752
The space of the home, part 3: how will we live on Mars
We talked about how people will live in space colonies and on the natural satellite of the Earth — the moon. It is time to discuss how to exist on other planets. It was the turn of Mars.
The red planet is closest to Earth, except for Venus. In just 9 months to reach the point of destination. Humanity develops technologies that will allow us to get to Mars, establish a permanent base there, set mining and even terraform the planet to make life easier for the people on it.

The USSR studied the Red planet in the framework of "Mars" and "Phobos". The spacecraft Mars-1, launched November 1, 1962, was the first to be launched on a trajectory to Mars. At a distance of 106 million kilometers from Earth the device last made contact, but his purpose was to collect data about the flight: intensity of cosmic radiation, the distribution of meteoric matter, the magnetic fields of the Earth and the interplanetary environment. The Orbiter Mars-2 for over 8 months, studying the planet from orbit. Lander Mars 3 became the first spacecraft successfully stranded on the planet's surface, though, and was disconnected after 20 seconds. The orbiters Mars-2 and Mars-3 helped to explore the properties of the surface and atmosphere of Mars by the nature of the radiation, to detect thermal anomalies, to measure the temperature of the Northern polar cap. Devices with sequence numbers 4, 5, 6, 7 was taking pictures of the surface, including color, and continued to collect various data about the planet, including himicheski the composition of the atmosphere.
From 1962 to 1972 in the framework of the "Mariner" NASA sent to Mars and Venera 10 spacecraft. Mariner 4 flew by at a distance of 9 846 kilometers from the planet's surface and became the first to photograph Mars at close range. The spacecraft Mariner 6 and Mariner 7 flew even closer, at a distance of less than 3.5 thousand kilometers from the planet. Mariner 9 became the first iskusstvennym another planet and photographed about 85% of the surface. In the 1970-ies, NASA launched the program "Viking". Two devices were shipped in 1975 and worked first prior to 1978, the second to 1980. Landers took soil samples for analysis for the presence of life.
In 1996, NASA sent an unmanned research station "Mars global surveyor". In 2005, the station became the first spacecraft, filmed by another camera on extraterrestrial orbit. After nearly a decade of work communication with the device was lost.
On Mars in 1997, nearly three months he worked the Rover Sojouner, from 2004 to 2010 he was a Spirit. The planet now study opportunity, which was supposed to work only 90 days, but there are several years since January 2004, and Curiosity descended to the surface in August 2012.
Today Mars is the most studied planet in the Solar system after Earth. But colonization will solve a lot of issues.
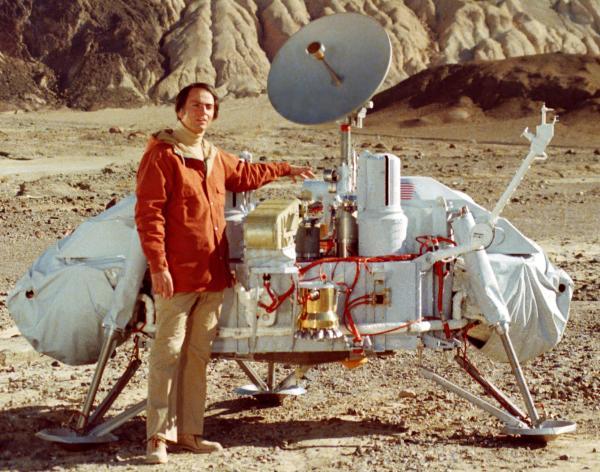

