845
Mars rover Curiosity is exploring dark dunes

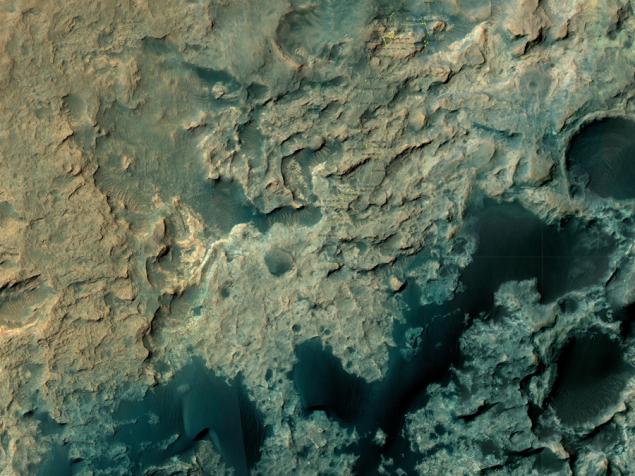
Long two years Curiosity did not dare to approach Mount Sharp, but was sent to study it. Meshali deposits of dark sand that blocked the way, so they had to get round. The rover moved along the mountains and the black dunes constantly loomed at the foot, sometimes resembling a frozen sea, sometimes - the old highway
.
The longer they floated away, the more I want to get closer to them, consider makrokameroy MAHLI, touch the APXS spectrometer, run them a bucket to fry in the microwave chromatograph SAM and enlighten the X-ray diffractometer CheMin .

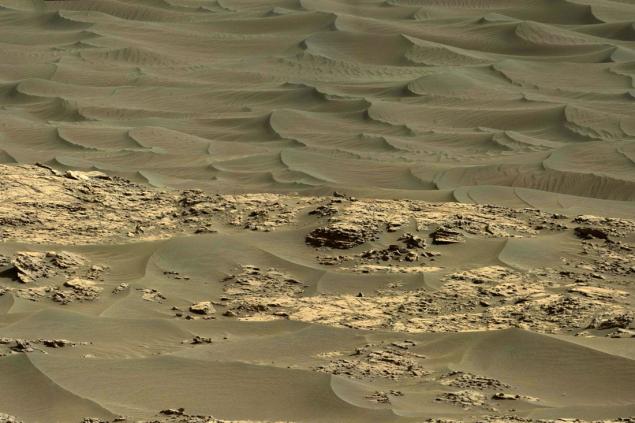
The rover in the summer of 2013 moved along the dark tresses tear dune in the desert, where for hard ground could get to the mountain slopes and canyons, which once was cut in the mountain streams of meltwater. While Curiosity was far from scientists and we had to settle for high resolution satellite images the MRO HiRISE camera. Pictures of the cameras transmit images in the "advanced" colors, which seemed dark sand blue or greenish.

