724
5 interesting facts about the microbes living within you
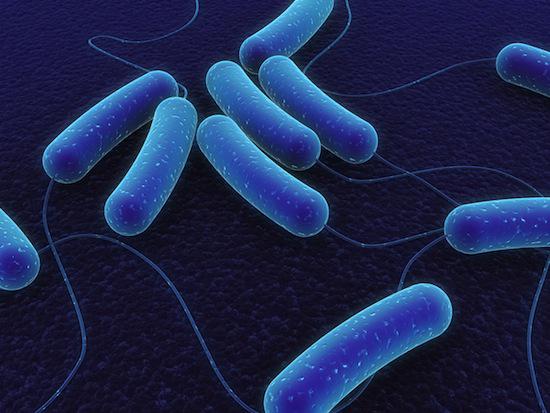
Animals, including man, are home to a broad array of microorganisms and bacteria. Some of these tiny creatures provide functions such as digestion, while others may be to blame for deadly diseases.

Microbiologist Martin Blaser of the School of Medicine at New York University defines the term "microbe" as "the collection of all the microorganisms that live in the human body and interact with each other and with themselves." Some of the inhabitants of the human body, among which there are bacteria, fungi, and various protists exhibit surprising properties. Here are 5 facts about the life within us.
1. The number of germs and bacteria in the body exceeds the number of cells in the body cheloveka
The human body is infested with microbes: according to some sources, bacterial cells within us is about ten times larger than the cells of the body. As stated in an interview with «LiveScience» Martin Blaser: "Of course, no one will consider how much bacteria living in the human, the exact number does not matter, but one thing is clear - the bacteria much more than the cells from which we are made».
The development of bacteria that inhabit our "inner world", occurred throughout human evolution, and is still ongoing. It is expected that in 2013 he completed a large-scale 5-year project for the cataloging and classification of the human microbiome - labored over it hundreds of scientists around the world.
2. People are born without bakteriy

Knowing the important role micro-organisms play in livelihood, you would think that the bacteria are born with man. However, as it turned out, this is not the case according to the Blazers, people are born without the bacteria and acquire them in the first few years of life.
The first "batch" of germs the baby gets when passing through the birth canal of the mother if the baby was born by caesarean section, it does not receive that percentage of microorganisms, which is why he may be at increased risk of some types of allergies, as well as obesity.
Most of the microbiome of the child is formed to three years - a period of intense development of all body systems.
3. One bacterium is able to bring both benefit and vred
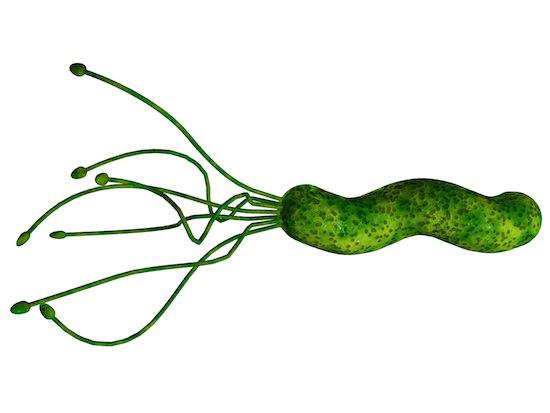
Some microbes cause diseases, others are able to protect them, and sometimes one and the same bacterium may hurt and make a positive impact.
For example, Helicobacter Pylori - once these bacteria were widespread, inhabiting the bodies of almost all people on Earth, but now they are only half of humanity. Most of these bacteria do not cause their "owners" no trouble, but in some cases may contribute to the formation of painful ulcers in the digestive tract (for his work on the effect of Helicobacter Pylori on the occurrence of gastritis and gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer Australian doctor Marshall Barry in 2005 he received the Nobel Prize).
Win a negative impact can be bacteria with antibiotics, but Blaser and his colleagues found that the absence of this organism can cause reflux esophagitis (damage to the mucosa) and even cancer of the esophagus.
Thus, some bacteria can be both useful and deadly.
4. Treatment with antibiotics can trigger asthma and ozhirenie
In 1928, Alexander Fleming invented penicillin, and it was a great breakthrough in medicine. Throughout the world, antibiotics are widely used to combat a wide variety of diseases, however, as shown by recent studies, the use of antibiotics can increase the risk of developing asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, and even obesity. In addition, microbes have learned to adapt to antibiotics: for example, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus can cause serious diseases such as pneumonia or sepsis.
Of course, there are cases where treatment with antibiotics is necessary, but, as stated «LiveScience» Martin Blaser, sometimes should refrain from using them, some children's ear infections or throat can go by themselves.
5. Probiotics are not as good as schitaetsya
In recent years around the world there is a craze probiotic (consisting of micro-organisms) food supplements; many take them after a course of antibiotic treatment, believing that it gives them health. As far as their use is justified?
"The concept of restoration of microflora after antibiotic use is good - says Blazer. - But it is naive to believe that taking probiotics that contain one or more species of microorganisms can be achieved impressive results - we have thousands of varieties in the body! ". Scientists believe that probiotics sellers exaggerate the positive effects of their medications.
"Perhaps in the future we will have probiotics that can overcome the disease, but this is far from - the industry is too young," - sums up the microbiologist.
via factroom.ru
The new theory is that the universe is not expanding, but simply "fat swims"
Plain water improves mental ability