697
How to overclock the metabolism: the 5 best ways
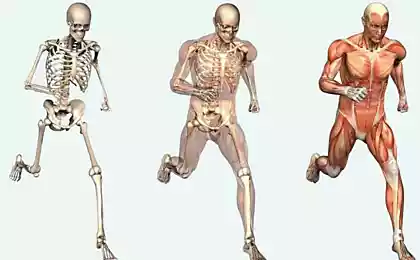
We live in a happy time. Despite all the crises and problems that is talked about in the news, we will definitely live better than our ancestors a hundred thousand and a hundred thousand years ago. We have electricity, gas, water and iPhones. And we have food, lots of quick and affordable meals we take for granted, but actually it was not always so.
Our ancestors lived very differently, remaining long without food. Short moments of fullness after a successful hunt gave way to long days and weeks when I had to feed on roots, berries and other pasture. The bodies of ancient people for millions of years well adapted to this regime and learned how to store energy and then spend it.
In the body of modern man are all of the same mechanisms, although we have long been hunting in the forest, and in the supermarket, and eat several times a day. But the body is still, he continues to live on cave laws and uses any opportunity to stock up on energy. What this means, we all know there is excess weight.
Forty six million one hundred eighty nine thousand three hundred twenty six
How to get rid of excess weight? Two logical ways – move more (wasting energy) and less to eat (to obtain energy). But not so simple – the body does not cheat, it feels great when you start to starve and goes into even more of storing fat. There are "swing" when at first you're on a diet, and then frustrated, and eventually gain even more weight. And, as I see it, the main issue of losing weight now is not just to lose weight, but,how to consistently lose weight until the desired weight for a long time.
One of the answers to this question: learn to control your metabolism.
A bit of science
Metabolism is the process of metabolism in the body. This is a complex process, has many wonderful properties, but in this article we are interested in one thing: metabolic flexibility.
Metabolic flexibility – the ability to switch between two energy sources, glucose (coming from carbohydrates) and fatty acids (coming from fat).
This is how our body uses food as energy:
When we eat, increases blood levels of insulin, the hormone that stimulates cells to get more glucose. Then the mitochondria in cells produce ATP from glucose (the substance that is the source of energy for all processes occurring in the body). If more glucose than the body needs, it needs to be put somewhere.
Some of the glucose stored in the liver and partially in muscle as glycogen is the "quick" inventory, which is used in the case when the body needs a lot of energy in a short period of time. When you run sprints or lift weights, it consumes the glycogen. All the rest is deposited as fat.
Your metabolic flexibility depends on how well your body will dispose of these two sources of energies. And there were no problems until recently.
Three events:
1. The food was affordable. We have no more need for weeks to earn their living, and if we have money, we can afford to eat not only to satisfy hunger, but for fun or for company.
2. Changed the quality of the food. The diet of an ordinary city dweller has become less natural and more processed food, poor in nutrients and contain excess sugar and chemical additives.
3. People have less to move.
All this leads to the fact that the body begins to correctly respond to the incoming food. The more we eat (this is especially true for products containing sugar), the more insulin is produced. Gradually the body gets used to it and considers it normal.This is called insulin resistance: in order to transport glucose into the cells, the concentration of insulin in the blood should be even greater. The body becomes confused, losing the ability to switch from one energy source to another, and the fat that is in the "cave" conditions were stored and spent evenly, begins to accumulate in large quantities, leading to obesity.
More about the terrible consequences of high blood sugar you must know. The cells of the pancreas, which produce insulin, are no longer cope with the load, and this leads to the emergence of type II diabetes. But now it's not about that.
The inability of the body to work with energy sources, in contrast to the metabolic flexibility, is called metabolic water.
How to determine that you have lost a metabolic flexibility?
But there is good news: you can fix everything, even if you are genetically predisposed to metabolic rigidity. A lifestyle change, quantity and time of meal will reset your body.
5 ways to restore metabolic flexibility
Any doctor to boost metabolism will tell you to lose weight and move more. But things are interrelated – how successfully you will lose weight and how intensively to train, and also depends on your metabolism. So here are five specific ways to restore metabolic flexibility.
1.Practice intermittent fasting
About the benefits of fasting for health wrote Paul Bragg, and what kind of quack it was, it works.
