522
Solar parks help farmers effectively manage land
Ecologists from the University of Lancaster and the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology in the course of the year have been monitoring large solar park near the English town of Swindon. In the study, they found that solar parks have changed the local climate. In summer, the temperature is below the battery panels was lower than in the rest of the territory, by as much as 5 ° C. But the effect varied depending on the time of year and time of day.
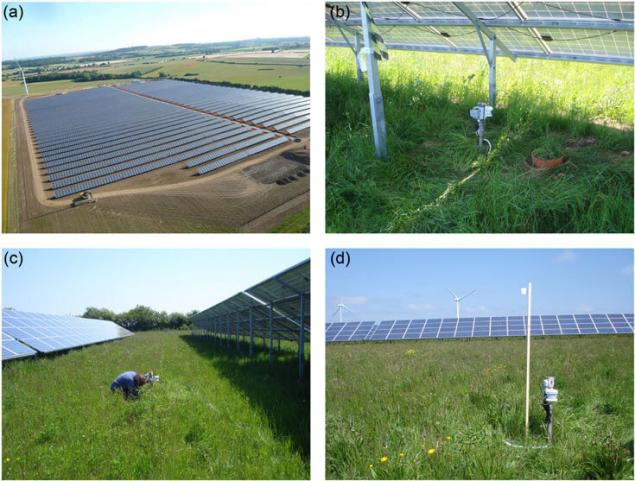

Due to the fact that the climate control biological processes such as the rate of plant growth, it is really important information that can help to understand how to better manage solar parks, to obtain additional environmental benefits in conjunction with the production of energy without the use of carbon.
Rising energy demand and the desire for the development of low-carbon energy sources have caused a rapid increase in ground mounted solar parks around the world. This means a significant change in land use on a global scale and encourages a detailed study of the impact of such parks in the areas under them.
According to Dr. Alon Armstrong from the University of Lancaster, solar parks are gradually becoming a part of our landscape, but no one does not know exactly how they impact on the local environment.

"Solar parks occupy more space per unit of energy compared with traditional sources. This has consequences for the ecosystem and the production of goods, such as agricultural crops, as well as the accumulation of carbon in the soil. But first we did not realize the impact the solar parks have on the environment and ecosystems. »
According to the authors, understanding the climate impact of the use parkovsolnechnyh batteries will give farmers and surveyors knowledge, thanks to which they can more efficiently dispose of the land and to choose what crops to grow, in order to maximize biodiversity and increase yields.
Dr Armstrong added that it can benefit the sunny regions and those suffering from water shortages. Shade under the panels can afford to grow crops that can not tolerate an excess of sunlight. In addition, to reduce the waste of water, can be used to irrigate the fields of water, collected from large surfaces of solar panels.
Article scientists called «Solar park microclimate and vegetation management effects on grassland carbon cycling» was published in the journal Environmental Research Letters.

Due to the fact that the climate control biological processes such as the rate of plant growth, it is really important information that can help to understand how to better manage solar parks, to obtain additional environmental benefits in conjunction with the production of energy without the use of carbon.
Rising energy demand and the desire for the development of low-carbon energy sources have caused a rapid increase in ground mounted solar parks around the world. This means a significant change in land use on a global scale and encourages a detailed study of the impact of such parks in the areas under them.
According to Dr. Alon Armstrong from the University of Lancaster, solar parks are gradually becoming a part of our landscape, but no one does not know exactly how they impact on the local environment.

"Solar parks occupy more space per unit of energy compared with traditional sources. This has consequences for the ecosystem and the production of goods, such as agricultural crops, as well as the accumulation of carbon in the soil. But first we did not realize the impact the solar parks have on the environment and ecosystems. »
According to the authors, understanding the climate impact of the use parkovsolnechnyh batteries will give farmers and surveyors knowledge, thanks to which they can more efficiently dispose of the land and to choose what crops to grow, in order to maximize biodiversity and increase yields.
Dr Armstrong added that it can benefit the sunny regions and those suffering from water shortages. Shade under the panels can afford to grow crops that can not tolerate an excess of sunlight. In addition, to reduce the waste of water, can be used to irrigate the fields of water, collected from large surfaces of solar panels.
Article scientists called «Solar park microclimate and vegetation management effects on grassland carbon cycling» was published in the journal Environmental Research Letters.