June 5th NASA released the results of the first phase of the program NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) for the fiscal year 2014.
The purpose of NIAC - collection of revolutionary ideas that will make great leaps in the development of the aerospace industry.
As a result of the competition were selected 12 concepts including 3 works from Jet Propulsion Laboratory (NASA).
The winners of the first stage, see below, and now a little bit about NIAC.
What is NIAC h4> In the mid-90s, at the headquarters of NASA, on the basis of aerospace technology was decided to appeal to people outside the agency to search for new ideas. So, in 1998, was created by NASA Institute of Advanced Concepts, which existed until 2007 and 9 years of work collected in 1309 of which 168 proposals were supported financially.
In 2008, NASA planned to resume exploration of the Moon and considered the possibility of resuscitation NIAC ideological support for their plans. But one desire was little and Congress requested the National Research Council (National Research Council) to evaluate the previous activities and make recommendations for improving the effectiveness of NIAC.
The research report was followed in 2009 and contained the one hand extremely positive characteristics, recommendations creation of such an institution, on the other hand - a few suggestions to optimize the structure.
In 2010, the NIAC was revived, but he was no longer a private institution, and presented himself as part of the Program Space Technology NASA.
The program is currently NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) remains part of Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD) and continues to accumulate innovative ideas that may one day change the boundaries of the possible.
The overall structure of the program h5> Each year, the program opens its virtual doors to all comers, with funding from NASA may receive only US residents.
Aggregation is performed by means of ideas:
NASA Solicitation and Proposal Integrated Review and Evaluation System (NSPIRES)
NIAC is composed of two phases:
Phase 1 for 9 months and consists of two parts.
Part A is a collection of brief descriptions of the projects meet the requirements of the program and the selection of the most promising ones for further discussion in Part B.
Finalists Part B receive funding of $ 100, $ 000 for further research.
Stage 2 lasts 2 years and is only available to those who have created or developed his concept on the basis of studies in Phase 1.
Work in Phase 2 are heavily filtered in accordance with established criteria.
NASA selects the winners of Phase 2, 500, 000 on the deeper study.
Some statistics h5> Pies below shows a breakdown of awards and amounts of investments for the period 2011-2013 recipients.
And in the table, there is also split into phases and fiscal year.
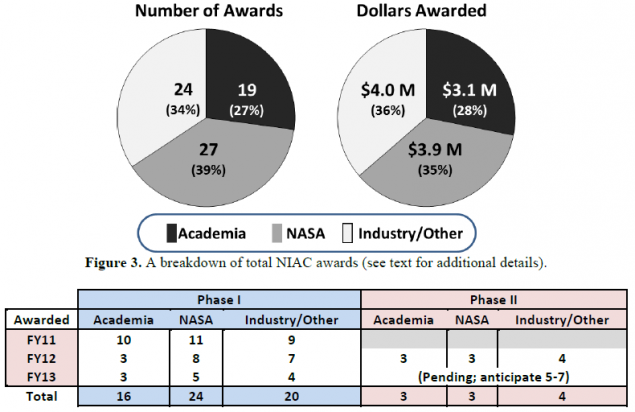
Academia - ideas from representatives of scientific institutions.
NASA - ideas from employees of NASA (naprimet Jet Propulsion Laboratory)
Industry / Other - other organizations / individuals.
Statistics from Publications Nasa Innovative Advanced Concepts
Phase January 2014 h4> This year, the finalists of the first phase of the program began, 12 projects, including such fantastic ideas as:
- A submarine to study methane lakes on Titan (Saturn).
- Using Neutrinos to explore the icy moons (Europa, Ginimed).
- Concept of safe capture asteroid fragments of rocks and other objects.
This year's finalists represent three of the eight key technology areas of Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD): support the development of life and utilization of resources, space robotic systems and space-based observations.
Just selected works affect NASA research in the study of asteroids and the outer planetary missions.