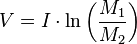Errors fiction or thinking about why stop astronautics

The entire twentieth century science fiction a lot of talent and wrote about space exploration. Heroes' Hius "gave humanity Uranium wealth of Golconda, the pilot worked Pirks Captain Space bulk carriers, the solar system went leader-konteyneronostsy and bulker-Trump, and I'm not talking about all the mystique of travel to the mysterious monoliths. However, the 21st century has not met expectations. Humanity stands shyly in the hallway of the cosmos is not selected on an ongoing basis on the Earth's orbit. Why did it happen and what to hope for those who would like to read in the news about the increase in the yield of the Martian apple?
Violinist does not need h4> The first paradox we face - people are not the most appropriate subject for space exploration. Science fiction writers who came up with the cosmic expedition could rely only on the historical experience of the pioneers of the Earth - navigators, explorers, the first aviators. Indeed, what, like, the conquest of Mars will be different from the conquest of the South Pole? Both are unsuitable for life without preparation environment need to carry with them supplies, and outside of the ship or at home can not go out without putting on special equipment. But fiction writers and futurists have not been able to predict the development of electronics and robotics, and robotics researchers are usually described in anecdotal vein:
I had a half-hour break from writing and hear complaints about my neighbor, kibernetista Shcherbakov. You probably know that north of raketodroma is building a grand underground plant for the processing of uranium and transuranidov. People work six shifts. Robots - around the clock; Great car, the last word of practical cybernetics. But, as the Japanese say, the monkey falls from the tree, too. Who came to me Shcherbakov, angry as hell, and said that the gang of idiots mechanical (his own words) tonight pilfered one of the largest warehouses ore, taking it obviously for an unusually rich deposit. Program robots were different, so in the morning part of the warehouse was in warehouses raketodroma, part - the entrance to the Geological Survey, and some do not know where. The search continues. I> blockquote> But none of the famous authors did not think that the robot in space has many advantages over man:
In contrast to the human, the robot only needs power and thermal balance. Do not have to drag along dozens of tons of greenhouses, food, water, oxygen, clothing and hygiene products, medicines and other things. The robot can be sent in one direction without return. The robot is able to work for years. Experience "Voyager", rovers or "Cassini" says that now is not correct to speak about the years and decades. The robot is able to work for years in conditions that are deadly to humans. Probe "Galileo" received a dose of 25 times the lethal to humans and then worked in orbit for 8 years.
We live in a logistic curve h4> The second error fiction was that they expected a linear or exponential development of astronautics. Although more in 1838 opened such a thing as the logistic curve. What is this terrible beast? For example, consider the history of aviation:
1900. The first clumsy shelves, the first records - flights to several kilometers with one passenger. 1910. The first scouts, fighters, bombers, mail and passenger planes. 1920-1930-e. Mastering fly at night, the first transcontinental flight. 1940. Aviation - a serious military force and transport. 1950. Jet engines give a new impetus to the development of aviation - new speed, range and altitude, even more passengers. 1960-70e. The first supersonic passenger aircraft and widebody, aviation qualitatively more accessible. 1980-90e. Braking. The development of more and more expensive, firms, developers are combined into a giant company. And planes more similar to each other. the 2000s. Limit. Two giant "Boeing" and "Airbus" makes an identical machine, supersonic passenger planes generally died out.
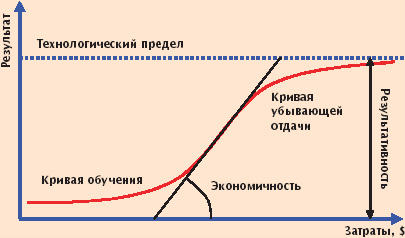
In astronautics situation is exactly the same:
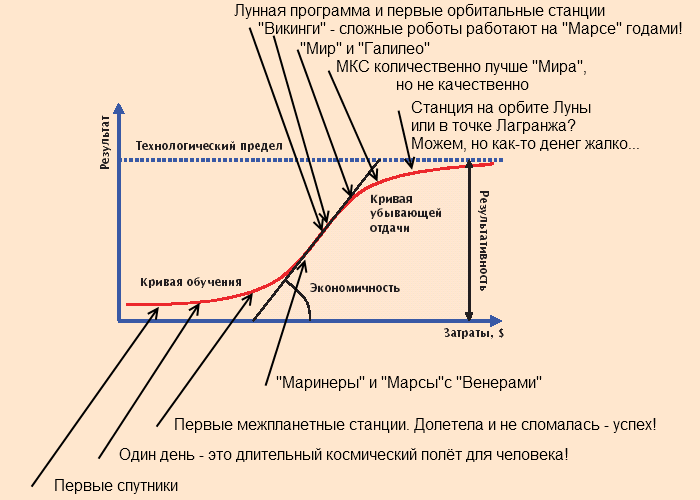
To simplify the graph S-curve graph can impose costs on the achievement of this level:
And the sadness of our "today" is that in space on existing technologies, we are close to saturation level. Technically, you can fly into the manned version to the moon and even Mars, but somehow I feel sorry for the money.
Lay KC - get gravitsapu h4> Next sad aspect braking leap into space - not yet found something very valuable that is worth spending money on space exploration beyond Earth orbit. Note that in Earth orbit is now plenty of commercial satellites - communication, TV and the Internet, weather, map. And all of them have a tangible benefit in money. And what is the use of manned flight program to the moon? Here официальный list results lunar program US worth about $ 170 billion (in 2005 prices):
The Moon - not the primary object is the terrestrial planets, with their evolution and internal structure similar to Earth. The Moon ancient and keeps a history of the first billion years of evolution of the terrestrial planets. Li > The youngest lunar rocks are about the same age as the oldest of the earth. Traces of the earliest processes and events that may have influenced the Moon and the Earth can be found now on the Moon. Moon and Earth are genetically related and formed from different proportions of a common set of materials. The moon is lifeless and does not contain live organisms or organic matter of local origin. The Moon rocks originated from high-temperature processes without water. They are divided into three types: basalt, anorthosite and breccia. A long time ago the Moon was melted to great depth and formed a magma ocean. Mountains of the Moon rocks contain fossils of early, low density, which floats on the surface of the ocean. The ocean of magma was formed by a series of huge asteroid impacts that formed the pools filled with lava flows. The Moon more asymmetric, possibly due to the influence of the Earth. Moon's surface is covered with pieces of rocks and dust. This is called the lunar regolith contains a unique radiation history of the Sun, which is important for understanding climate change on Earth. Cost-effective energy source. An integral element of the production of anything valuable and necessary. The food / drug / vitamin fundamentally new quality. Luxury or a source of pleasure.
The Curse of the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation h4> Here it is, Nemesis Space:
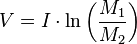
Here:
V - the final velocity of the rocket. I - engine specific impulse (how many seconds the engine for 1 kilogram of fuel can create cravings 1 Newton) M 1 sub> - initial mass of the rocket. M 2 sub> - the final mass of the rocket. What is the problem here? Take the metro scheme card required changes speed for solar system (большая picture ):
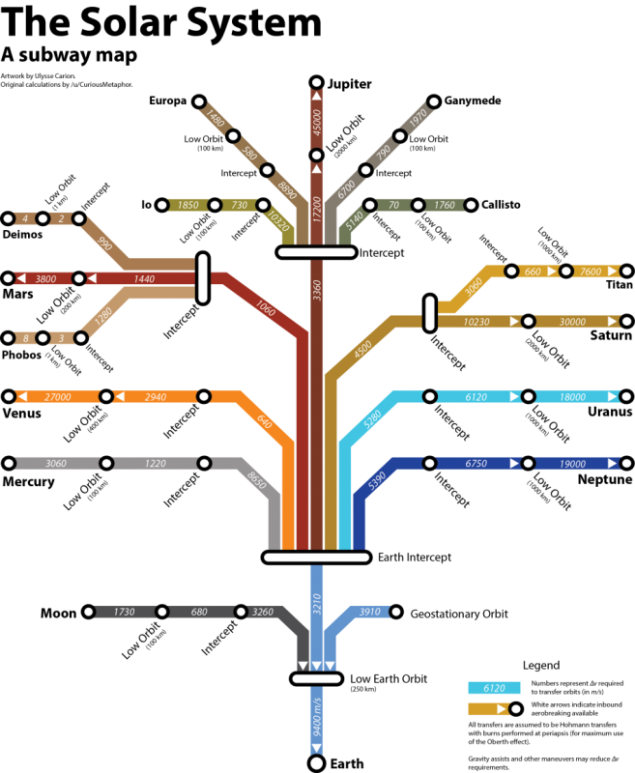
Imagine that we want to fly to Mars and back. This will be:
9400 m / s - start from the ground. 3210 m / s - withdrawal from the Earth's orbit. 1060 m / s - interception of Mars. Li > 0 m / s - entering into a low orbit of Mars (white triangle means the braking capability of the atmosphere). 0 m / s - landing on Mars (slowing down of the atmosphere). < 3800 m / s - start from Mars. 1440 m / s - acceleration from the orbit of Mars. 1060 m / s - to intercept the Earth. 0 m / s - access to low Earth orbit (slowing down of the atmosphere). 0 m / s - landing on Earth (slowing down of the atmosphere). The result is a beautiful figure 19970 m / s , which we round up to 20 000 m / s M 1 sub> = e V / I sup> * M 2 sub>
We use the free math packages Scilab. Take a final weight in the range of 10-1,000 tons specific momentum will vary from 2000 m / s (Chemical engines hydrazine) to 200 000 m / s ( theoretical estimate maximum pulse electric propulsion for today). I must say that for the maximum weight and minimum pulse will be very significant (22 million tons ), so the scale is logarithmic display.
