189
This information will not allow you to die in an extreme situation!
The modern city dweller is accustomed to a comfortable existence. Progress saved him from the daily struggle for survival. But even in a prosperous civilized time, you cannot be sure that you will be home today.
There are circumstances in which the human body has to mobilize all its resources for survival.
Forewarned means armed. In this article we have brought examples of extreme situations. It is important to understand what happens to the body and how to survive it.
A man in an extreme situation
We listed the most. dangerous and extreme situations, which may be human. It is not always possible to avoid them, but in any situation it is useful to listen to your body and know where and when to stop.
There are circumstances in which the human body has to mobilize all its resources for survival.
Forewarned means armed. In this article we have brought examples of extreme situations. It is important to understand what happens to the body and how to survive it.
A man in an extreme situation
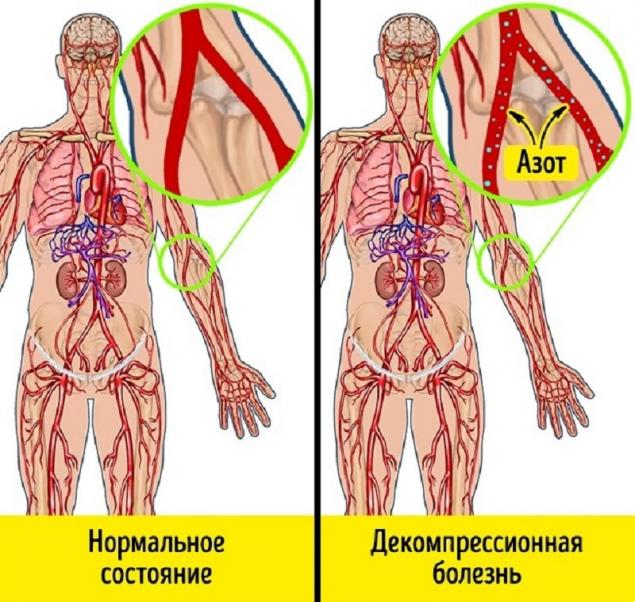
- Pressure differential A sharp decrease in the pressure of the inhaled gas mixture leads to the appearance of decompression sickness. It is encountered by divers during a rapid rise to the surface. As a result, gases dissolved in the blood and tissues of the body begin to be released as bubbles into the victim’s blood and destroy the walls of cells and blood vessels, blocking blood flow. In severe form, decompression sickness can lead to paralysis or death.
- Overloading For every person on Earth there is a load of 1 g. The passenger during the take-off of the aircraft experiences an overload of 1.5 g. When launching a rocket on astronauts, an overload of 3-4 g acts. In pilots, the overload can reach 10 g, which means that the body weight increases by 10 times.
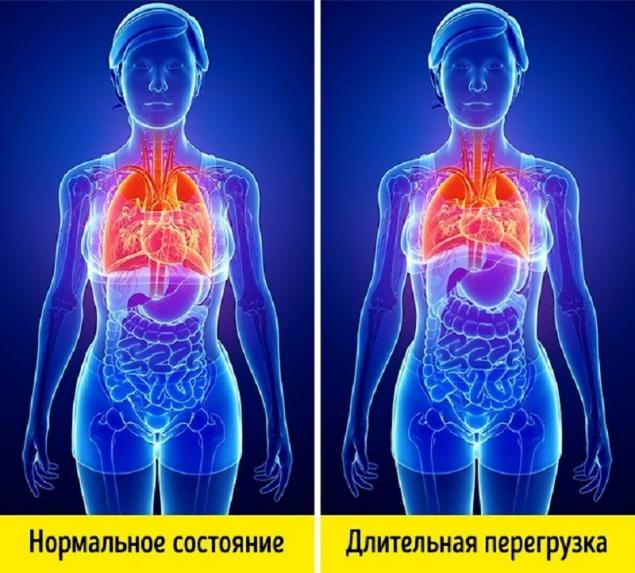
For a person, the direction of overload is very important. If the overload goes from the head to the legs, then with prolonged exposure, all internal organs shift downwards, and if from the legs to the head, then the abdominal organs are pressed against the diaphragm, creating pressure on the heart and lungs.
