552
Lettuce — surprisingly useful properties
Lettuce is one of the most popular leafy vegetables. Its crisp leaves, which can green combined with dark red, are one of the richest sources of important to maintaining health nutrients. Lettuce refers to a very common herbs, because it finds application not only vegetable salads but also in sandwiches.
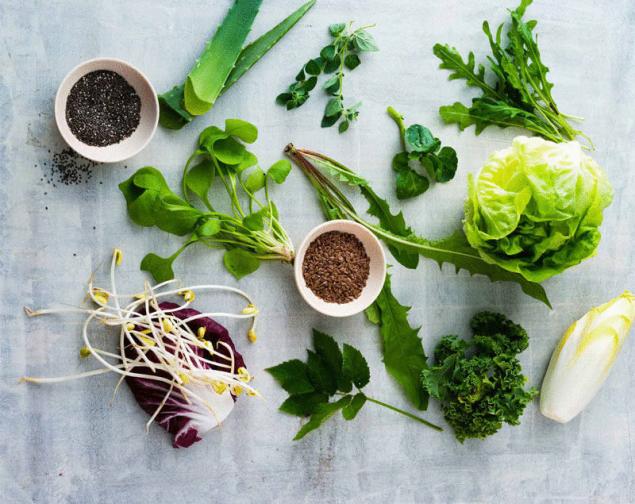

photo: www.jackgreens.com.au
Scientists even found a way vyrashivaniem vegetables on Mars and the moon. Lettuce leaves when they are cutting secrete molokopodobnye liquid. For this reason its name comes from the Latin word "lactuca" — "milk". Botanists attribute this surprising nutrient-rich plant to the Asteraceae family (Asteraceae). Its scientific name is Lactuca sativa.
Many interesting things about the salad-the lettuce, its useful properties and other qualities mentioned in the resource Nutrition And You.
Lactuca sativa — an annual plant of small size, prefers sandy, humus-rich soil. Cultivated six varieties of lettuce, which differ from each other in the form of cabbages and leaf structure. Deciduous varieties with more bitter taste is the most rich in nutrients and antioxidants.
What is lettuce?
Salad buttery lettuce has big heads of cabbage and is characterized by a buttery texture. This type of salad is the most popular and widespread in Europe.
The Chinese variety of "celtuce" is a hybrid of celery and lettuce. Usually has long, thin leaves with a strong flavor, not forming heads, in contrast to Western varieties. This variety has a long stem, which is also used as a vegetable. It is fried in hot oil or extinguish.
Varieties of head lettuce (crisp lettuce, iceberg) has a mild, delicate and fragrant leaves, forming a tuft-head. There are varieties with green and red leaves, and — "Valeria" ("Valeria") and "Lollo Rosso".
Romaine lettuce, or KOs-lettuce grows in a long head, consisting of sturdy leaves with firm ribs, almost reaching the tip of the leaf. Romaine lettuce is the most popular variety of lettuce in the United States.
Summer crisp varieties of lettuce form a head of moderate density flexible texture. This variety is a cross between deciduous and iceberg varieties of lettuce.
Benefits of lettuce for health
The leaves of lettuce are one of the most low-calorie vegetable products. 100 grams of fresh lettuce only contains 15 calories. Despite this, the salad is a real pantry of numerous phytonutrients that help to maintain the body in healthy condition and have the ability to prevent disease.
Lettuce full of vitamins. The fresh leaves are an excellent source of vitamin A and beta-carotene. Just 100 grams of fresh raw lettuce contains 247% of the recommended daily value of vitamin A, and 4443 micrograms of beta-carotene (Carotenes are converted by the body into vitamin A; 2 micrograms of carotene is considered equivalent to 1 international unit of vitamin A). These compounds have antioxidant properties. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy skin and mucous membranes, as well as useful for vision. Consumption of flavonoid-rich natural fruits and vegetables helps prevent lung cancer and oral cavity.
Lettuce is also rich in vitamin K, which presumably plays a role in bone metabolism. It is believed that it increases bone mass, promoting osteotropic activity in the bone tissue cells. It is also known that it plays a role in limiting damage to the neurons of the brain damage in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Fresh salad greens contain appreciable amounts of folic acid and vitamin C. Folic acid is one of the concomitant factors to enzymes in metabolism, necessary for DNA synthesis and thus plays a vital role in the prevention of a defect of the neural tube development of the fetus during pregnancy.
Vitamin C is a powerful natural antioxidant. Regular consumption of vitamin C rich foods helps the body develop resistance to infectious agents and to be cleansed of harmful, contributing to inflammation of free radicals.
Zeaxanthin, which the salad-the lettuce contains 1730 micrograms per 100 grams, is an important dietary carotenoid. It is selectively absorbed by the yellow spot of the retina, and it is believed that there has antioxidant effects and is a filter of ultraviolet rays entering the eye the retina. A diet rich in xanthine and carotenes, is considered to provide some protection against age-related macular degeneration in older people.
