847
How to harvest medicinal plants
There is a certain logic collection. If hoard seeds, fruits, it is best to do it during the period of full maturity, without conceding, however, since their shedding naturally. If it's flowers, leaves, grass, they are collected in the beginning of flowering and during the period of full bloom, before the beginning of fruiting. At this time, part of the listed accumulate the highest number of active substances.

BASIC RULES purveyors
Each harvester must know:
that the harvest (a plant, its symptoms, which parts)
when to harvest (time of year, time of day)
where the harvest (habitat, designated areas)
what and how to harvest (harvesting machinery)
Kidneys harvested in the winter or early spring when they are swollen, but not yet started to grow. This is usually in March or April. By the beginning of greening renal tops (birch, poplar) cease collection as medicinal value blooming buds are not. For medical purposes, often used birch buds, poplar, pine.
Birch buds, harvested with branches starting from February. The branches are cut, tied into small twigs, dried in the open air, threshed and cleaned of impurities caught. If the kidneys are harvested during the sap flow, then pluck them with your hands or immediately threshed. The kidneys black poplar, aspen terminated hands, being careful not to crease. Pine "buds" are harvested from the young trees. Cut off the tops of the shoots and to pluck them "buds".
Dry buds should be careful: a long time in a cool ventilated place, as in a warm room, they begin to blossom.
CORU collected only from young (no older than 3-4 years) Stalks, branches and shoots in early spring, in the period of intensive Sap and kidney swelling. At this time, it is rich in medicinal substances and is easily separated because of water-saturated layer of cambium which separates the bark from the wood.
Read the smooth bark. Old, cracked bark contains a lot of cork fabric and few active ingredients. Harvested bark forest felling. With the growing collection of plant materials is prohibited, as it leads to the formation of dead wood.
To remove the bark on the trunks or escape a sharp knife make two semicircular notch at a distance of 30-40 cm from each other and connect them to each other by two longitudinal incisions. The resulting grooves are separated from the bark of wood.
When collecting bark fall areas affected lichens, with the remnants of wood, blackened on the inside. Please note that the collection of raw materials can easily make a mistake in a plant species belonging, as the bark is removed in the absence of leaves. Therefore, it is necessary to be familiar with the outward signs of this plant.
LEAVES. Collection of leaves is usually carried out in the period of budding and flowering plants. Do this in dry weather, tearing leaves hands movement from top to bottom with or without stalks them. Please note that the thick and juicy stalks slow drying of leaves. In addition, they contain little of medicinal substances.
Collect only the developed lower and middle leaves, and faded, fading, affected by insects or fungi - discarded. Juicy leaves (mother-and-stepmother, Digitalis purpurea, etc.) Are folded loosely and quickly delivered to the place of drying.
Zagotavlivaya nettle leaves, mow the plants first, and when the leaves podvyanut (lose pungency), their pluck. Grass can be dried and then leaves thresh.
Wintering small leathery leaves (bearberry, cranberries) harvested before flowering in spring or autumn after the ripening of berries.
Grass, ie above-ground part of the plant, cut or mow at the level of the lower leaves. Some higher plants (wormwood, St. John's wort, motherwort, etc.) Are cut only leafy and flowering tops of 15-20 cm in length and lateral branches.
Thick, coarse woody stems contain few medicinal substances, so collect them impractical. If you have collected a lot of plant stems (thyme, sweet clover, marjoram), they are dried completely, and then threshed leaves from the stems. When collecting the grass you can not pull out the plant with its root (with the exception of uliginose).
Flowers and inflorescences harvested at the beginning of flowering, when they do not yet have signs of wilting. At this time, they contain a lot of active ingredients, can withstand drying, retain their color and less crumble during storage and processing.
Flowers and blossoms are harvested by hand, plucking them and cutting off flower stalk, cutting scissors or shears (from trees). Inflorescence (. Baskets chamomile, calendula, etc.) collected in the phase of the horizontal arrangement of reed petals, and those plants that have only tubular flowers (tansy, chamomile and other odorous.) - In the early blooming of marginal flowers. Overripe inflorescences scattered in the collection.
