1332
What is a Business Plan?
Business planning, feasibility study of the effectiveness of investments - a document without which it makes no sense to start a new venture or a new event in the company. It is a powerful management tool, the key to successful implementation of the project.
The objectives of the business plan may be different. A business plan is needed for:
External use, in order to attract investment. In this case we are talking about the document for a potential investor, obtaining credit.
Internal Use: to substantiate the effectiveness of investment for owners and shareholders.
Business Plan - a document which systematized the main aspects of the intended commercial activities. Development Process B.-P. allows to anticipate potential problems, avoid mistakes in management, identify and assess the two main types of risks present in any business: domestic, over which the entrepreneur as a whole has control (personnel, inventory, location of business) and external (economic conditions, behavior of partners, competitors, new legislation, weather), ie. e. the fact that the employer can not change.
Goals and objectives of business planning:
Description of the source and the desired state of the enterprise and the most effective way to achieve the goal.
Description of the risks of the enterprise, thus avoiding errors already in the planning process.
Evaluation of material and financial resources of the enterprise and their objectives.
Raising funds for business development.
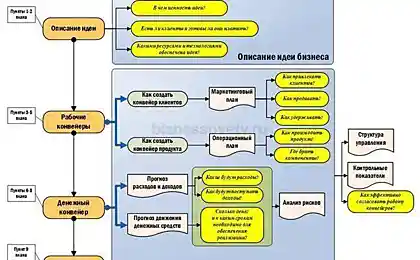
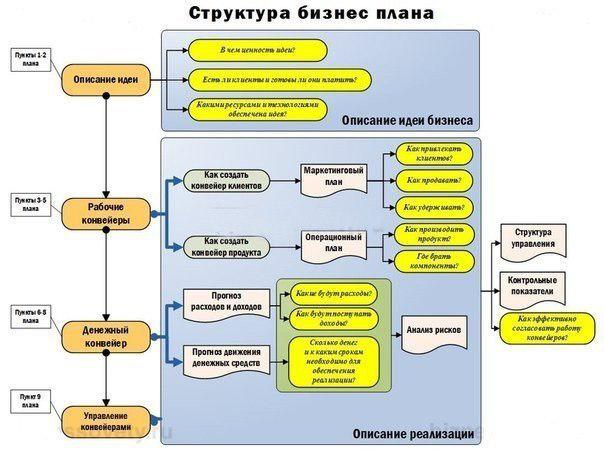
The structure of the business plan and its level of detail depends on the size of the proposed changes in it and the scope of their application, the size of the prospective markets for goods and services, the presence of competitors, investment financing sources.
Despite the differences, in any business plan are the following major sections:
Summary of the project.
Model of the project.
The investment plan.
The operational plan.
Marketing plan.
Organizational plan.
Financial plan.
Analysis of the project.
Applications.
1. Summary of the project.
This is an overview of the business, which makes it possible to understand what the company wants to achieve, what is its potential, how much money will require the project and how much profit it will bring. This section is drawn up after the development of the entire plan. Summary summarizes the forecasts and plans, informed and calculated in the following sections. It's safe to say that the business plan will not be read in full, if not resume interest of potential investors or partners. Must be very lucidly explain the mission (formulated global objective of the company, proceeding from the need to meet the needs of consumers) and the objectives of the enterprise (the projected results of operations).
2. Model project.
Development of the block diagram of the project in the form of the integrated business processes. Implemented as a visual flowchart of trade, financial and information flows, describing the conditions of supply, production and marketing.
As a result, the project proponent should as closely as possible to imagine a project in visual form and to understand how the project will be organized in the business environment and in geographical terms (especially important for the calculation of the logistics supply of raw materials, equipment, products).
For an effective presentation of a model plan to be tied to the location of the production area - location, communication, highways, resource base, etc.
3. Investment Plan.
Development of the investment plan is one of the most important parts of the project. As a result, the project proponent should as closely as possible to imagine that he has to do, at what time, at what cost. Planning is done by constructing a Gantt chart (work schedule indicating the timing of the end-responsible for the stages, the cost of the stages, resources. Depreciation relationship stages). The investment plan is designed to create a model of the project in time (from the start of work to launch the project into operation - operating activities) and the optimal allocation of investment resources.
For a thorough study of the plan should consider the following measures actual project:
Development of design documentation:
Identification of an organization for the development of project documentation.
Determining the cost, scope and timing of the work.
The structure of the business processes.
Statement of the document.
Selection and implementation of software for business process services (accounting, document management, budgeting, CRM *, integrated business management system (ERP) and other.).
Construction work (for new productions) or remedial (for renovation):
Determination of the organization (s), contractor (s).
Value, volume, timing works.
Purchase of equipment:
Supplier (s) of equipment.
