189
What foods to compensate for the lack of vitamin D
“Walk more in the sun, stock up on vitamin D” – this phrase we hear from parents since childhood. Despite this, doctors note vitamin D deficiency 60-80% of the population of central Russia. Why is this happening?

Among the reasons why the body may lack vitamin D, called insufficient sun exposure, age-related changes in the body, problems with the liver and kidneys, gastrointestinal diseases that lead to impaired absorption of vitamin intestines, and unbalanced nutrition, which we will talk about in more detail.
At the beginning of the last century, trying to find a cure for rickets, scientists found that the necessary bones calcium and phosphorus are not absorbed by the body without a certain substance, later called vitamin D (calciferol). The solution to the problem was fish oil from the liver of cod: it was he who began to give young children as a prevention of rickets.

To date, there is a whole group of biologically active substances, which have the general name vitamin D. Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is synthesized under the action of ultraviolet rays in the skin and enters the human body with food of animal origin. Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) we get only with food (yeast, bread, some types of mushrooms).
As already mentioned, the main task of vitamin D in the body is to regulate the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the blood, thereby ensuring the proper development of the musculoskeletal system, the health of teeth, bones, muscles. Vitamin D deficiency is the cause of fragile bones – osteoporosis. Moreover, women are more susceptible to this disease due to physiological factors.
In addition to strengthening bones, vitamin D is also involved in the full functioning of immunity. One of its most important functions is the production of cathelicidin. It is an antimicrobial peptide that helps the body cope with infections and inflammation.

It is known that vitamin D takes part in the synthesis of dopamine - a neurotransmitter that has a stimulating effect on the body. Its lack affects the mental state of a person and can cause depression, feelings of depression and a feeling of constant fatigue. Especially in autumn and winter, when there is almost no sunlight and it is difficult to get the vitamin naturally.
Poor mood or emotional distress caused by a lack of vitamin D often causes overeating and weight gain. That is why, before choosing a suitable weight loss plan, it is worth checking the level of vitamin D or identifying the reasons that interfere with its absorption.

According to the technical Director of Google and the famous futurist Raymond Kurzweil, today, vitamin D is one of the 3 main anti-aging drugs, which can be freely purchased at any pharmacy.
Intake of vitamin D
Vitamin D content is expressed in international units (ME): 1 ME includes 0.000025 mg (0.025 mg) of chemically pure vitamin D (1 μg = 40 IU). Different countries have different daily requirements for vitamin D. For example, according to the recommendations of the American Institute of Medicine, its daily doses for different ages are the same.
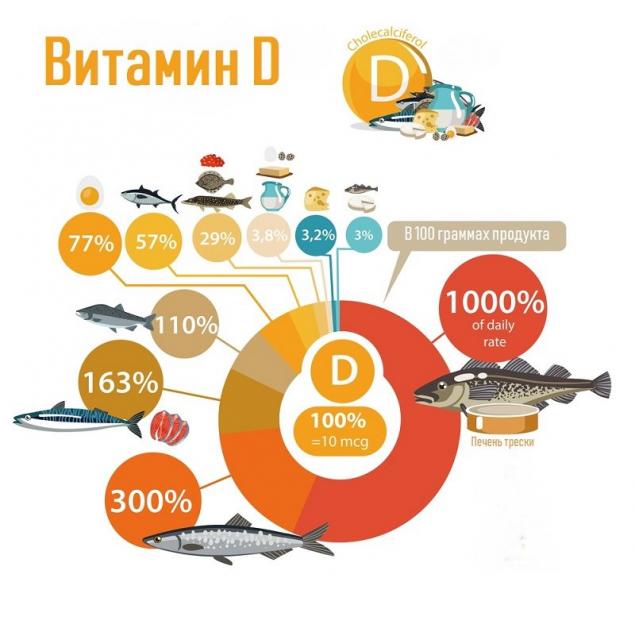

It should be admitted that getting the entire daily norm with food is quite difficult. 600 IU is, for example, more than a kilogram of calf liver, 20 egg yolks or 100-200 grams of salmon. That’s why it’s so important to be in the sun on a regular basis (of course, not forgetting to take precautions).
Foods rich in vitamin D
Vitamin D absorption Each person is different, and the need for it also manifests itself differently. To decide whether to take it additionally, in the form of tablets or injections, it is worth visiting an endocrinologist and taking tests.
There are also contraindications for taking vitamin D: increased calcium levels, hypervitaminosis D, hypercalciuria, urolithiasis, sarcoidosis, acute and chronic kidney disease, kidney failure.
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the causes of osteoporosis. How to recognize osteoporosis before a fracture? What can be done to prevent it? Find the answers in our article.
Hippocrates once said, “Tell me what you eat and I will tell you what you are sick.” To find a good figure and well-being, it is important to choose those products that bring the greatest benefit to the body.
Carbohydrates, which today many consider the cause of excess weight and various diseases, are also an indispensable source of energy for the body."Site" It explains why not all carbohydrates are equally useful and how to recognize those that should be excluded from the diet.