Flowers - the most delicate part of the plant, so they piled loose, thin layer, preferably in a wicker basket, being careful not to crease and protected from direct sunlight
. Fruits and seeds. The greatest accumulation of medicinal substances occurs in fruits and seeds during their full maturity. Therefore, they are collected selectively as they mature, picking by hand, without stalks. In plants, the fruits of which are located in umbels or corymbs, buds break off entirely, and after drying the fruit is separated from the stalks.
Hips advisable to gather together with a cup, which is removed after drying, rubbing the fruits of his hands. In many plants the seeds mature quickly showered (anise, cumin, coriander, etc.), So they should be collected before the full maturity, when they begin to grow brown. Cut off the tops of the stems with the fruit-bearing buds, tied into small bundles, suspended for final drying and ripening in a dry, ventilated place, then threshed seeds.
Juicy fruit (berries - blueberries, strawberries, currants, stone bramble - wild cherry,. Apples - mountain ash, etc.) collect only mature, healthy. Collection is carried out manually in a shallow wicker basket trimmed in cloth. Each layer in the 5-7 cm berries shift leaves, so they will not be compressed and not compressed against each other. Gather the berries to be careful, because even a slight pressure leads to the formation of dark spots, and these places begins rot. Wet berries are not recommended to collect, as well as the wash water due to rapid spoilage.
Roots, rhizomes, tubers and bulbs - the underground parts of plants. They are usually harvested during the withering away of the aerial parts of the autumn. By this time, the greatest number of active substances accumulated in the underground bodies. It should be noted that during the harvest should be preserved remnants of aerial parts, not to be mistaken as a harvested plant. The roots and rhizomes can be harvested and early spring, before the nutrients will flow away in the aerial parts of the plants growing in tronuvshegosya.
The underground parts of the plants are dug with shovels or other tools along with the earth. Then shake the ground, the roots were washed in cold running water. After washing or cleaning from the ground raw material is spread on the grass or litter that it dried up. Then the roots and rhizomes are cleaned from the remnants of stems, fine roots, damaged or rotten parts, and finally dried.
The underground parts of some plants containing mucus and saponins (orchids, cyanosis, and others.). wash in water nelya as swollen mucous substances, raw moldy. These roots, tubers shake off the ground, remove the upper skin, dried. If the underground part of the raw material harvested is relatively clean from the earth, there is no need to wash them.
The basic rules of harvesting medicinal plants
SECURITY MEASURES workpiece
1. When harvesting of underground organs of perennial plants (trees and shrubs), and renal cortex and requires a license from forestry or forestry.
2. When harvesting of underground organs of perennial herbaceous plants per 1m2 leave 3-5 adult plants developed (for seeding), as the seeds of plants harvested in shake well.
3. Repeated harvesting of underground organs in the territory may be no earlier than 5-8 years.
4. When harvesting the aerial parts of perennial plants (trees and shrubs) rip them no more than 40%, and herbaceous perennials - up to 60%
. 5. Above-ground plant organs must be harvested without damaging other parts of the plant that are not raw materials.
SPECIAL CASES BLANK poisonous plants
1. The preform is organizing a pharmacist or other person in charge of special education.
2. The harvesting is prohibited, except those persons who have attained the age of majority.
3. workpiece in any case no unauthorized persons and children are allowed.
When harvesting is strictly forbidden to eat, rub your eyes and face with his hands, use cosmetics.
4. At the same time, you can harvest only one name of a poisonous or potent medicinal plants.
5. Procurers should be aware of the steps of first aid in case of poisoning According to the raw material.
DRYING HERBS
Timely and correct the collected raw medicinal plants must pass the next important stage of preparation - drying. From compliance with the rules of drying it depends largely on the safety of the medicinal properties of plants. The purpose of drying is rapid cessation in plants intracellular biochemical processes by which cells under the action of enzymes active substances are destroyed.
The quickest way to natural termination of biochemical processes - a cell dehydration, since processes can only go in the aquatic environment. The freshly harvested plant material water content is 60-80%.
