982
Ten inventions named after people
March 26, 1814 died French physician Joseph Ignace Guillotin. It is in honor of this man has been called a known instrument of execution - a guillotine. Guillotin proposed to use it as a temporary and more humane means, but it was used until 1977, when France was held last execution by beheading.
10 photo.
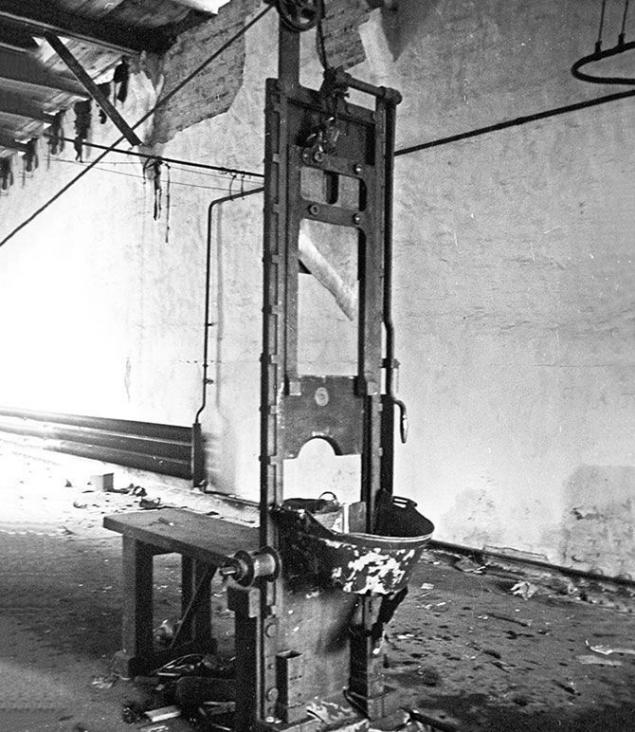

GUILLOTINE
Joseph Guillotin was a physician and a member of the National Assembly (the interim constituent assembly in France). In 1791, in one of the meetings of the Assembly, he proposed that all executions were carried out in one way - by cutting off the head, ie the guillotine. While hardly a guillotine generally someone's invention: the identity of the first person who took advantage of this tool of execution is unknown.
In the old days in France, the method of beheading was considered honorable, they executed mainly the elite of society, all the others awaited burning at the stake, quartering, or hanging.
Thanks to Joseph Gilotenu beheading as the punishment was introduced into the Criminal Code and ceased to be the preferred way to die.
Initially, the guillotine was used instead of the sword. April 25, 1792 was carried out the first execution using the machine, which was proposed for use Guillotin. The guillotine was widely used during the Great French Revolution and later used for a long time in many European countries. Only in 1981 the death penalty was abolished in France, like the guillotine that was used for the execution of the sentence.
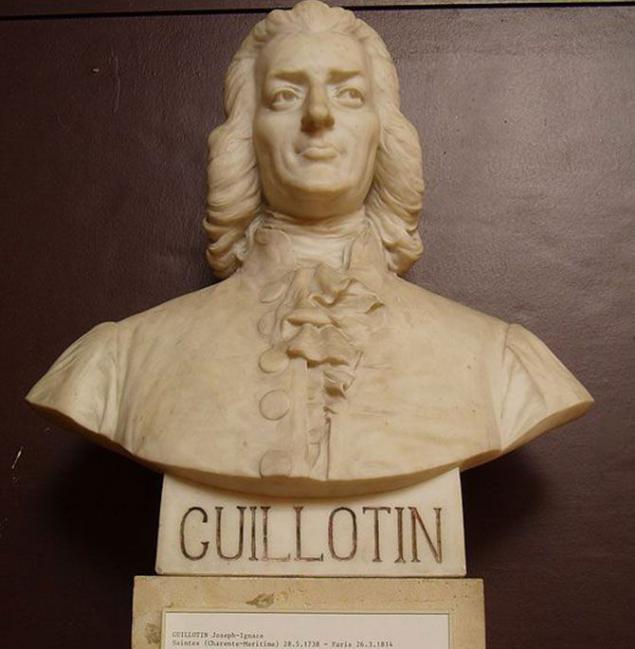