Part of this effect is not accidental. Satellite hyperspectrometer CRISM showed a high content of volcanic rocks pyroxene and olivine. The pyroxene is responsible for virtually all the dark rocks of Mars, observed from space. It pyroxene "seas" appear as dark spots when viewed through a telescope.
Blue-green shades of dark dunes of Mars acquired through olivine - also a volcanic rock, which received its name, for the green color, like olives
.
In the first months of Curiosity in the crater Gale remained the question of the density of the sand. Are they long since petrified monolith, preserving the ancient form of the desert (or seabed) or are the usual sand? Call and touch wheel rover engineers at first did not dare not to waste time. But the dunes began to observe the satellite, and to compare with pictures that made four years before the Curiosity landing. And the response has been received - they "live»
.
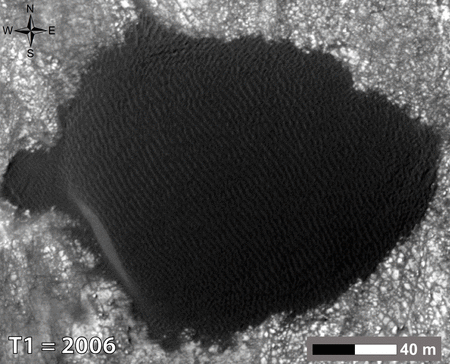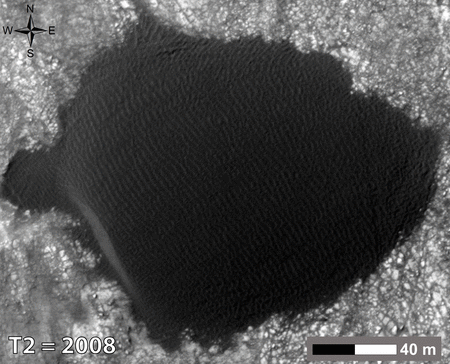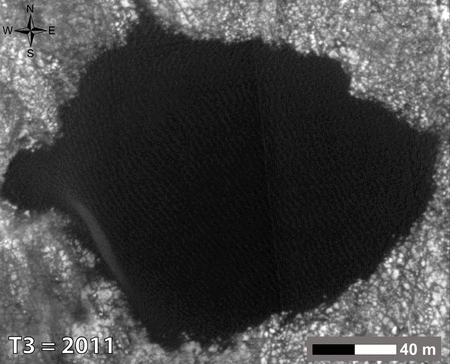
Moving dunes in the crater Gale is not unique to Mars. Scientists have several years of watching the dunes in several regions of the planet.
Here it is necessary to clarify that Mars dust storms are frequent, but not sand. The difference in the size and weight of the particles. The thin atmosphere and light winds can raise high fine dust and the sand turns to move only by centimeters, with the result that the dunes are crawling around a meter per year.
The isolated position of these dunes from sand and other dust explains the size, weight, and possibly form particles. Despite the fact that it sounds as if they are assembled and held together by some kind of magical power, when viewed from above it is clear that the dark sand dunes spread from quite a distance, and painted in dark tones terrain on the approach.
In part, this explains why distant dunes stood out sharply against the background of the surrounding area, and as you get closer to them, the contrast was reduced. Chance has the effect of "black and blue / white and gold".

While Curiosity was bypassing along the mountains, it was moving relatively quickly, for marsohodnym standards - about 6 kilometers per year. When he changed course and began a gradual climb , the speed of progress has decreased dramatically due to the long stop for a detailed soil survey .
Mount Sharp has attracted the attention of scientists for a long time due to its layered structure . Curiosity Moving up, with the analysis of all geological layers - this is his priority, so it is here and flying. Therefore, the remaining two kilometers from the foot to the dune fields had to wait for about a year.
Finally, we are here!

on the desktop. I>
Dyunnuyu braid stretching from the mountains, called Dune Bagnolda , in honor of the explorer of the Sahara. Two nearest pile of sand, for the study of which began Curiosity, received the name of the Namib, in honor of Earth's deserts.
The last half a kilometer to the sand dunes of the Namib rover drivers, it seems, do hurry, wanting to quickly see the dark dumps. However, the rush did not stop them to find the path of interesting deposits of soil with a high content of silicon. As he deposited there have yet to learn, and Curiosity has already moved on to the study of sand.
Dropping typed soil with a high content of silicon, the rover has created an entertaining still life of three "grades" of Mars: blue-gray brown soil produced from a depth of 5 cm, lay a solid sedimentary rock, covered with a light layer of red dust. Near visible scree dark sand disturbed by rover wheels.
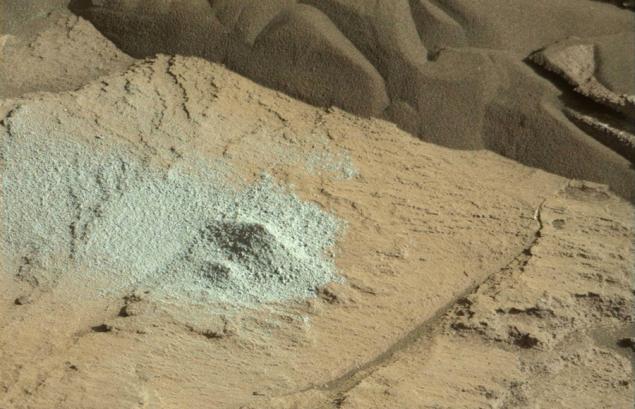

