1126
Empire Star Sword
In 1960-80-ies. the Soviet Union had done a few dozen fighters test satellites. The last such test was held June 18, 1982 This was part of the greatest scientists of the Soviet nuclear forces, known in the West, "seven-hour nuclear war". The exercises, during which the land and sea launched ballistic missiles, missiles, military satellites (including interceptor) fired on the leadership of the United States lasting impression. "Seven-hour nuclear war" gave irrefutable arguments the US military and politicians demanded to start work on the creation of an anti-US and anti-missile systems of new generation.

The decision on the development and deployment of anti-satellite system President Ronald Reagan announced a month after the "seven-hour nuclear war" - in July 1982 then March 23, 1983, Reagan announced the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI). This program was soon dubbed "Star Wars" in honor of the popular movie.
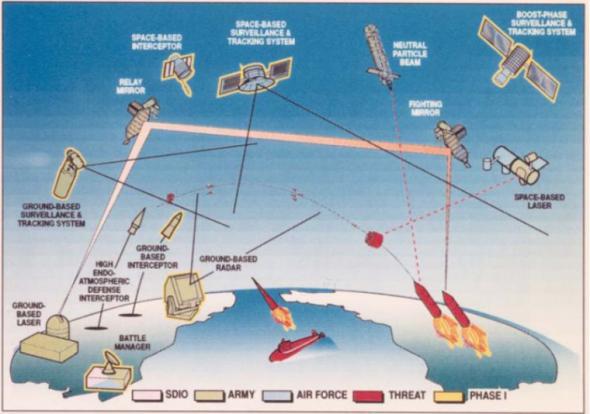
In the US, work on the creation of combat space stations were developed in the early 70s, before the announcement of Reagan's SDI program. We offer the most exotic designs using kinetic, laser and beam weapons.
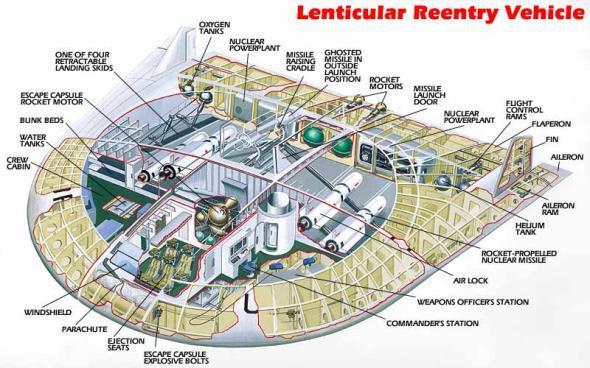
For example, the possibility to orbit powerful X-ray laser. The energy for it would provide a nuclear explosion. However, in practice it turned out to be not so easy as on paper. A series of tests of the laser beam weapons, and revealed a lot of problems that American scientists have not
managed to solve until the collapse of the official work of the SDI in 1993, the Soviet Union since the late 50s. We were working on the creation of means to combat the US military reconnaissance satellites. November 1, 1963 went into orbit the first Soviet satellite maneuver "Flight 1". April 12, 1964 started the "Flight 2". These satellites have been developed in the design office of Vladimir Nikolaevich Chelomeya and serve as a prototype automatic satellite interceptor IP (fighter satellites). Actually interception in space satellite IP was first successfully performed the day five years after the launch of the first Isa - November 1, 1968
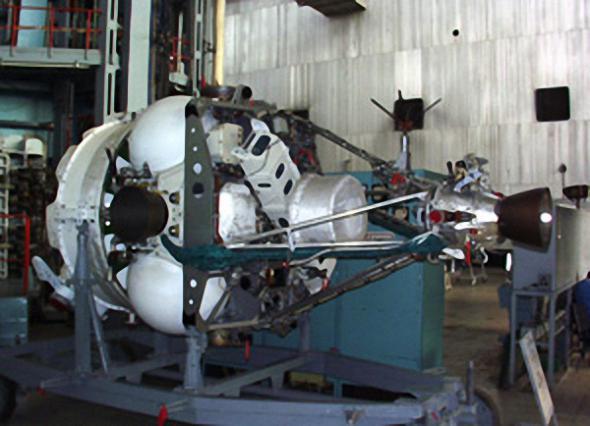

