344
What foundation to choose for your home
The editorial office often receives letters-questions about swaying houses, cracked basements or walls and similar problems. The reasons ultimately boil down to errors in the design or construction of the foundation. And this article is an attempt to answer our readers and tell future developers of country houses about the technically competent construction of the supporting part of the house - the foundation.
From heavy materials, the structure or from light, with walls or without, on clay soil or on sandy soil - it will not work without a foundation. Foundations are load-bearing structures that take on loads from overlying walls, floors, stairs, roofs, and transfer them to the ground.
They are different:
- by design - tape, column or plate type;
- The depth of the enclosure is shallow and buried;
- according to the method of implementation - prefabricated, monolithic and mixed.
Soil characteristicsThere are:
- rocky and rocky - they do not change their properties even in severe frosts and therefore are an ideal foundation in themselves;
- Cartilaginous - consist of gravel and fragments of stones and are characterized by high strength. The depth of the foundations on them does not depend on the depth of freezing;
- sandy - freeze weakly, to a slight depth (50-100 cm);
- clay - well retain moisture, so when freezing swell (for what it means, see below). The thickened clay swells less;
- loam and soups - a mixture of sand and clay, depending on which component prevails, the soil behaves either as sand or as clay;
- Peat - drained marsh, with a very high level of groundwater.
At negative temperatures, the water contained in the soil freezes, turning into ice, and noticeably increases in volume. This process, called swelling of the soil, often occurs unevenly, which has a negative and sometimes just fatal effect on the foundation.
The depth of soil freezing is affected by:
soil type: for example, sandy soils freeze to a greater depth than clay soils; climate: the lower the average annual temperature, the deeper the freezing of the soil; groundwater level: the higher it is, the stronger their influence on the foundation during freezing. For each region and soil type, its normative depth of freezing is calculated. For example, in MO it is:
- for clays and loams - 1.35 m;
- for sands and soups – 1.64 m;
- for coarse-grained sands - 1.76 m;
- for large-scale soils - 2 m.
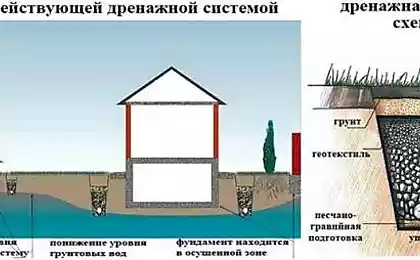
The level of groundwater significantly affects the behavior of the soil. It is good if the depth of freezing is less than the depth of groundwater. If it is more, then as frost increases, it will increase. And when it reaches the groundwater level, they will begin to freeze, the soil will increase in volume and swell.
The flow of soil almost never occurs evenly. The stronger the soil is saturated with water, the stronger it oozes when freezing, affecting the foundation. This can be expressed in pushing the foundation out of the ground in winter and especially in spring and lowering it in summer. The result is a distortion of the foundation, redistribution of loads in it and throughout the structure, the possibility of cracks in the foundation itself and in the walls of the house. And, as a result, the deformation of the foundation up to the destruction of the building.
Therefore, if the level of groundwater is high, and they are captured by the depth of freezing, then you can, regardless of the increase in the cost of construction, choose a reliable version of the foundation or drain the site or lay drainage.
The properties of the soil and the depth of freezing in the building site are immutable. Only the decision to purchase this site can be changed. And if it has not yet been finally adopted, it is worth thinking carefully.
Type of structureThe foundation serves to transfer the weight of the entire structure to the ground. Of course, the load on the foundation from a frame house and a brick cottage with ceilings of concrete slabs is different. The foundation must be different.
Construction on a watered clay site or on sandy soil will also have different features. The desire to make a basement or cellar in a country house will also affect the choice of foundation design. Therefore, each type of building needs its own foundation. But any foundation should be arranged so that its lower part is below the depth of freezing.
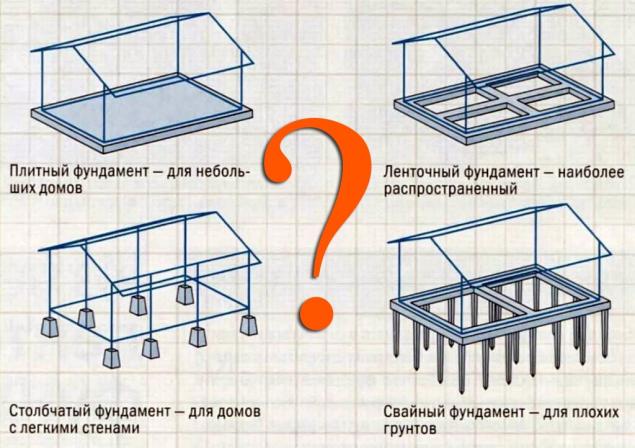
Types of foundation
- Tape foundation
The ribbon foundation is universal: it is laid for houses both from light and heavy building materials on soils with a very different bearing capacity. If the house is planned to arrange a basement or garage, they also need a ribbon foundation. Its thickness depends on the thickness of the walls, the material used, as well as the load from the building.
The technology is quite simple, but time-consuming and requires a large consumption of material.