The most favorable position of the human body, in which he can perceive the greatest overload, lying on his back, facing the direction of acceleration of movement. Astronaut chairs are exactly that.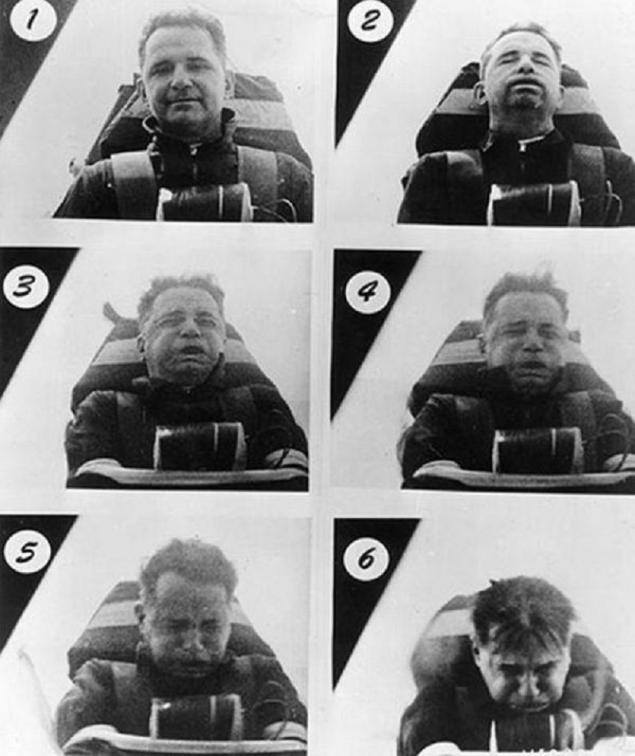
US Air Force officer John Stapp in a special installation with the help of rocket thrust accelerated to 1,017 km / h. During this acceleration, John sustained an overload of 46.2 g. For comparison: in order for a car driver to experience an overload of 46.2 g, he must accelerate to 100 km / h in 0.06 seconds! - Carbon monoxide poisoning This is the main cause of death during fires. At a very high concentration of this gas, death can occur within 1 minute.
Carbon monoxide, or CO, quickly enters the bloodstream. Under its influence, some part of hemoglobin turns into carboxyhemoglobin - a compound that prevents red blood cells from transferring oxygen to the cells and tissues of the body.
Nerve cells are more dependent on oxygen, so CO primarily affects the nervous system, which causes headache, nausea and loss of coordination of movements. - Hypothermia With a long stay in the cold, the body tries to reduce heat loss, because of which the vessels on the surface of the body begin to narrow. This defense mechanism allows us to retain more of the warm blood needed for the internal organs to function.
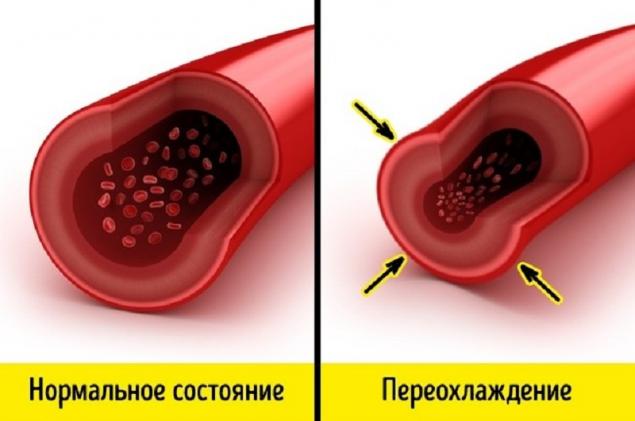
Prolonged exposure to cold causes changes in tissue cells, including due to insufficient blood supply. In particularly severe cases, tissues begin to die.
Contrary to popular belief, it is impossible to drink alcohol in the cold, because it contributes to the expansion of blood vessels, and therefore, an increase in body heat loss. - Sunstroke Long stay under sunlight leads to overheating of not only the skin, but also the surface of the brain due to exposure to infrared radiation. This leads to vasodilation, and later to swelling of the brain, in which there is compression of the brain substance.