The American astronomer Carl Sagan in the layout of the automatic Martian station "Viking"
Flight
To live on Mars, you need to fly. To send to people immediately it would be a huge mistake, so it is assumed to deliver to the planet a variety of equipment that will further enable you to deploy residential buildings, modules for growing plants, a plant for the production of rocket fuel (return same ever on the Earth!)
In the USSR in the early 1960s, began to develop the heavy interplanetary ship. In parallel developed two projects. The first device Maksimova with the crew on Board had the HAB, working with the gateway for access to open space, the lander, the corrective propulsion system. Camera Feoktistov suggested the Assembly of the ship in orbit, the crew of 4, lander. The project was closed due to the lunar race.
In the United States from 2004 to 2010 she worked on the program "Constellation", in which planned manned flights to Mars. One of the goals was a new manned exploration vehicle "Orion".
Us company SpaceX is working on the Interplanetary transport system. The project involves the development of a reusable space transport to deliver people to Mars. The system will consist of a return of the launch vehicle, spacecraft and interplanetary spacecraft for refueling.
One of the main threats to a manned mission to Mars — radiation. Solar flares, garantiruyu higher dose of irradiation might have to wait in special rooms. Full protection of the spacecraft can greatly weigh it down and increase the cost of the flight. But there's another way to create a magnetic field that will need to include when strong solar flares.
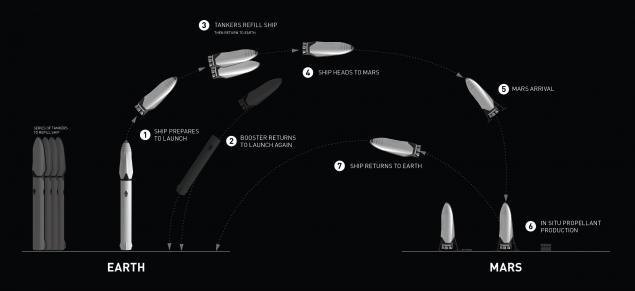
It is important to say about the failed Mars One program, which until 2015 was one of the most well-known due to the open recruitment of volunteers to fly to Mars and a huge amount of PR on the Internet, in the media and on television. Five years later, after it became clear that neither money nor technical solutions for the implementation of the project no.
Agriculture
Delivery of cargo to Mars in any case it will be quite an expensive task. Between the Windows for the flight is 26 months. The flight itself takes 9 months, plus we need time to study details, preparation and collection of the goods. Therefore, to create a colony the most important thing is as possible the Autonomous existence of people on the planet.
One of the main problems to be solved is the development of agriculture. For over fifty years scientists and astronauts investigate the effects of microgravity on seeds, think through the possible establishment of farms on space stations and other planets. In 1960, together with Belka and Strelka into orbit, sent the seeds of corn, wheat, peas and onions, and in 1974 on the orbital station "Salyut-4" was to install an "Oasis" for the cultivation of plants.
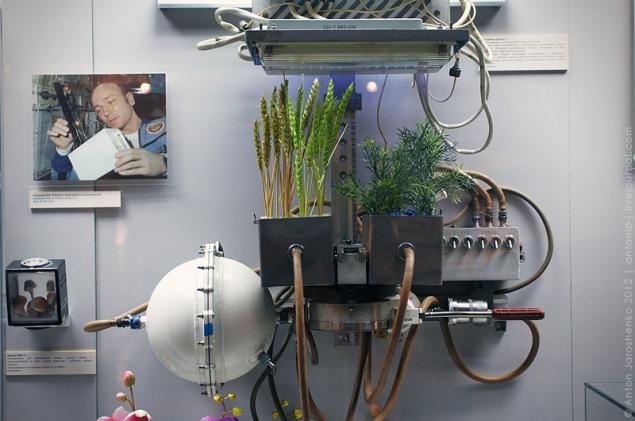

"Oasis-1" in the Memorial Museum of cosmonautics. Source
Crop space is not limited to experiments in microgravity. You need to understand how plants will behave in a non-earthly soil and in the atmosphere with a different composition. Meteor soil, as found in 2014 suitable for growing asparagus and potatoes, but for these purposes it is necessary to grind. On Mars a lot of sand and dust, it makes it easier. But there is another problem: heavy metals.
Since 2013, the Dutch scientists grow plants in simulated Martian soil. The content of heavy metals in peas, radish, rye, and tomatoes were safe for human consumption. Now research continues into other crops, such as potatoes.
The atmosphere of Mars is 95% carbon dioxide, which will help maintain the vegetation.