Terms of delivery main and auxiliary equipment.
Volumes of purchased equipment, the cost per unit, delivery times.
Into account the specificity of imports (import VAT, duties, transport, conditions INCOTERMS)
Equipment installation, connection to utilities: Commissioning (see. Claim 4.).
Determine the mounting and commissioning organization.
Time, cost, conditions.
Obtaining approvals: Certification (Certification conditions who, cost, time):
A list of organizations matching the design documentation or the execution of works.
Approximate dates of approvals, cost.
Initial marketing program: Development and production of business processes:
Identification of an organization to develop a marketing program,
Development of the initial marketing program (project)
Development of the brand, if you are planning to release new products
The program (advertising, promotions, and other activities in accordance with the project).
Timing, volume of work, the cost of works.
* CRM - Customer Relationship Management.
4. The operational plan.
Under the operational plan of the project refers to activities for the production of products (services). As a result, the project proponent should as closely as possible to imagine the organization of production of certain products (services).
In general, the project should include the following sections:
Description of the range of products or services of the enterprise (name, function, unit of measure, the planned start of sales)
Energy, materials and components for the production of these products or services. (Name, cost per unit, the cost per unit of output, the possible procurement schemes).
Overhead costs of production and sale of products or services (principle of formation, the name, the amount of cost per month or a percentage of)
Plan staff (personnel structure, quantity, salaries, bonus system)
Production plan (piecework wages, semi-specific costs, production schedule)
Sales plan (the price of products or services, the monthly sales volume, possible implementation schemes)
Tax Environment (list of taxes, rates, frequency of payments, special payments)
5.Marketingovy plan.
This is one of the most important sections of the project. On the importance of it can be put before the investment plan. This is understandable - there is no sense to start a project, if the analysis of the market says about his inappropriate. As a result, the project proponent must understand - whether to start a project or not. If there is, how to market that would eventually recoup investment costs, to fulfill all obligations on financing and start getting a steady income.
In general, the marketing plan of the project should include the following sections:
Analysis of the potential market (industry analysis, the structure of the proposed consumer products, market analysis products, competitive analysis, pricing analysis, etc.).
Market entry strategy (program product promotion, brand, advertising campaign, etc.)
The tactics used in sales and market presence (operating budget marketing tools work with consumers, incentive systems customers of attracting new customers, etc.)
6. Organizational plan.
Under the organizational plan means a system of project management (projectmanagement). As a result, the project proponent must imagine - how and by whom will be implemented before the start of the investment project operations. This is a very important section of the project to outside parties - the financier or partners. The fact that funding for the project (if it is not done at their own expense) and not only for a specific business idea, but also a specific project management team.
In general, the organizational plan of the project should include the following sections:
The organizational plan of the project (organizational model of the project, the project participants, their interaction, organizational structure, which will carry out operations)
Enterprise description of the project initiator (historical information, industry activity, prospects, governing bodies)
The project management team (who, education, work experience, qualifications)
Description of the structure and business process management company.
Following the development of the investment and operational plans of the project is calculated demand for project financing (PF).
PF = Investments + Working capital.
Investments are formed in the investment plan. Current assets are automatically calculated in accordance with the terms of the operational plan.
7. Financial Plan.
The financial section of the project is to describe the procedures for funding the investment costs and the formation of working capital. As a result, the project proponent must understand - how, and under what conditions will be financing the project.
Project financial plan should include the following sections:
Economic environment of the project (the refinancing rate, exchange rates, discount rates)
Description of sources of project financing (equity, budget, credit, leasing, private profit, depreciation, other sources).
Financing conditions (period receipt of funds, return policy, terms of service, warranty obligations)
The structure of the distribution of profits.
Exemptions from taxation (if any).
After the calculation model of the project financial viability can be assessed according to the tables:
Cash flows,
Profit and loss account,
Balance,
Financial ratios (for a more sophisticated analysis of the projected financial and economic activity)
Integral Indicators (net present value, payback period, internal rate of return on investment, return on investment index)
8.Analiz project
This section of the project is to analyze the design model by changing the values of the most important parameters of the project. For example: sales, product prices, the price of materials, etc. As a result, the project proponent must understand what will happen with the project in the event of certain events (both positive and negative).
In general, the analysis of the project should include the following sections:
Inflation analysis of the project;
Sensitivity analysis to changes in key parameters (sequential change in each parameter).
Analysis of currency risk (if the project is present currency component)
Break-even analysis.
Analysis of project risks.
What-if (What if?) Analysis. (Multiple changes)
9.Prilozheniya
This section is intended for the project participants (financiers, partners) to prove the feasibility of the project. This section is included any additional information confirming the effectiveness of the project - articles, photos, expert assessments, protocols of intentions, equipment specifications, etc. etc.