1959
Steampunk computer Albert Michelson
It turns out that in the 19th century there were computers that can perform complex mathematical calculations. One of the unique copies - harmonic analyzer Albert Michelson. The instrument performs the Fourier transform. This feature is widely used today in computer science, signal processing, physics, number theory, combinatorics, probability theory, cryptography and other fields.
In honor of the 100th anniversary of the harmonic analyzer Michelson published бесплатная eBook with magnificent illustrations, which describes the principle of operation of this wonderful instrument.
American physicist Albert Michelson known invention named after him Michelson interferometer and precise measurement of the speed of light. In 1907 he won the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the creation of precision optical instruments and the spectroscopic and metrological investigations carried out with their help." Creating a harmonic analyzer while seemed not the most important of his work.
So what's inside this device.
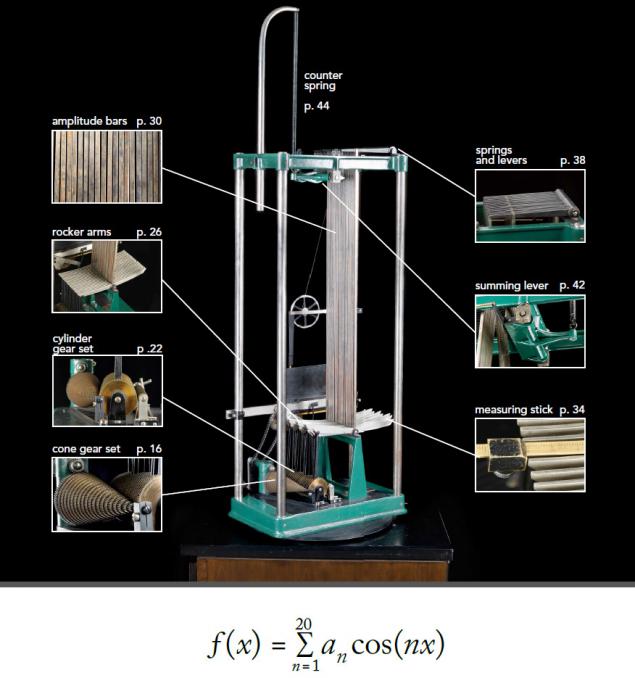
The whole system is driven by a chain.

Next, the action takes conical gearbox, fixed together (all transmission rotate together). The box converts the constant movement of the chain in one of the 20 values of the required machine. At the smallest gear teeth 6, the next 12, then 18 and so on to 120.

Conical gearbox transmits the rotation to the pre-calibrated cylindrical gearbox.

Vertical twigs transmit vibrations to the gears on the concave cylindrical box cranks.
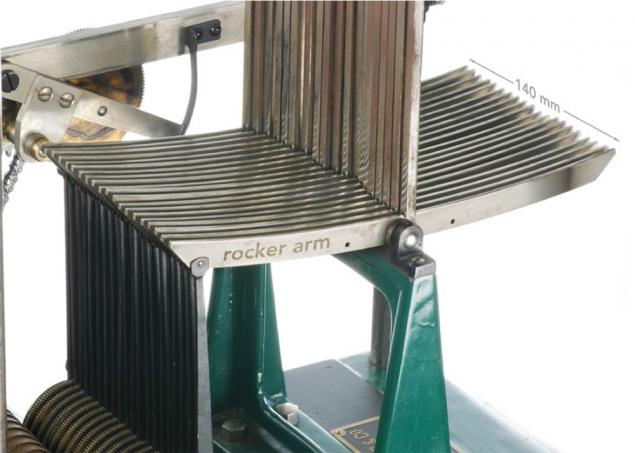

A number of rods varies up and down.
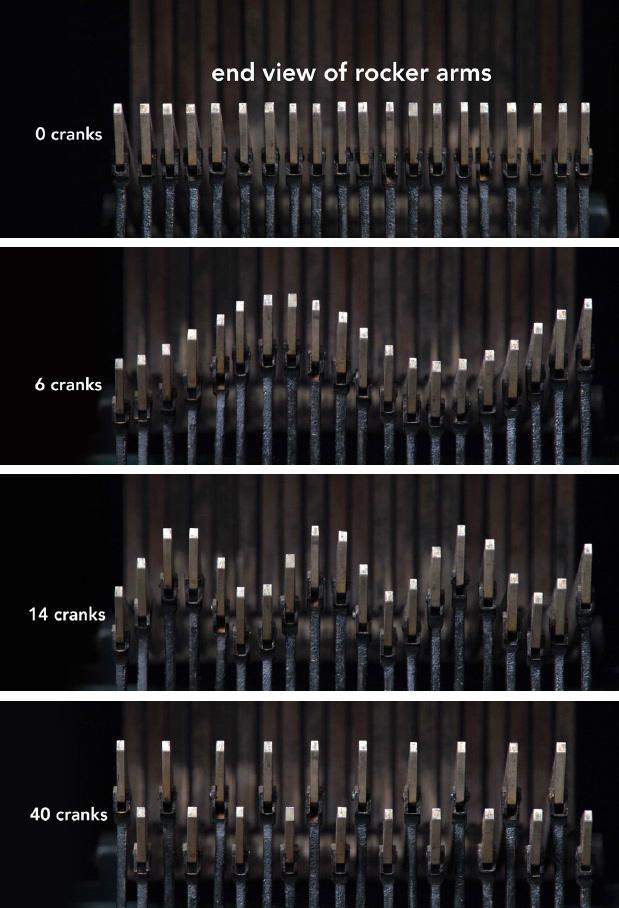
If you look at this series, it is a sine wave with a frequency corresponding to the number of turns of the handle.
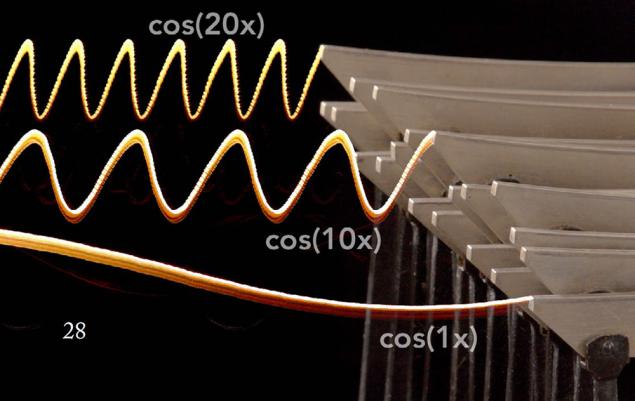
Twenty-long vertical rods of approximately 80 cm (amplitude bars) need to change the sine wave transmission levers at the top.

Moving the lower end of the rod on the surface of the rod, we set the value of the amplitude of harmonic oscillations. For the most accurate measurement device is equipped with a movable wooden ruler constipation.
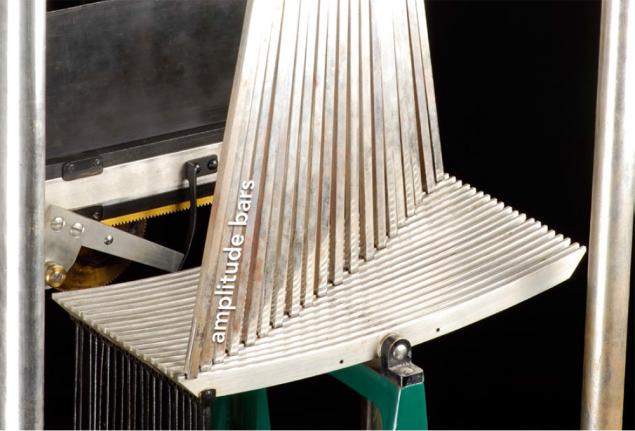

At the top of the machine levers 20 move in accordance with the movements of the rods.
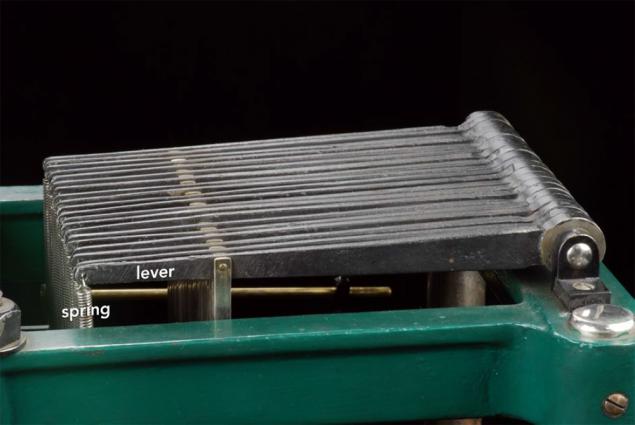

Their movement is transmitted to the one resulting lever bizarre (summing lever), and then - to the computational spring vertically disposed at the top of the structure.
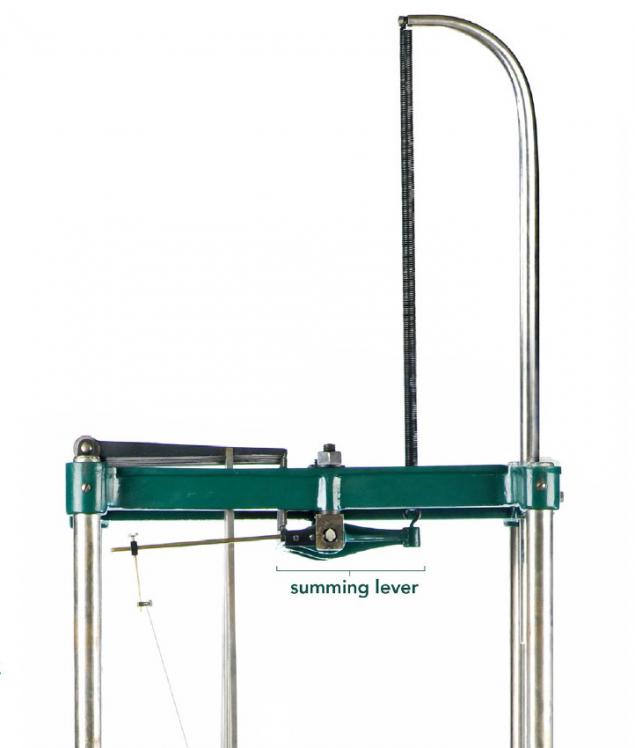

