682
10 major players private sector space race

Today, countries and companies, large and small, looking for a place in the suborbital race, and many analysts believe that it is good. Privatized rockets and space station will open up orbital access to Nations, businesses and even people. With sufficiently large financial resources, they can avoid economic and political risks in developing their own space program and find a niche in the General stream, whether orbital taxi, hotel on the space station or safe shipping.
Meanwhile, NASA uses its resources to start this process. Its commercial initiative for the delivery of crew to orbit supports space ambitions Boeing, SpaceX and Sierra Nevada. These companies gradually reveal their cards.
New space race, this decade could become what became the late 90s and early 2000s for the Internet: a time of uncertainty, ebullient creativity and economic reality eventually. Dozens of companies are working in this direction. Let's briefly go through the main initiatives in space exploration by private forces.
X Prize and other соревнования
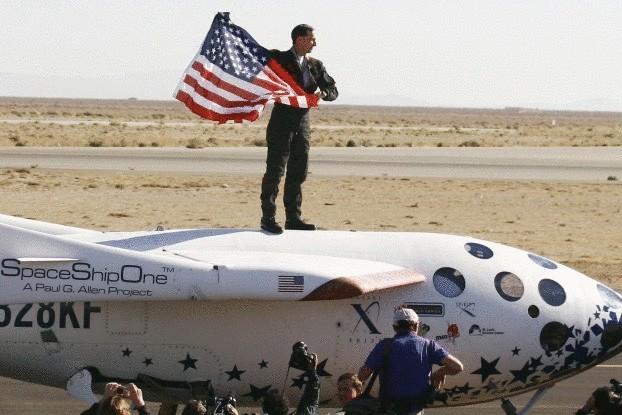

Pilot Brian Binnie celebrates victory in SS1 Ansari X Prize
Sometimes, in order to inspire innovation it is necessary to set bold goals and to promise a bag of money. Here, for example, nonprofit X Prize Foundation announced the award of the Ansari X Prize for space available flights. A reward of $ 10 million gave rise to the commercial development of space at $ 100 million.
Aerospace engineer Burt Rutan and his financial backer, Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen, won the prize in 2004 for creating the first private team to "build and launch a spacecraft capable of carrying three people to 100 kilometers above the Earth's surface, twice within two weeks." Subsequently, Rutan helped Virgin Galactic to develop its passenger space plane.
Examples of other competitions inspiring new space industry, include Centennial Challenges, NASA program that provides from 200 000 to $ 2 million of support to companies in the interests of the Agency and the Heinlein Prize, established in honor of science fiction writer Robert Heinlein, and also encourage activity in the field of commercial space activities.
Meanwhile, the X Prize Foundation continues to stimulate breakthroughs in space and on Earth. Google Lunar X Prize $ 30 million and will receive "the first privately funded team that successfully put a robot on the lunar surface, this robot will be 500 meters on the lunar surface and send images and data to Earth." NASA adds $ 30 million to those robots, which also will meet key objectives.
Bigelow Aerospace
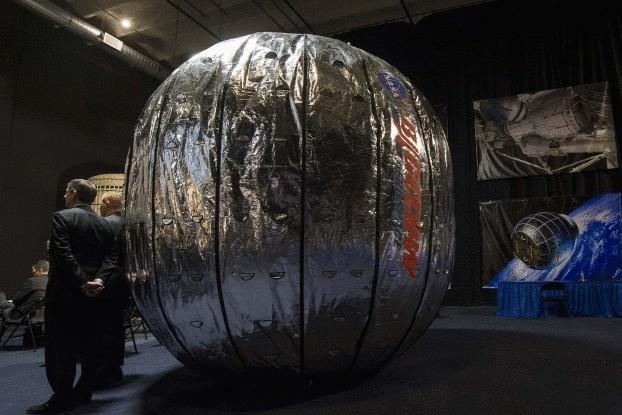

