301
Proper device of drainage system
The drainage system protects the foundation from the negative effects of the hydrostatic pressure of groundwater, which reduces the risk of its entry into the cap. Also, the drainage system protects the area from flooding, waterlogging or waterlogging.
If you neglect the device of the drainage system, it can lead to a decrease in the service life of the foundation due to its excessive moisture and the emergence of destructive forces of frost bloating.

Recommendations of MosComArchitecture "Guidelines for the design and arrangement of drainages, 2000".
The device of the drainage system is mandatory in cases of location:
It is not necessary to arrange the system if the site is dry and the level of groundwater during the flood and heavy precipitation does not reach critical levels.
For a preliminary assessment of the groundwater level at the site, the following method can be used: If the site or neighbors have a well, then UGV can be determined by the level of water in the well rings. It is best to do this in late July or early August. The closer the water is to the surface of the earth, the higher the groundwater level.
UGV can also be estimated by the level of water cut in a lake or river (if they are near the site).It should be remembered that the wetted area significantly complicates or makes it impossible to carry out landscape and landscaping.
Many plants cannot grow on wet soil. For example, apple trees do not tolerate excess water. In trees and shrubs, due to the lack of oxygen, rotting of the root system may begin.
Thus, in the case of high UGV and in the absence of drainage, the number of plant species, shrubs and trees that can grow and bear fruit in the garden plot is significantly reduced.
In addition, if you start to engage in the device of the drainage system after the house is built, garden paths are laid and the lawn is planted, then you will have to carry out the whole complex of earthworks on the already equipped territory, which will lead to damage to the landscape and additional monetary costs.
Although wetlands and clearly moistened areas are visible to the naked eye, it is not worth choosing methods of drainage and drainage for indirect reasons. The full picture can give only hydrogeological study of the soil on the site.
Why is hydrogeological research done?
Different types of soils have different characteristics that can significantly affect the choice of drainage system and its path. It should also be borne in mind that the groundwater level in the neighboring area may differ from the ground in the area where the foundation and drainage system are planned. Therefore, it is better to solve this issue not by eye, but by resorting to hydrogeological research.
This event will determine:
1. Performing drilling operations.
2. Groundwater level measurements.
3. Soil and water sampling.
4. Laboratory definitions of the physical characteristics of soils, including the determination of the filtration properties of soils.
Analysis of the results of the survey will allow you to choose the optimal foundation design and type of drainage system.
Types of drainage systems
Errors in the design and construction of the drainage system can occur several years after the start of its operation. Therefore, the device of the drainage system begins with its design, and first you need to understand the main types of drainage.
Drainage is divided into local and general. Local drainage is used to protect against groundwater flooding of the foundation and basement, general - to protect the site.
The following types of drainage can be distinguished:
The plastic drainage system protects the structure from both groundwater flooding and capillary moisture moisture. Plast drainage is widely used in the construction of underground structures erected on poorly permeable soils, as well as in the presence of a powerful aquifer under the foundation. To protect basements and structures in which, according to operating conditions, the appearance of dampness is not allowed, when these rooms are located in the zone of capillary soil moisture, reservoir drainage should be arranged.
Ring drainage (most often these are tubular drains) is located along the contour of the protected building or its section. The effect of ring drainage is based on lowering the level of groundwater inside the protected circuit, which provides protection against flooding of underground structures and buried parts of buildings. The depth of this decrease depends on the burying of pipes, galleries or filter part of wells relative to the level of groundwater, as well as on the size of the protected circuit. Ring drains are located at some distance from the structure, so they can be installed after its construction. In this respect, ring drainage is advantageously different from formation, which can be arranged only simultaneously with the construction of the structure.
Wall drainage consists of drainage wall structures (sprinkled, glued, installed) and tubular drains laid on the outside of the structure and serving simultaneously collecting and draining drainage water pipeline.
Wall drainage is used both independently and in conjunction with other types of drainage.
How to protect the basement from flooding?
If the site has a high level of groundwater, then even at the stage of digging the pit under the foundation it will be flooded with water. This can seriously affect the quality and speed of work. Therefore, it is necessary to provide in advance for measures to divert water.
It is necessary to clearly understand that there is a normal drainage of the foundation, for example, MZLF. In this case, we protect the foundation from the harmful effects of groundwater and reduce the risk of frost bloating forces. And there is a set of measures to protect against flooding of basement and basement premises.