The researcher Vager Wamelink inspects plants grown in simulated Martian soil. Photo: Joep Frissel/AFP/Getty Images
Besides the nutrition of plants, algae and microorganisms can play a special role in the terraforming of the planet — the establishment of a suitable environment for human life.
Terraforming
Mars and now on a number of characteristics suitable for life in the presence of special equipment, including pneumonectomy. A day on Mars lasts 24 hours 39 minutes 35. The planet is the change of seasons, although Mars is twice longer. The atmosphere with a density of 0.007 to earth gives some protection from solar and cosmic radiation. There just is ice, and possibly water in liquid form.
In the process of terraforming it is possible to solve several problems. First, it is the increase in atmospheric pressure, in which water will exist in liquid form. Now water on the planet boils at +10 degrees, that is, the ice turns directly to vapor. Also when the pressure will be instead of spacesuits to use a full-pressure suit.
Secondly, the planet can raise the temperature to 10-20 degrees Celsius. Now the average temperature is -50 °C and ranges from -153 °C at the pole in winter and up to +20 °C at the equator at noon.
Third, you need to create a biosphere — populate the planet with plants, fungi, bacteria.

The dark bands — the expected flows of liquid water on Mars. Photo: NASA
At the moment there are a number of ways that, as scientists assume, will change Mars. On the planet's surface can, for example, to bring down the asteroid to heat up the atmosphere and fill it with water and gases. In orbit, you can put artificial satellites to focus the sunlight on its surface to heat up.
In order for Mars to allocate greenhouse gases and to large volumes of the necessary materials from those that are already on the planet, suggest the use of extremophiles are living creatures, including bacteria and microorganisms that can live and reproduce in extreme conditions. Some species of lichens and cyanobacteria in 34 days could adapt to simulated Martian conditions and to begin the process of photosynthesis.
Elon Musk has suggested that the most efficient method of terraforming Mars — multiple explosions nuclear warheads on its surface in certain regions. But with exposure to radiation in this case could nullify the result.
At the moment, exact solutions for the problem of terraforming no, all the methods listed above are only assumptions.
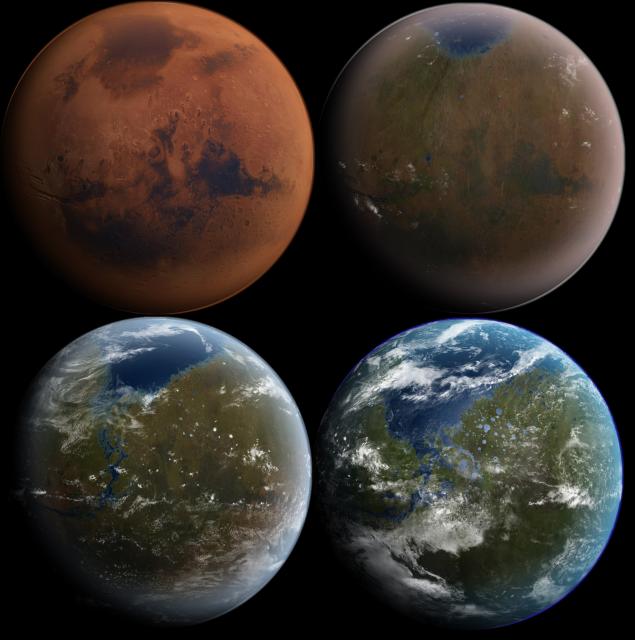