Dehumidification only up to 20% has reduced the rate of biochemical reactions and enzyme activity, and its contents at 10-14% enzyme activity ceases completely, i.e. stops intracellular processes leading to the decomposition of the active ingredients. Furthermore, the decrease in weight of the plant leads to the development of moisture retention and termination therein various fungi and micro-organisms, which also reduces the quality of raw materials.
The methods and drying conditions of different plants vary depending on the kind of raw material, the content of active substance in it, moisture, etc. Raw materials containing essential oils (thyme, thyme, marjoram, and others.), Dried slowly at a temperature not higher than 35 ° C, since at higher oil evaporate.
Conversely, feedstock comprising glycosides (lily, Adonis) must be dried rapidly at 50-60 ° C, when the activity of enzymes that decompose glycosides quickly terminated. Some plants are dried at an even higher temperature - 80-90 ° C (hips, primrose leaves) to protect the raw materials contained in ascorbic acid (vitamin C), against oxidation.
The collected raw materials dried using natural or artificial heat. In good weather - outdoors in the sun or in the shade under the eaves, in well ventilated areas, in bad weather - in dryers, furnaces, ovens. Effective drying in attics, under a tin roof.
Most herbs should be dried in the shade, because under the influence of direct sunlight they lose their natural color, and they contain the active ingredients are destroyed. Do not dry in the sun essential-oil plants (oregano, thyme, etc.), Glikozidsoderzhaschee raw materials (Adonis, lily of the valley, zheltushnik).
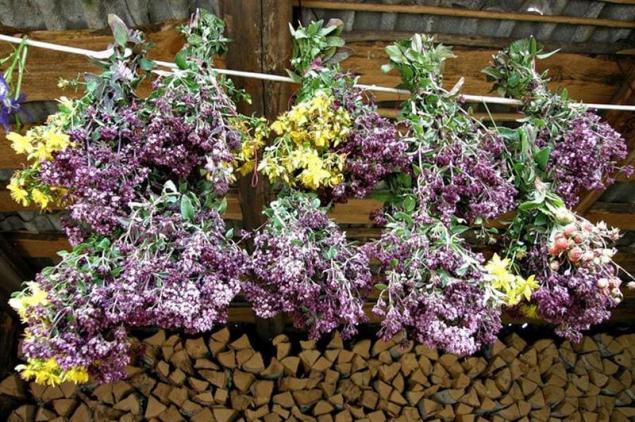

TYPES OF DRY are divided:
1. Drying of natural heat: shady and sunny (it can not be subjected dyed raw materials)
. 2. drying with artificial heating (in the dryer). Its advantages: speed, temperature-controlled, can be used at any time of the year. Disadvantages (for use in industrial environments): special equipment is required, we need a special maintenance personnel, uneconomical for small batches of raw material, is expensive and not available to small businesses
. SIGNIFICANT DRYING:
1. Timeliness drying (no later than 2 hours after collection)
2. Preparation of the raw material to the drying
3. Selecting the temperature
4. Clean the drying room
FEATURES
Buds are dried carefully, for a long time in a cool place at temperatures not above 20 ° C, spreading a thin layer. During drying, the kidney is often mixed in order to avoid their caking and moldy, after - cleaned of impurities caught.
For crust is desired thermal drying, but allowed drying and outdoors in the sun. Pieces of bark (tube, gutter) laid out separately and periodically inverted.
Leaves with thin slices dry unevenly after drying lamina stems and petioles still soft, so they are dried until the stalks are not yet become brittle. After drying, the leaves are not removed for several days - due to the high hygroscopicity are slightly moistened and less crumble during storage. Large leaves (mother-and-stepmother, Datura, and others.) During drying is spread apart from each other at the top of the drying them flip to the other side.