Among the reasons why the body may lack vitamin D, called insufficient sun exposure, age-related changes in the body, problems with the liver and kidneys, gastrointestinal diseases that lead to impaired absorption of vitamin intestines, and unbalanced nutrition, which we will talk about in more detail.
At the beginning of the last century, trying to find a cure for rickets, scientists found that the necessary bones calcium and phosphorus are not absorbed by the body without a certain substance, later called vitamin D (calciferol). The solution to the problem was fish oil from the liver of cod: it was he who began to give young children as a prevention of rickets.

To date, there is a whole group of biologically active substances, which have the general name vitamin D. Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is synthesized under the action of ultraviolet rays in the skin and enters the human body with food of animal origin. Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) we get only with food (yeast, bread, some types of mushrooms).

As already mentioned, the main task of vitamin D in the body is to regulate the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the blood, thereby ensuring the proper development of the musculoskeletal system, the health of teeth, bones, muscles. Vitamin D deficiency is the cause of fragile bones – osteoporosis. Moreover, women are more susceptible to this disease due to physiological factors.
In addition to strengthening bones, vitamin D is also involved in the full functioning of immunity. One of its most important functions is the production of cathelicidin. It is an antimicrobial peptide that helps the body cope with infections and inflammation.

It is known that vitamin D takes part in the synthesis of dopamine - a neurotransmitter that has a stimulating effect on the body. Its lack affects the mental state of a person and can cause depression, feelings of depression and a feeling of constant fatigue. Especially in autumn and winter, when there is almost no sunlight and it is difficult to get the vitamin naturally.
Poor mood or emotional distress caused by a lack of vitamin D often causes overeating and weight gain. That is why, before choosing a suitable weight loss plan, it is worth checking the level of vitamin D or identifying the reasons that interfere with its absorption.

According to the technical Director of Google and the famous futurist Raymond Kurzweil, today, vitamin D is one of the 3 main anti-aging drugs, which can be freely purchased at any pharmacy.
Intake of vitamin D

Vitamin D content is expressed in international units (ME): 1 ME includes 0.000025 mg (0.025 mg) of chemically pure vitamin D (1 μg = 40 IU). Different countries have different daily requirements for vitamin D. For example, according to the recommendations of the American Institute of Medicine, its daily doses for different ages are the same.
- Children under one year - 400 IU, the safest dose - 1000-1500.
- Children under 13 years - 600 IU, the safest dose - 2500-4000.
- Children 14-18 years old - 800 IU, the safest dose is 4000.
- People aged 19-70 years - 600 IU, the safest dose is 4000.
- People 71 years and older - 800 IU, the safest dose - 4000.