Maneuvering the satellite Flight 1
In the mid-70s. work space strike weapons were launched in NGOs "Energy", headed by Valentin Petrovich Glushko. Leading role of the "Energy" has been issued a special Resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers "On the investigation of the possibility of creating weapons of warfare in and from space."
The official history of the RSC "Energia". Korolev, published in 1996, these works read as follows:
"... In the 70-80-ies. Complex research was conducted to identify possible ways to create space vehicles able to meet the challenges of CA lesions military, ballistic missiles in flight, as well as critical air, sea and ground targets. The objective is to achieve the desired characteristics of these funds through the use of the then available scientific
technical basis with a view to the development of these resources in the capacity constraints and financing. For the military defeat of space objects have been developed two combat spacecraft on a single constructive basis, with a variety of types of airborne weapon systems - laser and missile ...
Less weight on-board armament with missiles, compared with a set of laser weapons allowed to carry on board the spacecraft greater fuel capacity, so it seemed appropriate to create a system with a constellation, consisting of combat spacecraft, one part of which is equipped with a laser, and the other - missile weapons. In this first type of apparatus should be used for low-orbit objects, and the second - on the objects located in the medium-altitude and geostationary orbits .. »
Both types of combat spacecraft developed by NPO "Energy" was decided to create a single design concept. Based on estimates of the mass characteristics of future combat systems as a basic platform has been chosen space station type 17K DOS. NGOs "Energy" was already a great experience in operating devices of this class. On the basis of the underlying platform, as mentioned above, it has been developed two combat systems:
17F19 "Skif" - a system that provides for the use of lasers.
17F111 "Cascade" - a system with missiles. NGOs "Energy" was the umbrella organization for the entire program of anti-missile defense and space-based weapons. The parent company of laser systems for the "Scythian" became NGO "Astrophysics" - leading Soviet firm lasers. Missile complex "cascade" was developed in the company A.E.Nudelmana known Soviet weapons designer for aircraft and spacecraft. In orbit "Skif" and "cascades" were the first (pilot) phase 8K82K rocket "Proton-K", and later - 11F35OK orbiter "Buran". For longer alerting each type of spacecraft was able to refuel, which had to provide ships "Buran". In addition, the possibility of a visit martial station crew of two people for up to 7 days on ships such as "Union».
Missile Station "Cascade».
Interceptor missile.
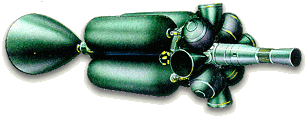
Less weight on-board armament "Cascade" with missiles, compared with the complex "Skif" laser weapons allowed to carry on board the spacecraft greater fuel capacity, so it seemed appropriate to create a system with a constellation consisting of combat spacecraft, one part of the which is equipped with a laser, and the other -raketnym weapons. In this first type of spacecraft was to be used for low-orbit objects, and the second - on the objects located in the medium-altitude and geostationary orbits.
To defeat the launch of ballistic missiles and their parent units in the flight phase in NGOs "Energy" for the complex "Cascade" project was developed interceptor missile space-based. In the practice of NGOs "Energy" it was the smallest, but the most power-rocket. Suffice it to say that the starting weight measured just tens of kilograms, interceptor missile had a margin of characteristic velocity, comparable with the characteristic velocity missiles that bring modern payloads into orbit satellites. High performance is achieved by using technical solutions based on the latest achievements of domestic science and technology in the field of miniaturization of instrumentation. Authoring NGOs "Energy" was a unique propulsion system that uses non-traditional non-cryogenic fuel, and heavy-duty composite materials. For orbital missile tests, it was decided to install them on the cargo ship "Progress».

The first stage in 1986-88. They were scheduled five flights of such ships in the framework of the "Cascade". In the industrial base of NGOs "Energy" - Experimental Engineering Plant (MEM) began production of these ships under the hull numbers 129, 130, 131, 132 and 133. However, flight tests, it never came. To defeat the critical ground targets developed the space station, which is based on a series of 17K DOS station and on which were based stand-alone modules with warheads of ballistic or plan type. According to a special team units were separated from the plant by maneuvering they were to occupy the desired position in space with
followed by separation of the blocks on the team for combat use. The design and the main system of autonomous units were taken from the orbital ship "Buran". Alternatively, the combat unit was considered device based on the experimental model OK "Buran" (family vehicles "BOR»).
Fighting Space Station.
1 - the base unit; 2 - Control Center warheads; 3 - Reusable transport ship "Dawn"; 4 - Battle station modules with sighting systems; 5 - fighting units (based on the fuselage OK "Buran»)