[m2 I] = meshgrid (10: 50: 1000, 2000: 5000: 200,000); m1 = log (exp (20000 * I. ^ - 1). * m2); surf (m2, I, m1) pre> blockquote>
This beautiful plot, in fact, a clear verdict chemical engines. This is not news - chemical engines, as well in practice, you can normally run a small probe, but even fly to the moon with the crew already somewhat difficult.
Ease the conditions. First, let us assume that we start already with the Earth's orbit, and instead of 20 km / s, we need 10. Second, cut off the "tail" of inefficient chemical engines, putting a minimum value I 4400 m / s (MI hydrogen engine Space Shuttle RS-25 ):
[m2 I] = meshgrid (10: 50: 1000, 4400: 5000: 200,000); m1 = log (exp (10000 * I. ^ - 1). * m2); surf (m2, I, m1) pre> blockquote>
Logarithmic scale:
Linear scale:
Give up entirely on the chemical engines. NERVA nuclear engine had MI 9000 seconds. Restated:
[m2 I] = meshgrid (10: 50: 1000, 9000: 5000: 200,000); m1 = exp (10000 * I. ^ - 1). * m2; surf (m2, I, m1) pre> blockquote>
Linear scale:
Why I repeat these repetitive graphics? The fact that a flat area, designated as "cause for optimism" shows that, when there will be more engines MI 50000 m / s in the solar system will be possible to more or less tolerable to fly without a launch mass of ships in millions of tons. And ERE, which are now, have IAs 25000-30000 m / s ( example, SPD 2300 ). < br /> However, it should be understood that the reason for optimism is very discreet. Firstly, they need to deliver thousands of tons into Earth orbit (which is extremely difficult). Second, the existing ERE have little traction, and to accelerate from a suitable acceleration should be put mnogomegavattnye reactors.
We construct another interesting chart. Let us know the final weight - 1,000 tons. Construct the dependence of the initial mass of the specific impulse, and final velocity:
[VI] = meshgrid (10000: 2000: 100000 50000: 5000: 200,000); m1 = exp (V. * (I. ^ - 1)) * 1000; surf (V, I, m1) pre> blockquote>
This graph is interesting because it is in some sense a look into the more distant future of mankind. If we want a comfortable and fast trip through the solar system, you will have to go by another order of magnitude higher in the development of specific impulse - need engines with the IAs in the hundreds of thousands of meters per second.
There are no fish h4> Mankind differs cunning and ingenuity. Therefore, many ideas have been invented in order to facilitate access to space. One of the most important parameters characterizing the barrier that we want to jump - the price of a kilogram launch into orbit. Now, according to various estimates (from Vicky removed this column, here, for example, другой source ) for various launch vehicles, the price is in the range of $ 4000- $ 13000 per kg into low Earth orbit. They tried to come up with in order to make it easier, cheaper and easier to get at least into orbit?
Reusable system. Historically, this idea has already once fall in the "Space Shuttle". Who is doing Elon Musk, planning to plant the first step. We wish him every success, but based on its past failure do not think it will be a qualitative leap. In the best case, the cost will fall to a few percent. Single Stage to Orbit. not gone beyond projects , despite repeated attempts. Air Launch. There successful project for a small payload, but does not scale under heavy loads. Безракетный space launch . Invented a lot of projects, but they all have a fatal flaw - require astronomical investments that can not be "recapture" without the full completion of the project. While the space elevator, a fountain or a mass driver will not be completely built and launched, no profit from it.
What heart to calm down h4> How can cheer up after these sad thoughts? I have two arguments - one abstract and fundamental, the other more specific.