It should be admitted that getting the entire daily norm with food is quite difficult. 600 IU is, for example, more than a kilogram of calf liver, 20 egg yolks or 100-200 grams of salmon. That’s why it’s so important to be in the sun on a regular basis (of course, not forgetting to take precautions).
Foods rich in vitamin D
- Fish oil
Fish oil is one of the oldest food additives, or, as we call them today, dietary supplements, which are obtained from sea fish, most often from the liver of cod. It contains both omega-Z and vitamin D, as well as vitamin A, omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids.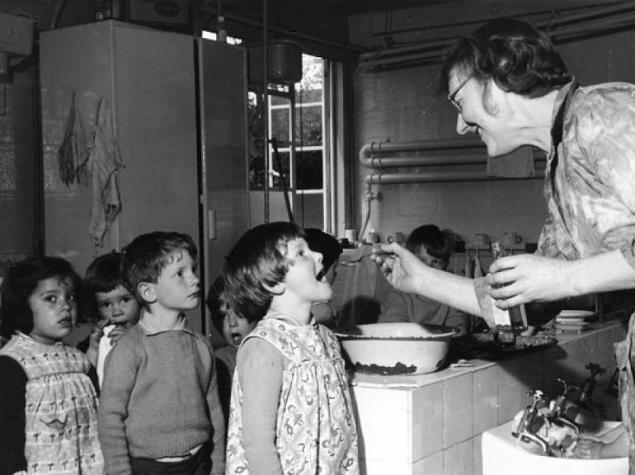
The taste of fish oil is well remembered by everyone who was born in the USSR. At that time, compulsory preventive reception of this tool was introduced in schools and kindergartens. Gelatin capsules were not yet, so the product was consumed in the form of a bitter oily solution with an unpleasant odor.
Today, fish oil is a means of preventing many serious diseases, such as heart attack, stroke, atherosclerosis. It strengthens the immune system, improves brain function, helps to cope with stress and get rid of depression.
In terms of vitamin D, fish oil is unmatched. 100 grams of this supplement contains 10,000 to 16,000 IU, or nearly 30 times the daily norm. - Fat herring
Perceiving herring as an inexpensive snack, most of us do not even realize how useful it is. Meanwhile, for all its budget, it is really one of the most useful fish - no less than expensive salmon, eel or halibut. Surprisingly, herring is useful for the prevention of flu and colds. And all because the herring contains the essential amino acid lysine. It has an antiviral effect, which is especially important in the autumn-winter cold season.
Depending on the cooking method, greasy herring can contain between 600 and 1,200 international units of vitamin D. There is a saying: “A herring on the table is a doctor on the side.”
- Salmonfish
A standard serving of salmon served in restaurants contains up to 700 IU (international units) of vitamin D, slightly above the recommended daily allowance for an adult.
- Cod liver.
Cod is one of the most important commercial fish. Its liver is a source of fish oil and a raw material for the production of canned foods rich in vitamins A and D, as well as omega-3 fatty acids. A hundred-gram portion of canned cod liver contains up to 500 IU of vitamin D.
Interestingly, the two most important vitamins - vitamin A and vitamin D - were isolated for the first time in history from the cod liver! In 1914, American biochemist Elmer McCollum discovered vitamin A in cod liver oil. And in 1922, he proved that the anti-rickets factor contained in cod liver oil is a new, previously unknown vitamin, and called it vitamin D.
- Red caviar
The composition of red caviar contains vitamins A, B, C and D, natural lecithin, folic acid and many minerals. Vitamin D contains 120 IU per 100 grams of product. Much less than fish oil, but the taste is not comparable!
- Beef liver
100 grams of beef liver contains 27% of the daily protein requirement. The liver also contains a lot of minerals (iron, copper, calcium, zinc, sodium, etc.), vitamins (A, B, C, D, B6, B12) and amino acids (tryptophan, lysine, methionine). Vitamin D in beef liver contains up to 50 IU per 100 grams.
- Sour cream, hard cheese
In the spring, during the period of general vitamin deficiency, cheeses can be a real salvation. After all, they contain the entire line of vitamins B, as well as vitamins A, C, D, E, PP. Vitamin D in cheeses contains from 4 IU (ricotta) to 40 IU (cheddar).
- Butter
Butter contains fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K, as well as 20 essential fatty acids. "Sun" vitamin in oil a little - up to 40 IU. Therefore, doctors consider it only as an addition to foods rich in vitamin D. Its high content (60-70 IU) boasts the now forgotten butter. - Chicken eggs
Eggs are the easiest and cheapest source of vitamin D. We often eat them for breakfast and add them to salads, but not everyone knows that they contain a lot of “sunshine” vitamin. The maximum concentration falls on the yolk - about 25 IU (0.625 μg) per 100 grams of product. Interestingly, eggs laid in the summer have a higher concentration of vitamin D.
- Meat.
Unlike the liver, pork and beef clipping contains very little – about 10-15 IU of vitamin D.
Vitamin D absorption Each person is different, and the need for it also manifests itself differently. To decide whether to take it additionally, in the form of tablets or injections, it is worth visiting an endocrinologist and taking tests.
There are also contraindications for taking vitamin D: increased calcium levels, hypervitaminosis D, hypercalciuria, urolithiasis, sarcoidosis, acute and chronic kidney disease, kidney failure.
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the causes of osteoporosis. How to recognize osteoporosis before a fracture? What can be done to prevent it? Find the answers in our article.
Hippocrates once said, “Tell me what you eat and I will tell you what you are sick.” To find a good figure and well-being, it is important to choose those products that bring the greatest benefit to the body.
Carbohydrates, which today many consider the cause of excess weight and various diseases, are also an indispensable source of energy for the body."Site" It explains why not all carbohydrates are equally useful and how to recognize those that should be excluded from the diet.