Intermittent fasting is when you during the day, eat only within a certain window of time, and all the while starving. This is distinguished from what we are accustomed to understand under "normal" fasting when a person does not eat whole day or more.
There are studies that show that the food in the morning when metabolism is most active, and fasting during the second improve metabolism and promote weight loss.
So, a recent study at the University of Alabama showed that eating between 8:00 to 14:00 with 18-hour fasting contributed to the metabolism much better than a standard diet in which we eat from morning to evening.
Effect of periodic fasting is based on the ability of our body to distribute energy in accordance with diurnal or circadian rhythms. Day and night, the change of hungry and well-fed state the body works in cycles, and its operation is optimal when you are subject to these cycles. Constantly being in the fed state without hunger can be compared to the constant wakefulness without sleep. If fed lasts for weeks and months, it is not surprising that the body starts to act up, and your metabolism will slow down.
So that regular intermittent fasting is a great way to disperse the metabolism.
If you have not had experience periodic starvation, to enter into the process gradually. Let's see how long you can go without eating? Try to start with three hours, gradually increasing the time. And, in order to avoid breakdowns, at first, do not limit yourself to the usual food. Let your brain knows that fasting is temporary, and the next morning you will eat up.
2. Restrict carbohydrates
The fewer carbs you eat, the more the body turns to fat reserves for energy replenishment. It is a fact.
We should not abandon carbohydrates completely, since glucose is the main fuel for our brain. But you can quite afford to abandon processed food with high sugar content of sweets, flour products, carbonated drinks, fruit juices, nectars and sweetened dairy products (yoghurts and curds with additives).
Useful carbohydrate foods, such as vegetables, tend to contain much less carbs than sweets, and the problems with insulin is not create.
3. Eat natural food
Don't remember who said it, but the definition I liked: natural food is what was grown in the ground or walked on the earth.
On the ground, and not in the factory, in a bakery or in the laboratory.
Forty five million seven hundred ninety nine thousand one hundred one
Eat more vegetables. Eat fruits, nuts and berries, but not particularly lean, if you have problems with weight. I myself try to adhere to a vegetarian diet, but if you have no particular problems on this occasion, eat meat, fish and seafood. But not finished products and not works of the chemical industry, which according to the label the number of components with complex names.
In all this the third point in common with the second.
4. Flush the body with antioxidants
Your body is composed of countless molecules. Need more accurate data? OK, you have about a hundred trillion trillion. And Yes, I made a mistake by writing the last word twice.
Now imagine that among this set of molecules encountered defective – oxygen molecules, atoms which lack one or more electrons. These defectives are committed to eliminating injustice, taking away electrons from normal molecules, which it makes, in turn, defective and unstable. Cells comprising such molecules, damage is called oxidative stress. If you don't remember chemistry, you should know that what is happening between molecules reaction called oxidation, and defective molecules – free radicals.
In a normal body's oxidative processes are under supervision. But under adverse conditions – from stress and fatty foods to increased solar activity and radiation – our defense can't cope and reactions get out of control.
Free radicals lead to inflammation, and alteration of metabolism. It is also believed that free radicals can induce various inflammation diseases such as arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis and other heart disease, cataracts and even cancer. But to us now it is important is the effect of free radicals on metabolism and how to cope with them.
To combat free radicals are used antioxidants, or antioxidants. In large quantities they are found in vegetables and greens – e.g. Kale, spinach, peppers, and berries – cranberries, blueberries, plums, blackberries. There are also antioxidants in green tea and cocoa. To add the antioxidants in everyday foods, use spices – turmeric, cinnamon, cloves.
Five million two hundred ninety nine thousand eight hundred thirty three
5. Diversify the exercises
Than more active you are, the more energy you require and the more your body takes from the pending inventory. Here's another tip: get moving, and if you so much move, add variety to your workouts, so the body constantly adapts to the new loads. In addition to the devastation of body fat it will give you a whole bunch of other bonuses. And aerobic exercise directly promote fat oxidation – that is, their use as energy.
Thirty six million one hundred forty one thousand nine hundred eighty six
Sum up:Configure the correct operation of the metabolism and level of metabolic flexibility.
