731
What do we know about Mars?

On the occasion of the fourth anniversary of the landing of the rover Curiosity talk about the current knowledge about Mars.
Planet Shelezyaka: no water, no minerals, inhabited by robots ... '. It seems to Mars, but the same item only with robots, the rest are there, though not as much as on Earth. What about Mars is well known? The fourth planet from the sun. Less of the Earth, larger than Mercury. Volcano Olympus - the largest mountain in the solar system, it is the same - the largest volcano. Valles Marineris - the largest canyon in the solar system, which is hundreds of times greater than the largest canyon in the world
.
Global dust storms. The rarefied atmosphere carbon dioxide. Red color due to iron oxide covering the surface. I think this is the minimum that knows or should know of a neighboring planet the overwhelming majority of the inhabitants of the planet Earth.
However, the study of Mars continues, new facts and discoveries are announced regularly on almost every planetologicheskoy conference. Let's try to update our knowledge, adding it freshness and fullness.
Let's start with the atmosphere. In spite of its sparseness, the atmosphere - this is the "live" part of Mars, where there is a lot of interesting processes. The density of the atmosphere of Mars is an average of 1/125 th of the density of Earth's atmosphere. Thus its thickness slightly less than the thickness of the Earth's atmosphere - this occurs because of the lower gravity. Therefore, research satellites Terrans are forced to fly at altitudes of more than 250 km to the atmosphere did not have a significant effect on the orbit.
Global Martian dust storms are irregular and occur approximately every 6 Earth years. At the same time each year, the Martian atmosphere is undergoing large-scale processes of evaporation of carbon dioxide polar cap in the summer hemisphere, and freezing the same cap on winter pole of the planet. In such a pumping part to a quarter of the mass of the atmosphere.

This dynamic creates local storms, which are frequent at the poles, but rarely get to the equator. For example, the rover Curiosity, working at 5 degrees south of the equator, only once in the two days ended up in the dust, limit the visibility of ten kilometers. At other times, the visibility is maintained up to 40 km, and in some quiet winter weeks, you can see the mountain peaks in the distance of 80 km.
At almost any time of the year hanging red dust in the Martian atmosphere, although depending on the time of year, its concentration varies. Most "dusty" times - the fall and spring, when there is a transfer of the atmosphere from one pole to another. At this time the color of the sky orange-beige up to brown during storms. In the quiet months of the dust settles, the zenith is black, and beige color of the sky down to the horizon. At such a time can be observed bluish hues of the sky when the sun approaches the horizon and atmospheric gases little time to dispel the blue component of the solar spectrum.
In addition to large-scale dust storms that cover the entire planet, or substantial portion thereof, on Mars you can watch the activities of small vortices, which American scientists called Dust Devil. Most often, they look like a dusty trunk, rising to a height of several meters to several hundred meters.

Dust Devil may be invisible. For example, air pressure sensors Curiosity has repeatedly recorded the passage of a small vortex at the machine, at the same time, the camera could not never pull off such a whirlwind, although attempts are made regularly. But Opportunity periodically can not see small vortices, which at the same time help to clean its solar panels from dust.