Combat unit goes into the goal.
The same base unit as on the orbital station "Mir", those are the side (it is no secret that the "spectrum", for example, suggests testing the optical detection of missile launches. A stable platform with television cameras and at the "Crystal" - what a sight not?), but instead of astrophysical "Quantum" - the module with a set of command and control. Under the "ball" of the transition compartment - another adapter, which hang four modules (based on "Buranovskie" fuselage) with warheads. This so-called "original position." On alarm, they are separated and the costs of operating the orbit chosen for the following reasons: to each unit went to his goal at the moment when it will fly over the control center.
Fuselage "Burana" is used in this project on a "do not disappear as good": large stocks of fuel in the combined propulsion system and a very good management system can actively maneuver in orbit, with a payload - combat units are in a container, hidden from prying Eye, as well as the unfavorable factors of space flight.
That is essential in the context of strategic deterrence - the weapon system will cause the impact, "surgical" strike, even if the rest will be destroyed. As nuclear submarines, it is able to ride out the first volley.
Military target load for the OK "Buran" was developed on the basis of a special secret decree of the CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers "On the investigation of the possibility of creating weapons of warfare in and from space" (1976)
Combat units are essentially planning nuclear bombs were placed in a compact payload bay martial percussion module with folded wing panels in three or four series established revolving catapult launchers.
Dimensions payload bay "Buran" can be placed on each rotating catapult installation of up to five warheads, as shown in the figure. In view of the possible side-maneuver each combat unit during the descent in the atmosphere of not less than plus / minus 1100 - 1500 km one stroke module could in a short time its twenty maneuvering warheads to wipe all life off the face of the earth in a strip width of up to 3,000 km.

There are also reports of other military aspects of the use of orbiters. In particular, under the "asymmetric response" American program "Star Wars" (SDI - Strategic Defense Initiative) addressed issues of mining through "Buran" near-Earth space with the creation of an irresistible veil for the space segment of the SDI.
Moreover, the Soviet Union conducted research with experimental testing ground for the creation of orbital blasting clouds, quickly and completely, "clearing out" of the spacecraft all near-Earth space to an altitude of 3000 km. Of course, after that near-Earth space became completely unavailable for several months, but that these measures are intended to be used only during (or just before) a full-scale military conflict between the USSR and the USA. And as you know, "chop wood - chips fly» ...

But far more advanced work on laser weapons. Therefore, the creation of a space laser weapons worth discussing in more detail.
The history of the "SKIF".
Fight against ballistic missiles proved to be too difficult a problem. Because the customer - the Ministry of Defense, first decided to start the development of effective anti-satellite weapons. After disable the spacecraft is much easier than to find and destroy the flying warhead. Thus, in the Soviet Union began to develop what is known as "anti-SDI." This system would destroy future American combat spacecraft, thereby depriving the US anti-nuclear missiles. These Soviet station- "killer" well within the scope of the military doctrine of the Soviet Union, which provided for the so-called "anticipatory retaliation", according to which the first Soviet space stations "anti-SOI" should have been put out of action the US station SOI, and then started to Soviet ballistic missiles to strike at the enemy's territory.
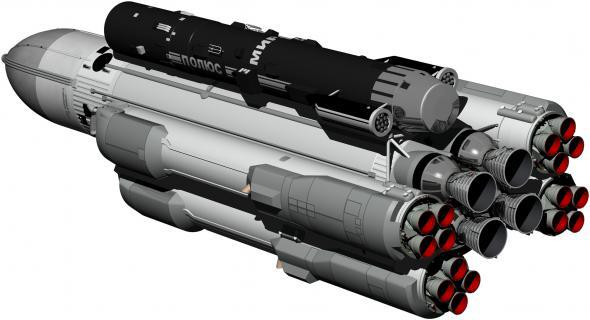
The decision was at first glance quite simple: install on the spacecraft already created and tested a laser to test it in space. The choice fell on a laser installation 1 MW, created by one of the affiliates of the Institute of Atomic Energy. Kurchatov. This gas-dynamic laser operating in the carbon dioxide has been developed for installation on the aircraft IL-76. By 1983, he had already passed flight tests.

The history of aviation laser project, which is closely intertwined with the project of space laser. Therefore, despite the fact that it lies beyond the scope of articles about it is to talk briefly. Besides the description of the laser on the IL-76 gives an idea of laser testing in space.