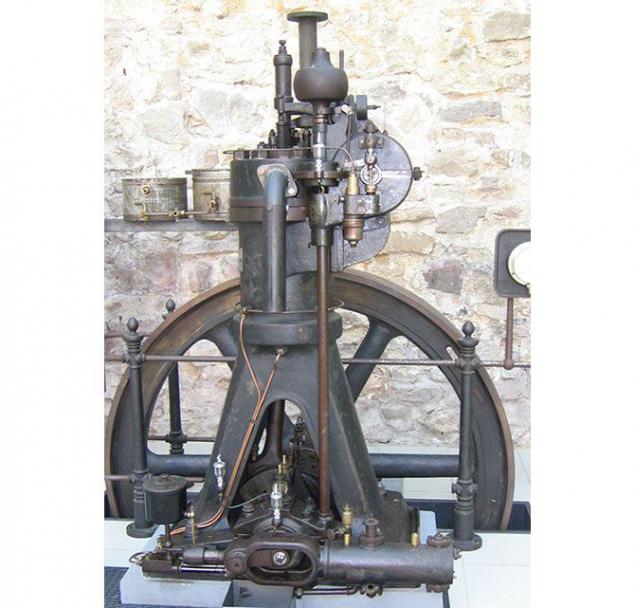
DIESEL
The diesel engine appeared in 1890, when Rudolf Diesel was offered a new type of thermal piston engine. The engine, which is called the inventor of the "diesel engine", it was patented 23 February 1892. In 1897, Rudolf Diesel has tested his engine, they were successful.
Compared with the steam engine, this engine has several advantages: much higher efficiency and lower weight and size. The main fuel of the present invention to serve as a light mineral oil and vegetable oils.
In 1989 the license for diesel engine gained Emmanuel Nobel and was able to adapt the invention for use in the oil. At the Paris World Fair in 1900. Diesel's invention received the Grand Prix. And in St. Petersburg began production of the engines under the leadership of Nobel, and the engine was called "Russian Diesel».
Even today, diesel engines used for the propulsion of locomotives, as well as some cars.

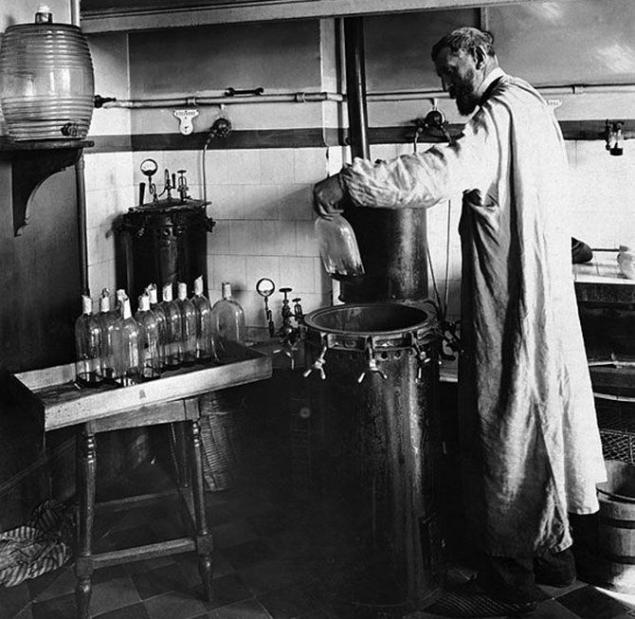
PASTEURIZATION
In the middle of the XIX century, Louis Pasteur proposed the use of a special technology that is used for disinfection products. During the heat treatment, which was a single prompt heating to 60-80 degrees versus time, it ensured also extend the shelf life of the product.
This technology began to wear the name of their inventor - "pasteurization." With this technique destroys bacteria that inhabit in the product, but the spores, from which the bacteria can reappear not die. Therefore products that are subjected to pasteurization, still should be stored at low temperatures.
Now the process of who invented Louis Pasteur, is widely used for the treatment of beer, many types of dairy products and so on. D.

