701
Is it possible to wash down a meal
There's this common stereotype: drinking with meals – it means "to extinguish the fire of digestion". Dmitry Pikul with the help of science dealing with this topic.
A little tired of people's desire all the effort to cling to the absurd dogmas, hammered them into the heads of the mass media, miracle nutritionists, fanatics, crooks and other active “mosgosexpertise”.
At this particular moment I'm talking about all the famous unwavering sheldonwh-Ayurvedic dogma that water admitted during or right after meals, dilutes the digestive enzymes and acids and impedes digestion, and thus "dampens digestive fire".

Against the background of available scientific data about human physiology this dogma looks at least ridiculous. Given that many chemical reactions occurring with the participation of digestive enzymes, in fact just the opposite need water. Strictly speaking, consist of water and saliva, and gastric juice, which, with the participation of a number of enzymes and sequential processes break down food for further digestion and absorption in the intestine.
Briefly and as the main conclusion — drink water when you want it: before meal, just after, during, just before eating. Follow a sensible measure, do not pour a liter or more of water, she just will not have time to leave the stomach, but the acidity and digestion is substantially no effect.
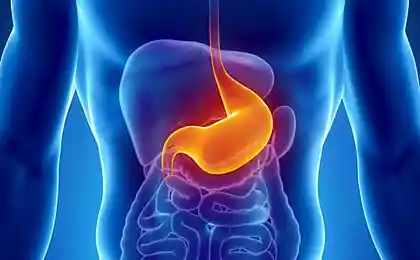
About the physiology of digestion: the stomach
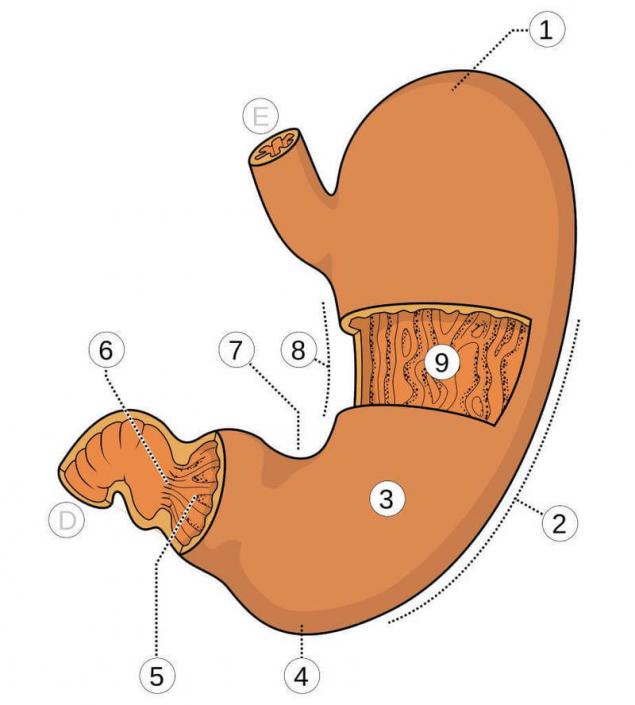
(1) the bottom of the stomach, (2) large curvature, (3) body, (4) lower pole of the stomach, (5) privratnikovym (pyloric) part (6) opening of the pylorus, (7) corner fillets, (8) small curvature (9) of the folds of the mucous membrane.
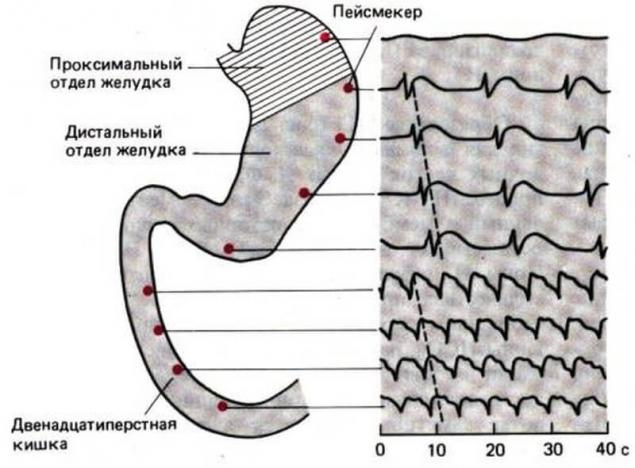
Anatomically the stomach involves several departments — cardiac section of the stomach, gastric fundus, body of stomach pacemaker area, the antral section of the stomach, pylorus, and then begins the duodenum.
