638
Difficult road to Mars

Crash of the Mars lander "Schiaparelli" is still under investigation, but according to coming news Prime suspect is software — the parachute was dropped on 41 seconds before landing thrusters worked for only three seconds, and the on-Board computer, confident, what is on the surface, even managed to include scientific instruments. Alas, designed to work on the surface, they are unable to collect useful data during the fall from the height of 2-4 km. The road to Mars has never been easy, and the success of recent years does not guarantee that subsequent mission will be successful. Rather, if you rely on historical statistics, the probability of success of the Mars mission is approximately equal to one second. Only humanity managed to send to Mars more than 50 vessels. Of them has not fulfilled its task in about 30 (depending on the criteria of the accident and methods of calculation devices get different numbers). At what stages and how were they killed?
Not went into orbit
The first stage of a long and difficult journey to Mars is that the device goes into orbit of the Earth. The boosters will never be 100% reliable, so each spacecraft will have the chance to suffer an accident at no fault of their own.
From the Soviet space program was a pretty simple rule of hiding the failures — if the device did not go into orbit, its launch was not announced. If he couldn't break orbit to the target, it was called "Sputnik" or "Cosmos", and reported in the media that the launch is successful. And only if the interplanetary station went to target, gave her name for the purpose of flight and number in order, for example, "Mars-1". Therefore, some units were called later, and now known by several names at once.

1M No. 1 and 2, they are the same 1960А and Mars B, which started in October 1960, failed to reach earth orbit. It was the same type of machines, whose aim was the study of Mars with the span of the trajectory. As a booster used the PH "Lightning". In one case refused control system, in other — the engine of the third stage, and both spacecraft climbed to an altitude above 100 km only for a few minutes.

2M No. 521 and 522, they Mars 1969А and B was supposed to enter orbit around Mars. They were launched in March and April 1969 in the proton. In the first case collapsed, the engine of the third stage, and the device fell in the Altai, and in the second case, the fire on the first stage led to the loss of control, emergency shutdown of the engines and the fall of the rocket near the start.

Mariner 8 was one of two spacecraft whose mission was also the first ever orbit around Mars, and was launched on may 9, 1971 But he also had no luck — the second stage immediately after power began to sway. When the vibrations increased so that turned into a somersault, the fuel stopped flowing into the engine, and step from the payload fell into the Atlantic ocean. Subsequent investigation revealed that the culprit most likely was the one diode in the circuit of amplifier loop control system, which is responsible for pitch. Damage during installation or repair was not caught on the pre-launch tests, and the cheap part killed dear interplanetary station. First entered the orbit of Mars, brother of the deceased, Mariner 9, just days before the Soviet "Mars" -2 and -3. Mariner 8 and for 2016 is the last American interplanetary station, lost during the withdrawal.
Did not leave earth's orbit
As a rule, Mars probes went to an intermediate orbit around the Earth, and from there were dispersed to Mars. And not all succeeded. Due to the fact that the intermediate orbit is chosen low enough (it saves fuel), these probes quickly was slowed down and burned in the atmosphere.

2MV-4 No. 1, Mars 1962А, was to photograph Mars with span of the trajectory started on 24 October 1962. He was going to send to Mars the upper stage L (in the photo), but his 17 seconds of work destroyed the engine. Fragments of the upper stage on the background of aggravation of the Cuban missile crisis a us radar was even taken for ballistic missiles, but fortunately, nothing happened, and the peaceful space station did not cause the Third world war.
A similar fate befell Mars 2MV-3 No. 1 (Mars 1962B). Start November 4, 1962 was successful, but after turning on the engine of the booster program-a temporary device due to vibrations prematurely gave the signal to shut down the engine, leaving the station in low earth orbit.