Battle laser tested for IL-76MD, tail number USSR-86879 (otherwise called him Il-76LL with BC - flying laboratory IL-76 combat lasers). The aircraft looked peculiar. To power the laser and associated equipment on each side of the bow was equipped with two turbo-generator AI-24W capacity of 2.1 MW. Instead of the regular weather radar on the nose was a huge bulbous fairing on a special adapter, to which was attached an oblong bottom cowl smaller. Obviously, there was placed the antenna aiming system, which turned in all directions, trying to catch the goal.

Ground combat variant of the laser system is mounted on the IL-76LL
Originally it was decided accommodation laser gun: not to spoil the aerodynamics of the aircraft has one fairing, made retractable gun. The top of the fuselage between the wings and the keel was cut out and replaced with huge wings, consisting of several segments. They cleaned the inside of the fuselage, and then get out the top turret with a gun. For wing were protruding outside the contour of the fuselage fairings with a profile similar to the profile of the wing. Cargo ramp is retained, but the leaf of the cargo hatch was removed and sewn metal hatch.
More details about the structure of IL-76MD laser installation
Tuning of aircraft performed Tagonrogsky Aviation Research Complex (Beriev) them. Beriev Taganrog and Machine-Building Plant. Georgi Dimitrov.
The spacecraft, designed for the installation of its megawatt laser Il-76LL with BC, received the designation 17F19D "Skif-D." The letter "D" stands for "demonstration." August 27, 1984 Minister of General Machine Building Oleg D. Baklanov signed an order N343 / 0180 on the establishment of 17F19D "Skif-D." CB "Salute" was determined by the head of its creation. The same order was formally approved a program to build future military spacecraft heavy type. Then the order of the IOM N168 from May 12, 1985 was established cooperative enterprises that manufacture "Skif-D." Finally, due to the fact that the anti-missile theme was one of the priorities of "Skif-D" published January 27, 1986 Mr. Decision CPSU Central Committee and USSR Council of Ministers N135-45. Such an honor awarded every Soviet spacecraft. According to this Resolution the first launch into orbit "Skif-D" was to be held in the second quarter 1987
"Skif-D" was primarily an experimental spacecraft, which have been practiced not only laser, but some of the staff of these devices produced in the framework of the "Soviet SDI." It was a system of separation and orientation, traffic control system, power supply system, control system onboard complex.
Apparatus 17F19D should also demonstrate the fundamental possibility of creating spacecraft to destroy targets in space. To test the laser "Skif-D" was planned to set specific targets simulating enemy missiles, warheads and satellites. However, the place is such a powerful laser device class station DOS was impossible. The yield was found quickly. By 1983, he became visible "light at the end of the tunnel" with RN
11K25 "Energy". This carrier could accelerate to a speed close to the first space, a payload of approximately 95 tons. It was such a mass of the unit and fit with air megawatt laser.
To accelerate work on "Skif-D" KB "Salyut" it was decided to make the most of the experience of previous and ongoing work at the time. The structure of "Skif-D" includes elements of the transport ship of TCS and the orbiter "Buran", the base unit and modules "Mir", "Proton-K".
SA
Source:

The decision on the development and deployment of anti-satellite system President Ronald Reagan announced a month after the "seven-hour nuclear war" - in July 1982 then March 23, 1983, Reagan announced the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI). This program was soon dubbed "Star Wars" in honor of the popular movie.

In the US, work on the creation of combat space stations were developed in the early 70s, before the announcement of Reagan's SDI program. We offer the most exotic designs using kinetic, laser and beam weapons.

For example, the possibility to orbit powerful X-ray laser. The energy for it would provide a nuclear explosion. However, in practice it turned out to be not so easy as on paper. A series of tests of the laser beam weapons, and revealed a lot of problems that American scientists have not
managed to solve until the collapse of the official work of the SDI in 1993, the Soviet Union since the late 50s. We were working on the creation of means to combat the US military reconnaissance satellites. November 1, 1963 went into orbit the first Soviet satellite maneuver "Flight 1". April 12, 1964 started the "Flight 2". These satellites have been developed in the design office of Vladimir Nikolaevich Chelomeya and serve as a prototype automatic satellite interceptor IP (fighter satellites). Actually interception in space satellite IP was first successfully performed the day five years after the launch of the first Isa - November 1, 1968