Functionally the stomach is divided into proximal (tonic contraction: the function of food storage) and distal (mixing and processing).
In the proximal gastric tone is maintained, depending on the filling of the stomach. The main purpose of the proximal stomach – storage of food submitted to him.
When you receive a portion of food into the stomach relatively hard components are arranged in layers, and fluid and gastric juice flow around the outside and enter the distal stomach. The food is gradually moved towards the pylorus. The fluid is quickly evacuated into the duodenum, and its volume in the stomach decreases exponentially.
Solid food components do not pass through the pylorus until then, until it is crushed to a particle size of not more than 2-3 mm, 90% of the particles exiting the stomach have a diameter of not more than 0.25 mm. When the peristaltic wave reaches the distal portion of the antrum, the pylorus is reduced.
The pyloric division, which forms the narrowest part of the stomach in the place of its connection with the duodenum, closes before the antral Department is fully fenced off from the body of the stomach. The food under pressure moves back into the stomach, while the solid particles RUB against one another and even more crushed.
Gastric emptying is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, intramural nervous plexus and hormones. In the absence of impulses from the vagus nerve (for example, when the interruption) the motility of the stomach is much weaker, and gastric emptying slowed.
Gastric peristalsis is enhanced under the influence of hormones such as cholecystokinin and especially gastrin and is inhibited by secretin, glucagon, VIP, and somatostatin.
Thanks to the free passage of fluid through the pylorus, the speed of evacuation depends mainly on the difference of pressure in the stomach and in the duodenum, and the main regulator is the pressure in the proximal stomach. Evacuation from the stomach of solid food particles depends mainly on the resistance of the pylorus, and, consequently, the size of the particles. In the regulation of gastric emptying in addition to its content, particle size and viscosity of the contents play the role of receptors of the small intestine.
Acidic contents evacuated from the stomach more slowly than neutral hyperosmolar contents slower than Hypo, and lipids (particularly those containing fatty acids with chains of more than 14 carbon atoms) slower than the cleavage products of proteins (except tryptophan). In the regulation of evacuation involves both nervous and hormonal mechanisms, and its inhibition plays a particularly important role secretin.
Can I drink water during a meal, immediately before/ after meal?
There is one important feature of the whole of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is its ability to partially absorb the water and to transport it in the blood.
From the textbook "HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY", edited by R. Schmidt and G. Thews, volume 3.
Water, drink on an empty stomach, is not retained in the proximal stomach, and immediately gets in the distal his Department, where she is quickly evacuated into the duodenum.
The water drunk with food, behaves similarly, i.e. it is not retained in the proximal stomach, distal hits in his Department, and accepted food at this time, remains in the proximal.
What's interesting is that liquid nutrient solutions (containing glucose), taken with food, behave somewhat differently, they just pre-delayed with food in the proximal.
There are quite a lot of research, where studied the rate of movement of various types of liquids from the stomach further along the digestive system. According to them, the water volume to 300 ml leaves the stomach within an average of 5-15 minutes.
Also using MRI, scientists have revealed that the stomach and the small intestine there are so-called "pockets" to store water (their number in the small intestine can reach up to 20 (in the fasted state about 8, in the future their number may increase depending on the number of adopted liquid), they are able to accommodate from 1 to 160 ml of water), the stomach wall has folds, which run along the walls of the stomach from the pylorus to the esophagus to the pylorus of the duodenum.