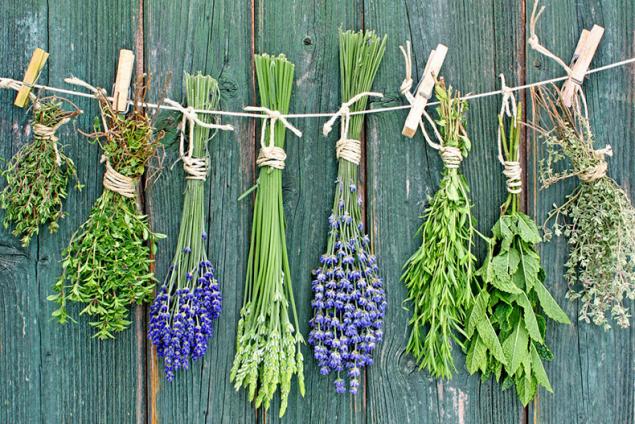
Grass hung on ropes, wire, nails in a dry ventilated area or under a canopy outdoors. It can be dried, the leaves and flowers.
Flowers and inflorescences must be dried quickly without access to sunlight, with good ventilation, laying them in a layer of 1 cm on a lattice framework, covered with gauze, etc. Cornflower, mullein and others. Do not turn, so they do not crumble and do not wrinkle. Inflorescence (marigold, tansy, chamomile, etc.) During drying can stir.
Juicy fruits before drying is purified from impurities and separate the damaged, contaminated, provyalivayut outdoors in the sun. To save the vitamin in fruits they are dried at a high temperature of 70-90 ° C (in a Russian stove, oven, and so on. D.). To check the temperature in the furnace istoplennoy have to throw it a piece of paper if it will not char and much yellowing, the raw material can be put into the oven. The valve is closed by half to create a draft of air.
When drying in the oven gas stove burner flame should be minimal, and the closet door was ajar. After drying the raw materials to be maintained in the room, so that it has absorbed moisture from the air and has an air-dry as a raw material or oven frequently overdried, and this is undesirable.
Dried fruits and seeds (fennel, anise, carrots, etc.) Lose moisture before obmolachivaniya and almost do not need drying. If necessary, they finally dried in the open air or indoors.
The roots and rhizomes (especially thick, fleshy) before drying cut lengthwise or crosswise into pieces, some plants remove bark (marshmallow, licorice, etc.). Thus the roots of many plants turn black because of the content of tannins and the effect of atmospheric oxygen, so when cutting is better to use a copper knife.
To preserve medicinal substances roots and rhizomes first provyalivayut outdoors, then dried in the sun (burnet, cinquefoil, etc.), In the Russian stove or oven. Drying start optimally at 30-40 ° C and finishing at 50-60 ° C.
Under such conditions, it provided a uniform drying of all parts of the roots, preserving their color, prevented the expansion of the active ingredients. During the drying process the roots turn over several times a day. Small roots (valerian, cyanosis blue and others.) Are dried completely, not cutting.
Korneklubni orchid (Platanthera sheeted, orchids and others.) Before drying is lowered for a few minutes in boiling water, to prevent their germination during storage, as well as to reduce the bitter taste. Dry the tubers as roots, or strung on a thread.
Drying is considered complete if the raw material contains 8-15% of free (hygroscopic) moisture.
Author: Sergei Skorobogatov

BASIC RULES purveyors
Each harvester must know:
that the harvest (a plant, its symptoms, which parts)
when to harvest (time of year, time of day)
where the harvest (habitat, designated areas)
what and how to harvest (harvesting machinery)
Kidneys harvested in the winter or early spring when they are swollen, but not yet started to grow. This is usually in March or April. By the beginning of greening renal tops (birch, poplar) cease collection as medicinal value blooming buds are not. For medical purposes, often used birch buds, poplar, pine.
Birch buds, harvested with branches starting from February. The branches are cut, tied into small twigs, dried in the open air, threshed and cleaned of impurities caught. If the kidneys are harvested during the sap flow, then pluck them with your hands or immediately threshed. The kidneys black poplar, aspen terminated hands, being careful not to crease. Pine "buds" are harvested from the young trees. Cut off the tops of the shoots and to pluck them "buds".
Dry buds should be careful: a long time in a cool ventilated place, as in a warm room, they begin to blossom.