Maneuvering the satellite Flight 1
In the mid-70s. work space strike weapons were launched in NGOs "Energy", headed by Valentin Petrovich Glushko. Leading role of the "Energy" has been issued a special Resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers "On the investigation of the possibility of creating weapons of warfare in and from space."
The official history of the RSC "Energia". Korolev, published in 1996, these works read as follows:
"... In the 70-80-ies. Complex research was conducted to identify possible ways to create space vehicles able to meet the challenges of CA lesions military, ballistic missiles in flight, as well as critical air, sea and ground targets. The objective is to achieve the desired characteristics of these funds through the use of the then available scientific
technical basis with a view to the development of these resources in the capacity constraints and financing. For the military defeat of space objects have been developed two combat spacecraft on a single constructive basis, with a variety of types of airborne weapon systems - laser and missile ...
Less weight on-board armament with missiles, compared with a set of laser weapons allowed to carry on board the spacecraft greater fuel capacity, so it seemed appropriate to create a system with a constellation, consisting of combat spacecraft, one part of which is equipped with a laser, and the other - missile weapons. In this first type of apparatus should be used for low-orbit objects, and the second - on the objects located in the medium-altitude and geostationary orbits .. »
Both types of combat spacecraft developed by NPO "Energy" was decided to create a single design concept. Based on estimates of the mass characteristics of future combat systems as a basic platform has been chosen space station type 17K DOS. NGOs "Energy" was already a great experience in operating devices of this class. On the basis of the underlying platform, as mentioned above, it has been developed two combat systems:
17F19 "Skif" - a system that provides for the use of lasers.
17F111 "Cascade" - a system with missiles. NGOs "Energy" was the umbrella organization for the entire program of anti-missile defense and space-based weapons. The parent company of laser systems for the "Scythian" became NGO "Astrophysics" - leading Soviet firm lasers. Missile complex "cascade" was developed in the company A.E.Nudelmana known Soviet weapons designer for aircraft and spacecraft. In orbit "Skif" and "cascades" were the first (pilot) phase 8K82K rocket "Proton-K", and later - 11F35OK orbiter "Buran". For longer alerting each type of spacecraft was able to refuel, which had to provide ships "Buran". In addition, the possibility of a visit martial station crew of two people for up to 7 days on ships such as "Union».
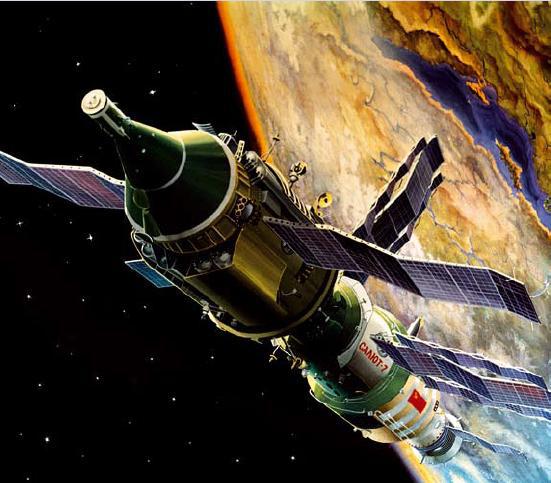
Missile Station "Cascade».
Interceptor missile.

Less weight on-board armament "Cascade" with missiles, compared with the complex "Skif" laser weapons allowed to carry on board the spacecraft greater fuel capacity, so it seemed appropriate to create a system with a constellation consisting of combat spacecraft, one part of the which is equipped with a laser, and the other -raketnym weapons. In this first type of spacecraft was to be used for low-orbit objects, and the second - on the objects located in the medium-altitude and geostationary orbits.
To defeat the launch of ballistic missiles and their parent units in the flight phase in NGOs "Energy" for the complex "Cascade" project was developed interceptor missile space-based. In the practice of NGOs "Energy" it was the smallest, but the most power-rocket. Suffice it to say that the starting weight measured just tens of kilograms, interceptor missile had a margin of characteristic velocity, comparable with the characteristic velocity missiles that bring modern payloads into orbit satellites. High performance is achieved by using technical solutions based on the latest achievements of domestic science and technology in the field of miniaturization of instrumentation. Authoring NGOs "Energy" was a unique propulsion system that uses non-traditional non-cryogenic fuel, and heavy-duty composite materials. For orbital missile tests, it was decided to install them on the cargo ship "Progress».