And Cosmos 419 failed the people who had prepared to fly the upper stage D, standing for "the Proton". The station was launched may 10, 1971, but because of an error in the discharge when programming the on-Board computer engine start-up was to be held a hundred and fifty hours instead of tens of minutes, and a bunch of upper stage and interplanetary spacecraft burned up in the atmosphere.
Block D also failed station "Mars-96" (starting Nov 16, 1996), which was to become the heaviest and most ambitious. The reason that the maneuver was not performed is unknown.

The station "Phobos-Grunt" (launched 9 November 2011) was to accelerate from low earth orbit on its own. To do this, it put a modified upper stage "Fregat". But due to restarting the on-Board computer, is not caused by a heavy charged particle, not a mistake in the programming, the engine does not turn on. Attempts to contact the probe also did not succeed, and, two months later, the station burned in the atmosphere.
Flew to Mars healthy
Flight to Mars takes about six months depending on the positions of the planets and the speed of the probe. During this time many things can happen, and many vehicles flying in the Marsa dead.

First it went to Mars which was launched on 1 November 1962 "Mars-1", the same type mentioned above WW2. But immediately after the launch into the trajectory, the machine was "terminally ill" — in one of the valves in the orientation system started leaking. To the device was lost right now, its spun. In this mode, the solar battery was constantly directed to the Sun, but to Orient a directional antenna and make the correction of the trajectory was impossible. The last session was held at a distance of 106 million kilometers, then it was a record. "Mars-1", it is possible in a healthy state, flew past Mars on 19 June 1963 at a distance of 193 thousands of miles away, but he had no way to contact.

Launched November 5, 1964 Mariner 3 can be attributed to this category of accidents, and to the previous. He was trapped under the fairing is not reset. The extra mass led to an unplanned trajectory of millions of kilometers away from Mars, but it didn't matter, because "Mariner-3" failed to disclose a solar panel, and after eight hours he had got batteries.

A sad story happened with the "Probe-2", which could be "Mars-2". The station was successfully launched on 30 November 1964 and is on a trajectory to Mars. But after separation from the upper stage did not deploy one of the solar panels. Assuming the failure of the mission station called a "Probe", they say, it only fulfills the technology of long-haul flights, and scientific tasks are associated. Two weeks later, the panel was able to reveal, shaking the station, but the time for correction of the trajectory has already been lost, and the devices are poorly experienced reduced power and began to refuse. The last communication with the "Probe-2" was held in may 1965 and flew past Mars on 6 August of the same year.

Launched in July 1988, the "Phobos-1" flew to the moons of Mars, Phobos. After a month and a half due to an error ground-based mission control center the unit lost orientation in the Sun. Relationship with him cannot be established, and the station batteries quickly sat down, moving it down finally.
This group also optionally include the same type of "Phobos-2", a relationship that disappeared in the final stages of rendezvous with Phobos and after quite a big research program.

Just three days until the orbit of Mars has lost contact with the Mars Observer. Presumably, due to improper design of the valve in the fuel system has accumulated a pair of tapiwa and oxidizer, which exploded while trying to perform a regular correction of the trajectories, destroying the machine.

Probe "Nozomi", which started in 1998, died after a long and heroic struggle. First was abnormally flyby of the Earth — because of a failed valve speed gain was less than necessary, and fuel cost more. But the Japanese TSUP did not give up — was calculated trajectory, which still will lead to "Nozomi" on Mars, albeit four years later. But when approaching the Earth for another gravity assist, the station came under the solar flare that caused a short in the electrical system. Broken heater, and the fuel froze. It thawed out enough that the station is on a trajectory to Mars, after two flybys of the Earth, but during the approach to Mars is completely frozen. Deprived of the possibility to maneuver "Nozomi" passed 1000 km from Mars on 9 December 2003.
Are unable to enter the orbit/trajectory of the landing
Fly to Mars — that's not all. Need to go to the desired orbit if you orbit a probe, or to enter the atmosphere at the right angle, if you are a lander.