Whatman
In the mid-1750s, James Whatman, Sr., who at the time was the owner of the paper mill, for the first time made the drawing paper. He changed the paper form and was able to produce a sheet of paper on which there was a distinct textured mesh.
His invention named James Whatman wove paper - in a literal translation into Russian sounds like "fabric of paper." Whatman is often used watercolor artists, as it is quite impressive and dense. That is why it is also not subject to abrasion.
In the second half of the XIX century Whatman paper it appeared in Russia, but the name given by its creator, did not stick. The paper came to be called simply the name of the inventor - "Whatman».
First, in our country whatman used for printing of engravings and lithographs, as they do the drawings. Now whatman are widely used by artists all over the world.

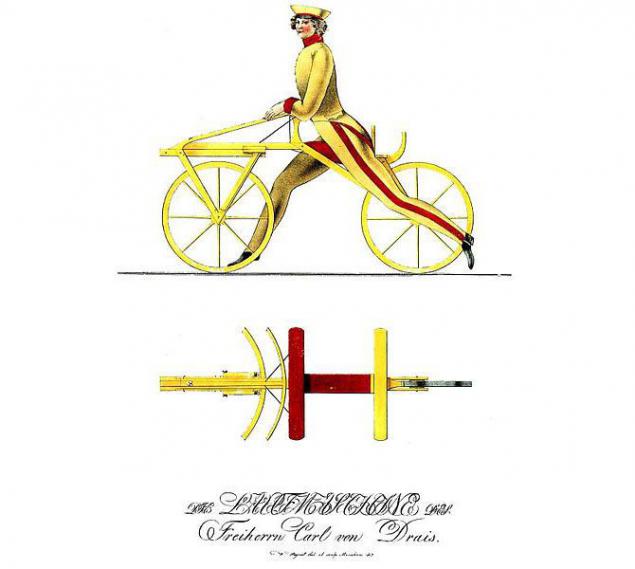
Trolley
In 1817 the German Baron Karl railcars invented the crew, with whom he moved with two wheels. This invention can be considered a prototype of the modern bicycle.
Now called the trolley a special trolley, which moves on rails and transporting railway workers, to inspect the railway track. Currently, the trolley can be coupled to the trains and travel long distances.
In the first trolley use of engines running on the basis of steam engines. In the Soviet Union produced an easy trolley standard TD-5 "Pioneer". Later this name became a household word in all the CIS countries has been used to refer to any home-made devices.
KUHLMAN
The name of the special drawing instrument drawing board, which is used by engineers all over the world, erroneously associated with the name of Karl Kuhlmann. This man was also an engineer, but his main merit is the basis of statistics graphics.
In fact, the first Kuhlman began producing German company Franz Kuhlman. So its name Kuhlman obliged founder and director Franz Kuhlmann.
Kuhlman is a board which is mounted at an angle or vertically. Its use allows us to develop projects in different planes. Before the advent of special computer programs without drawing board does not cost the work of designers, engineers and draftsmen.

ZEPPELIN
Since 1874, Count Zeppelin begins work on aeronautical vehicles. In 1896, he founded the German company "Lyuftshiffbau Zeppelin GmbH". And in July 1900 successfully tested the first aircraft designed by Ferdinand von Zeppelin.
These devices were the most perfect system of rigid airships. They got their name from the inventor - "zeppelins».
Total company count had built more than 100 zeppelins, for their names to apply a combination of letters LZ. These devices are used in military and civilian purposes. By 1914, zeppelins were committed more than 1,500 flights in which it was transported 30 000 passengers.

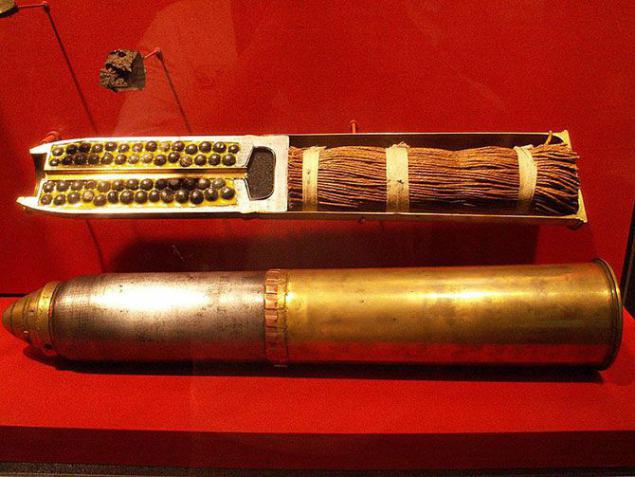
Shrapnel
At the beginning of the XIX century, Henry Shrepnel invented a special artillery charge, it was a ball, which was placed in charge of gunpowder and bullets. The main feature of the new charge was that he had broken off on the approach to the enemy, and thus caused great damage to the enemy's manpower.
Sam Henry Shrepnel was the military and served as a captain. The British Army has adopted a grenade Shrepnela into service in 1803. They were very effective, and almost immediately began to call on the name of the inventor - "shrapnel».
In the same year Henry Shrepnel was promoted to the rank of colonel of the service, and in 1814 he was granted a pension of 1200 pounds, and the rank of general. Who is the principle of the charges of shrapnel built some anti-aircraft missiles.