The first stage in 1986-88. They were scheduled five flights of such ships in the framework of the "Cascade". In the industrial base of NGOs "Energy" - Experimental Engineering Plant (MEM) began production of these ships under the hull numbers 129, 130, 131, 132 and 133. However, flight tests, it never came. To defeat the critical ground targets developed the space station, which is based on a series of 17K DOS station and on which were based stand-alone modules with warheads of ballistic or plan type. According to a special team units were separated from the plant by maneuvering they were to occupy the desired position in space with
followed by separation of the blocks on the team for combat use. The design and the main system of autonomous units were taken from the orbital ship "Buran". Alternatively, the combat unit was considered device based on the experimental model OK "Buran" (family vehicles "BOR»).
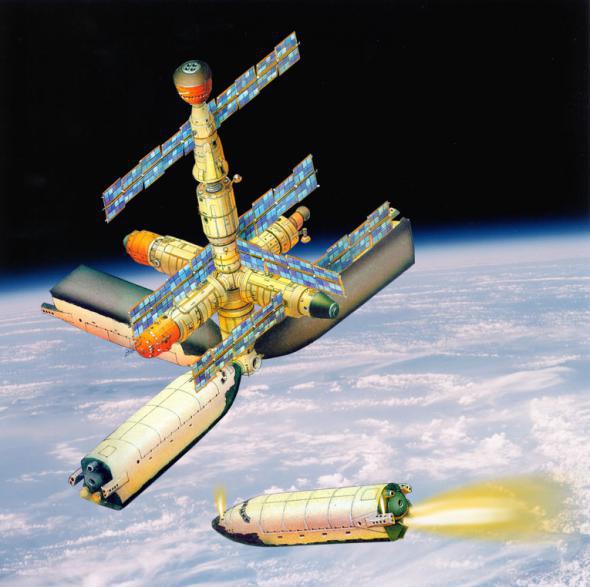
Fighting Space Station.
1 - the base unit; 2 - Control Center warheads; 3 - Reusable transport ship "Dawn"; 4 - Battle station modules with sighting systems; 5 - fighting units (based on the fuselage OK "Buran»)

Combat unit goes into the goal.
The same base unit as on the orbital station "Mir", those are the side (it is no secret that the "spectrum", for example, suggests testing the optical detection of missile launches. A stable platform with television cameras and at the "Crystal" - what a sight not?), but instead of astrophysical "Quantum" - the module with a set of command and control. Under the "ball" of the transition compartment - another adapter, which hang four modules (based on "Buranovskie" fuselage) with warheads. This so-called "original position." On alarm, they are separated and the costs of operating the orbit chosen for the following reasons: to each unit went to his goal at the moment when it will fly over the control center.
Fuselage "Burana" is used in this project on a "do not disappear as good": large stocks of fuel in the combined propulsion system and a very good management system can actively maneuver in orbit, with a payload - combat units are in a container, hidden from prying Eye, as well as the unfavorable factors of space flight.
That is essential in the context of strategic deterrence - the weapon system will cause the impact, "surgical" strike, even if the rest will be destroyed. As nuclear submarines, it is able to ride out the first volley.
Military target load for the OK "Buran" was developed on the basis of a special secret decree of the CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers "On the investigation of the possibility of creating weapons of warfare in and from space" (1976)
Combat units are essentially planning nuclear bombs were placed in a compact payload bay martial percussion module with folded wing panels in three or four series established revolving catapult launchers.
Dimensions payload bay "Buran" can be placed on each rotating catapult installation of up to five warheads, as shown in the figure. In view of the possible side-maneuver each combat unit during the descent in the atmosphere of not less than plus / minus 1100 - 1500 km one stroke module could in a short time its twenty maneuvering warheads to wipe all life off the face of the earth in a strip width of up to 3,000 km.

There are also reports of other military aspects of the use of orbiters. In particular, under the "asymmetric response" American program "Star Wars" (SDI - Strategic Defense Initiative) addressed issues of mining through "Buran" near-Earth space with the creation of an irresistible veil for the space segment of the SDI.
Moreover, the Soviet Union conducted research with experimental testing ground for the creation of orbital blasting clouds, quickly and completely, "clearing out" of the spacecraft all near-Earth space to an altitude of 3000 km. Of course, after that near-Earth space became completely unavailable for several months, but that these measures are intended to be used only during (or just before) a full-scale military conflict between the USSR and the USA. And as you know, "chop wood - chips fly» ...