Because of the frequent dust storms someone may form the impression that Mars is just the eyeballs littered with dust, which is why it is impossible to study its geology in situ - on the spot. Semisantimetrovy drill last rover many surprising its short length. Dust, of course, covers the entire area of Mars where the wind can reach, but the thickness of the dust layer sometimes no more than a millimeter. The process of atmospheric erosion on Mars is still ongoing, it helps to increase the volume of dust, but the surface areas exposed to erosion, bare. In one of these places just works Curiosity.
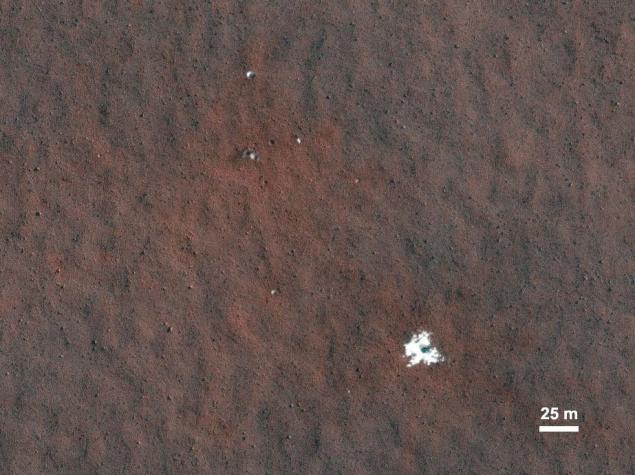
A good argument in favor of low-intensity deposits weathering products can serve as an example of a parachute landing module of automatic space stations of the last century. In 2012, it managed to find a parachute "Mars-3" (1971, the year of planting), and then the unit itself.
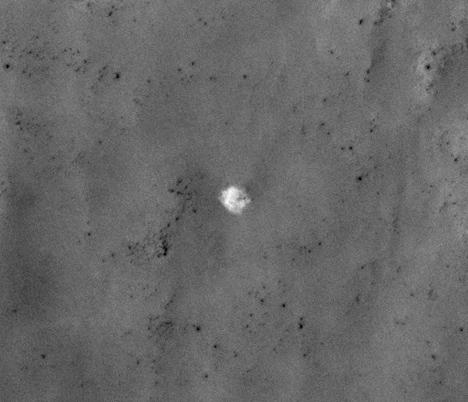
Documented parachutes stations Viking-1 (1976) and Mars Pathfnder (1997). Hidden under layers of dust can be regarded as the Viking-2 parachute, and you can not even detect signs of a parachute, "Mars 6", although numerous attempts.
Dust in the atmosphere can be distributed in several layers to form clouds, including high-rise, and rise to heights of at least 50 kilometers or even higher by several tens of kilometers.
Often the mass media publications confused dust and sand. It is on Earth possible sandstorms and carrying sand for hundreds of kilometers. For Mars is relevant only for the dust - the size of the particles of which is less than 0, 1 mm. A larger sand moved by the wind, too, but a few centimeters -. Up to a meter within a year

Mars carefully studied volcanic crater Nili Patera, the bottom of which "crawl" the sand dunes. During their movement for many years monitored using a high-resolution camera HiRISE the MRO satellite. The movement of sand dunes have found in other places of Mars.
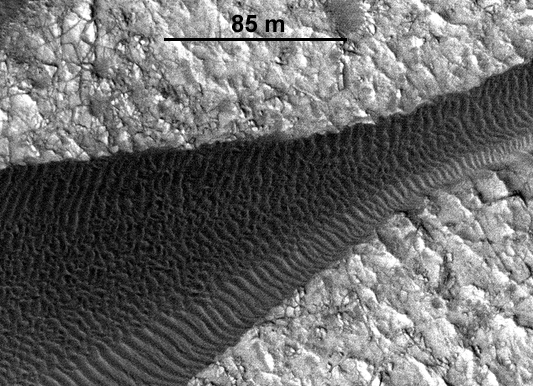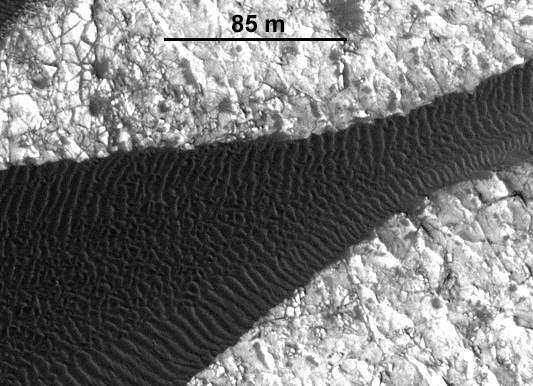
Another interesting object of study are the polar ice caps. Polar glaciers - this is probably the first objects on the surface of Mars that have been identified in human beings. When astronomers saw the similarity of the Earth and Mars poles, and then distinguished the dark spots on the sides of the red planet, Mars seemed a full copy of the Earth, and the idea of the local people was quite logical.
Initially, the polar caps of Mars were regarded as water, and their annual variability has generated hypotheses about the regular floods of melt water, which are superimposed on erroneous observations of the Martian "canals." However, in the mid-twentieth century, it was found that the main area of the winter pole closes the carbon dioxide ice, and the water remains in the small area of summer polar caps. Thanks to Mars Express radar, MARSIS satellite managed to set the power of the polar water deposits in the north - 1, 7 km to the south - up to 3 km. If you take the polar ice caps to melt and it will turn out entirely fill with water height of 21 m perfectly smooth planet the size of Mars. Accordingly, if the melt here these stocks, then to a small okeanchik or several small seas of Mars we have enough.

Studies of Mars indicate that there was more water earlier. On the planet there are empty river beds, river deltas, the remnants of the lakes, and there are even some signs of the former Ocean, occupied a quarter to a third of the entire planet. The question is, where are the vast reserves of Martian water, does not yet have a precise answer, but there are two hypotheses: first - the water went into the ground, got in touch with minerals and glaciers formed the ground; the second - the water dissipated into space. Although more and more arguments, inclines to the second hypothesis, the water on Mars is not only at the poles and in the circumpolar regions. Subsurface glaciers are determined in the northern hemisphere to the 40th parallel to the equator - for the Earth is the latitude of Sochi. There are ice deposits to the east of the Hellas valleys, and even at the equator, the water content ranges from 5% to 10% in the ground.