Dark sand reviewed using makrokamery MAHLI.
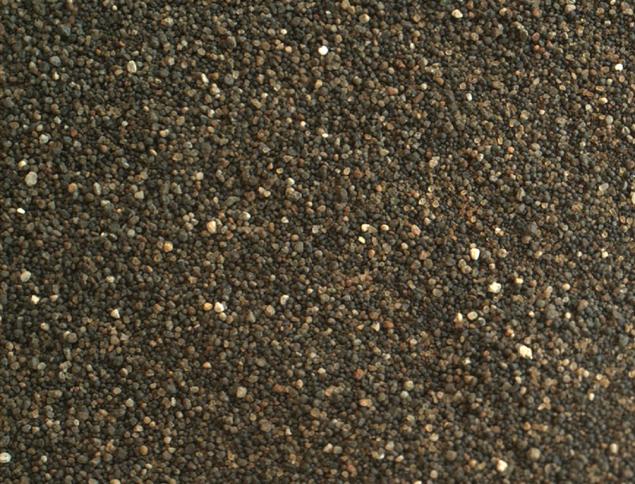

For comparison, we can recall the other deposits of sand - red, which investigated the rover is still in the first year of his expedition
.
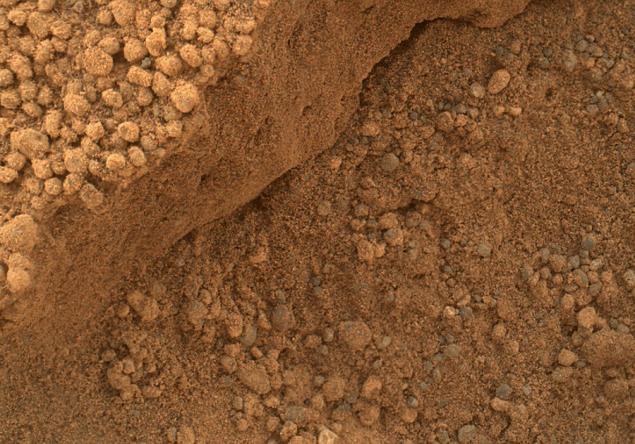

You can see that the dark sand more "granular" size particles of about the same, interspersed with larger. Golden sand is composed of two factions - the relatively large grains of sand, mixed with dust (more silt - a transitional form between the dust and sand)
.
The difference in the physical properties of sand and explains the fact that the dark and red dunes do not mix. Although the behavior of sand interacting with the wind - it is now the leading trend in research, and a lot of unknowns. The rover can stay in one place for a few months only to yourself, to see how the surface of the dunes creep.

Initially, Curiosity crept to a small valley filled with dark sand. Here, the primary studies were made, and it was clear that the dunes here are the most common, with no signs of fossilization. Then the rover moved to a more impressive dune, several meters high. At first, it was made a careful inspection, and then Curiosity unceremoniously disturbed the tranquility of dunes and a small trench dug his wheel.
This place is recognized as sufficiently promising to be able to start an in-depth study of the samples. The rover used his shovel to make a turn three soil samples.

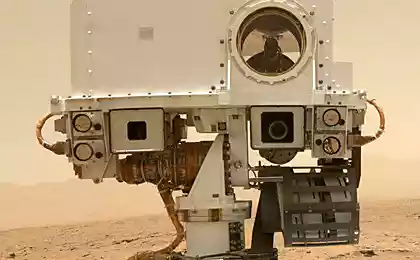
In the process, Curiosity made a self-portrait, which can be viewed on the impressive panorama, which was captured by the camera on the rover's robot arm and reduced to интерактивную panorama photo artist Andrei Bodrov.