CORU collected only from young (no older than 3-4 years) Stalks, branches and shoots in early spring, in the period of intensive Sap and kidney swelling. At this time, it is rich in medicinal substances and is easily separated because of water-saturated layer of cambium which separates the bark from the wood.
Read the smooth bark. Old, cracked bark contains a lot of cork fabric and few active ingredients. Harvested bark forest felling. With the growing collection of plant materials is prohibited, as it leads to the formation of dead wood.
To remove the bark on the trunks or escape a sharp knife make two semicircular notch at a distance of 30-40 cm from each other and connect them to each other by two longitudinal incisions. The resulting grooves are separated from the bark of wood.
When collecting bark fall areas affected lichens, with the remnants of wood, blackened on the inside. Please note that the collection of raw materials can easily make a mistake in a plant species belonging, as the bark is removed in the absence of leaves. Therefore, it is necessary to be familiar with the outward signs of this plant.
LEAVES. Collection of leaves is usually carried out in the period of budding and flowering plants. Do this in dry weather, tearing leaves hands movement from top to bottom with or without stalks them. Please note that the thick and juicy stalks slow drying of leaves. In addition, they contain little of medicinal substances.
Collect only the developed lower and middle leaves, and faded, fading, affected by insects or fungi - discarded. Juicy leaves (mother-and-stepmother, Digitalis purpurea, etc.) Are folded loosely and quickly delivered to the place of drying.
Zagotavlivaya nettle leaves, mow the plants first, and when the leaves podvyanut (lose pungency), their pluck. Grass can be dried and then leaves thresh.
Wintering small leathery leaves (bearberry, cranberries) harvested before flowering in spring or autumn after the ripening of berries.
Grass, ie above-ground part of the plant, cut or mow at the level of the lower leaves. Some higher plants (wormwood, St. John's wort, motherwort, etc.) Are cut only leafy and flowering tops of 15-20 cm in length and lateral branches.
Thick, coarse woody stems contain few medicinal substances, so collect them impractical. If you have collected a lot of plant stems (thyme, sweet clover, marjoram), they are dried completely, and then threshed leaves from the stems. When collecting the grass you can not pull out the plant with its root (with the exception of uliginose).
Flowers and inflorescences harvested at the beginning of flowering, when they do not yet have signs of wilting. At this time, they contain a lot of active ingredients, can withstand drying, retain their color and less crumble during storage and processing.
Flowers and blossoms are harvested by hand, plucking them and cutting off flower stalk, cutting scissors or shears (from trees). Inflorescence (. Baskets chamomile, calendula, etc.) collected in the phase of the horizontal arrangement of reed petals, and those plants that have only tubular flowers (tansy, chamomile and other odorous.) - In the early blooming of marginal flowers. Overripe inflorescences scattered in the collection.
Flowers - the most delicate part of the plant, so they piled loose, thin layer, preferably in a wicker basket, being careful not to crease and protected from direct sunlight
. Fruits and seeds. The greatest accumulation of medicinal substances occurs in fruits and seeds during their full maturity. Therefore, they are collected selectively as they mature, picking by hand, without stalks. In plants, the fruits of which are located in umbels or corymbs, buds break off entirely, and after drying the fruit is separated from the stalks.
Hips advisable to gather together with a cup, which is removed after drying, rubbing the fruits of his hands. In many plants the seeds mature quickly showered (anise, cumin, coriander, etc.), So they should be collected before the full maturity, when they begin to grow brown. Cut off the tops of the stems with the fruit-bearing buds, tied into small bundles, suspended for final drying and ripening in a dry, ventilated place, then threshed seeds.
Juicy fruit (berries - blueberries, strawberries, currants, stone bramble - wild cherry,. Apples - mountain ash, etc.) collect only mature, healthy. Collection is carried out manually in a shallow wicker basket trimmed in cloth. Each layer in the 5-7 cm berries shift leaves, so they will not be compressed and not compressed against each other. Gather the berries to be careful, because even a slight pressure leads to the formation of dark spots, and these places begins rot. Wet berries are not recommended to collect, as well as the wash water due to rapid spoilage.