The lettuce also contains appreciable amounts of minerals such as iron, calcium, magnesium and potassium which are very essential for metabolism in the body. Potassium is an important component fluids of the cells and organism, helps control heart rate and blood pressure. Manganese is used by the body as a support factor for the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase. Copper is required for production of red blood cells. Iron is essential for their formation.
Lettuce is also rich in B-complex vitamins, including thiamin, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) and Riboflavin.
It is known that a regular addition to salads of lettuce is considered to prevent osteoporosis, iron-deficiency anemia. Many people believe that lettuce provides protection against cardiovascular disease, age-related macular degeneration, Alzheimer's and cancer.
Caution
When growing lettuce are widely used pesticides. The most common pesticides, which can be lettuce, organophosphates, permethrin, and others. Therefore, before eating the salad should be thoroughly washed with cold water. In addition, the salad contains moderate amounts of oxalic acid (0.33 milligrams per 100 grams of fresh leaves), and it is also necessary to take into account.
Nutritional value of lettuce
In parentheses are the percentage of the daily allowance. Nutritional value is based on 100 grams of raw green crispy leaves of lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. crispa) according to information from the Ministry of agriculture of the USA, shown in the resource Nutrition And You.
General information:
energy value 15 kcal (1%);
carbohydrates — 2.79 grams (2%);
protein — 1.36 grams (2%);
fats — 0.15 grams (0.5 per cent);
fiber, part of food is 1.3 grams (3%).
Vitamins:
folic acid (vitamin B9) — 38 micrograms (9,5%);
nicotinic acid (vitamin B3) — 0.375 milligram (2%);
Pantothenic acid — 0,134 milligrams (2,5%);
pyridoxine (vitamin B6) — 0,090 mg (7%);
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is 0.080 milligrams (6%);
thiamine (vitamin B1) — 0,070 milligrams (6%);
vitamin a, which very much is contained in dandelion — 7405 international units (IU, IU) is 247%;
vitamin C — 9.2 mg (15%);
vitamin E — 0.29 mg (2%);
vitamin K, an incredibly rich source of which is sage — 126,3 micrograms (105%);
Electrolytes:
sodium — 28 mg (2%);
potassium 194 mg (4%).
Minerals:
calcium 36 mg (3,5%);
copper — 0.029 milligram (3%);
iron — 0.86 mg (10%);
magnesium — 13 mg (3%);
manganese — 0.250 mg (11%);
phosphorus 29 mg (4%);
zinc — 0.18 mg (1,5%).
Phytonutrients:
beta-carotene (ß-carotene), which is rich in carrots — 4443 micrograms;
beta-cryptoxanthin (ß-cryptoxanthin) — 0 micrograms;
lutein-zeaxanthin — 1730 micrograms. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: hi-news.ru/science/biologiya-salat-latuk-izobiluet-vitaminom-a-i-beta-karotinom.html

photo: www.jackgreens.com.au
Scientists even found a way vyrashivaniem vegetables on Mars and the moon. Lettuce leaves when they are cutting secrete molokopodobnye liquid. For this reason its name comes from the Latin word "lactuca" — "milk". Botanists attribute this surprising nutrient-rich plant to the Asteraceae family (Asteraceae). Its scientific name is Lactuca sativa.
Many interesting things about the salad-the lettuce, its useful properties and other qualities mentioned in the resource Nutrition And You.
Lactuca sativa — an annual plant of small size, prefers sandy, humus-rich soil. Cultivated six varieties of lettuce, which differ from each other in the form of cabbages and leaf structure. Deciduous varieties with more bitter taste is the most rich in nutrients and antioxidants.
What is lettuce?
Salad buttery lettuce has big heads of cabbage and is characterized by a buttery texture. This type of salad is the most popular and widespread in Europe.
The Chinese variety of "celtuce" is a hybrid of celery and lettuce. Usually has long, thin leaves with a strong flavor, not forming heads, in contrast to Western varieties. This variety has a long stem, which is also used as a vegetable. It is fried in hot oil or extinguish.
Varieties of head lettuce (crisp lettuce, iceberg) has a mild, delicate and fragrant leaves, forming a tuft-head. There are varieties with green and red leaves, and — "Valeria" ("Valeria") and "Lollo Rosso".
Romaine lettuce, or KOs-lettuce grows in a long head, consisting of sturdy leaves with firm ribs, almost reaching the tip of the leaf. Romaine lettuce is the most popular variety of lettuce in the United States.
Summer crisp varieties of lettuce form a head of moderate density flexible texture. This variety is a cross between deciduous and iceberg varieties of lettuce.