That is, the water taken while eating does not flow waterfall the esophagus into the stomach, washing away a trail of mucus, gastric juices and enzymes, as you can imagine some, but gradually enters the stomach (distal). So, drunk on an empty stomach with 240 ml of water, in full do to the largest gastric pocket (underneath scientists, in this case, mean distal part of the stomach) only in 2 minutes.
If the water puts out the "digestive fire"?
Go to the pH of the stomach and supposedly exerted on the disastrous effects of water taken along with food.
Water taken during meals (like just before/ after eating) has no significant effect either on the acidity (pH) in the stomach or the work of enzymes in the gastric juice. The stomach is a rather complex mechanism, which in a healthy person, is able to regulate the necessary concentration of gastric juice, and receiving a reasonable number of waters in this period, on the contrary is likely to improve its performance.
The pH value in the gastrointestinal tract is a function of many variables, including the terms of eating, time, volume and content of food, and amount of flow, and varies along the length of the gastrointestinal tract.
People have pH in the stomach in the fasted state is within the range of 1-8, a typical average values 1-2.
After eating the pH in the stomach rises to values of 6.0–7.0, and decreases gradually until pH values the hungry state after about 4 hours, depending on such factors as the composition of food, the amount and individual pH level.
The pH value in the stomach in the fed state varies in the range 2.7–6.4.
Water, adopted on an empty stomach
Water, adopted on an empty stomach, such as may have a minor influence on the pH of gastric juice. In one study, scientists modeled as a hungry stomach, 20 minutes after the introduction of 250 ml of water, the pH was 2.4, after 60 minutes the pH dropped to 1.7.
But we remember that the water in the stomach of a living person does not stay so long, and the specified volume of liquid depending on various factors will be displayed in the duodenum of a maximum of 30 minutes.
There is a considerable amount of scientific research in which the researchers measured the level of stomach acid in patients taking the water either on empty stomach or together with food or before or after surgery. Data from all these studies suggests that stomach pH is not significantly changed as a result of the use of water.
For example, in one research, it was found that the adoption of 2 hours before surgery and 300 ml of water on an empty stomach in patients with obesity do not affect the fluid volume in the stomach and pH levels, as when you drink on an empty stomach, or in combination with food.
Water, taken with food
The very acceptance of food due to the launch of a number of processes (at the stage of anticipation of eating, the visualization of the smell of food emanating reflexes — Hello Professor I. P. Pavlov and his dogs), affect the level of acidity: it grows. And decreases with time.
So, after taking the standard of the food per 1000 kcal, was found to increase the pH to ~5. After 60 min, the pH was about 3, and after 2 hours the pH had dropped to 2 and below.
Conclusion
Water, in fact, is crucial for digestion.
Drink water when you want it: before meal, just after, during, just before eating. Follow a sensible measure, do not pour a liter or more of water, she just will not have time to leave the stomach, but the acidity and digestion is substantially no effect.
If you are thirsty, drink. Thirst is the best indicator that your body requires more water. And, in fact, if you feel good, drinking water food, continue to do so, if you want.
Also interesting: Protiva water — the Secret of centenarians
Alkaline water will help to normalize the acid-alkaline balance of Your body
Water (or any beverage consisting primarily of water) has several functions during a meal:
— improving transport food particles through the esophagus into the stomach;
— help in erosion of large pieces of food;
— using acids and enzymes to gain access to food particles.
Author: Dmitry Pikul
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.zozhnik.ru/mozhno-nuzhno-li-zapivat-edu/
A little tired of people's desire all the effort to cling to the absurd dogmas, hammered them into the heads of the mass media, miracle nutritionists, fanatics, crooks and other active “mosgosexpertise”.
At this particular moment I'm talking about all the famous unwavering sheldonwh-Ayurvedic dogma that water admitted during or right after meals, dilutes the digestive enzymes and acids and impedes digestion, and thus "dampens digestive fire".