Roots, rhizomes, tubers and bulbs - the underground parts of plants. They are usually harvested during the withering away of the aerial parts of the autumn. By this time, the greatest number of active substances accumulated in the underground bodies. It should be noted that during the harvest should be preserved remnants of aerial parts, not to be mistaken as a harvested plant. The roots and rhizomes can be harvested and early spring, before the nutrients will flow away in the aerial parts of the plants growing in tronuvshegosya.
The underground parts of the plants are dug with shovels or other tools along with the earth. Then shake the ground, the roots were washed in cold running water. After washing or cleaning from the ground raw material is spread on the grass or litter that it dried up. Then the roots and rhizomes are cleaned from the remnants of stems, fine roots, damaged or rotten parts, and finally dried.
The underground parts of some plants containing mucus and saponins (orchids, cyanosis, and others.). wash in water nelya as swollen mucous substances, raw moldy. These roots, tubers shake off the ground, remove the upper skin, dried. If the underground part of the raw material harvested is relatively clean from the earth, there is no need to wash them.
The basic rules of harvesting medicinal plants
SECURITY MEASURES workpiece
1. When harvesting of underground organs of perennial plants (trees and shrubs), and renal cortex and requires a license from forestry or forestry.
2. When harvesting of underground organs of perennial herbaceous plants per 1m2 leave 3-5 adult plants developed (for seeding), as the seeds of plants harvested in shake well.
3. Repeated harvesting of underground organs in the territory may be no earlier than 5-8 years.
4. When harvesting the aerial parts of perennial plants (trees and shrubs) rip them no more than 40%, and herbaceous perennials - up to 60%
. 5. Above-ground plant organs must be harvested without damaging other parts of the plant that are not raw materials.
SPECIAL CASES BLANK poisonous plants
1. The preform is organizing a pharmacist or other person in charge of special education.
2. The harvesting is prohibited, except those persons who have attained the age of majority.
3. workpiece in any case no unauthorized persons and children are allowed.
When harvesting is strictly forbidden to eat, rub your eyes and face with his hands, use cosmetics.
4. At the same time, you can harvest only one name of a poisonous or potent medicinal plants.
5. Procurers should be aware of the steps of first aid in case of poisoning According to the raw material.
DRYING HERBS
Timely and correct the collected raw medicinal plants must pass the next important stage of preparation - drying. From compliance with the rules of drying it depends largely on the safety of the medicinal properties of plants. The purpose of drying is rapid cessation in plants intracellular biochemical processes by which cells under the action of enzymes active substances are destroyed.
The quickest way to natural termination of biochemical processes - a cell dehydration, since processes can only go in the aquatic environment. The freshly harvested plant material water content is 60-80%.
Dehumidification only up to 20% has reduced the rate of biochemical reactions and enzyme activity, and its contents at 10-14% enzyme activity ceases completely, i.e. stops intracellular processes leading to the decomposition of the active ingredients. Furthermore, the decrease in weight of the plant leads to the development of moisture retention and termination therein various fungi and micro-organisms, which also reduces the quality of raw materials.
The methods and drying conditions of different plants vary depending on the kind of raw material, the content of active substance in it, moisture, etc. Raw materials containing essential oils (thyme, thyme, marjoram, and others.), Dried slowly at a temperature not higher than 35 ° C, since at higher oil evaporate.
Conversely, feedstock comprising glycosides (lily, Adonis) must be dried rapidly at 50-60 ° C, when the activity of enzymes that decompose glycosides quickly terminated. Some plants are dried at an even higher temperature - 80-90 ° C (hips, primrose leaves) to protect the raw materials contained in ascorbic acid (vitamin C), against oxidation.
The collected raw materials dried using natural or artificial heat. In good weather - outdoors in the sun or in the shade under the eaves, in well ventilated areas, in bad weather - in dryers, furnaces, ovens. Effective drying in attics, under a tin roof.