The risk of flooding exists when installing basements in clay and loamy soils and with a difference of UGV marks and basement floor marks (basement) less than 0.5 meters. In these cases, the drainage device is required.
The foundation drainage device allows:
If the flooding of the ground floor has already begun, the following measures should be taken:
1. First, it is necessary to understand and assess the extent of flooding. The further work plan depends on this. If the leak appeared somewhere locally, then you can use special hydrophobic compounds with an injectable injection system.
2. If the flooding began throughout the ground floor, then without drainage, the device of pits and additional measures for waterproofing the basement can not do.
How is the area drained?
One of the technologies of the drainage system is as follows:
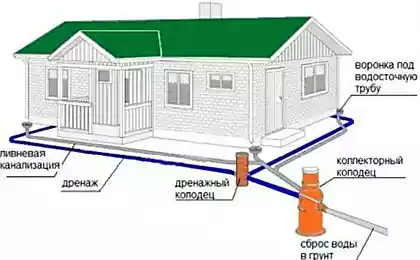
1. Along the perimeter of the building, around which it is necessary to arrange drainage, a trench is dug and the necessary slope necessary for natural water flow is maintained.
According to standards, it is necessary to withstand a slope of 1 cm per 1 p / meter.
2. The bottom of the trench is tamped and filled with river sand with a layer of 10 cm, withstanding a given slope.
3. The trench is lined with geotextile. This is necessary to separate the layers and prevent silting of rubble.
4. Granite crushed stone is covered with a layer of 5-10 cm, withstanding a given slope.
5. The drainage pipes are being laid. A pipe or drain (usually 110 mm diameter pipes) has a slit perforation or holes with a diameter of 1.5-5 mm.
They are located along the entire circumference of the pipe. Some drainage pipes are equipped with shells of filtering materials – a geotextile “shirt”, which protects the pipe from rapid silting.
Pipe wrapped with geotextile is used only in clean medium- and coarse-grained sands. In other conditions, it quickly, within 2-4 years of operation, colmatates (silted), so other soils use a pipe without a geotextile wrapper.
6. After laying the drain, it is sprinkled with granite rubble of the fraction 5-20. It turns out that the pipe on all sides is surrounded by a crushed “shirt”, which is separated from the layer of sand and soil by a geotextile fabric.
7. The edges of the geotextiles with flyover are stacked on top of each other, and then the trench is filled with excavated soil.
To monitor the work of drainage and periodic cleaning of pipes (for which a fire hydrant is used), observation wells are arranged. According to the requirements of the SNIP, they are arranged at least in 50 meters on rectilinear drainage areas, as well as in places of turns, intersections and changes in pipe slopes. The water collected by the drains enters the water well. It is excavated at the lowest point of the site.
Often the question arises – where to drain this water. It can be diverted:
In this regard, the use of the pump gives greater freedom in deciding where and how to divert water. This simplifies the work, because you do not need to monitor the slope of the drainage pipe.
It also allows you to reduce the amount of excavation work due to the absence of the need to dig deep under the slope. Installation of the pump requires competent selection and adjustment of engineering equipment, as well as supplying the power line.
The main errors that are allowed during the device drainage system:
Moreover, it is impossible to combine shower and drainage in one pipe, since this will lead to the opposite effect - during the rainy season, the drainage system will not cope with excess water. There will be moisture of the soil near the foundation, frosts will strike, and this will cause soil swelling, which can lead to deformation of the pavement, movement of the foundation or its destruction. published
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consciousness – together we change the world!
Source: //vk.com/al_feed.php?w=wall-50784188_50301
If you neglect the device of the drainage system, it can lead to a decrease in the service life of the foundation due to its excessive moisture and the emergence of destructive forces of frost bloating.

Recommendations of MosComArchitecture "Guidelines for the design and arrangement of drainages, 2000".
The device of the drainage system is mandatory in cases of location:
- Operated deep rooms below the calculated level of groundwater or in excess of the clean floor of the basement above the calculated level of groundwater less than 500 mm.
- Operated deep rooms in clay and loamy soils, regardless of the presence of groundwater.
- Technical subfields in clay and loamy soils when they are buried more than 1.5 m from the surface of the earth, regardless of the presence of groundwater.
- Any structures located in the zone of capillary moisture, when the conditions of their operation are associated with a rigid temperature and humidity regime.