Benefits of lettuce for health
The leaves of lettuce are one of the most low-calorie vegetable products. 100 grams of fresh lettuce only contains 15 calories. Despite this, the salad is a real pantry of numerous phytonutrients that help to maintain the body in healthy condition and have the ability to prevent disease.
Lettuce full of vitamins. The fresh leaves are an excellent source of vitamin A and beta-carotene. Just 100 grams of fresh raw lettuce contains 247% of the recommended daily value of vitamin A, and 4443 micrograms of beta-carotene (Carotenes are converted by the body into vitamin A; 2 micrograms of carotene is considered equivalent to 1 international unit of vitamin A). These compounds have antioxidant properties. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy skin and mucous membranes, as well as useful for vision. Consumption of flavonoid-rich natural fruits and vegetables helps prevent lung cancer and oral cavity.
Lettuce is also rich in vitamin K, which presumably plays a role in bone metabolism. It is believed that it increases bone mass, promoting osteotropic activity in the bone tissue cells. It is also known that it plays a role in limiting damage to the neurons of the brain damage in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Fresh salad greens contain appreciable amounts of folic acid and vitamin C. Folic acid is one of the concomitant factors to enzymes in metabolism, necessary for DNA synthesis and thus plays a vital role in the prevention of a defect of the neural tube development of the fetus during pregnancy.
Vitamin C is a powerful natural antioxidant. Regular consumption of vitamin C rich foods helps the body develop resistance to infectious agents and to be cleansed of harmful, contributing to inflammation of free radicals.
Zeaxanthin, which the salad-the lettuce contains 1730 micrograms per 100 grams, is an important dietary carotenoid. It is selectively absorbed by the yellow spot of the retina, and it is believed that there has antioxidant effects and is a filter of ultraviolet rays entering the eye the retina. A diet rich in xanthine and carotenes, is considered to provide some protection against age-related macular degeneration in older people.
The lettuce also contains appreciable amounts of minerals such as iron, calcium, magnesium and potassium which are very essential for metabolism in the body. Potassium is an important component fluids of the cells and organism, helps control heart rate and blood pressure. Manganese is used by the body as a support factor for the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase. Copper is required for production of red blood cells. Iron is essential for their formation.
Lettuce is also rich in B-complex vitamins, including thiamin, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) and Riboflavin.
It is known that a regular addition to salads of lettuce is considered to prevent osteoporosis, iron-deficiency anemia. Many people believe that lettuce provides protection against cardiovascular disease, age-related macular degeneration, Alzheimer's and cancer.
Caution
When growing lettuce are widely used pesticides. The most common pesticides, which can be lettuce, organophosphates, permethrin, and others. Therefore, before eating the salad should be thoroughly washed with cold water. In addition, the salad contains moderate amounts of oxalic acid (0.33 milligrams per 100 grams of fresh leaves), and it is also necessary to take into account.
Nutritional value of lettuce
In parentheses are the percentage of the daily allowance. Nutritional value is based on 100 grams of raw green crispy leaves of lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. crispa) according to information from the Ministry of agriculture of the USA, shown in the resource Nutrition And You.
General information:
energy value 15 kcal (1%);
carbohydrates — 2.79 grams (2%);
protein — 1.36 grams (2%);
fats — 0.15 grams (0.5 per cent);
fiber, part of food is 1.3 grams (3%).
Vitamins:
folic acid (vitamin B9) — 38 micrograms (9,5%);
nicotinic acid (vitamin B3) — 0.375 milligram (2%);
Pantothenic acid — 0,134 milligrams (2,5%);
pyridoxine (vitamin B6) — 0,090 mg (7%);
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is 0.080 milligrams (6%);
thiamine (vitamin B1) — 0,070 milligrams (6%);
vitamin a, which very much is contained in dandelion — 7405 international units (IU, IU) is 247%;
vitamin C — 9.2 mg (15%);
vitamin E — 0.29 mg (2%);
vitamin K, an incredibly rich source of which is sage — 126,3 micrograms (105%);
Electrolytes:
sodium — 28 mg (2%);
potassium 194 mg (4%).
Minerals:
calcium 36 mg (3,5%);
copper — 0.029 milligram (3%);
iron — 0.86 mg (10%);
magnesium — 13 mg (3%);
manganese — 0.250 mg (11%);
phosphorus 29 mg (4%);
zinc — 0.18 mg (1,5%).
Phytonutrients:
beta-carotene (ß-carotene), which is rich in carrots — 4443 micrograms;
beta-cryptoxanthin (ß-cryptoxanthin) — 0 micrograms;
lutein-zeaxanthin — 1730 micrograms. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: hi-news.ru/science/biologiya-salat-latuk-izobiluet-vitaminom-a-i-beta-karotinom.html
Amazing house out of the stump of canadian artist Noel Wattana
Loosestrife or Plakun-grass — an ideal plant for any garden