722
NASA has selected contractors for the development of housing in the deep space

Concept Interior habitable stations in deep space. Image: NASA
NASA has selected six US companies to develop prototypes of residential units in deep space. These developments are necessary for the mission with astronauts landing on Mars, which is scheduled for 2030-ies.
In carrying out the design and engineering work, NASA will provide the six companies to $ 65 million over two years, with the possibility of additional funding in 2018. Each company has to cover at least 30% of the cost of the work at his own expense. The following are the recipients of grants (including specific regional corporate units).
- Bigelow Aerospace, Las Vegas
- Boeing, Texas
- Lockheed Martin, Denver
- Orbital ATK, Virginia
- Sierra Nevada Corporation's Space Systems of Louisville, Colorado
- NanoRacks, Texas
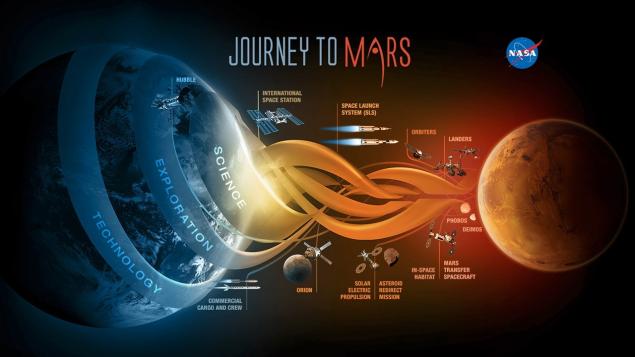
American plan for the development of Mars
As is known, according to the plan development of the Mars rocket Space Launch System (SLS) must write to the deep space spacecraft with the first astronauts to set foot on the surface of Mars. On the way to the Red Planet they need long-term housing, where people are able to live and work in the months and years without getting food and other goods from the Earth.
Each of the six companies have up to 24 months to produce a fully functional prototype of the ground and / or to conduct a thorough study of dwelling in deep space.
Made terrestrial prototypes will be used for three main purposes: to test complex 1) systems; 2) the human factor; 3) health, to determine the overall functionality of the complex. The collected information is used for the manufacture of flight of the real module, which will be sent for testing in orbit.
According to NASA conditions, residential unit must be a sealed compartment with an integrated set of comprehensive systems and components, including docking function, climate control, life support system, logistics management system, radiation protection and monitoring system, fire safety technologies and maintaining health of the crew. < br>
That's how today look projects of residential units of six companies.
Bigelow Aerospace LLC

"Inflatable" (Expandable) XBASE module (Expandable Bigelow Advanced Station Enhancement) volume 330 m3 is based on real-BEAM module volume of 16 m3, which recently deployed on the ISS.
Boeing

Lockheed Martin

Lockheed Martin intends to alter its universal module into a complete living unit.
Orbital ATK

Concept of Orbital ATK based on the cargo spaceship Cygnus, which now serves the ISS.
Sierra Nevada Corporation's Space Systems of Louisville

Prototype Sierra Nevada Corporation based on the cargo module Dream Chaser.
NanoRacks
NanoRacks partners with Space Systems Loral and United Launch Alliance united in Ixion Team alliance. They intend to explore the possibility of converting a multistage rocket upper stage in a residential unit. This low-budget solution should be suitable for any of the carrier rocket, including the SLS.
Developed residential units will be suitable for living, not only in outer space, but also in orbit. They also will be useful in future lunar missions. Generally, NASA seeks to encourage private development in this area to private companies more actively mastered the Earth's orbit, including space tourism.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/279382/
Cool men's den «The Barn»
Research: the level of physical activity should be in five to seven times higher than it is now recommended by the WHO






