Stages of terraforming Mars. Wikipedia
Housing
Elon Musk described his plans for the colonization of Mars. The third stage is delivery of equipment for the construction of Mars Base Alpha, and the construction of a plant for the production of rocket fuel. For people who are postrony geodesic domes of glass panels with frames made from carbon fiber. These domes protect the colonists from the wind during dust storms. In the house will eventually be inflated to the air pressure that will allow people to live in a pleasant ecosystem surrounded by plants.
As in the case of the Moon, there is an assumption that life will be easier under the surface. Mars has lava tubes and caves that can be used for these purposes. The soil will allow and protect from radiation and to protect people and equipment from the meteor shower.
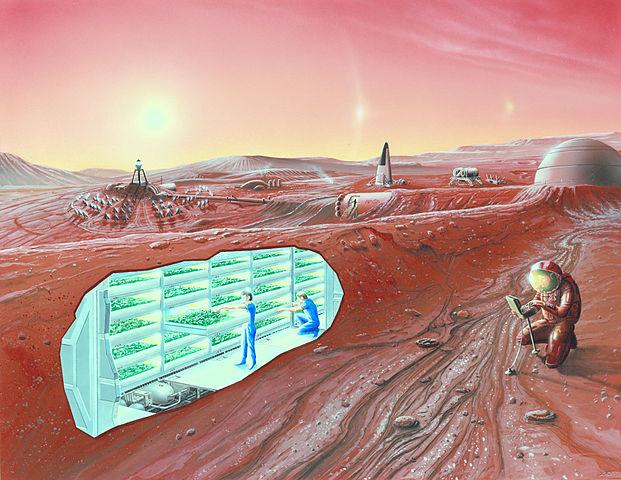
At the moment the technology of construction of buildings on Mars. In fact, all limited to any sketches and plans, the details of which will be less than in the case of the colonization of the moon. To get new ideas, NASA in 2015, held a contest among the participants: architects, engineers, and scientists. All projects must meet one point: to create some or all of the elements necessary to use a 3D printer. Also in terms of the prescribed area of the housing is not less than 93 square metres and the presence of life-support systems, sanitary units, space for cooking and sleeping places.
One of the best ideas was the project LavaHive. It's an inflatable system, some elements of which will need to be printed. One of the useful properties of such building — the ability to blow away, to collect and carry.

At least, at first glance, a realistic project — Staye A While. The building is proposed to be located under the ground under a frozen sea near the equator.
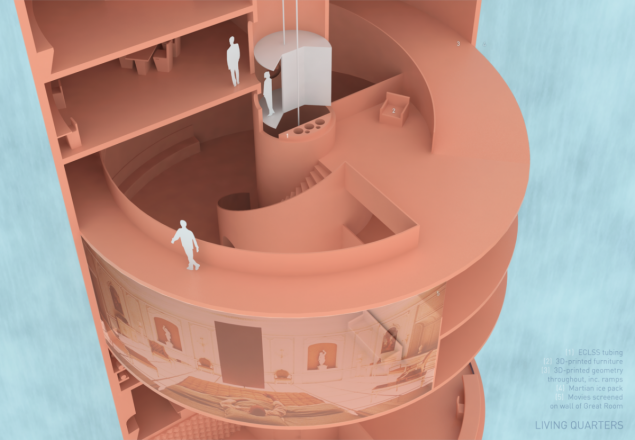
Today we have technology that allows with high probability to deliver the Mars cargo. What about people — you need to solve a host of problems, including radiation, to talk about such a long flight, which the crew will remain alive and healthy. On the planet there are materials that are in theory suitable for the construction of buildings using the same 3D printers, but the technology will need to break in to talk about its effectiveness. Taking into account the time between the launches of the ships of the colony must support themselves. To take provisions, materials and tools for such period would be wasteful, so it is important to consider agriculture on Mars.
When we fly to Mars? Will look like the home of the colonist? The exact answer is no, neither I, nor NASA nor the Russian space Agency.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/282016/
The red planet is closest to Earth, except for Venus. In just 9 months to reach the point of destination. Humanity develops technologies that will allow us to get to Mars, establish a permanent base there, set mining and even terraform the planet to make life easier for the people on it.