All this time we were talking about the water in the solid phase or in a bound state of aggregation. Mars Atmospheric pressure is not conducive to the maintenance of liquid water even in low-lying areas with high pressure water boils already at +10 ° C, and taking into account seasonal variations in atmospheric density and temperature above +10 ° C in summer days, long-term conservation of water on the surface it is virtually eliminated. But recent studies hyperspectrometer CRISM HiRise camera and added arguments hypothesis that in the soil of Mars possible to maintain water in a liquid state at sub-zero temperatures in the form of brine salts of perchloric acid.
Until recently, scientists could not give an affirmative answer to the question about the presence of organic compounds on Mars. The first data were at ground-based observations, when it is determined the presence of methane in the Martian atmosphere. To search for organics went to the Red Planet rover Curiosity. His first data from the end of 2012 were encouraging, but it turned out that there was an error, and the rover "discovered" organic, which he himself had brought with him and - corrupted solvent capacity for the "wet" soil analysis. A year later, when the machine has accumulated statistics studies of different types of soils, managed to say more confident - there are organic. They found chlorobenzene.
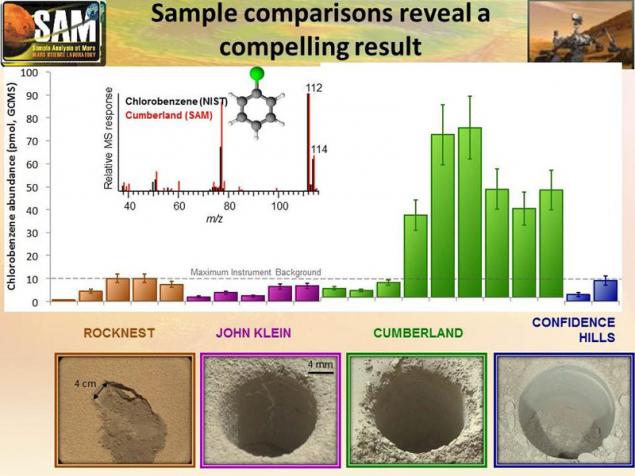
A year later, it was able to confirm the appearance of methane in the Martian atmosphere, while the processes that cause the allocation of gas is no single opinion.
Note that the organic compounds are found are not a direct confirmation of the presence of Mars in the past biological activity. Organic compounds are known to Mercury, on comets, asteroids, satellites of giant planets, themselves in the atmosphere of the giant planets and in other places near and distant universe. Identify biomarkers in organic compounds Mars rover ExoMars mission will, whose launch is planned for 2020.
An important finding from the point of view of possible past or future life - nitrates in certain geological layers in the crater Gale. For Earth nitrate fertilizer are considered and used as intended. For Mars found nitrates means that in the past were the conditions that allow us to develop the known forms of life, and this finding opens up prospects for the future of agriculture (or rather, marsodeliya) and agriculture.
An analysis of the Martian soil, carried out by mass spectrometry SAM aboard the rover Curiosity, showed that heating the soil up to +400 ° C, the release of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen, which are generally suitable for use in the future of human activities on Mars. < br>
In the context of a manned flight to Mars, necessarily raises the question of radiation hazards during flight and when working on the surface. Studies of radiation conditions during the flight to Mars and on its surface occasion and held RAD instrument aboard the rover Curiosity.
Studying the effects of cosmic rays during the flight to Mars, given the not very encouraging data: a risk for people in more than half the allowable for astronauts and cosmonauts to tolerances even stricter. On the surface, the conditions are more acceptable. Exposure to ionizing particles on the surface of Mars is approximately twice lower than in the conditions of space flight, and low solar activity corresponds to the background radiation on board the International Space Station.
A mandatory stage in the study of Mars will be the delivery of soil samples back to Earth. While this task is quite complicated, but it remains to NASA and the Russian Space Agency projects. While there is the possibility of studying meteorites that are thought to have arrived from Mars. In the 1990s, it was reported that in one of the meteorites discovered fossil, similar to bacteria, but most scientists challenged this hypothesis. Recently curious fossilized structures were found in another meteorite.
Externally discovery resembles a cage, in which you can define the cell vacuoles and even the pores, but it is an isolated case and not enough evidence to declare sensation. One can only hope for more productive findings of current and future exploration missions.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/279218/