Tape foundation (LF) is of two types - deep and shallow.
Deep-deep LFOne of the most reliable for houses with heavy walls or ceilings. Here, the entire monolithic "ribbon" is usually laid 20-30 cm below the level of freezing of the soil. This ensures the stability of the structure on almost any soil, at the same time forming the space of the basement or basement floor, cellar or garage, but requires more material consumption.
A shallow-deep version of LFIt has become widespread due to its low cost and is a monolithic reinforced concrete "ribbon" on a sand cushion 20-30 cm thick and a brick superstructure. The depth of the tape is 50-70 cm. A shallow foundation is laid on weakly bulging and non-bulky soils. Sometimes, when installing such a foundation, after 1.5-2 m or more often, grooves in the form of pits are drilled. The depth of the pits is below freezing depth. Such a foundation allows you to build any low-rise building with hollow reinforced concrete slabs of flooring. With good waterproofing inside the perimeter of the foundation, you can arrange a small basement or even a cellar.
Keep in mind: A shallowly buried foundation cannot be laid on a frozen base and left unloaded for the winter. Otherwise, the foundation and soil around it must be temporarily insulated with sawdust, ceramsite or similar materials that can protect the soil from freezing, and waterproofing is applied to the surface of the foundation.
Pillar foundationOne of the most common and cheap options. It is most effective for soils that are not subject to swelling and movements. It is economical, reliable, does not require additional work on waterproofing, but it can not be used in the construction of heavy houses on weak soils: it is applicable only for light houses of frame or wooden type.
The process consists in the construction of pillars at the corners and at the intersection of the walls of the building, as well as under load-bearing and heavy walls, beams and other places with increased load. The distance between the pillars is 1.5-2.5 m.
The columnary foundation is made of stone, brick, concrete, wooden and reinforced concrete pillars, metal and asbestos cement pipes. According to the consumption of materials and labor costs, the columnary foundation is 1.5-2 times, and with deep laying - 3-5 times cheaper than the belt one. Make it easy and fast enough.
However, in horizontally mobile soils, the resistance to tipping of the columnar foundation is insufficient, and to compensate for the lateral shift - the "walking" of the pillars - it is necessary to install an ligation between them. It is located either on the surface of the soil, or with a slight depth, arranging a sand pillow under it. But the dressing device significantly increases the cost and complicates the foundation, although it allows you to build even brick buildings with thick walls on it. In addition, to preserve heat in the underground space and protect it from moisture and dust between the pillars, a “tip” is made – a wall of brick, concrete, etc. 10-20 cm thick, buried in the ground by 10-20 cm. If the soil is bubbly, then a sand pillow of 15-20 cm is arranged under the testicle.
When using a columnar foundation, it is forbidden to link the attached porch, veranda, terrace into a single whole. For these premises, they make their own foundation, that is, the house and attached structures should be separated by a deformation seam, since the load from the porch is incomparable with the load from the walls of the main building, and therefore the sludge will vary greatly.
Plate foundationThis is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab, which is located under the entire area of the house. The slab foundation is advisable to use in the construction of houses on all types of soils and at any depth of groundwater.
This is a good option when the construction is carried out on unevenly and strongly compressed, thick soils, sand pillows. Thanks to its design - a monolithic slab under the entire area of the house - such a foundation is not afraid of any displacement of the soil.
This type of foundation is advisable to use in the construction of brick, wooden or frame houses, in which the plate itself acts as the base of the floor.
The slab foundation device requires a significant amount of earthworks, sand cushion dumping, waterproofing device and a large consumption of concrete and reinforcement, so the total cost of a monolithic foundation slab is quite high.
For the construction of PF there are only 2 restrictions:
The site should not have a strong slope, because the pillow will slowly slide; it is difficult to arrange a basement and cellar. If the basement is still needed, they do the following:
Dig the pit to the required depth. At the bottom of the pit, a pillow of sand and rubble is arranged and a monolithic plate is cast. On the stove is erected from blocks or monolithic concrete wall basement. On the outside, the walls are thoroughly waterproofed. Then the space between the walls of the basement and the walls of the pit is filled (sometimes with the device of a clay water lock). This method is the most expensive, since it requires a large volume of earth, concrete, and installation work. But in the end, you will have almost a ready basement.
Screw foundationThe foundation on screw piles is a good option if the house is built:
- in areas with high groundwater levels,
- on the shaky, unstable soils,
- in areas with complex landscapes.
The foundations on screw piles are reliable and economical. They do not require the leveling of the site, earthworks and the use of heavy construction equipment. Construction can be carried out on mobile, watered soils, on slopes and near large trees. If the house is wooden or frame, then the foundation can be laid in a few days.
Properly constructed foundation solves many construction problems. Therefore, if there are already residential buildings near the planned construction site, it is worth asking the owners what foundation they chose and why, and also find out if there are any problems with it - in short, take advantage of someone else's experience.
The choice of the foundation should be approached carefully also because the cost of the device of a particular type of foundation differ not even several times, but tens of times.
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consciousness – together we change the world!
Join us on Facebook, VKontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: www.7dach.ru
Hybrid solar battery generates electricity due to heat and light
Apple will release an electric car by 2019