the connection between UMK and insulin resistance. Thus, hyperuricemia in patients with arterial hypertension may indicate insulin resistance, which is clearly associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity.
Uric acid is increased in abdominal obesity
Elevated levels of uric acid, apparently associated also with renal vascular resistance and has an inverse dependence on renal blood flow. Uric acid levels correlated with excretion of albumin in the urine, which are the precursors of the development of nephrosclerosis and impaired renal hemodynamics precedes the violation of the metabolism of uric acid in patients with nephropathy. Thus, hyperuricemia in patients with arterial hypertension most likely reflects impairment of renal hemodynamics, it is a good prognostic factor.
Many studies found that the level of the bladder is associated with hyperlipidemia, especially hypertriglyceridemia. A stronger correlation was found with triglycerides, not cholesterol, which has led to the assumption that triglycerides are the intermediate link between increased uric acid and increased cholesterol levels. Was noted a weak relationship between uric acid and high density lipoproteins.
The relationship of uric acid with atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is observed in birds, being usually asymptomatic. Birds, like primates, eat lots of fruits and excrete uric acid. Consideration of models of atherosclerosis in animals, which have a different metabolism often leads to potentially incorrect results. For example, the famous cholesterol rabbit, often do not apply to the person.
Uric acid is Pro-inflammatory substance in relation to the cardiovascular system, stimulating the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. Assume that there are several potential mechanisms by which uric acid may play a pathogenetic role in the development of cardiovascular morbidity or, conversely, to influence the clinical manifestations in patients with established atherosclerosis, but none of them is yet to be confirmed.
It is obvious that an increased level of uric acid increases oxidation of low-density lipoproteins and promotes lipid peroxygenation. and is also associated with increased production of free oxygen radicals. Oxidative stress and improve oxygenation of low density lipoprotein in the arterial wall may play a role in the progression of atherosclerosis. Uric acid may be involved in adhesion and aggregation of platelets. This gave rise to the hypothesis that hyperuricemia increases the risk of coronary thrombosis in patients with existing coronary disease.
Assume that the increase of uric acid reflects the endothelial damage. Endothelial dysfunction, manifested by reduced endothelium–dependent vascular relaxation as a result of NO, usually for patients with diabetes and arterial hypertension and plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis. Endothelial cells present xanthine oxide, which is the generator of free oxygen radicals. Uric acid and xanthine oxide increased and determined a much higher concentration in blood vessels affected by atherosclerosis than in healthy vascular tissue. If this mechanism is correct, then the increase in uric acid may be an accurate marker of a biological phenomenon, closely associated with the progression of atherosclerosis, not being the direct cause of the development of the process of vascular damage, which may be guilty of a xanthine oxide.
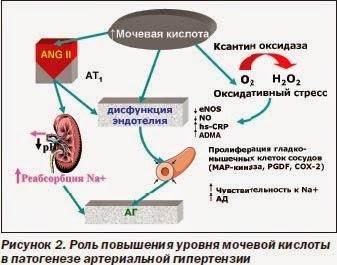
In turn, at a constant hyperuricemia hypertension is associated with the development of preglomerular arteriopathy and tubulointerstitial lesions. Increase in uric acid stimulates activation of the renin-angiotensin system and contributes to endothelial dysfunction. In addition, ischemia is the transformation of xantinoxydasy in the enzyme xanthine oxidase, which leads to a change of metabolism xantinov, the transformation of uric acid from antioxidants to prooxidants and stimulate oxidative stress. Hyperuricemia leads to endothelial dysfunction due to inhibition of NO synthesis. This effect of uric acid are due to its prooxidant properties in the conditions of the changed metabolism.
Uric acid also stimulates the proliferation of smooth muscle cells of blood vessels by activation of growth factors, vasoconstrictor and proinflammatory molecules. Thus, uric acid is not only a marker but also an active component of hypertension development.
However, the most important thing is that in the group of patients where the use of thiazide diuretics has led to increased levels of MK, the number of cardiovascular events was 42% higher than in the group of patients who had a marked increase in MK.
The relationship between hyperuricemia (high uric acid) and the risk of cardiovascular disease established in the course of large epidemiological studies. Proven correlation of high levels of uric acid with hypertension, diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and atherosclerosis caused by cardiovascular diseases.