Eat less, move more
And:
Author: Mikhail Soloviev
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © econet
Source: folkextreme.ru/2017/01/kak-razognat-metabolizm-periodicheskoe-golodanie-antioksidanty-i-drugie-sposoby/
Our ancestors lived very differently, remaining long without food. Short moments of fullness after a successful hunt gave way to long days and weeks when I had to feed on roots, berries and other pasture. The bodies of ancient people for millions of years well adapted to this regime and learned how to store energy and then spend it.
In the body of modern man are all of the same mechanisms, although we have long been hunting in the forest, and in the supermarket, and eat several times a day. But the body is still, he continues to live on cave laws and uses any opportunity to stock up on energy. What this means, we all know there is excess weight.
Forty six million one hundred eighty nine thousand three hundred twenty six
How to get rid of excess weight? Two logical ways – move more (wasting energy) and less to eat (to obtain energy). But not so simple – the body does not cheat, it feels great when you start to starve and goes into even more of storing fat. There are "swing" when at first you're on a diet, and then frustrated, and eventually gain even more weight. And, as I see it, the main issue of losing weight now is not just to lose weight, but,how to consistently lose weight until the desired weight for a long time.
One of the answers to this question: learn to control your metabolism.
A bit of science
Metabolism is the process of metabolism in the body. This is a complex process, has many wonderful properties, but in this article we are interested in one thing: metabolic flexibility.
Metabolic flexibility – the ability to switch between two energy sources, glucose (coming from carbohydrates) and fatty acids (coming from fat).
This is how our body uses food as energy:
When we eat, increases blood levels of insulin, the hormone that stimulates cells to get more glucose. Then the mitochondria in cells produce ATP from glucose (the substance that is the source of energy for all processes occurring in the body). If more glucose than the body needs, it needs to be put somewhere.
Some of the glucose stored in the liver and partially in muscle as glycogen is the "quick" inventory, which is used in the case when the body needs a lot of energy in a short period of time. When you run sprints or lift weights, it consumes the glycogen. All the rest is deposited as fat.
Your metabolic flexibility depends on how well your body will dispose of these two sources of energies. And there were no problems until recently.
Three events:
1. The food was affordable. We have no more need for weeks to earn their living, and if we have money, we can afford to eat not only to satisfy hunger, but for fun or for company.
2. Changed the quality of the food. The diet of an ordinary city dweller has become less natural and more processed food, poor in nutrients and contain excess sugar and chemical additives.
3. People have less to move.
All this leads to the fact that the body begins to correctly respond to the incoming food. The more we eat (this is especially true for products containing sugar), the more insulin is produced. Gradually the body gets used to it and considers it normal.This is called insulin resistance: in order to transport glucose into the cells, the concentration of insulin in the blood should be even greater. The body becomes confused, losing the ability to switch from one energy source to another, and the fat that is in the "cave" conditions were stored and spent evenly, begins to accumulate in large quantities, leading to obesity.
More about the terrible consequences of high blood sugar you must know. The cells of the pancreas, which produce insulin, are no longer cope with the load, and this leads to the emergence of type II diabetes. But now it's not about that.
The inability of the body to work with energy sources, in contrast to the metabolic flexibility, is called metabolic water.
How to determine that you have lost a metabolic flexibility?
- You find it hard to spend a few hours without food (well-developed metabolic flexibility is not a day or more).
- After a heavy meal you need to take a NAP.
- If you eat sweets and feel tired.
- You feel tired more often than cheerful.
- You can't follow a diet food restrictions — you can easily break
But there is good news: you can fix everything, even if you are genetically predisposed to metabolic rigidity. A lifestyle change, quantity and time of meal will reset your body.
5 ways to restore metabolic flexibility
Any doctor to boost metabolism will tell you to lose weight and move more. But things are interrelated – how successfully you will lose weight and how intensively to train, and also depends on your metabolism. So here are five specific ways to restore metabolic flexibility.
1.Practice intermittent fasting
About the benefits of fasting for health wrote Paul Bragg, and what kind of quack it was, it works.
Intermittent fasting is when you during the day, eat only within a certain window of time, and all the while starving. This is distinguished from what we are accustomed to understand under "normal" fasting when a person does not eat whole day or more.
There are studies that show that the food in the morning when metabolism is most active, and fasting during the second improve metabolism and promote weight loss.
