642
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN USE vegetable protein in comparison to animal proteins
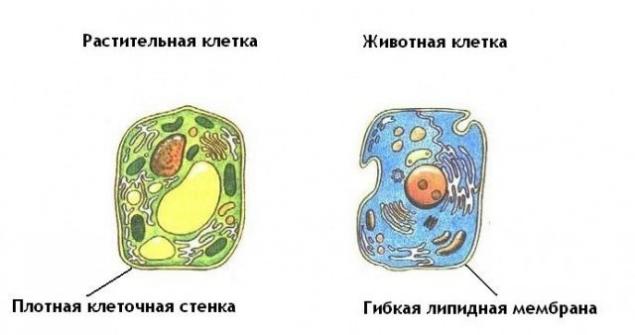
The advantage of the use of high-protein plant foods as compared to an animal is its low bioavailability of proteins. In the human stomach
after chewing food in the remaining cells of animal membrane tissue easily dissolved by digestive juices. Therefore, their contents freely enters a cavity in the gastrointestinal tract, where it is exposed putrefactive microflora. Quite a different situation is with the plant cells, which are surrounded by thick cell wall of cellulose, resistant to digestive juices and enzymes of the human body.
Plant cells into particles of food are not targeted by mechanical destruction during chewing retain part of its contents inside, and with it removed from the body, thereby reducing the bioavailability of nutrients in the food substrate, both human and for its intestinal microflora. Surely raw foodists who consume nuts, noticed after a visit to the toilet in their natural secretions of virtually the whole or pieces of poorly chewed maloizmenёnnye nuts, which are not able to digest in their gastrointestinal tract.
The low bioavailability of plant proteins is that at about the same percentage of protein in the diet from raw foodists compared with adherent thermally processed plant or animal food putrid microflora develops slowly.