In the study I NHANES (the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey) revealed an independent Association between hyperuricemia and the increase in cardiovascular mortality. With higher levels of MK, the risk of death from ischemic heart disease increased by 77% in men and 300% among women. Increasing the concentration of MK per 1 mg/DL (to 59.5 µmol/l) was associated with a significant increase in mortality both among men and among women. A 12–year study (PIUMA), which was attended by more than 1,500 previously treated patients with arterial hypertensia also demonstrated that the level of uric serum is a strong predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
The study of patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 showed a significant increase in the frequency of the stroke when the rate of uric acid. In this case the relationship remained significant even after the exclusion of other cardiovascular risk factors. Meanwhile, the results of the Framingham study there was no significant relationship between uric acid level and cardiovascular morbidity.
Hyperuricemia was detected in almost 90% of adolescents with newly diagnosed arterial hypertension. The results show that the correction of hiresuite can prevent the development of cardiovascular catastrophes.
So what to do with asymptomatic increase uric acid?
It is shown that not only the crystals Manorama of sodium, but soluble uric acid in the asymptomatic GU can lead to increased levels of inflammatory mediators and to induce the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Many of these "Pro-inflammatory" mediators are fundamental in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic vascular lesions and its complications. Therefore it is necessary to slightly change the meals about this in the next article.
Researchers from the Medical University Johns Hopkins (Baltimore, MD, USA) found that individuals with "high normal" levels of uric acid a volume of hyperintense white matter of the brain is 2.6 times greater than in the population with medium or low level. This confirms the role of uric acid in increased risk of cerebrovascular disease and may explain the Association between elevated uric acid and a slight cognitive deficit in elderly patients. There is an obvious correlation between high levels of uric acid and diseases such as hypertension, type II diabetes and metabolic syndrome. All of these States are known risk factors for the development of dementia.
It is noteworthy that the average level of uric acid in the presence of disorder has erectiepil higher (about 12 mg/DL) than patients with normal sexual function (approximately 5 mg/DL). In the result, it was found that the presence of excessive levels of the substance in the blood increases the risk of erectile dysfunction almost 6 times. And the increase level of uric acid for each 1 mg/DL is accompanied by a renewed increase in the likelihood of disorders of erection.
The positive aspects of the action of uric acid
According to some researchers, the increase in urinary can favorably influence the body. Chemical structure of uric acid is similar to trimethylaluminum xanthine caffeine and is therefore able to improve mental and physical performance. Numerous studies in 1960-70–ies have confirmed that people with hyperuricemia have a higher intelligence and speed of reaction. However, adenosine receptors (which stimulate the caffeine), uric acid is not in effect, in most studies shows a relatively small biological effect, besides the possible influence of socio–economic status of participants.
Another nice feature of MK is its ability to act as antioxidant, blocking superoxide, peroxynitrite, and iron-catalyzed oxidative reactions. A number of authors suggest that increased MC can be one of the key antioxidants of the plasma and to prevent associated with aging oxidative stress, thereby contributing to prolongation of life. Studies have shown that transfusion of uric acid people increases the antioxidant activity of serum and improves endothelial function.
If the uric acid has a negative effect within the Central nervous system it plays a completely different role. Uric acid is known as a powerful neuroprotective agent and an inhibitor of neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. How it works there, there are different opinions. But, in people with hyperuricemia have noted a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases, like Parkinson's disease or Alzheimer's and there is evidence for diffuse sclerosis.
The ability of high levels of uric acid to reduce peroxynitrite–mediated formation of nitrotyrosine evidence of neuroprotective properties, which is especially important in multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, stroke and other neurological diseases. According to epidemiological studies, people with GU is much less likely to suffer from multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, and infusion of uric acid can reduce the neurological manifestations obtained through experimentation (for example, in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis).
High level of urate (uric acid salts) in the blood slows the progression of Parkinson's disease. Normal urate is contained in blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid. These substances are potent antioxidants that protect the body from harmful molecules — free radicals. It was found that participants with the highest urate levels in the blood, the disease developed more slowly.
Recent studies have shown that the beneficial effect of uric acid in these conditions is connected, rather than with her nitrotyrosin–overwhelming antioxidant, with the ability to block blood–brain barrier or the impact on astroglial cells.
The paradox of uric acid.
So, if acute rise in uric acid (uric acid increased) has an antioxidant effect and beneficial effect on endothelial function, chronic hyperuricemia, on the contrary, contributes to the development of oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Perhaps this is due to various intracellular and intravascular effects of acute and chronic hyperuricemia.