This silver pumpkin can live in space
While Henry Ford of a new space era compete in creating affordable space craft, Robert Bigelow is planning to build a place for passengers in which they can relax: easy private space station.
Lightweight inflatable materials will allow to overcome the limitations of rocket to space. NASA has been developing this idea for many years. Moreover, the idea of an inflatable Bungalow Bigelow was taken from the patented idea of the Agency's TransHab, an inflatable elastic housing for possible use on Mars or on the moon.
In January 2013, NASA signed a contract for 17.8 million dollars from the company for the supply module, the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module, or BEAM, to the International space station. This module is a 4 by 3 meters, 16 cubic meters of volume, was compressed ten times during transport and, unlike solid structures, do not bursting at the seams from impacts of micrometeorites.
Bigelow has already placed such a deserted station in orbit and plans to bring a large enough to accommodate a dozen people, in 2016 — unless, of course, the company can rocket to transport them.
A two-month stay in this Bungalow will cost a person to $ 26 million, including transportation. In any case, it's a little compared to the 70 million dollars that NASA pays for one seat in the spaceship "the Union" for delivery to the ISS.
Money, money, деньги

Heike Dusterhoft just won a trip into space at McDonald's
Rich is not only a target audience to market diamond-encrusted Bluetooth headset for 50 thousand dollars. It is also those who in 1984 bought the first mobile phone Motorola DynaTAC 8000X, weighing 1 kilogram and cost 10-15 thousand dollars. In other words, the cycle of development, improvement, sales, which is beginning to produce cheap and good products often begins with early rasprsivanja money.
At least for now, space tourism is a province for Mitasov. Currently about a dozen private citizens went into space for their own money, and each of them laid out millions of dollars for the Golden ticket to the International space station. However, their determination to use their money on space travel suggests that such a market exists and it is a necessary first step to space flight became finally available for all of us.
Meanwhile, those who have such deep, like a black hole, pockets for the construction of these space dynasties? As you can guess, the super-rich founders and heads of such companies as Microsoft, Amazon, PayPal and Virgin Records. So do not be surprised that can meet familiar names, reading further.
Virgin Galactic
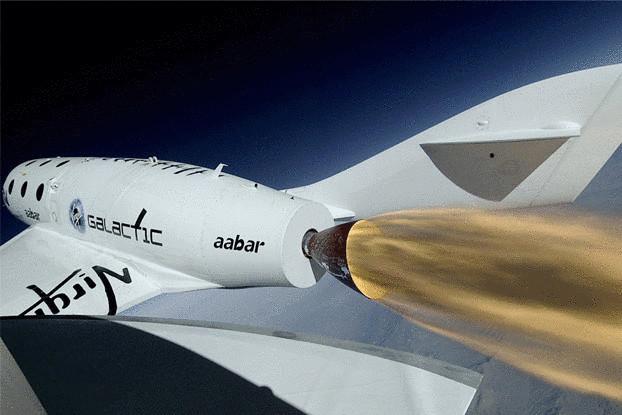

The founder of Virgin Group, Richard Branson, rich is about the same as Donald trump, so it may be little surprise that his Virgin Galactic has become almost synonymous with space tourism. It will be like to fly aboard SpaceShipTwo?
After a 2-3-day training, the travellers sit in SS2, an 18-metre rocket glider for 6 people. This boat with two fuselages with a wingspan of 43 meters will rise to 15 240 m before the release of SS2. SS2 to turn on its rocket engines will go to the border of space in a parabolic flight. After five minutes of weightlessness the plane will begin to plan, slowing down to re-enter the atmosphere at 21 336 meters and then will descend to Earth like a regular plane.
Tests of the SpaceShipTwo are successful. Billionaire Branson says that the first commercial flights will begin, but the place will cost $ 250,000.
Government and space агентства