Against the background of available scientific data about human physiology this dogma looks at least ridiculous. Given that many chemical reactions occurring with the participation of digestive enzymes, in fact just the opposite need water. Strictly speaking, consist of water and saliva, and gastric juice, which, with the participation of a number of enzymes and sequential processes break down food for further digestion and absorption in the intestine.
Briefly and as the main conclusion — drink water when you want it: before meal, just after, during, just before eating. Follow a sensible measure, do not pour a liter or more of water, she just will not have time to leave the stomach, but the acidity and digestion is substantially no effect.
About the physiology of digestion: the stomach

(1) the bottom of the stomach, (2) large curvature, (3) body, (4) lower pole of the stomach, (5) privratnikovym (pyloric) part (6) opening of the pylorus, (7) corner fillets, (8) small curvature (9) of the folds of the mucous membrane.
Anatomically the stomach involves several departments — cardiac section of the stomach, gastric fundus, body of stomach pacemaker area, the antral section of the stomach, pylorus, and then begins the duodenum.
Functionally the stomach is divided into proximal (tonic contraction: the function of food storage) and distal (mixing and processing).

In the proximal gastric tone is maintained, depending on the filling of the stomach. The main purpose of the proximal stomach – storage of food submitted to him.
When you receive a portion of food into the stomach relatively hard components are arranged in layers, and fluid and gastric juice flow around the outside and enter the distal stomach. The food is gradually moved towards the pylorus. The fluid is quickly evacuated into the duodenum, and its volume in the stomach decreases exponentially.
Solid food components do not pass through the pylorus until then, until it is crushed to a particle size of not more than 2-3 mm, 90% of the particles exiting the stomach have a diameter of not more than 0.25 mm. When the peristaltic wave reaches the distal portion of the antrum, the pylorus is reduced.
The pyloric division, which forms the narrowest part of the stomach in the place of its connection with the duodenum, closes before the antral Department is fully fenced off from the body of the stomach. The food under pressure moves back into the stomach, while the solid particles RUB against one another and even more crushed.
Gastric emptying is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, intramural nervous plexus and hormones. In the absence of impulses from the vagus nerve (for example, when the interruption) the motility of the stomach is much weaker, and gastric emptying slowed.
Gastric peristalsis is enhanced under the influence of hormones such as cholecystokinin and especially gastrin and is inhibited by secretin, glucagon, VIP, and somatostatin.
Thanks to the free passage of fluid through the pylorus, the speed of evacuation depends mainly on the difference of pressure in the stomach and in the duodenum, and the main regulator is the pressure in the proximal stomach. Evacuation from the stomach of solid food particles depends mainly on the resistance of the pylorus, and, consequently, the size of the particles. In the regulation of gastric emptying in addition to its content, particle size and viscosity of the contents play the role of receptors of the small intestine.
Acidic contents evacuated from the stomach more slowly than neutral hyperosmolar contents slower than Hypo, and lipids (particularly those containing fatty acids with chains of more than 14 carbon atoms) slower than the cleavage products of proteins (except tryptophan). In the regulation of evacuation involves both nervous and hormonal mechanisms, and its inhibition plays a particularly important role secretin.
Can I drink water during a meal, immediately before/ after meal?
There is one important feature of the whole of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is its ability to partially absorb the water and to transport it in the blood.

From the textbook "HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY", edited by R. Schmidt and G. Thews, volume 3.
Water, drink on an empty stomach, is not retained in the proximal stomach, and immediately gets in the distal his Department, where she is quickly evacuated into the duodenum.
The water drunk with food, behaves similarly, i.e. it is not retained in the proximal stomach, distal hits in his Department, and accepted food at this time, remains in the proximal.
What's interesting is that liquid nutrient solutions (containing glucose), taken with food, behave somewhat differently, they just pre-delayed with food in the proximal.
There are quite a lot of research, where studied the rate of movement of various types of liquids from the stomach further along the digestive system. According to them, the water volume to 300 ml leaves the stomach within an average of 5-15 minutes.