Oxidative stress is a main factor of brain damage in patients with ischemic stroke. Uric acid is a potent endogenous antioxidant molecule. In the course of experimental ischemia in rats, the exogenous administration of uric acid has a neuroprotective effect, intravenous urinary kisloid is safe, prevents an early decline in uric acid levels and reduces an early increase in markers of oxidative stress.
The greatest benefits from the use of uric acid had women, patients with moderate-to-large stroke and patients with high content of glucose in the blood. Dr. Chamorro explained this by the fact that these patients may have higher levels of oxidative stress and uric acid is a powerful antioxidant.published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
Materials used:
www.rmj.ru/articles_6234.htm
www.rmj.ru/articles_996.htm
www.mif-ua.com/education/symposium/korrekciya-giperurikemii-kak-faktora-riska-serdechno-sosudistoj-zabolevaemosti-i-smertnosti
Alderman MH: Serum Uric Acid As a Cardiovascular Risk Factor for Heart Disease. Current Hypertension Reports 2001, 3:184-189.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2015/02/blog-post_9.html#more
Asymptomatic high uric acid levels is a powerful risk factor for cardiovascular disease, obesity, atherosclerosis, senile dementia, impotence, etc. the Normal level of MK is 6.5–7 mg/DL in men and 6-6. 5 mg/DL in women. Concentration of 5.75 mg/DL and above for men and 4.8 mg/DL and above for women classified as "high normal", which means a certain impact on health. Uric acid is elevated if its level is more than 7.0 mg/DL and is associated with an increased risk of developing gout or kidney stones.

A new wave of interest to uric acid connected with understanding of the role of asymptomatic hyperuricemia (defined most often as the level of uric acid in the plasma of 7.0 mg/DL ) as a powerful, independent and modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality based on data from numerous epidemiological and prospective studies.
The most common causes that affect the level of uric acid are obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, arterial hypertension, use of diuretics and low dose acetylsalicylic acid, excessive use of alcohol, older age, renal failure. Among them, the leader of the metabolic syndrome and its components. Alcohol, impaired renal function and obesity are also associated with higher levels of uric acid.
Asymptomatic increases in uric acid.
According to the recommendations of the EULAR (European Antirheumatic League) hyperuricemia (Hu) is considered to increase uric acid (MK) serum above 360 µmol/L. it Often happens that you have elevated levels of uric acid, but it is not a disease, this condition happens according to some estimates, Belarus and the Russian Federation every fifth. According to more modest estimates, an asymptomatic increase in the level of MK have 5-8% of the population, of which, only 5-20% develop podagra the period from 1950 to 1980 in the population average level of MK in the serum increased from 5 to 6 mg/DL.
Currently proved the role of hyperuricemia as an independent predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with coronary heart disease, chronic and acute cardiac insufficiency, arterial hypertension and pre-hypertension and metabolic syndrome.
Currently all the more urgent becomes the question: how "harmless" asymptomatic increases in uric acid? Read about it below.
The relationship of increased level of uric acid in insulinorezistentnost and obesity Increase the amount of uric acid, together with increased low density lipoprotein, is considered part of the syndrome of insulin resistance which leads to cardiovascular morbidity. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia can reduce renal excretion of uric acid independently of obesity, and renal function. Probably, insulin increases tubular reabsorption of sodium is accompanied by increased reabsorption of uric acid. Binds insulin resistance, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia and hyperuricemia. However, urinary associated with triglycerides independently of insulin level fasting and obesity, showing that the mechanism underlying this connection is only partially relates to insulin resistance and obesity.
Selective insulin resistance are characteristic of patients with arterial hypertension, and insulin has a strong natriyureticeski effect, which is accompanied by decreased renal excretion of uric acid. Hyperinsulinemia also can increase the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which can contribute to uric acid in the blood. The view that hyperuricemia may be an indicator of insulin resistance, has recently confirmed an 8–year study proved the connection between UMK and insulin resistance. Thus, hyperuricemia in patients with arterial hypertension may indicate insulin resistance, which is clearly associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity.

Uric acid is increased in abdominal obesity
Elevated levels of uric acid, apparently associated also with renal vascular resistance and has an inverse dependence on renal blood flow. Uric acid levels correlated with excretion of albumin in the urine, which are the precursors of the development of nephrosclerosis and impaired renal hemodynamics precedes the violation of the metabolism of uric acid in patients with nephropathy. Thus, hyperuricemia in patients with arterial hypertension most likely reflects impairment of renal hemodynamics, it is a good prognostic factor.