But far more advanced work on laser weapons. Therefore, the creation of a space laser weapons worth discussing in more detail.
The history of the "SKIF".
Fight against ballistic missiles proved to be too difficult a problem. Because the customer - the Ministry of Defense, first decided to start the development of effective anti-satellite weapons. After disable the spacecraft is much easier than to find and destroy the flying warhead. Thus, in the Soviet Union began to develop what is known as "anti-SDI." This system would destroy future American combat spacecraft, thereby depriving the US anti-nuclear missiles. These Soviet station- "killer" well within the scope of the military doctrine of the Soviet Union, which provided for the so-called "anticipatory retaliation", according to which the first Soviet space stations "anti-SOI" should have been put out of action the US station SOI, and then started to Soviet ballistic missiles to strike at the enemy's territory.

The decision was at first glance quite simple: install on the spacecraft already created and tested a laser to test it in space. The choice fell on a laser installation 1 MW, created by one of the affiliates of the Institute of Atomic Energy. Kurchatov. This gas-dynamic laser operating in the carbon dioxide has been developed for installation on the aircraft IL-76. By 1983, he had already passed flight tests.

The history of aviation laser project, which is closely intertwined with the project of space laser. Therefore, despite the fact that it lies beyond the scope of articles about it is to talk briefly. Besides the description of the laser on the IL-76 gives an idea of laser testing in space.

Battle laser tested for IL-76MD, tail number USSR-86879 (otherwise called him Il-76LL with BC - flying laboratory IL-76 combat lasers). The aircraft looked peculiar. To power the laser and associated equipment on each side of the bow was equipped with two turbo-generator AI-24W capacity of 2.1 MW. Instead of the regular weather radar on the nose was a huge bulbous fairing on a special adapter, to which was attached an oblong bottom cowl smaller. Obviously, there was placed the antenna aiming system, which turned in all directions, trying to catch the goal.

Ground combat variant of the laser system is mounted on the IL-76LL
Originally it was decided accommodation laser gun: not to spoil the aerodynamics of the aircraft has one fairing, made retractable gun. The top of the fuselage between the wings and the keel was cut out and replaced with huge wings, consisting of several segments. They cleaned the inside of the fuselage, and then get out the top turret with a gun. For wing were protruding outside the contour of the fuselage fairings with a profile similar to the profile of the wing. Cargo ramp is retained, but the leaf of the cargo hatch was removed and sewn metal hatch.

More details about the structure of IL-76MD laser installation
Tuning of aircraft performed Tagonrogsky Aviation Research Complex (Beriev) them. Beriev Taganrog and Machine-Building Plant. Georgi Dimitrov.
The spacecraft, designed for the installation of its megawatt laser Il-76LL with BC, received the designation 17F19D "Skif-D." The letter "D" stands for "demonstration." August 27, 1984 Minister of General Machine Building Oleg D. Baklanov signed an order N343 / 0180 on the establishment of 17F19D "Skif-D." CB "Salute" was determined by the head of its creation. The same order was formally approved a program to build future military spacecraft heavy type. Then the order of the IOM N168 from May 12, 1985 was established cooperative enterprises that manufacture "Skif-D." Finally, due to the fact that the anti-missile theme was one of the priorities of "Skif-D" published January 27, 1986 Mr. Decision CPSU Central Committee and USSR Council of Ministers N135-45. Such an honor awarded every Soviet spacecraft. According to this Resolution the first launch into orbit "Skif-D" was to be held in the second quarter 1987
"Skif-D" was primarily an experimental spacecraft, which have been practiced not only laser, but some of the staff of these devices produced in the framework of the "Soviet SDI." It was a system of separation and orientation, traffic control system, power supply system, control system onboard complex.
Apparatus 17F19D should also demonstrate the fundamental possibility of creating spacecraft to destroy targets in space. To test the laser "Skif-D" was planned to set specific targets simulating enemy missiles, warheads and satellites. However, the place is such a powerful laser device class station DOS was impossible. The yield was found quickly. By 1983, he became visible "light at the end of the tunnel" with RN
11K25 "Energy". This carrier could accelerate to a speed close to the first space, a payload of approximately 95 tons. It was such a mass of the unit and fit with air megawatt laser.
To accelerate work on "Skif-D" KB "Salyut" it was decided to make the most of the experience of previous and ongoing work at the time. The structure of "Skif-D" includes elements of the transport ship of TCS and the orbiter "Buran", the base unit and modules "Mir", "Proton-K".
SA
Source: