1267
Interesting lunar space and tasks

The Moon and Mars are vying for a place in the most promising space body for manned missions in the XXI century. In a previous publication I brought the case for the moon. And now we will talk about what a place on the Moon will be the most interesting, and what it can do.
General characteristics h4> The fact that the moon is constantly turned to one side of us, lunar day and night last for approximately two weeks, and its axis of rotation is almost perpendicular to the plane of the ecliptic, meaning that some of its parts have special properties:
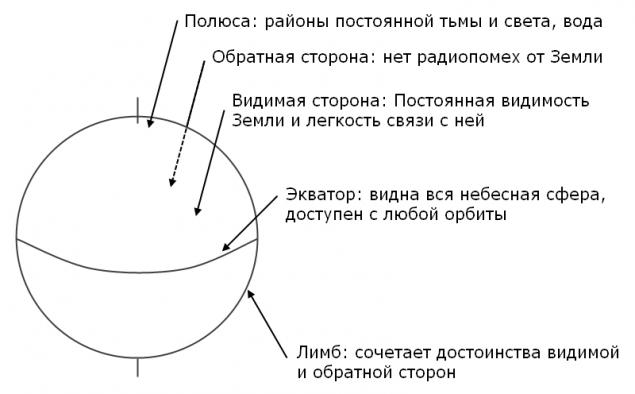
Pole
Land of Eternal Light are the obvious candidates for the installation of solar panels, which is the polar circle two weeks lunar night would be useless.
But craters abound located at the poles, forming areas where sunlight never looks:
On the surface of the moon water ice can only be maintained in places sunlight and heat the surface over 100 ° C under vacuum vaporize all the ice. In addition to water in these depressions can be of simple organic compounds of non-biological origin (such as methane), brought by comets. Water and hydrocarbons can be used for the operation of the base, reducing the volume requirements of goods shipped from the Earth. And if they would be quite a lot, and production will be easy, it will be possible to produce and fuel for missiles launched from the moon.
Equator
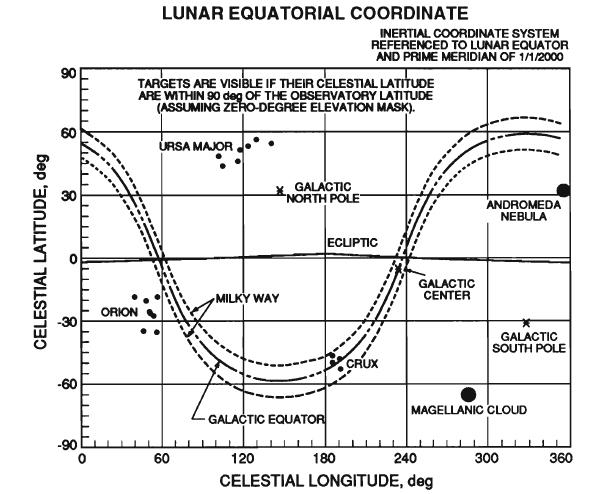
Example celestial maps projected on the surface of the moon. The object is seen when the difference of the object and the observer latitude smaller than 90 °. Longitude object varies with the movement of the moon in its orbit i>
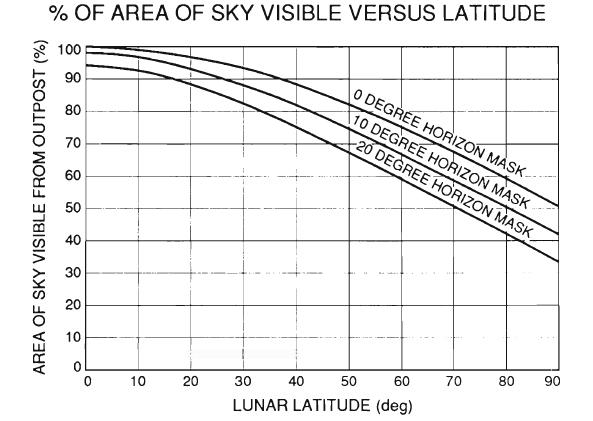
The graph shows the appearance of the sky, depending on the latitude of the observer on the moon. Except in the case of sight to the horizon shows the visibility for the partial overlap of the horizon relief. I>
An optical telescope on the moon would work in close to the space conditions without suffering from atmospheric interference.
Besides the astronomical benefits, the lunar equator is convenient in terms of ballistics. The fact that the landing near the equator can be any inclination of the orbit of the spacecraft. In contrast to the pole to which it is necessary to spend extra fuel on the formation of the orbit with an inclination of -90 °.
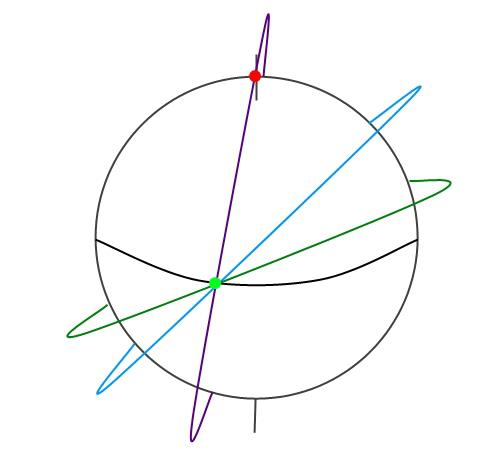
Any orbit crosses the equator. A pole is only available for polar orbits i>
The fact that on the surface of the lunar equator can not be water ice does not completely inhibit the operation of local resources. First of all, you can use the lunar regolith as a building material. The solar oven allows relatively easy to create a molten regolith bricks or more complex units. And if you heat the regolith to 700-1000 ° C, then it will be possible to remove nitrogen, oxygen and carbon, in small quantities it is present. Yes, a small concentration is expected, about 100 grams of each element per cubic meter of soil, but in the case of a serious construction of these valuable elements can be incorporated into a closed life-support system.
The Other Side of the Moon

The visible side of the Moon

Limb

Thus, the areas near the limb of the moon will go on the back side and reappear on the visible. Using terrain features will be available almost any desired percentage of visibility of the Earth. In the area of the limb would be very interesting to place telescopes of various ranges. Direct connection to the Earth will create a unique record interferometer base. And if the angular resolution of the radio band, though achieved in the project will exceed the "Radioastron" but not by orders of magnitude, the optical interferometer is a range of more than 60 times "vigilantly" any combination of only ground-based telescopes. A permanent lunar base will allow to serve these telescopes and their failure is not fatal.
narrows the range of h4> From the general considerations that the moon has four of the most interesting area: the South Pole, the North Pole, the eastern equatorial dial, western equatorial limb:

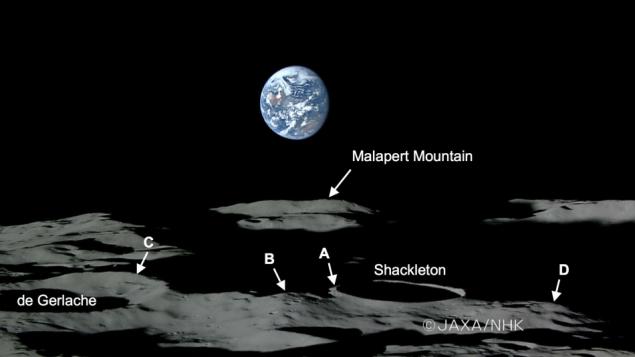
North Pole
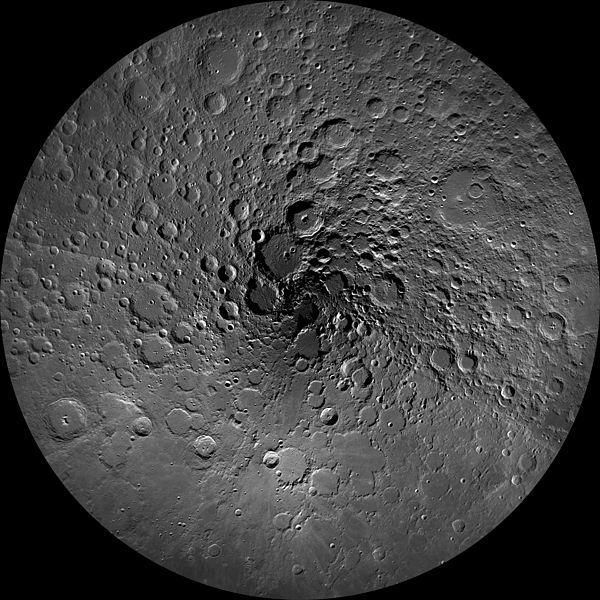

A general view of the North Pole of the Moon i>
Pole
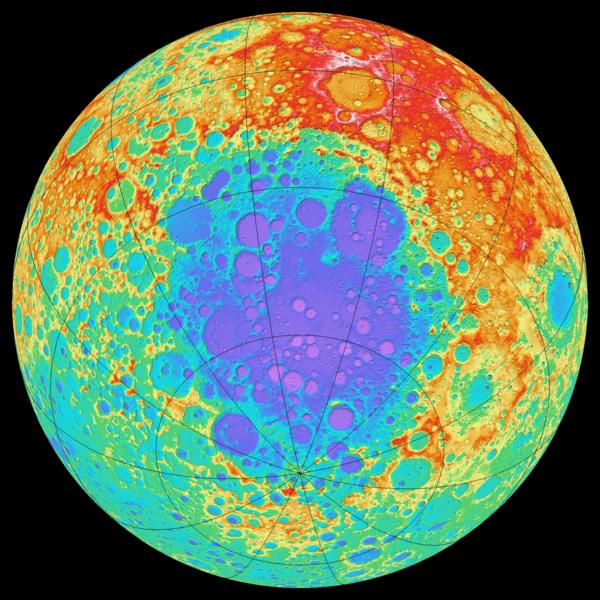
Topographic map of the lunar south pole. Blue - lower field, red - high i>

Photo South Pole Infrared i>
In considering options NASA lunar base at 88 ° S, 50 ° E:

eastern equatorial limb
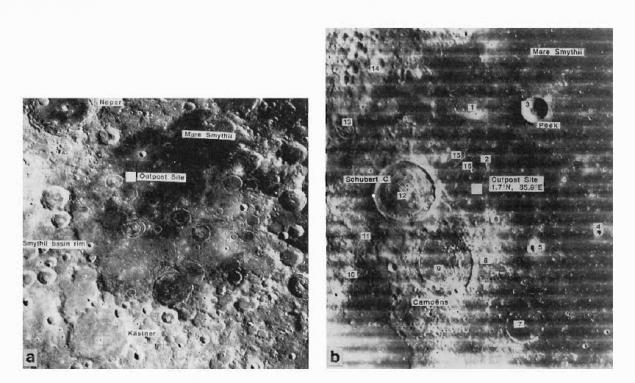
These numbers refer to the place special geological interest i>
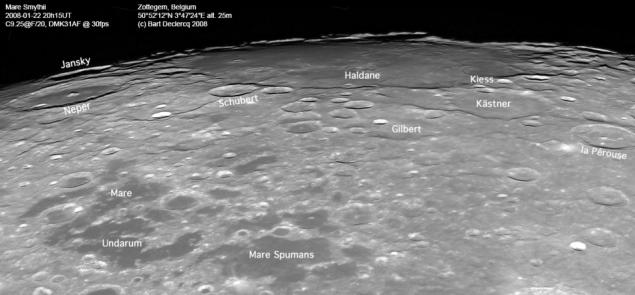
The same area, shooting from the ground, a small height of the sun emphasizes the terrain i>
western equatorial limb
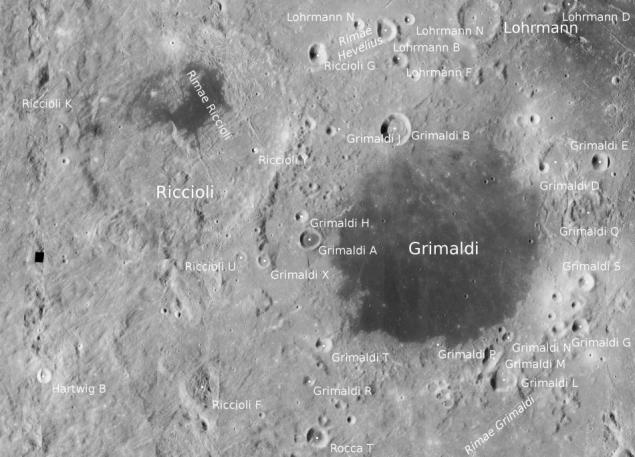

In addition to these areas as potentially of interest specified: Sea of Dreams, Sea of Tranquility, the crater Aristarchus (which is very often observed transient lunar phenomena), Pyrenees lunar crater Tsiolkovsky and others.
In a future article we will talk about the projects of lunar bases and on more specific technical aspects.
Similar publications are tagged with «мысли the future of space exploration ».
Additional Resources h4>
head to place a lunar base from the book "Near-Earth resources». list of interesting places < / a> on the Moon, prepared the program "Constellation». about lunar Long Baseline Interferometry. the visible side of the moon (for the general development).Source:






