Many studies found that the level of the bladder is associated with hyperlipidemia, especially hypertriglyceridemia. A stronger correlation was found with triglycerides, not cholesterol, which has led to the assumption that triglycerides are the intermediate link between increased uric acid and increased cholesterol levels. Was noted a weak relationship between uric acid and high density lipoproteins.
The relationship of uric acid with atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is observed in birds, being usually asymptomatic. Birds, like primates, eat lots of fruits and excrete uric acid. Consideration of models of atherosclerosis in animals, which have a different metabolism often leads to potentially incorrect results. For example, the famous cholesterol rabbit, often do not apply to the person.
Uric acid is Pro-inflammatory substance in relation to the cardiovascular system, stimulating the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. Assume that there are several potential mechanisms by which uric acid may play a pathogenetic role in the development of cardiovascular morbidity or, conversely, to influence the clinical manifestations in patients with established atherosclerosis, but none of them is yet to be confirmed.
It is obvious that an increased level of uric acid increases oxidation of low-density lipoproteins and promotes lipid peroxygenation. and is also associated with increased production of free oxygen radicals. Oxidative stress and improve oxygenation of low density lipoprotein in the arterial wall may play a role in the progression of atherosclerosis. Uric acid may be involved in adhesion and aggregation of platelets. This gave rise to the hypothesis that hyperuricemia increases the risk of coronary thrombosis in patients with existing coronary disease.
Assume that the increase of uric acid reflects the endothelial damage. Endothelial dysfunction, manifested by reduced endothelium–dependent vascular relaxation as a result of NO, usually for patients with diabetes and arterial hypertension and plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis. Endothelial cells present xanthine oxide, which is the generator of free oxygen radicals. Uric acid and xanthine oxide increased and determined a much higher concentration in blood vessels affected by atherosclerosis than in healthy vascular tissue. If this mechanism is correct, then the increase in uric acid may be an accurate marker of a biological phenomenon, closely associated with the progression of atherosclerosis, not being the direct cause of the development of the process of vascular damage, which may be guilty of a xanthine oxide.

In turn, at a constant hyperuricemia hypertension is associated with the development of preglomerular arteriopathy and tubulointerstitial lesions. Increase in uric acid stimulates activation of the renin-angiotensin system and contributes to endothelial dysfunction. In addition, ischemia is the transformation of xantinoxydasy in the enzyme xanthine oxidase, which leads to a change of metabolism xantinov, the transformation of uric acid from antioxidants to prooxidants and stimulate oxidative stress. Hyperuricemia leads to endothelial dysfunction due to inhibition of NO synthesis. This effect of uric acid are due to its prooxidant properties in the conditions of the changed metabolism.
Uric acid also stimulates the proliferation of smooth muscle cells of blood vessels by activation of growth factors, vasoconstrictor and proinflammatory molecules. Thus, uric acid is not only a marker but also an active component of hypertension development.
However, the most important thing is that in the group of patients where the use of thiazide diuretics has led to increased levels of MK, the number of cardiovascular events was 42% higher than in the group of patients who had a marked increase in MK.
The relationship between hyperuricemia (high uric acid) and the risk of cardiovascular disease established in the course of large epidemiological studies. Proven correlation of high levels of uric acid with hypertension, diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and atherosclerosis caused by cardiovascular diseases.
In the study I NHANES (the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey) revealed an independent Association between hyperuricemia and the increase in cardiovascular mortality. With higher levels of MK, the risk of death from ischemic heart disease increased by 77% in men and 300% among women. Increasing the concentration of MK per 1 mg/DL (to 59.5 µmol/l) was associated with a significant increase in mortality both among men and among women. A 12–year study (PIUMA), which was attended by more than 1,500 previously treated patients with arterial hypertensia also demonstrated that the level of uric serum is a strong predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
The study of patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 showed a significant increase in the frequency of the stroke when the rate of uric acid. In this case the relationship remained significant even after the exclusion of other cardiovascular risk factors. Meanwhile, the results of the Framingham study there was no significant relationship between uric acid level and cardiovascular morbidity.
Hyperuricemia was detected in almost 90% of adolescents with newly diagnosed arterial hypertension. The results show that the correction of hiresuite can prevent the development of cardiovascular catastrophes.
So what to do with asymptomatic increase uric acid?
It is shown that not only the crystals Manorama of sodium, but soluble uric acid in the asymptomatic GU can lead to increased levels of inflammatory mediators and to induce the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Many of these "Pro-inflammatory" mediators are fundamental in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic vascular lesions and its complications. Therefore it is necessary to slightly change the meals about this in the next article.
Researchers from the Medical University Johns Hopkins (Baltimore, MD, USA) found that individuals with "high normal" levels of uric acid a volume of hyperintense white matter of the brain is 2.6 times greater than in the population with medium or low level. This confirms the role of uric acid in increased risk of cerebrovascular disease and may explain the Association between elevated uric acid and a slight cognitive deficit in elderly patients. There is an obvious correlation between high levels of uric acid and diseases such as hypertension, type II diabetes and metabolic syndrome. All of these States are known risk factors for the development of dementia.
It is noteworthy that the average level of uric acid in the presence of disorder has erectiepil higher (about 12 mg/DL) than patients with normal sexual function (approximately 5 mg/DL). In the result, it was found that the presence of excessive levels of the substance in the blood increases the risk of erectile dysfunction almost 6 times. And the increase level of uric acid for each 1 mg/DL is accompanied by a renewed increase in the likelihood of disorders of erection.
The positive aspects of the action of uric acid
According to some researchers, the increase in urinary can favorably influence the body. Chemical structure of uric acid is similar to trimethylaluminum xanthine caffeine and is therefore able to improve mental and physical performance. Numerous studies in 1960-70–ies have confirmed that people with hyperuricemia have a higher intelligence and speed of reaction. However, adenosine receptors (which stimulate the caffeine), uric acid is not in effect, in most studies shows a relatively small biological effect, besides the possible influence of socio–economic status of participants.
Another nice feature of MK is its ability to act as antioxidant, blocking superoxide, peroxynitrite, and iron-catalyzed oxidative reactions. A number of authors suggest that increased MC can be one of the key antioxidants of the plasma and to prevent associated with aging oxidative stress, thereby contributing to prolongation of life. Studies have shown that transfusion of uric acid people increases the antioxidant activity of serum and improves endothelial function.
If the uric acid has a negative effect within the Central nervous system it plays a completely different role. Uric acid is known as a powerful neuroprotective agent and an inhibitor of neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. How it works there, there are different opinions. But, in people with hyperuricemia have noted a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases, like Parkinson's disease or Alzheimer's and there is evidence for diffuse sclerosis.
The ability of high levels of uric acid to reduce peroxynitrite–mediated formation of nitrotyrosine evidence of neuroprotective properties, which is especially important in multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, stroke and other neurological diseases. According to epidemiological studies, people with GU is much less likely to suffer from multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, and infusion of uric acid can reduce the neurological manifestations obtained through experimentation (for example, in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis).
High level of urate (uric acid salts) in the blood slows the progression of Parkinson's disease. Normal urate is contained in blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid. These substances are potent antioxidants that protect the body from harmful molecules — free radicals. It was found that participants with the highest urate levels in the blood, the disease developed more slowly.
Recent studies have shown that the beneficial effect of uric acid in these conditions is connected, rather than with her nitrotyrosin–overwhelming antioxidant, with the ability to block blood–brain barrier or the impact on astroglial cells.
The paradox of uric acid.
So, if acute rise in uric acid (uric acid increased) has an antioxidant effect and beneficial effect on endothelial function, chronic hyperuricemia, on the contrary, contributes to the development of oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Perhaps this is due to various intracellular and intravascular effects of acute and chronic hyperuricemia.
Oxidative stress is a main factor of brain damage in patients with ischemic stroke. Uric acid is a potent endogenous antioxidant molecule. In the course of experimental ischemia in rats, the exogenous administration of uric acid has a neuroprotective effect, intravenous urinary kisloid is safe, prevents an early decline in uric acid levels and reduces an early increase in markers of oxidative stress.
The greatest benefits from the use of uric acid had women, patients with moderate-to-large stroke and patients with high content of glucose in the blood. Dr. Chamorro explained this by the fact that these patients may have higher levels of oxidative stress and uric acid is a powerful antioxidant.published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
Materials used:
www.rmj.ru/articles_6234.htm
www.rmj.ru/articles_996.htm
www.mif-ua.com/education/symposium/korrekciya-giperurikemii-kak-faktora-riska-serdechno-sosudistoj-zabolevaemosti-i-smertnosti
Alderman MH: Serum Uric Acid As a Cardiovascular Risk Factor for Heart Disease. Current Hypertension Reports 2001, 3:184-189.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2015/02/blog-post_9.html#more