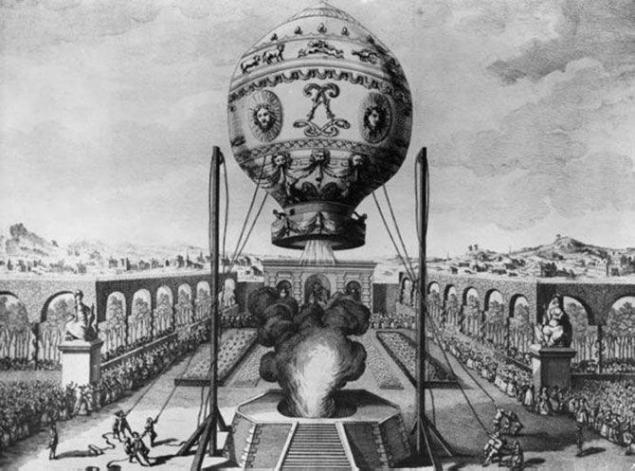
Balloon
Brothers Jean-Etienne and Joseph Michel Montgolfier in 1728 began their experiments to create a flying ball that should have been filled with hydrogen. In the summer of 1783 was a demonstration of the balloon, which lasted ten minutes in the air and climbed to an altitude of 500 meters.
From that moment the aircraft was called "balloon", which quickly came into use in France, and soon all over the world.
In the second half of the XX century there were balloons, as well as solar hot air balloons. Such hot air balloons can fly only in sunny weather and are very popular. At the world famous festivals and various competitions for the balloon, called fiestas. These fiestas can see many large and colorful aircrafts - a spectacle that is truly a delight.
Internet
Source:
10 photo.

GUILLOTINE
Joseph Guillotin was a physician and a member of the National Assembly (the interim constituent assembly in France). In 1791, in one of the meetings of the Assembly, he proposed that all executions were carried out in one way - by cutting off the head, ie the guillotine. While hardly a guillotine generally someone's invention: the identity of the first person who took advantage of this tool of execution is unknown.
In the old days in France, the method of beheading was considered honorable, they executed mainly the elite of society, all the others awaited burning at the stake, quartering, or hanging.
Thanks to Joseph Gilotenu beheading as the punishment was introduced into the Criminal Code and ceased to be the preferred way to die.
Initially, the guillotine was used instead of the sword. April 25, 1792 was carried out the first execution using the machine, which was proposed for use Guillotin. The guillotine was widely used during the Great French Revolution and later used for a long time in many European countries. Only in 1981 the death penalty was abolished in France, like the guillotine that was used for the execution of the sentence.

DIESEL
The diesel engine appeared in 1890, when Rudolf Diesel was offered a new type of thermal piston engine. The engine, which is called the inventor of the "diesel engine", it was patented 23 February 1892. In 1897, Rudolf Diesel has tested his engine, they were successful.
Compared with the steam engine, this engine has several advantages: much higher efficiency and lower weight and size. The main fuel of the present invention to serve as a light mineral oil and vegetable oils.
In 1989 the license for diesel engine gained Emmanuel Nobel and was able to adapt the invention for use in the oil. At the Paris World Fair in 1900. Diesel's invention received the Grand Prix. And in St. Petersburg began production of the engines under the leadership of Nobel, and the engine was called "Russian Diesel».
Even today, diesel engines used for the propulsion of locomotives, as well as some cars.

