
In 1976, the surface of the Moon launched the returned capsule of the Soviet space probe "Luna 24". She successfully arrive to Earth in 1978 will find a column of soil water, but the "Luna-24" will be the last device the "golden era" of lunar exploration.
Next probe will be released on its orbit only in 1990, 14 years later, and following a soft landing will be held on
only in 2013 , as many as 37 years later. No wonder that the lunar bases and projects have become a rarity. But after a period of cooling of interest in the projects of the Moon lunar bases began to appear again, especially since there are new technologies that could be used during the development of the Moon.
The first swallow h4> Already in 1986 the project combines the two is still relevant ideas - active construction on the basis of local resources and deployment of units from the transport position. If, in the projects 50s and 60s , base, in the best case, covered by regolith, or dug a tunnel in the wall crater, here, as protection against meteorites, cosmic rays and temperature extremes, offered to produce in place of the lunar regolith concrete. In the laboratory of forty grams of lunar soil made this a one-inch (2, 54 cm) cube of concrete, which was twice as strong as conventional concrete earth. For the production of concrete needs water, it is extremely impractical to carry on Earth, and is difficult to produce locally. Therefore, in the following years, scientists conducted experiments on the lunar concrete with sulfur. Seru easier to get on the moon, and the resulting material has a very good performance.
The idea of deploying units from the transport position was first proposed in the draft Soviet base "Star", but there were hard-ins. It also proposed to use inflatable modules that under the concrete dome could be developed from small containers in full working and living areas without the risk of being punctured by a meteorite. Here is an interesting video about the project:
Lunar nineties h4> In 1989, the twentieth anniversary of landing a man on the moon, US President George HW Bush announced a program which later became known as "Initiative Space Exploration» (Space Exploration Initiative, SEI). It was supposed to build the space station «Freedom», the return of man to the moon on a regular basis and the flight to Mars. With such an incentive in the United States has several well-developed projects lunar bases.
First Lunar Outpost (FLO), 1992
In 1992, this project seemed paradoxically - in the era of reusable space shuttle all elements FLO were disposable. Superheavy rocket, built on technology "the Saturn-V», deduced the moon two modules - manned and unmanned:

Withdrawal manned module i>
The unmanned module had a height of as much as 14 meters and after landing weighed 35 tons. On board were supplies for the expedition lasting 45 days. Residential unit served module station Freedom, and Energy is provided by solar panels.

The unmanned module on the Moon i>
Piloted unit had an initial mass of 95 tons, two thirds of which was fuel, and a crew of 4 people. Unlike missions "Apollo" manned unit sat on the Moon in its entirety. It was not very economical in terms of fuel, but in this case may be selected for any part of the moon landing - "Apollo" with the scheme meeting in lunar orbit could only sit at the equator.

Manned Module i>
45-day expedition included three eight-surfacing a week for each astronaut and nine trips to the rover at a distance of 25 km. The weight of scientific equipment up to three tons, which includes a set of experiments in physics, geology, astronomy, and biology. Also, the astronauts had to carry out experiments on extraction of mineral resources and production of construction materials from the lunar regolith.
The project has ruined the high cost and lack of commercial use of technologies in parallel exploration of the Moon - extra heavy missile was overkill for commercial satellite launches. And the ambitious program SEI decreased sharply - despite winning the Cold War, the US has enough economic problems.
LUNOX, 1993
The high cost of FLO has created a project that tried his best to save money. The US has no extra-heavy missiles? But the Cold War is over, and it is possible to agree with Russia, which has "Energy". And the astronauts can run on a modification of the Space Shuttle, which instead of reusable spacecraft can deliver a one-time step. To carry the fuel to the moon is very expensive? Well, just bring hydrogen and oxygen 's get on the ground.
It was assumed that in the "Energy" will be launched unmanned components:

And the astronauts will fly on a one-time modification of the space shuttle:
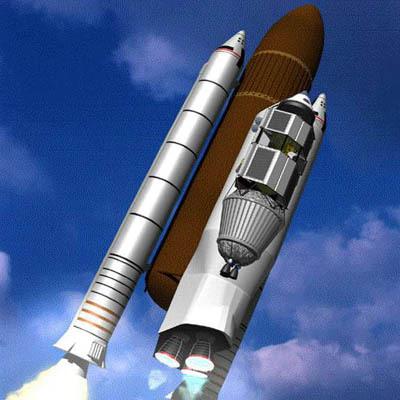
But in case of accidents or delays system components designed versatile and can start at any of the two boosters.
First on the Moon flew reactor and oxygen plant. The second flight departs set of six machines - two "harvester" is going to the ground, the two "tanker" transporting oxygen, and two "porter" had to be used for working with heavy loads. And the next flight came two rover central hub station and mobile energy sources, scientific equipment, supplies and spare parts.

Works Oxygen Plant, left, foreground, "harvester" right "tanker» i>
After six unmanned launches "Energy" / "Shuttle-C" to the Moon had to go first 2 people for two weeks - to collect base. Fully assembled base could then take an expedition of 4 for up to 45 days. The supplies for each required a separate expedition unmanned launch.
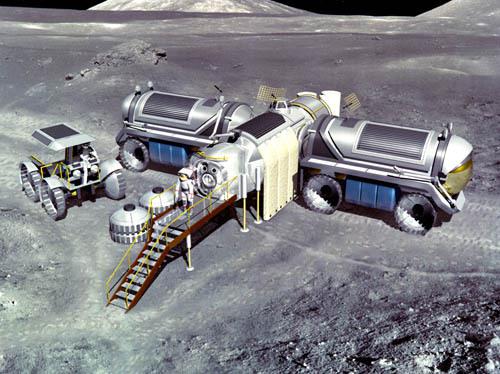
The collected database i>
Two rover mobile energy sources could go on an expedition to hundreds of kilometers. And after 45 days, a manned module refueled ten tons mined from the soil of oxygen and went to the Earth:

But in 1993, NASA has shifted to the construction of the ISS and plans to fly to Mars.
Early Lunar Access (ELA), 1993
The desire to further reduce the cost of lunar missions led to project ELA, where the maximum use of existing achievements. First rocket "Ariane 5" or "Titan-IV» in orbit booster "Centaurus". Then manned module is based on the "Apollo" put into the orbit Space shuttle docked with the upper stage and went to the moon.
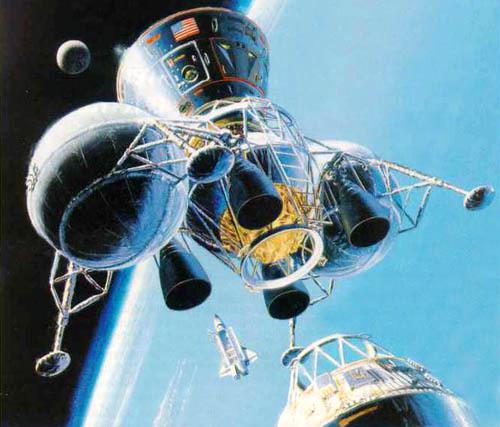

The docking with the upper stage in Earth orbit i>
LANTR, 1994
For the trip to the moon, landing on its surface, launch and return to Earth requires a lot of fuel. The desire to reduce the amount of fuel on each mission has generated an interesting project LANTR - for flights "Earth's orbit - an orbit of the Moon" was supposed to use nuclear tug and manned spacecraft, which would be based between flights to the ISS. And for the flights "the orbit of the moon - the surface - orbit" - the shuttle to chemical engines, which brings the hydrogen to be from the Earth at a nuclear shuttle, and oxygen have been mined from the lunar soil.

Start a nuclear shuttle to orbit the Earth i>
«Mouse" in Russian h4> «dashing ninetieth" could not completely stifle the dream of space. And the convenience of mobile base "Star" domestic developers do not want to lose. As a result, 93-95 Years Designer IA Kozlov and astronomer VV Shevchenko, who worked at the State Astronomical Institute. Sternberg, drafted a completely mobile base. On three legs with a crawler drive were three cylinder with a diameter of 5 m and a height of 7 m. The construction was assembled in orbit and land on the Moon in its entirety. Then, for protection from cosmic rays space between the cylinders is filled with lunar soil. It remained to wait for the lunar spacecraft with the crew, and "lunar supertank" could hit the road.

By the way, it is not located on top of the solar panels. Not far from the mobile base was to go nuclear reactor and transmit 100 kW of power at microwave frequencies. The design of the top, the so-called "Rectenna", protruding antennas and the receiver of this radiation.
Dejavu h4> In 2004, President George W. Bush (now a junior) has announced a program to return to the moon. As part of the "Constellation" was considered many options for lunar missions that relied on interesting technological solutions. For example, the base modules can be loaded on a special six-legged wheel chassis and transported them:

And in the foreground shows two rover LER (Lunar Electric Rover), a prototype of which was built in life-size, was tested in the world and even now entertains the a spectacular shot .
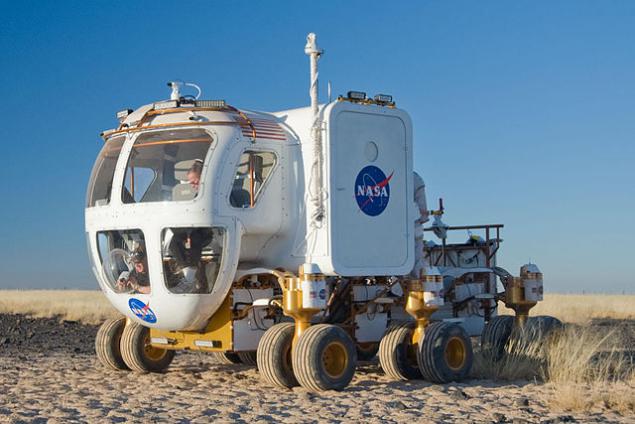

But in 2010 President Obama has closed the program "Constellation", and now NASA, as well as 20 years ago, aims to Mars.
Private initiative h4> An interesting project has appeared in recent years in Russia. The "Seven moon" Lin Industrial companies involves the use of existing domestic developments. As a manned spacecraft to be used mastered the "Soyuz" (recently I had the idea to use the TCS, which in the 80s flew in the cargo version), the upper stage to do on the basis of "Frigate" and run it "Angara". As an objective named Malapert mountain near the moon's south pole. There can not do without a nuclear reactor, some solar panels, and at the bottom of craters should be water. An interesting solution is to protect against radiation and meteorites - modules are not immediately covered with soil, and put them on the roof, which has covered the ground. This scheme allows to rebuild the database with no problems digging modules. More information - in presentation .
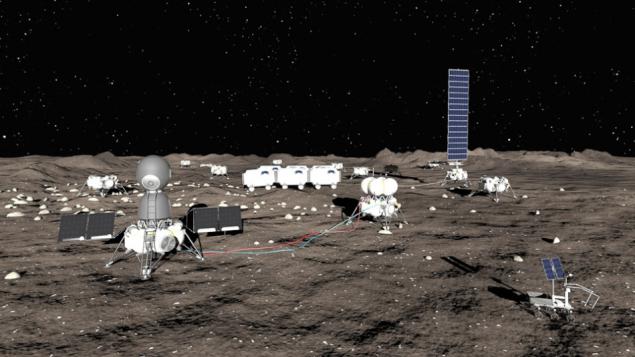
In the foreground to the left of manned spacecraft to the right - a tanker with fuel for the return journey. In the background is seen the base modules and solar power i>

Scene from the presentation of the scheme base i>
New Technologies h4> The new director of the European Space Agency, Johann-Dietrich Werner is known as a supporter of the idea of a lunar base. It is interesting and symbolic that the current draft ESA something repeats the project in 1986. Again proposed to use an inflatable module, but to replace the lunar concrete came to a 3D printer - the rover will print a porous base and fill it collected lunar soil. On the outer cover construction is supposed to require about three months. Video shows the idea is understandable without translation:
Return to the Moon - it is not fast, technology does not stand still, I think, we will see a lot of interesting ideas for lunar bases.
Similar publications on the tag «освоение Moon ».
Source: geektimes.ru/post/262374/






