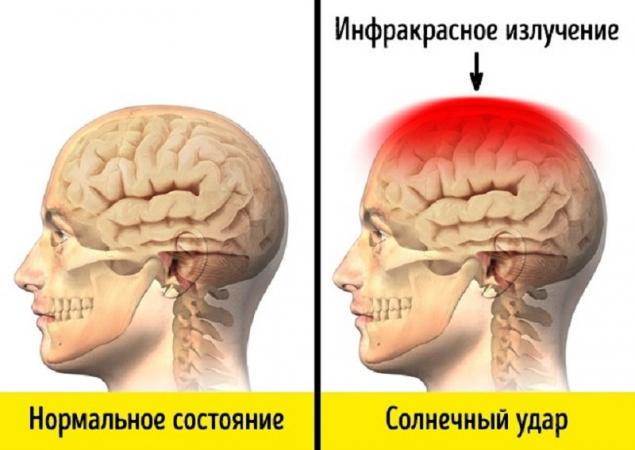
In addition, due to the lack of oxygen, neurons begin to die, which disrupts the work of all body systems. - Altitude sickness Altitude sickness develops due to lack of oxygen in the air and, as a result, in the blood. Being at high altitude, climbers suffer from its variety - mountain sickness, in which hypoxia is aggravated by fatigue, hypothermia and other factors.
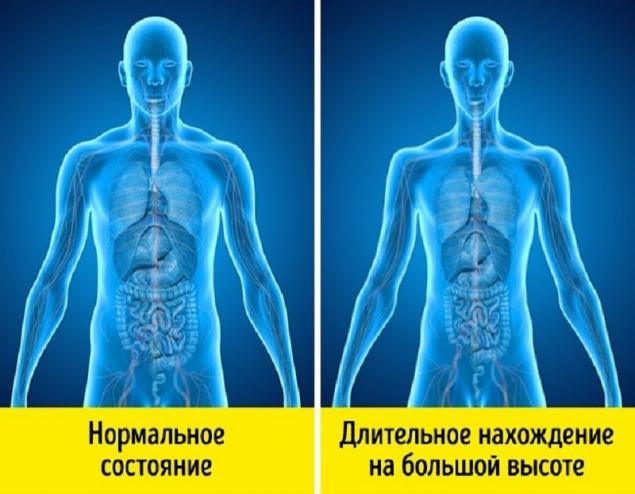
At an altitude of more than 4000 meters above sea level, there is a high probability of pulmonary edema and brain, which can cause death. It is noted that one of the symptoms of mountain sickness is often a violation of consciousness. For example, climbers may resist attempts to save them and rush up or refuse to go down, wanting to stay in the mountains forever. - Hunger. Blood glucose levels begin to decline a few hours after eating. To get the necessary glucose, the body begins to take it from strategic stores stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
Therefore, during fasting, muscles primarily suffer, but the decrease in adipose tissue begins only when the body consumes all stores of glucose. After that, the body is taken for proteins, which leads to the destruction of bones and subsequently leads to a weakening of the immune system.
A resident of Australia Ricky Migi got lost in the desert and for 10 weeks ate leeches and grasshoppers. The result of prolonged fasting can be estimated in the photo.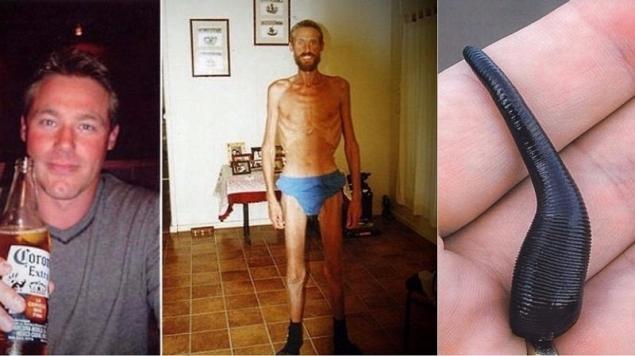
We listed the most. dangerous and extreme situations, which may be human. It is not always possible to avoid them, but in any situation it is useful to listen to your body and know where and when to stop.
Mathematical tricks for worried moms
Poor circulation? To prevent heart attack, stroke and attacks of angina pectoris will help only 1 product.