PASTEURIZATION
In the middle of the XIX century, Louis Pasteur proposed the use of a special technology that is used for disinfection products. During the heat treatment, which was a single prompt heating to 60-80 degrees versus time, it ensured also extend the shelf life of the product.
This technology began to wear the name of their inventor - "pasteurization." With this technique destroys bacteria that inhabit in the product, but the spores, from which the bacteria can reappear not die. Therefore products that are subjected to pasteurization, still should be stored at low temperatures.
Now the process of who invented Louis Pasteur, is widely used for the treatment of beer, many types of dairy products and so on. D.

Whatman
In the mid-1750s, James Whatman, Sr., who at the time was the owner of the paper mill, for the first time made the drawing paper. He changed the paper form and was able to produce a sheet of paper on which there was a distinct textured mesh.
His invention named James Whatman wove paper - in a literal translation into Russian sounds like "fabric of paper." Whatman is often used watercolor artists, as it is quite impressive and dense. That is why it is also not subject to abrasion.
In the second half of the XIX century Whatman paper it appeared in Russia, but the name given by its creator, did not stick. The paper came to be called simply the name of the inventor - "Whatman».
First, in our country whatman used for printing of engravings and lithographs, as they do the drawings. Now whatman are widely used by artists all over the world.

Trolley
In 1817 the German Baron Karl railcars invented the crew, with whom he moved with two wheels. This invention can be considered a prototype of the modern bicycle.
Now called the trolley a special trolley, which moves on rails and transporting railway workers, to inspect the railway track. Currently, the trolley can be coupled to the trains and travel long distances.
In the first trolley use of engines running on the basis of steam engines. In the Soviet Union produced an easy trolley standard TD-5 "Pioneer". Later this name became a household word in all the CIS countries has been used to refer to any home-made devices.

KUHLMAN
The name of the special drawing instrument drawing board, which is used by engineers all over the world, erroneously associated with the name of Karl Kuhlmann. This man was also an engineer, but his main merit is the basis of statistics graphics.
In fact, the first Kuhlman began producing German company Franz Kuhlman. So its name Kuhlman obliged founder and director Franz Kuhlmann.
Kuhlman is a board which is mounted at an angle or vertically. Its use allows us to develop projects in different planes. Before the advent of special computer programs without drawing board does not cost the work of designers, engineers and draftsmen.

ZEPPELIN
Since 1874, Count Zeppelin begins work on aeronautical vehicles. In 1896, he founded the German company "Lyuftshiffbau Zeppelin GmbH". And in July 1900 successfully tested the first aircraft designed by Ferdinand von Zeppelin.
These devices were the most perfect system of rigid airships. They got their name from the inventor - "zeppelins».
Total company count had built more than 100 zeppelins, for their names to apply a combination of letters LZ. These devices are used in military and civilian purposes. By 1914, zeppelins were committed more than 1,500 flights in which it was transported 30 000 passengers.

Shrapnel
At the beginning of the XIX century, Henry Shrepnel invented a special artillery charge, it was a ball, which was placed in charge of gunpowder and bullets. The main feature of the new charge was that he had broken off on the approach to the enemy, and thus caused great damage to the enemy's manpower.
Sam Henry Shrepnel was the military and served as a captain. The British Army has adopted a grenade Shrepnela into service in 1803. They were very effective, and almost immediately began to call on the name of the inventor - "shrapnel».
In the same year Henry Shrepnel was promoted to the rank of colonel of the service, and in 1814 he was granted a pension of 1200 pounds, and the rank of general. Who is the principle of the charges of shrapnel built some anti-aircraft missiles.

Balloon
Brothers Jean-Etienne and Joseph Michel Montgolfier in 1728 began their experiments to create a flying ball that should have been filled with hydrogen. In the summer of 1783 was a demonstration of the balloon, which lasted ten minutes in the air and climbed to an altitude of 500 meters.
From that moment the aircraft was called "balloon", which quickly came into use in France, and soon all over the world.
In the second half of the XX century there were balloons, as well as solar hot air balloons. Such hot air balloons can fly only in sunny weather and are very popular. At the world famous festivals and various competitions for the balloon, called fiestas. These fiestas can see many large and colorful aircrafts - a spectacle that is truly a delight.
Internet

Source:























