1064
Why are we in space do not fly on holiday
It was possible then to fly on Veterans domestic civil aircraft: Yak-42 and Tu-154, and looking at the ragged band of sealing gaskets, shabby paint on the fuselage, and the wing of sweep under shaking clouds, thinking about space. Namely, the question: why has not our ships travel through outer space, no flight "Moscow-Moon" and why no hurry to Jupiter in search of alien Obelisk?
To some it's hard to believe, but the Earth technology long ago reached a level that can provide at least the mass flights to the Moon and back. You can fly to Mars and if you are lucky with the weather. In fact, in many modern aircraft are not inferior to spaceships, but in something and excel.
What's the difference?
The pressure drop in a normal passenger flight is not as strong as in space flight, but the body of the aircraft during the operation have had to endure drops hundreds of times, in contrast to the spacecraft, if this is not the Shuttle / Buran. At an altitude of 10 km atmospheric pressure is ⅓ of the surface, i.e. the pressure difference, which maintains the aircraft and spacecraft in orbit - it is only a third of the atmosphere.
One atmosphere is a lot or a little? For example, one can afford to feel that the two atmospheres is immersed in water for 10 meters. This dive on the shoulder just trained person without any equipment, and athletes in general ныряют 100 meters or more, to say nothing about the possibility of nuclear submarines and submersibles. For example, a record bathyscaphe "Trieste" in 1960 successfully passed nearly 1,100 atmospheres, which is more than eleven times higher than the pressure at the surface of Venus.

In 1985 the submarine & quot; Комсомолец" set a record dive to 1027 m, ie withstood 100 atmospheres, equivalent to landing on Venus. The normal depth of immersion of modern nuclear submarine is 300 meters, which is, again, 30 times the load on the spacecraft.
Another thing is that when you start from the Earth to orbit the ship can withstand much more severe congestion due to high acceleration, so the UC-42 is unlikely to fly to the space, if it is simply bolted to the rocket. But if you use the traditional crafts for flight into orbit, and a light carrier on the route "the Earth's orbit Moon", the task is simplified.
Space cold is also not so dangerous as it might seem. I once talked about this and repeat. Here we have a graph of the thermometer near-Earth satellite TechedSat 2. Readings in Celsius:
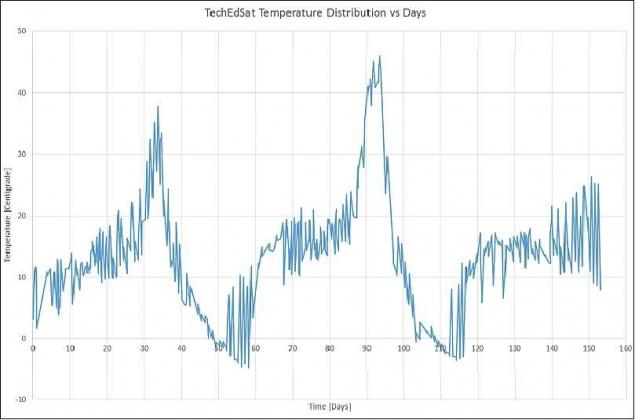
As we can see no horror with "minus one hundred" or "absolute zero».
Spaceship freezes only when it is in the shade, but if we're talking about interplanetary flights, the flight will be difficult to find shade. Although on the surface of the Moon would have to be warmed ... or build amusement parks in the пиках Eternal Light . As the distance from the Sun, will become colder, but the scale of the solar system Mars is not so far away, and in the way to Jupiter already have to grab a stove.
The problem of thermal insulation of the aircraft difficult. Vacuum - it's a great thermos, and the plane is constantly cooled by ram air. The submarine is even worse: the heat capacity of water is much higher, though there is no water cooler -1 Celsius. On board the space shuttle or the station is constantly working mass units which heat internal environment. Therefore, the spacecraft often urgent cooling rather than heating. Wind in space no fans out in the cold, too useless, so they had to drop heat only through the infrared. You can look at the huge radiators International Space Station. They can be confused with the solar panels, but the difference is that the radiators are always located in a perpendicular plane to the batteries.
The system of maintaining the thermal regime - is an important component of the spacecraft, which we will talk separately.
The risk of radiation in space is also seriously overrated. Until now, go on the Internet myths like mission to the moon is not possible because of the damaging effects of space radiation. The crew of the ISS, according to supporters of this myth, lives only by the magnetic field of the Earth.
In fact, the Earth's magnetic field provides only partial protection from cosmic radiation, and able to withstand high-energy particles, interstellar and intergalactic . The real barrier to cosmic radiation is only the Earth's atmosphere, and the closer to the ground the better. So I would not recommend sunbathing on alpine resorts, or at least do it in aluminum shorts.
For pilots in the open space of cosmic radiation exposure is about twice more intense than at the height of the ISS, but not because of the fact that the station is flying under the cover of the magnetic field, so that it covers the Earth itself. Ie near-Earth cosmic particles bombarding the station only "from above", and interplanetary trajectories travelers get from all sides.
Even the finest Martian atmosphere reduces the radiation exposure by half, in contrast to the conditions in orbit. Thus, on the surface of Mars, background radiation on board the ISS. This is despite the fact that the magnetic field of a planet at all. Accordingly, in the open space of Mars, in a calm sunny weather, radiation only twice higher than the ISS.
However, after examining the radiation conditions during flight rover Curiosity, NASA concluded that the flight to Mars is too dangerous for people because it exceeded the total cumulative dose. But it is in excess of half, and only when the path in one direction takes 360 days. If, however, provide for more efficient engines for the trip to Mars, and reduce flight times at least twice, the threat of radiation have fit into the limits of the permissible.
The only thing that is a real radiation risk to astronauts - is a solar flare and solar proton events. Here, of course it requires serious protection, but above it already works. Even though the body of the spacecraft is able to provide significant protection to pilots.
Here is a chart comparing the intensity of the radiation exposure to the satellite NASA ACE (red line), which is located at a distance of 1, 5 million km from the Earth to the Sun, with the sensor RAD aboard the Mars rover Curiosity (white dots), which at the time of observation is in the lowered capsules on the migratory path.
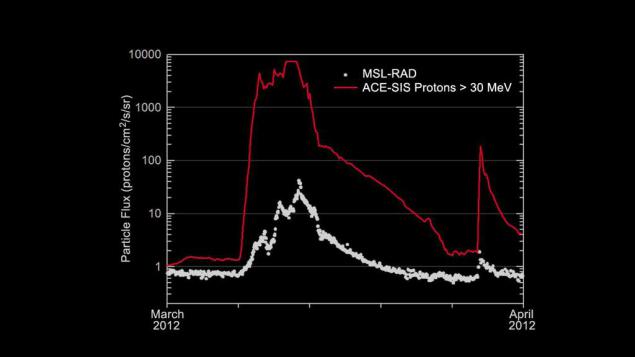
Visible evidence a direct correlation, but "naked" ACE receives exposure of several orders of magnitude greater. If, however, inhabited bay pilots and passengers to use a more complicated protection scheme, the effect of solar radiation will be even weaker. The easiest option - shielded by a layer of water or fuel, they still have to take with them a lot. In addition, the probability of hitting a solar flare in the ship is quite low - it happens from time to six months, if you focus on the results of Curiosity. Ie Going to a week-long tour to the moon, it is enough to consult the forecast sunny weather, not loading a heavy radiation protection.
The radiation belts, which are formed around the Earth under the influence of the magnetic field of the planet, also pose a risk only in a solar flare. At such times, the intensity of particles in them increases a thousand times. But in the quiet time they can be overcome relatively safe short path, in the footsteps of "Apollo».
In his review, I'm not trying to prove that travel to other planets, it is easy and simple. The spacecraft is more difficult than an airplane or a submarine, it must work in an absolutely hostile environment, because it does not jump out with a parachute, not vyplyvesh to the surface with the breathing mask. Numerous life-support devices to duplicate and troirovat, and then still manage to fit them in a very limited and to make them as light as possible. Therefore, the spacecraft so far - in fact, piece-manual work, and the development of the new - a long and complicated case.
Blog test cosmonaut ship PTK NP
But while mankind has managed to create a huge aviation industry, for example alone, Boeing-747 in 1969 produced nearly 1,500 pieces. And during the Cold voynushki two powers competed with hundreds (!) Of submarines. Why are there air force and navy, with the current technology, any Maybach or Bentley for technical excellence not give spacecraft. So now there are no technological barriers nastrogat couple dozen kosmolaynerov "Earth-Moon," heel "Earth-Mars" and send one to Jupiter, with Tetris instead of the on-board computer.

Why are they still there?
To some it may seem that the case in the high cost of the space program. But, for example, for the development of spacecraft CST-100 NASA paid Boeing about to less than half that spent on the development of aircraft Sukhoi Superjet 100. And all US spending on civil space from 1958 to 2011 was not exceeded the defense budget for 2011.
The reason for the underdevelopment of the passenger space industry is at a low interest of people in such flights. Civil aviation has evolved to a large extent due to the close economic ties between the US and Europe. For quick crossing of the Atlantic for a long time struggled sailors, and they took the baton from aviation. The development of science, technology and the aviation industry passed in response to commercial demand.
In other words, airline tickets, submarines and Maybach have buyers. On the Moon and Mars are no buyers. There's no amusement parks, no oil fields and gold pits, no stock exchanges, no hostile lunatics / Martians under the Stars and Stripes hammer and sickle ... So it turns out, humans for a long time can fly, but no one wanted to pay for industry kosmoperevozok. More precisely there, but their number is negligible and solvency.
For the development of manned space flight, start of the regular cosmic messages of interplanetary economics and business, humanity needs an outpost in another world. Will it be on the Moon or Mars, it is not so important, but it is not, and we will hang out at the surface of the Earth, which is just retelling the Soviet doctrine of "the study of the solar system with machine guns," born after the defeat in the lunar race.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/233119/
To some it's hard to believe, but the Earth technology long ago reached a level that can provide at least the mass flights to the Moon and back. You can fly to Mars and if you are lucky with the weather. In fact, in many modern aircraft are not inferior to spaceships, but in something and excel.
What's the difference?
The pressure drop in a normal passenger flight is not as strong as in space flight, but the body of the aircraft during the operation have had to endure drops hundreds of times, in contrast to the spacecraft, if this is not the Shuttle / Buran. At an altitude of 10 km atmospheric pressure is ⅓ of the surface, i.e. the pressure difference, which maintains the aircraft and spacecraft in orbit - it is only a third of the atmosphere.
One atmosphere is a lot or a little? For example, one can afford to feel that the two atmospheres is immersed in water for 10 meters. This dive on the shoulder just trained person without any equipment, and athletes in general ныряют 100 meters or more, to say nothing about the possibility of nuclear submarines and submersibles. For example, a record bathyscaphe "Trieste" in 1960 successfully passed nearly 1,100 atmospheres, which is more than eleven times higher than the pressure at the surface of Venus.

In 1985 the submarine & quot; Комсомолец" set a record dive to 1027 m, ie withstood 100 atmospheres, equivalent to landing on Venus. The normal depth of immersion of modern nuclear submarine is 300 meters, which is, again, 30 times the load on the spacecraft.
Another thing is that when you start from the Earth to orbit the ship can withstand much more severe congestion due to high acceleration, so the UC-42 is unlikely to fly to the space, if it is simply bolted to the rocket. But if you use the traditional crafts for flight into orbit, and a light carrier on the route "the Earth's orbit Moon", the task is simplified.
Space cold is also not so dangerous as it might seem. I once talked about this and repeat. Here we have a graph of the thermometer near-Earth satellite TechedSat 2. Readings in Celsius:

As we can see no horror with "minus one hundred" or "absolute zero».
Spaceship freezes only when it is in the shade, but if we're talking about interplanetary flights, the flight will be difficult to find shade. Although on the surface of the Moon would have to be warmed ... or build amusement parks in the пиках Eternal Light . As the distance from the Sun, will become colder, but the scale of the solar system Mars is not so far away, and in the way to Jupiter already have to grab a stove.
The problem of thermal insulation of the aircraft difficult. Vacuum - it's a great thermos, and the plane is constantly cooled by ram air. The submarine is even worse: the heat capacity of water is much higher, though there is no water cooler -1 Celsius. On board the space shuttle or the station is constantly working mass units which heat internal environment. Therefore, the spacecraft often urgent cooling rather than heating. Wind in space no fans out in the cold, too useless, so they had to drop heat only through the infrared. You can look at the huge radiators International Space Station. They can be confused with the solar panels, but the difference is that the radiators are always located in a perpendicular plane to the batteries.
The system of maintaining the thermal regime - is an important component of the spacecraft, which we will talk separately.
The risk of radiation in space is also seriously overrated. Until now, go on the Internet myths like mission to the moon is not possible because of the damaging effects of space radiation. The crew of the ISS, according to supporters of this myth, lives only by the magnetic field of the Earth.
In fact, the Earth's magnetic field provides only partial protection from cosmic radiation, and able to withstand high-energy particles, interstellar and intergalactic . The real barrier to cosmic radiation is only the Earth's atmosphere, and the closer to the ground the better. So I would not recommend sunbathing on alpine resorts, or at least do it in aluminum shorts.