It is not necessary to arrange the system if the site is dry and the level of groundwater during the flood and heavy precipitation does not reach critical levels.
For a preliminary assessment of the groundwater level at the site, the following method can be used: If the site or neighbors have a well, then UGV can be determined by the level of water in the well rings. It is best to do this in late July or early August. The closer the water is to the surface of the earth, the higher the groundwater level.
UGV can also be estimated by the level of water cut in a lake or river (if they are near the site).It should be remembered that the wetted area significantly complicates or makes it impossible to carry out landscape and landscaping.
Many plants cannot grow on wet soil. For example, apple trees do not tolerate excess water. In trees and shrubs, due to the lack of oxygen, rotting of the root system may begin.
Thus, in the case of high UGV and in the absence of drainage, the number of plant species, shrubs and trees that can grow and bear fruit in the garden plot is significantly reduced.
In addition, if you start to engage in the device of the drainage system after the house is built, garden paths are laid and the lawn is planted, then you will have to carry out the whole complex of earthworks on the already equipped territory, which will lead to damage to the landscape and additional monetary costs.
Although wetlands and clearly moistened areas are visible to the naked eye, it is not worth choosing methods of drainage and drainage for indirect reasons. The full picture can give only hydrogeological study of the soil on the site.
Why is hydrogeological research done?
Different types of soils have different characteristics that can significantly affect the choice of drainage system and its path. It should also be borne in mind that the groundwater level in the neighboring area may differ from the ground in the area where the foundation and drainage system are planned. Therefore, it is better to solve this issue not by eye, but by resorting to hydrogeological research.
This event will determine:
- Geological structure of the site.
- Physical and mechanical characteristics of soils.
- Groundwater power sources.
- Levels of groundwater, their chemical analysis. This will allow you to understand at what levels groundwater is relative to the surface of the earth and the projected foundation.
- What type of water: pressure or not, its chemical composition and corrosive aggressiveness.
- The presence of waterproofs. It happens that the water is high enough, but is covered with upper water. Without violating it, i.e. without deepening the foundation, you can avoid the impact on the base of the house groundwater.
- Filtration properties of soils and granulometric composition of sands, which are the main conductor of groundwater - to understand how the drainage device will affect the composition of sands, whether there will be suffosive removal of particles, which can lead to precipitation of the foundation.
1. Performing drilling operations.
2. Groundwater level measurements.
3. Soil and water sampling.
4. Laboratory definitions of the physical characteristics of soils, including the determination of the filtration properties of soils.
Analysis of the results of the survey will allow you to choose the optimal foundation design and type of drainage system.
Types of drainage systems
Errors in the design and construction of the drainage system can occur several years after the start of its operation. Therefore, the device of the drainage system begins with its design, and first you need to understand the main types of drainage.
Drainage is divided into local and general. Local drainage is used to protect against groundwater flooding of the foundation and basement, general - to protect the site.
The following types of drainage can be distinguished:
- The wall protects against the top.
- Ring - protects basement and basement premises from flooding with groundwater.
- Plastic - protects basement and basement premises from flooding with groundwater in the conditions of the layered structure of the aquifer and the pressure of groundwater.
- Systematic. It is used to drain large areas.
- Radiation. It is used to drain existing parklands. A characteristic feature of this drainage is the sensitivity to the root system of plants.
The plastic drainage system protects the structure from both groundwater flooding and capillary moisture moisture. Plast drainage is widely used in the construction of underground structures erected on poorly permeable soils, as well as in the presence of a powerful aquifer under the foundation. To protect basements and structures in which, according to operating conditions, the appearance of dampness is not allowed, when these rooms are located in the zone of capillary soil moisture, reservoir drainage should be arranged.
Ring drainage (most often these are tubular drains) is located along the contour of the protected building or its section. The effect of ring drainage is based on lowering the level of groundwater inside the protected circuit, which provides protection against flooding of underground structures and buried parts of buildings. The depth of this decrease depends on the burying of pipes, galleries or filter part of wells relative to the level of groundwater, as well as on the size of the protected circuit. Ring drains are located at some distance from the structure, so they can be installed after its construction. In this respect, ring drainage is advantageously different from formation, which can be arranged only simultaneously with the construction of the structure.
Wall drainage consists of drainage wall structures (sprinkled, glued, installed) and tubular drains laid on the outside of the structure and serving simultaneously collecting and draining drainage water pipeline.