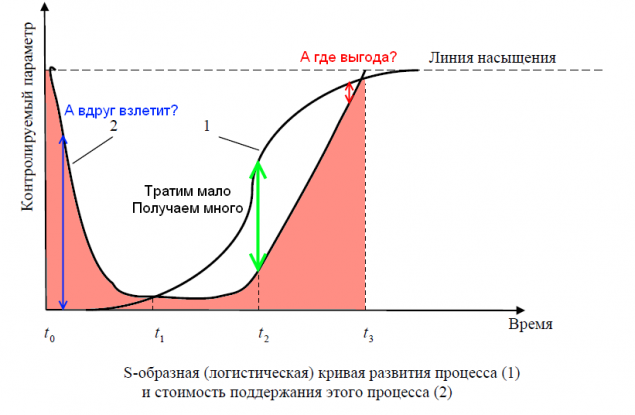
First, progress in general - is not one S-curve and a lot of them, that constitutes just such an optimistic picture here:
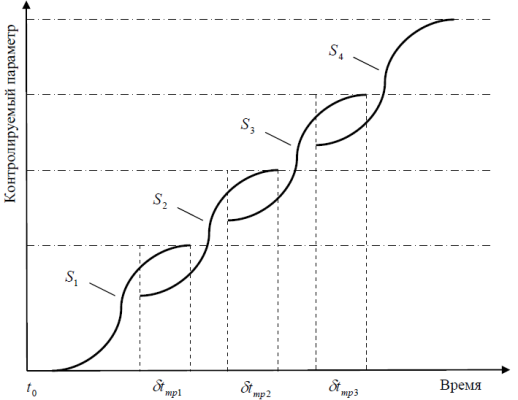
In the history of aviation can be identified, for example:
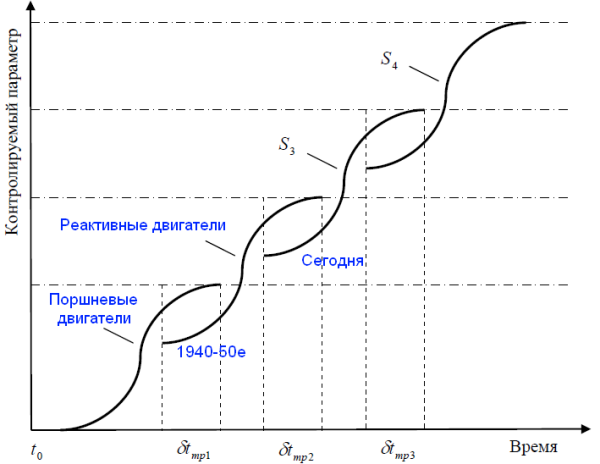
And, certainly, we are standing in a similar point in space development. Yes, there has been some stagnation, and even a possible setback, but humanity heads are better representatives pierces the wall of knowledge, and in some cases, not yet seen, the emerging shoots of a new future.
The second argument - is going without much hype news about the development of a nuclear reactor for transport and energy module:
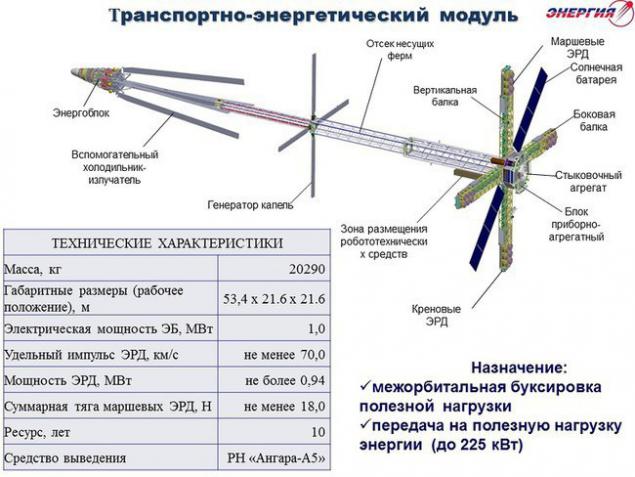
The most recent news on this project were in the summer - собрали first TVEL . Work, even without regular publicity, obviously being on, and we can hope for an appearance in the next few years a fundamentally new device - a tug of nuclear electric propulsion.
PS h4> This is somewhat unkempt thought, let's call them the first iteration. I would like to get feedback - maybe I had missed or incorrectly identified the significance of the phenomenon. Who knows, maybe after treatment feedbacks will be more harmonious concept or come up with something interesting?
KDPV here . Illustrations S-curves from old Alexis Learn Anpilogova .
Source: geektimes.ru/post/242168/