So, a recent study at the University of Alabama showed that eating between 8:00 to 14:00 with 18-hour fasting contributed to the metabolism much better than a standard diet in which we eat from morning to evening.
Effect of periodic fasting is based on the ability of our body to distribute energy in accordance with diurnal or circadian rhythms. Day and night, the change of hungry and well-fed state the body works in cycles, and its operation is optimal when you are subject to these cycles. Constantly being in the fed state without hunger can be compared to the constant wakefulness without sleep. If fed lasts for weeks and months, it is not surprising that the body starts to act up, and your metabolism will slow down.
So that regular intermittent fasting is a great way to disperse the metabolism.
If you have not had experience periodic starvation, to enter into the process gradually. Let's see how long you can go without eating? Try to start with three hours, gradually increasing the time. And, in order to avoid breakdowns, at first, do not limit yourself to the usual food. Let your brain knows that fasting is temporary, and the next morning you will eat up.
2. Restrict carbohydrates
The fewer carbs you eat, the more the body turns to fat reserves for energy replenishment. It is a fact.
We should not abandon carbohydrates completely, since glucose is the main fuel for our brain. But you can quite afford to abandon processed food with high sugar content of sweets, flour products, carbonated drinks, fruit juices, nectars and sweetened dairy products (yoghurts and curds with additives).
Useful carbohydrate foods, such as vegetables, tend to contain much less carbs than sweets, and the problems with insulin is not create.
3. Eat natural food
Don't remember who said it, but the definition I liked: natural food is what was grown in the ground or walked on the earth.
On the ground, and not in the factory, in a bakery or in the laboratory.
Forty five million seven hundred ninety nine thousand one hundred one
Eat more vegetables. Eat fruits, nuts and berries, but not particularly lean, if you have problems with weight. I myself try to adhere to a vegetarian diet, but if you have no particular problems on this occasion, eat meat, fish and seafood. But not finished products and not works of the chemical industry, which according to the label the number of components with complex names.
In all this the third point in common with the second.
4. Flush the body with antioxidants
Your body is composed of countless molecules. Need more accurate data? OK, you have about a hundred trillion trillion. And Yes, I made a mistake by writing the last word twice.
Now imagine that among this set of molecules encountered defective – oxygen molecules, atoms which lack one or more electrons. These defectives are committed to eliminating injustice, taking away electrons from normal molecules, which it makes, in turn, defective and unstable. Cells comprising such molecules, damage is called oxidative stress. If you don't remember chemistry, you should know that what is happening between molecules reaction called oxidation, and defective molecules – free radicals.
In a normal body's oxidative processes are under supervision. But under adverse conditions – from stress and fatty foods to increased solar activity and radiation – our defense can't cope and reactions get out of control.
Free radicals lead to inflammation, and alteration of metabolism. It is also believed that free radicals can induce various inflammation diseases such as arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis and other heart disease, cataracts and even cancer. But to us now it is important is the effect of free radicals on metabolism and how to cope with them.
To combat free radicals are used antioxidants, or antioxidants. In large quantities they are found in vegetables and greens – e.g. Kale, spinach, peppers, and berries – cranberries, blueberries, plums, blackberries. There are also antioxidants in green tea and cocoa. To add the antioxidants in everyday foods, use spices – turmeric, cinnamon, cloves.
Five million two hundred ninety nine thousand eight hundred thirty three
5. Diversify the exercises
Than more active you are, the more energy you require and the more your body takes from the pending inventory. Here's another tip: get moving, and if you so much move, add variety to your workouts, so the body constantly adapts to the new loads. In addition to the devastation of body fat it will give you a whole bunch of other bonuses. And aerobic exercise directly promote fat oxidation – that is, their use as energy.
Thirty six million one hundred forty one thousand nine hundred eighty six
Sum up:Configure the correct operation of the metabolism and level of metabolic flexibility.
Eat less, move more
And:
- Practice intermittent fasting
- Reduce the amount of carbohydrates in the diet and get rid of unnatural food
- Take antioxidants
- Move more and surprise your body with different load.published
Author: Mikhail Soloviev
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © econet
Source: folkextreme.ru/2017/01/kak-razognat-metabolizm-periodicheskoe-golodanie-antioksidanty-i-drugie-sposoby/