Due to a software error on-Board computer "Mars-2" was to give commands to the incorrect orientation of the lander. So he entered the atmosphere of Mars, on 21 November 1971 at a greater angle than necessary and failed to slow down. The unit crashed somewhere in the valley Nanedi Land Xanthus.
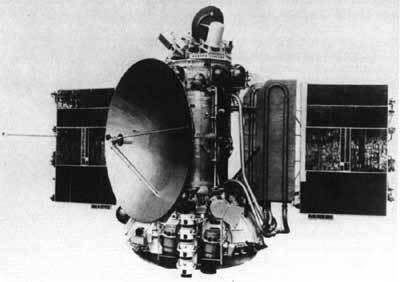
Due to the failure of on-Board computers did not happen the inhibition of the Mars Orbiter "Mars-4". Having become acquainted with Mars to a distance of 1844 km, the probe is gone forever, to become a satellite of the Sun.

Lander "Mars-7" failed to reach the trajectory of entry into the atmosphere and flew past Mars. Different sources call the reason for the failure of the onboard computer or engine brake.
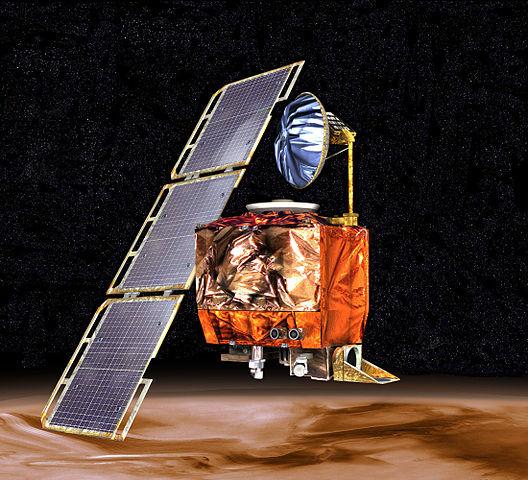

September 23, 1999, due to confusion in the units in the development of the device came at a much lower orbit and quickly burned up in the atmosphere the probe Mars Climate Orbiter. The most insulting, that error almost saw and was able to fix it, even called a meeting about the possibility of holding another maneuver trajectory correction, but this maneuver was not completed.
Successfully to sit down and get to work
In addition to spacecraft that crashed during landing, there were those who successfully boarded, but was unable to completely go into a working configuration or paused soon after a successful landing, and did not pass useful data.

2 December 1971 successfully landed, fifteen minutes preparing for work and 14.5 seconds passed the panorama of the "Mars-3". Alas, after this he was silent forever, and in the panorama we can't see anything useful. The reason for the failure is unknown, it assumed the loss of connection due to the departure from the Orbiter or a corona discharge in the antenna of the transmitter.
12 March 1974 lander "Mars-6", the same "Mars-7" above, has informed that has given the command to switch on the engines of soft landing, but stopped after that forever. The cause of the accident is not established.

3 December 1999 gave the last telemetry before landing the Mars Polar Lander. The division of vehicles (he was flying together with a small penetrators, Deep Space 2) and the process of landing telemetry was reported. But in vain — no signals from either the main unit or from the penetrators never did. In the basic version, the opening of the landing legs was taken on-Board computer for a successful landing, and the machine fell from a height of 40 metres and crashed. The silence of the penetrators, which were very simple, explanation is not received.

How to look like a Mars lander Beagle 2 — he successfully sat on the surface on 25 December 2003, but could not fully disclosed. But the law of meanness antenna was in the lower petal and demanded full disclosure. The cause of the accident was set in 2015, when the camera found on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
The main source was this great list in the Wiki, but there are not without error. The list is not marked, the Rover Prop-M on "Mars-2" and landing the spacecraft "Phobos" also, in my opinion, unfair in a complete failure recorded "Mars-5", which was able to work 9 days in orbit.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/282038/
NASA: scientists to underestimate the speed of the raising water level of the oceans
Reliable protection and high quality