For pilots in the open space of cosmic radiation exposure is about twice more intense than at the height of the ISS, but not because of the fact that the station is flying under the cover of the magnetic field, so that it covers the Earth itself. Ie near-Earth cosmic particles bombarding the station only "from above", and interplanetary trajectories travelers get from all sides.
Even the finest Martian atmosphere reduces the radiation exposure by half, in contrast to the conditions in orbit. Thus, on the surface of Mars, background radiation on board the ISS. This is despite the fact that the magnetic field of a planet at all. Accordingly, in the open space of Mars, in a calm sunny weather, radiation only twice higher than the ISS.
However, after examining the radiation conditions during flight rover Curiosity, NASA concluded that the flight to Mars is too dangerous for people because it exceeded the total cumulative dose. But it is in excess of half, and only when the path in one direction takes 360 days. If, however, provide for more efficient engines for the trip to Mars, and reduce flight times at least twice, the threat of radiation have fit into the limits of the permissible.
The only thing that is a real radiation risk to astronauts - is a solar flare and solar proton events. Here, of course it requires serious protection, but above it already works. Even though the body of the spacecraft is able to provide significant protection to pilots.
Here is a chart comparing the intensity of the radiation exposure to the satellite NASA ACE (red line), which is located at a distance of 1, 5 million km from the Earth to the Sun, with the sensor RAD aboard the Mars rover Curiosity (white dots), which at the time of observation is in the lowered capsules on the migratory path.

Visible evidence a direct correlation, but "naked" ACE receives exposure of several orders of magnitude greater. If, however, inhabited bay pilots and passengers to use a more complicated protection scheme, the effect of solar radiation will be even weaker. The easiest option - shielded by a layer of water or fuel, they still have to take with them a lot. In addition, the probability of hitting a solar flare in the ship is quite low - it happens from time to six months, if you focus on the results of Curiosity. Ie Going to a week-long tour to the moon, it is enough to consult the forecast sunny weather, not loading a heavy radiation protection.
The radiation belts, which are formed around the Earth under the influence of the magnetic field of the planet, also pose a risk only in a solar flare. At such times, the intensity of particles in them increases a thousand times. But in the quiet time they can be overcome relatively safe short path, in the footsteps of "Apollo».
In his review, I'm not trying to prove that travel to other planets, it is easy and simple. The spacecraft is more difficult than an airplane or a submarine, it must work in an absolutely hostile environment, because it does not jump out with a parachute, not vyplyvesh to the surface with the breathing mask. Numerous life-support devices to duplicate and troirovat, and then still manage to fit them in a very limited and to make them as light as possible. Therefore, the spacecraft so far - in fact, piece-manual work, and the development of the new - a long and complicated case.
Blog test cosmonaut ship PTK NP
But while mankind has managed to create a huge aviation industry, for example alone, Boeing-747 in 1969 produced nearly 1,500 pieces. And during the Cold voynushki two powers competed with hundreds (!) Of submarines. Why are there air force and navy, with the current technology, any Maybach or Bentley for technical excellence not give spacecraft. So now there are no technological barriers nastrogat couple dozen kosmolaynerov "Earth-Moon," heel "Earth-Mars" and send one to Jupiter, with Tetris instead of the on-board computer.

Why are they still there?
To some it may seem that the case in the high cost of the space program. But, for example, for the development of spacecraft CST-100 NASA paid Boeing about to less than half that spent on the development of aircraft Sukhoi Superjet 100. And all US spending on civil space from 1958 to 2011 was not exceeded the defense budget for 2011.
The reason for the underdevelopment of the passenger space industry is at a low interest of people in such flights. Civil aviation has evolved to a large extent due to the close economic ties between the US and Europe. For quick crossing of the Atlantic for a long time struggled sailors, and they took the baton from aviation. The development of science, technology and the aviation industry passed in response to commercial demand.
In other words, airline tickets, submarines and Maybach have buyers. On the Moon and Mars are no buyers. There's no amusement parks, no oil fields and gold pits, no stock exchanges, no hostile lunatics / Martians under the Stars and Stripes hammer and sickle ... So it turns out, humans for a long time can fly, but no one wanted to pay for industry kosmoperevozok. More precisely there, but their number is negligible and solvency.
For the development of manned space flight, start of the regular cosmic messages of interplanetary economics and business, humanity needs an outpost in another world. Will it be on the Moon or Mars, it is not so important, but it is not, and we will hang out at the surface of the Earth, which is just retelling the Soviet doctrine of "the study of the solar system with machine guns," born after the defeat in the lunar race.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/233119/
The principle of operation Media
Backtracker: an early warning system for the cyclist on the car back