Not all countries who want to enter the space race, there are deep pockets or the correct policy, therefore, governments have to make do with what they have: the ability to provide private support, gather at the table key stakeholders and to combine brainpower and resources to best effect.
The European space Agency, for example, uses intellectual capital and research institutions from different European countries, invites specialized companies and research groups to create cosmic clusters — collaborations to work on near projects.
NASA is helping private companies, signing a contract with them and a Arsenal of some of their instruments and missiles for rent. In 2008 the U.S. space Agency has signed multibillion-dollar contracts with SpaceX and Orbital Sciences to haul cargo to the International space station and back: 8 flights with Orbital ($1.9 billion) and 12 flights from SpaceX ($1.6 billion). At the moment of the flights have already been successfully completed.
But if you rely on public capital, raises a difficult question: will you continue funding?
Blue Origin
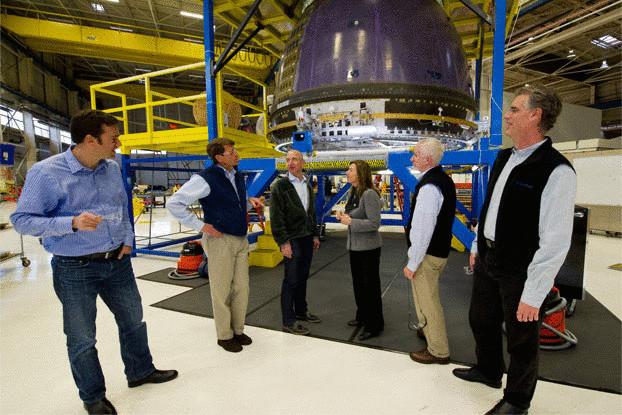

Ever heard the phrase "gradatim ferociter"? If rough, it is translated as "step by step, ferociously".
This is the motto of Blue Origin, a developer of a spacecraft with a vertical takeoff and landing New Shepard: step by step, ferociously and in secret. The company, created by the founder Amazon.com Jeff Bezosa, working mostly behind closed doors, opening them only to check the operation of the prototype. Suborbital transport for astronauts was created based on the old DC-X, developed McDonnell Douglas for NASA and Department of defense.
As quiet as possible, the company whispers NASA to sit and watch. And NASA provides powerful support Blue Origin, along with the Congress.
Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and United Launch Alliance

In any space race, old or new, it would be a mistake to dismiss players like Lockheed Martin and Boeing.
Lockheed Martin, which built each camera sent by NASA to Mars, from Viking to Curiosity Rover and MAVEN spacecraft, which has yet to fly regularly displays new spacecraft into orbit and is developing a capsule Orion for launch SLS, which we recently wrote.
In October 2011, Boeing signed a 15-year lease for the use of the hangar for the space Shuttle at Kennedy Space center to build the spacecraft CST-100. NASA has financed this vehicle for the Commercial Crew Development program at $ 110 million. In addition, Boeing will do the Central stage for the SLS rocket, which has recently been successfully tested and will be, perhaps, the most powerful rocket in the history of space exploration.
Meanwhile, United Launch Alliance, a joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin continues to do the rocket Atlas-V, a platform on which several commercial ventures plan to launch their spacecraft or capsule with the crew.
However, the main question remains whether NASA's financial support to these companies for a long time?
Sierra Nevada Space Systems
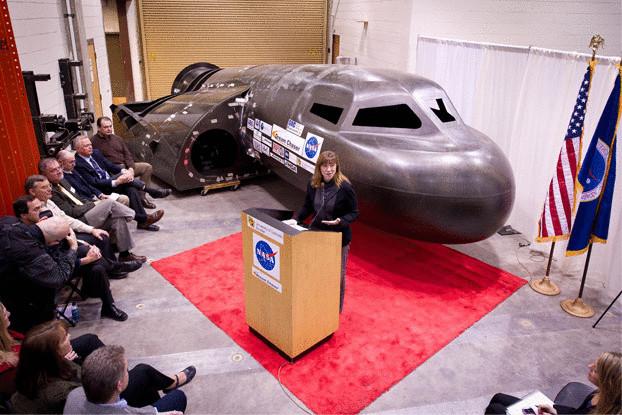