Wall drainage is used both independently and in conjunction with other types of drainage.
How to protect the basement from flooding?
If the site has a high level of groundwater, then even at the stage of digging the pit under the foundation it will be flooded with water. This can seriously affect the quality and speed of work. Therefore, it is necessary to provide in advance for measures to divert water.
It is necessary to clearly understand that there is a normal drainage of the foundation, for example, MZLF. In this case, we protect the foundation from the harmful effects of groundwater and reduce the risk of frost bloating forces. And there is a set of measures to protect against flooding of basement and basement premises.
The risk of flooding exists when installing basements in clay and loamy soils and with a difference of UGV marks and basement floor marks (basement) less than 0.5 meters. In these cases, the drainage device is required.
The foundation drainage device allows:
- increase the stability of the construction;
- remove unfavorable factors of tumult in winter;
- improve the performance of hydroprotection of foundation structures.
If the flooding of the ground floor has already begun, the following measures should be taken:
1. First, it is necessary to understand and assess the extent of flooding. The further work plan depends on this. If the leak appeared somewhere locally, then you can use special hydrophobic compounds with an injectable injection system.
2. If the flooding began throughout the ground floor, then without drainage, the device of pits and additional measures for waterproofing the basement can not do.
How is the area drained?
One of the technologies of the drainage system is as follows:
1. Along the perimeter of the building, around which it is necessary to arrange drainage, a trench is dug and the necessary slope necessary for natural water flow is maintained.
According to standards, it is necessary to withstand a slope of 1 cm per 1 p / meter.
2. The bottom of the trench is tamped and filled with river sand with a layer of 10 cm, withstanding a given slope.
3. The trench is lined with geotextile. This is necessary to separate the layers and prevent silting of rubble.
4. Granite crushed stone is covered with a layer of 5-10 cm, withstanding a given slope.
5. The drainage pipes are being laid. A pipe or drain (usually 110 mm diameter pipes) has a slit perforation or holes with a diameter of 1.5-5 mm.
They are located along the entire circumference of the pipe. Some drainage pipes are equipped with shells of filtering materials – a geotextile “shirt”, which protects the pipe from rapid silting.
Pipe wrapped with geotextile is used only in clean medium- and coarse-grained sands. In other conditions, it quickly, within 2-4 years of operation, colmatates (silted), so other soils use a pipe without a geotextile wrapper.
6. After laying the drain, it is sprinkled with granite rubble of the fraction 5-20. It turns out that the pipe on all sides is surrounded by a crushed “shirt”, which is separated from the layer of sand and soil by a geotextile fabric.
7. The edges of the geotextiles with flyover are stacked on top of each other, and then the trench is filled with excavated soil.
To monitor the work of drainage and periodic cleaning of pipes (for which a fire hydrant is used), observation wells are arranged. According to the requirements of the SNIP, they are arranged at least in 50 meters on rectilinear drainage areas, as well as in places of turns, intersections and changes in pipe slopes. The water collected by the drains enters the water well. It is excavated at the lowest point of the site.
Often the question arises – where to drain this water. It can be diverted:
- (a) the settlement network;
- In the ditch.
- into the ravine;
- into the stream;
- c absorbent tanks.
In this regard, the use of the pump gives greater freedom in deciding where and how to divert water. This simplifies the work, because you do not need to monitor the slope of the drainage pipe.
It also allows you to reduce the amount of excavation work due to the absence of the need to dig deep under the slope. Installation of the pump requires competent selection and adjustment of engineering equipment, as well as supplying the power line.
The main errors that are allowed during the device drainage system:
- the use of wall drainage (pipe in the marks of the sole of the foundation) for the removal of groundwater;
- the use of the pipe in the geotextile filter in loamy soils and soups, which inevitably leads to colmatation of the filter;
- use of levels when laying pipes instead of level and theodolite;
- Installation of drainage wells instead of drainage.
Moreover, it is impossible to combine shower and drainage in one pipe, since this will lead to the opposite effect - during the rainy season, the drainage system will not cope with excess water. There will be moisture of the soil near the foundation, frosts will strike, and this will cause soil swelling, which can lead to deformation of the pavement, movement of the foundation or its destruction. published
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consciousness – together we change the world!
Source: //vk.com/al_feed.php?w=wall-50784188_50301
The easiest method of grafting trees
The method of Dr. Mac-Ferrini: cleansing of the body through the skin