Most herbs should be dried in the shade, because under the influence of direct sunlight they lose their natural color, and they contain the active ingredients are destroyed. Do not dry in the sun essential-oil plants (oregano, thyme, etc.), Glikozidsoderzhaschee raw materials (Adonis, lily of the valley, zheltushnik).

TYPES OF DRY are divided:
1. Drying of natural heat: shady and sunny (it can not be subjected dyed raw materials)
. 2. drying with artificial heating (in the dryer). Its advantages: speed, temperature-controlled, can be used at any time of the year. Disadvantages (for use in industrial environments): special equipment is required, we need a special maintenance personnel, uneconomical for small batches of raw material, is expensive and not available to small businesses
. SIGNIFICANT DRYING:
1. Timeliness drying (no later than 2 hours after collection)
2. Preparation of the raw material to the drying
3. Selecting the temperature
4. Clean the drying room
FEATURES
Buds are dried carefully, for a long time in a cool place at temperatures not above 20 ° C, spreading a thin layer. During drying, the kidney is often mixed in order to avoid their caking and moldy, after - cleaned of impurities caught.
For crust is desired thermal drying, but allowed drying and outdoors in the sun. Pieces of bark (tube, gutter) laid out separately and periodically inverted.
Leaves with thin slices dry unevenly after drying lamina stems and petioles still soft, so they are dried until the stalks are not yet become brittle. After drying, the leaves are not removed for several days - due to the high hygroscopicity are slightly moistened and less crumble during storage. Large leaves (mother-and-stepmother, Datura, and others.) During drying is spread apart from each other at the top of the drying them flip to the other side.
Grass hung on ropes, wire, nails in a dry ventilated area or under a canopy outdoors. It can be dried, the leaves and flowers.
Flowers and inflorescences must be dried quickly without access to sunlight, with good ventilation, laying them in a layer of 1 cm on a lattice framework, covered with gauze, etc. Cornflower, mullein and others. Do not turn, so they do not crumble and do not wrinkle. Inflorescence (marigold, tansy, chamomile, etc.) During drying can stir.
Juicy fruits before drying is purified from impurities and separate the damaged, contaminated, provyalivayut outdoors in the sun. To save the vitamin in fruits they are dried at a high temperature of 70-90 ° C (in a Russian stove, oven, and so on. D.). To check the temperature in the furnace istoplennoy have to throw it a piece of paper if it will not char and much yellowing, the raw material can be put into the oven. The valve is closed by half to create a draft of air.
When drying in the oven gas stove burner flame should be minimal, and the closet door was ajar. After drying the raw materials to be maintained in the room, so that it has absorbed moisture from the air and has an air-dry as a raw material or oven frequently overdried, and this is undesirable.
Dried fruits and seeds (fennel, anise, carrots, etc.) Lose moisture before obmolachivaniya and almost do not need drying. If necessary, they finally dried in the open air or indoors.
The roots and rhizomes (especially thick, fleshy) before drying cut lengthwise or crosswise into pieces, some plants remove bark (marshmallow, licorice, etc.). Thus the roots of many plants turn black because of the content of tannins and the effect of atmospheric oxygen, so when cutting is better to use a copper knife.
To preserve medicinal substances roots and rhizomes first provyalivayut outdoors, then dried in the sun (burnet, cinquefoil, etc.), In the Russian stove or oven. Drying start optimally at 30-40 ° C and finishing at 50-60 ° C.
Under such conditions, it provided a uniform drying of all parts of the roots, preserving their color, prevented the expansion of the active ingredients. During the drying process the roots turn over several times a day. Small roots (valerian, cyanosis blue and others.) Are dried completely, not cutting.
Korneklubni orchid (Platanthera sheeted, orchids and others.) Before drying is lowered for a few minutes in boiling water, to prevent their germination during storage, as well as to reduce the bitter taste. Dry the tubers as roots, or strung on a thread.
Drying is considered complete if the raw material contains 8-15% of free (hygroscopic) moisture.
Author: Sergei Skorobogatov
How to cook a super medicated oil nettle
This pizza recipe you are not familiar. After trying to bake it again, you'll cook it always!