The USSR studied the Red planet in the framework of "Mars" and "Phobos". The spacecraft Mars-1, launched November 1, 1962, was the first to be launched on a trajectory to Mars. At a distance of 106 million kilometers from Earth the device last made contact, but his purpose was to collect data about the flight: intensity of cosmic radiation, the distribution of meteoric matter, the magnetic fields of the Earth and the interplanetary environment. The Orbiter Mars-2 for over 8 months, studying the planet from orbit. Lander Mars 3 became the first spacecraft successfully stranded on the planet's surface, though, and was disconnected after 20 seconds. The orbiters Mars-2 and Mars-3 helped to explore the properties of the surface and atmosphere of Mars by the nature of the radiation, to detect thermal anomalies, to measure the temperature of the Northern polar cap. Devices with sequence numbers 4, 5, 6, 7 was taking pictures of the surface, including color, and continued to collect various data about the planet, including himicheski the composition of the atmosphere.
From 1962 to 1972 in the framework of the "Mariner" NASA sent to Mars and Venera 10 spacecraft. Mariner 4 flew by at a distance of 9 846 kilometers from the planet's surface and became the first to photograph Mars at close range. The spacecraft Mariner 6 and Mariner 7 flew even closer, at a distance of less than 3.5 thousand kilometers from the planet. Mariner 9 became the first iskusstvennym another planet and photographed about 85% of the surface. In the 1970-ies, NASA launched the program "Viking". Two devices were shipped in 1975 and worked first prior to 1978, the second to 1980. Landers took soil samples for analysis for the presence of life.
In 1996, NASA sent an unmanned research station "Mars global surveyor". In 2005, the station became the first spacecraft, filmed by another camera on extraterrestrial orbit. After nearly a decade of work communication with the device was lost.
On Mars in 1997, nearly three months he worked the Rover Sojouner, from 2004 to 2010 he was a Spirit. The planet now study opportunity, which was supposed to work only 90 days, but there are several years since January 2004, and Curiosity descended to the surface in August 2012.
Today Mars is the most studied planet in the Solar system after Earth. But colonization will solve a lot of issues.

The American astronomer Carl Sagan in the layout of the automatic Martian station "Viking"
Flight
To live on Mars, you need to fly. To send to people immediately it would be a huge mistake, so it is assumed to deliver to the planet a variety of equipment that will further enable you to deploy residential buildings, modules for growing plants, a plant for the production of rocket fuel (return same ever on the Earth!)
In the USSR in the early 1960s, began to develop the heavy interplanetary ship. In parallel developed two projects. The first device Maksimova with the crew on Board had the HAB, working with the gateway for access to open space, the lander, the corrective propulsion system. Camera Feoktistov suggested the Assembly of the ship in orbit, the crew of 4, lander. The project was closed due to the lunar race.
In the United States from 2004 to 2010 she worked on the program "Constellation", in which planned manned flights to Mars. One of the goals was a new manned exploration vehicle "Orion".
Us company SpaceX is working on the Interplanetary transport system. The project involves the development of a reusable space transport to deliver people to Mars. The system will consist of a return of the launch vehicle, spacecraft and interplanetary spacecraft for refueling.
One of the main threats to a manned mission to Mars — radiation. Solar flares, garantiruyu higher dose of irradiation might have to wait in special rooms. Full protection of the spacecraft can greatly weigh it down and increase the cost of the flight. But there's another way to create a magnetic field that will need to include when strong solar flares.

It is important to say about the failed Mars One program, which until 2015 was one of the most well-known due to the open recruitment of volunteers to fly to Mars and a huge amount of PR on the Internet, in the media and on television. Five years later, after it became clear that neither money nor technical solutions for the implementation of the project no.
Agriculture
Delivery of cargo to Mars in any case it will be quite an expensive task. Between the Windows for the flight is 26 months. The flight itself takes 9 months, plus we need time to study details, preparation and collection of the goods. Therefore, to create a colony the most important thing is as possible the Autonomous existence of people on the planet.
One of the main problems to be solved is the development of agriculture. For over fifty years scientists and astronauts investigate the effects of microgravity on seeds, think through the possible establishment of farms on space stations and other planets. In 1960, together with Belka and Strelka into orbit, sent the seeds of corn, wheat, peas and onions, and in 1974 on the orbital station "Salyut-4" was to install an "Oasis" for the cultivation of plants.

"Oasis-1" in the Memorial Museum of cosmonautics. Source
Crop space is not limited to experiments in microgravity. You need to understand how plants will behave in a non-earthly soil and in the atmosphere with a different composition. Meteor soil, as found in 2014 suitable for growing asparagus and potatoes, but for these purposes it is necessary to grind. On Mars a lot of sand and dust, it makes it easier. But there is another problem: heavy metals.
Since 2013, the Dutch scientists grow plants in simulated Martian soil. The content of heavy metals in peas, radish, rye, and tomatoes were safe for human consumption. Now research continues into other crops, such as potatoes.
The atmosphere of Mars is 95% carbon dioxide, which will help maintain the vegetation.