Since the scope of rods only enough to move the spring only a few millimeters, the device provides amplification mechanism to provide a vivid picture of the output (height). Plus six assists to compress / stretch across the width of the graph.
To record on a moving belt used in many ways. For example, in this instance insert a marker.
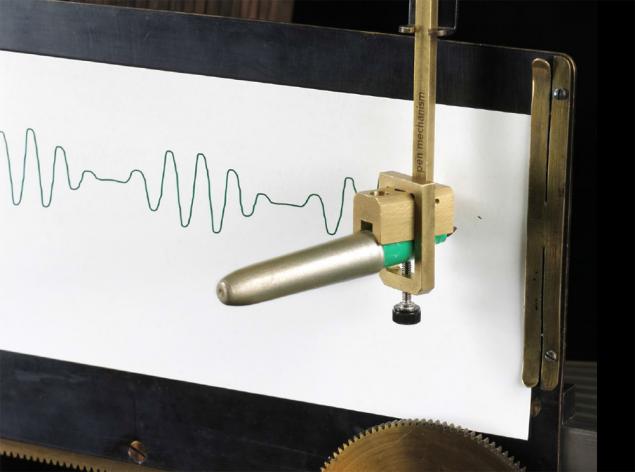
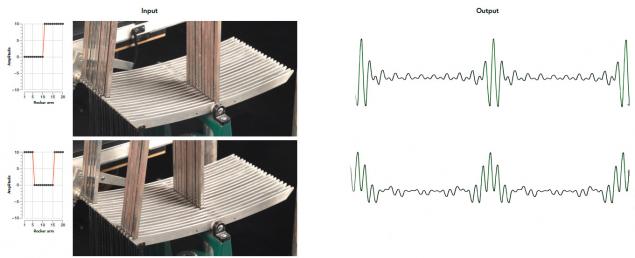
Here are some examples of sinusoids, which are obtained at the output of the different settings of the amplitude rods.
Photos with descriptions harmonic analyzer collected in бесплатной eBook (PDF) . There is series of videos about the computer Michelson. Published an introductory video below.
In the following three details the principles of operation and design of the device.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/242260/
In honor of the 100th anniversary of the harmonic analyzer Michelson published бесплатная eBook with magnificent illustrations, which describes the principle of operation of this wonderful instrument.

American physicist Albert Michelson known invention named after him Michelson interferometer and precise measurement of the speed of light. In 1907 he won the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the creation of precision optical instruments and the spectroscopic and metrological investigations carried out with their help." Creating a harmonic analyzer while seemed not the most important of his work.
So what's inside this device.
The whole system is driven by a chain.

Next, the action takes conical gearbox, fixed together (all transmission rotate together). The box converts the constant movement of the chain in one of the 20 values of the required machine. At the smallest gear teeth 6, the next 12, then 18 and so on to 120.

Conical gearbox transmits the rotation to the pre-calibrated cylindrical gearbox.

Vertical twigs transmit vibrations to the gears on the concave cylindrical box cranks.

A number of rods varies up and down.

If you look at this series, it is a sine wave with a frequency corresponding to the number of turns of the handle.

Twenty-long vertical rods of approximately 80 cm (amplitude bars) need to change the sine wave transmission levers at the top.

Moving the lower end of the rod on the surface of the rod, we set the value of the amplitude of harmonic oscillations. For the most accurate measurement device is equipped with a movable wooden ruler constipation.

At the top of the machine levers 20 move in accordance with the movements of the rods.

Their movement is transmitted to the one resulting lever bizarre (summing lever), and then - to the computational spring vertically disposed at the top of the structure.

Since the scope of rods only enough to move the spring only a few millimeters, the device provides amplification mechanism to provide a vivid picture of the output (height). Plus six assists to compress / stretch across the width of the graph.
To record on a moving belt used in many ways. For example, in this instance insert a marker.

Here are some examples of sinusoids, which are obtained at the output of the different settings of the amplitude rods.

Photos with descriptions harmonic analyzer collected in бесплатной eBook (PDF) . There is series of videos about the computer Michelson. Published an introductory video below.
In the following three details the principles of operation and design of the device.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/242260/