Also using MRI, scientists have revealed that the stomach and the small intestine there are so-called "pockets" to store water (their number in the small intestine can reach up to 20 (in the fasted state about 8, in the future their number may increase depending on the number of adopted liquid), they are able to accommodate from 1 to 160 ml of water), the stomach wall has folds, which run along the walls of the stomach from the pylorus to the esophagus to the pylorus of the duodenum.
That is, the water taken while eating does not flow waterfall the esophagus into the stomach, washing away a trail of mucus, gastric juices and enzymes, as you can imagine some, but gradually enters the stomach (distal). So, drunk on an empty stomach with 240 ml of water, in full do to the largest gastric pocket (underneath scientists, in this case, mean distal part of the stomach) only in 2 minutes.
If the water puts out the "digestive fire"?
Go to the pH of the stomach and supposedly exerted on the disastrous effects of water taken along with food.
Water taken during meals (like just before/ after eating) has no significant effect either on the acidity (pH) in the stomach or the work of enzymes in the gastric juice. The stomach is a rather complex mechanism, which in a healthy person, is able to regulate the necessary concentration of gastric juice, and receiving a reasonable number of waters in this period, on the contrary is likely to improve its performance.
The pH value in the gastrointestinal tract is a function of many variables, including the terms of eating, time, volume and content of food, and amount of flow, and varies along the length of the gastrointestinal tract.
People have pH in the stomach in the fasted state is within the range of 1-8, a typical average values 1-2.
After eating the pH in the stomach rises to values of 6.0–7.0, and decreases gradually until pH values the hungry state after about 4 hours, depending on such factors as the composition of food, the amount and individual pH level.
The pH value in the stomach in the fed state varies in the range 2.7–6.4.
Water, adopted on an empty stomach
Water, adopted on an empty stomach, such as may have a minor influence on the pH of gastric juice. In one study, scientists modeled as a hungry stomach, 20 minutes after the introduction of 250 ml of water, the pH was 2.4, after 60 minutes the pH dropped to 1.7.
But we remember that the water in the stomach of a living person does not stay so long, and the specified volume of liquid depending on various factors will be displayed in the duodenum of a maximum of 30 minutes.
There is a considerable amount of scientific research in which the researchers measured the level of stomach acid in patients taking the water either on empty stomach or together with food or before or after surgery. Data from all these studies suggests that stomach pH is not significantly changed as a result of the use of water.
For example, in one research, it was found that the adoption of 2 hours before surgery and 300 ml of water on an empty stomach in patients with obesity do not affect the fluid volume in the stomach and pH levels, as when you drink on an empty stomach, or in combination with food.
Water, taken with food
The very acceptance of food due to the launch of a number of processes (at the stage of anticipation of eating, the visualization of the smell of food emanating reflexes — Hello Professor I. P. Pavlov and his dogs), affect the level of acidity: it grows. And decreases with time.
So, after taking the standard of the food per 1000 kcal, was found to increase the pH to ~5. After 60 min, the pH was about 3, and after 2 hours the pH had dropped to 2 and below.
Conclusion
Water, in fact, is crucial for digestion.
Drink water when you want it: before meal, just after, during, just before eating. Follow a sensible measure, do not pour a liter or more of water, she just will not have time to leave the stomach, but the acidity and digestion is substantially no effect.
If you are thirsty, drink. Thirst is the best indicator that your body requires more water. And, in fact, if you feel good, drinking water food, continue to do so, if you want.
Also interesting: Protiva water — the Secret of centenarians
Alkaline water will help to normalize the acid-alkaline balance of Your body
Water (or any beverage consisting primarily of water) has several functions during a meal:
— improving transport food particles through the esophagus into the stomach;
— help in erosion of large pieces of food;
— using acids and enzymes to gain access to food particles.
Author: Dmitry Pikul
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.zozhnik.ru/mozhno-nuzhno-li-zapivat-edu/
Strengthening the banks of the pond: how to build a pond in the garden
Why didn't anybody tell me that in 20?