The researcher Vager Wamelink inspects plants grown in simulated Martian soil. Photo: Joep Frissel/AFP/Getty Images
Besides the nutrition of plants, algae and microorganisms can play a special role in the terraforming of the planet — the establishment of a suitable environment for human life.
Terraforming
Mars and now on a number of characteristics suitable for life in the presence of special equipment, including pneumonectomy. A day on Mars lasts 24 hours 39 minutes 35. The planet is the change of seasons, although Mars is twice longer. The atmosphere with a density of 0.007 to earth gives some protection from solar and cosmic radiation. There just is ice, and possibly water in liquid form.
In the process of terraforming it is possible to solve several problems. First, it is the increase in atmospheric pressure, in which water will exist in liquid form. Now water on the planet boils at +10 degrees, that is, the ice turns directly to vapor. Also when the pressure will be instead of spacesuits to use a full-pressure suit.
Secondly, the planet can raise the temperature to 10-20 degrees Celsius. Now the average temperature is -50 °C and ranges from -153 °C at the pole in winter and up to +20 °C at the equator at noon.
Third, you need to create a biosphere — populate the planet with plants, fungi, bacteria.

The dark bands — the expected flows of liquid water on Mars. Photo: NASA
At the moment there are a number of ways that, as scientists assume, will change Mars. On the planet's surface can, for example, to bring down the asteroid to heat up the atmosphere and fill it with water and gases. In orbit, you can put artificial satellites to focus the sunlight on its surface to heat up.
In order for Mars to allocate greenhouse gases and to large volumes of the necessary materials from those that are already on the planet, suggest the use of extremophiles are living creatures, including bacteria and microorganisms that can live and reproduce in extreme conditions. Some species of lichens and cyanobacteria in 34 days could adapt to simulated Martian conditions and to begin the process of photosynthesis.
Elon Musk has suggested that the most efficient method of terraforming Mars — multiple explosions nuclear warheads on its surface in certain regions. But with exposure to radiation in this case could nullify the result.
At the moment, exact solutions for the problem of terraforming no, all the methods listed above are only assumptions.

Stages of terraforming Mars. Wikipedia
Housing
Elon Musk described his plans for the colonization of Mars. The third stage is delivery of equipment for the construction of Mars Base Alpha, and the construction of a plant for the production of rocket fuel. For people who are postrony geodesic domes of glass panels with frames made from carbon fiber. These domes protect the colonists from the wind during dust storms. In the house will eventually be inflated to the air pressure that will allow people to live in a pleasant ecosystem surrounded by plants.
As in the case of the Moon, there is an assumption that life will be easier under the surface. Mars has lava tubes and caves that can be used for these purposes. The soil will allow and protect from radiation and to protect people and equipment from the meteor shower.

At the moment the technology of construction of buildings on Mars. In fact, all limited to any sketches and plans, the details of which will be less than in the case of the colonization of the moon. To get new ideas, NASA in 2015, held a contest among the participants: architects, engineers, and scientists. All projects must meet one point: to create some or all of the elements necessary to use a 3D printer. Also in terms of the prescribed area of the housing is not less than 93 square metres and the presence of life-support systems, sanitary units, space for cooking and sleeping places.
One of the best ideas was the project LavaHive. It's an inflatable system, some elements of which will need to be printed. One of the useful properties of such building — the ability to blow away, to collect and carry.

At least, at first glance, a realistic project — Staye A While. The building is proposed to be located under the ground under a frozen sea near the equator.

Today we have technology that allows with high probability to deliver the Mars cargo. What about people — you need to solve a host of problems, including radiation, to talk about such a long flight, which the crew will remain alive and healthy. On the planet there are materials that are in theory suitable for the construction of buildings using the same 3D printers, but the technology will need to break in to talk about its effectiveness. Taking into account the time between the launches of the ships of the colony must support themselves. To take provisions, materials and tools for such period would be wasteful, so it is important to consider agriculture on Mars.
When we fly to Mars? Will look like the home of the colonist? The exact answer is no, neither I, nor NASA nor the Russian space Agency.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/282016/
Traditional fishing for carp in the Czech Republic
Jeff Bezos: people have to colonize not only the planet but also outer space






