Sierra Nevada Corporation manufactures defense electronics since 1963 and is an American leader in the production of small satellites.
But we'll talk about Dream Chaser, a commercial vehicle, the Sierra Nevada, is scheduled to carry up to seven astronauts and cargo to the International space station and back. The company hopes that the reusable mini-Shuttle that can be launched from earth using rockets and fly like a plane, staked a significant segment of space tourism. While Dream Chaser passes the active test.
To go from small satellites to managed spacecraft, Sierra Nevada put together the "dream team" together with partners from Draper Laboratory, a research center at NASA Langley, Boeing, and United Launch Alliance.
Must be that Sierra Nevada is doing everything right. In 2010, the company assumed $ 20 million of the 50 million of funding for the preliminary development of NASA. In 2011, NASA added another $ 80 million in a second round of funding. Moreover, its hybrid rocket engine that carried SpaceShipOne to win the Ansari X Prize, and also work on SpaceShipTwo in successful supersonic test flights.
SpaceX
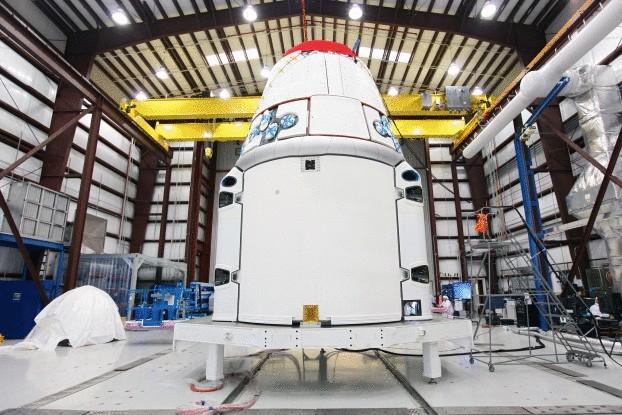

December 8, 2010 Space Exploration Technologies Corporation, or SpaceX, launched the first private ship that returned safely from Earth's orbit. The Dragon capsule that was sent into space atop the Falcon 9 rocket literally made history, but its famous Creator, Elon Musk, is not resting on its laurels. Three years later he made his famous statement that his company was going to send astronauts into space for $ 20 million/seat.
Being a dark horse for a long time, SpaceX surprised everyone. Having signed a contract for $ 1.6 billion cargo delivery to the International space station with NASA, the company set another record, becoming the first private space company, which will deliver an unmanned spacecraft to the ISS. In addition, the company participates in a race with Boeing, Lockheed Martin and other companies for the delivery of the living members of the ISS crew.
Not so long ago as a result of planned overload self-destruct F9R rocket that should launch the first reusable rocket in the history of space exploration.
Orbital Sciences
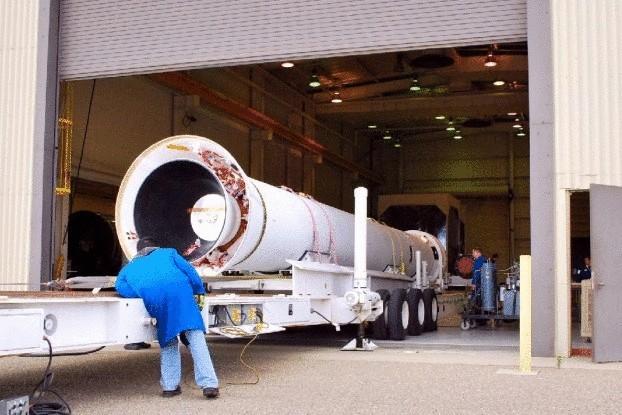

Open space directory Corporation Orbital Sciences of Virginia and you'll find rockets of small and medium class as well as the list of services on launching of orbital satellites, space probes and delivery payloads to great heights. Its customers include commercial, military and civil segments, including NASA, which signed a 1.9 billion dollars contract for eight missions to deliver cargo to the International space station.
Like many other companies in the space race, Orbital Sciences has undergone a series of setbacks: in June 2011 during a ground test, the engine caught fire its staff, and NASA refused to Finance a space ship Prometheus, as a result the company had to abandon the project altogether.
Nevertheless, among the contenders for the new space race, Orbital remains quite strong. She is developing a system abort the launcher for the Orion capsule and remains in a share of future endeavors space Agency. Orbital, a survivor of non-permanent space budgets since 1982, knows how to keep the scales in their favor. This is a good lesson for any bidder who wants to survive and thrive in a new space era.
Source: hi-news.ru