The first samples off to a laboratory SAM instrument for determining the chemical and isotopic composition of sand minerals.
But then there is a problem: it seems stuck tool Chimra, which is located in the keypad and is used for sifting soil. Sifting soil - a necessary procedure before loading the samples in the internal laboratory instruments. Research instruments can only fine particles of not more than 0, 15 mm. To weed out the superfluous, the larger grains of sand, used Chimra - a set of multiple cavities and gratings with different mesh size to allow for soil clean up the necessary parameters
.
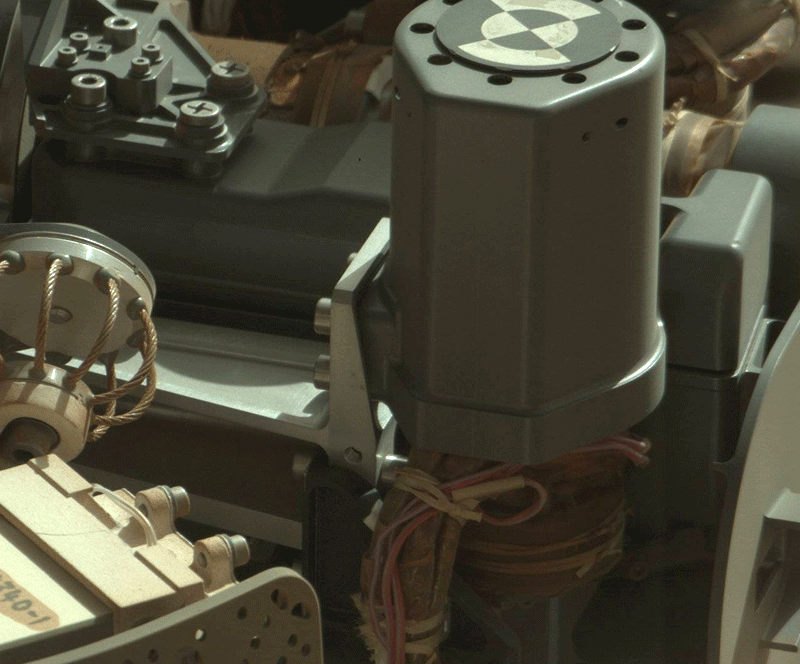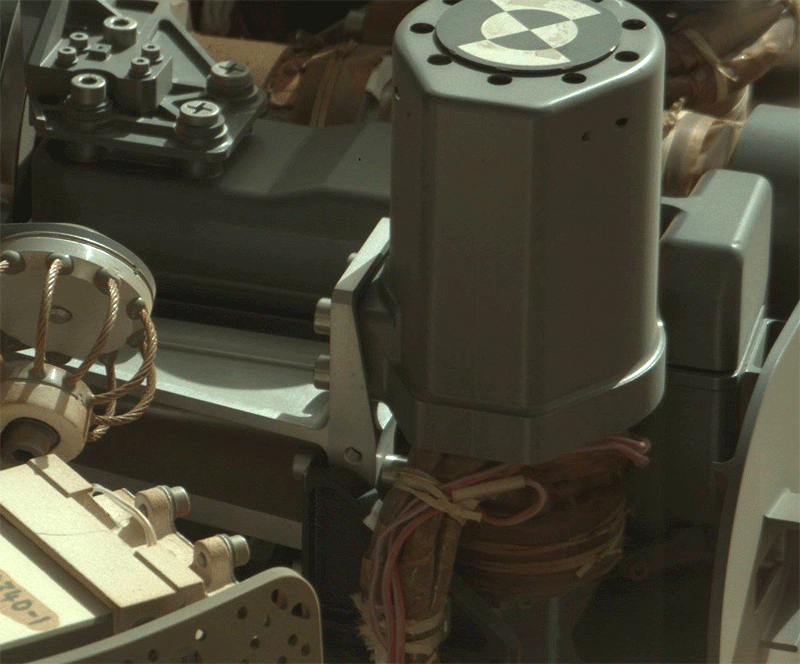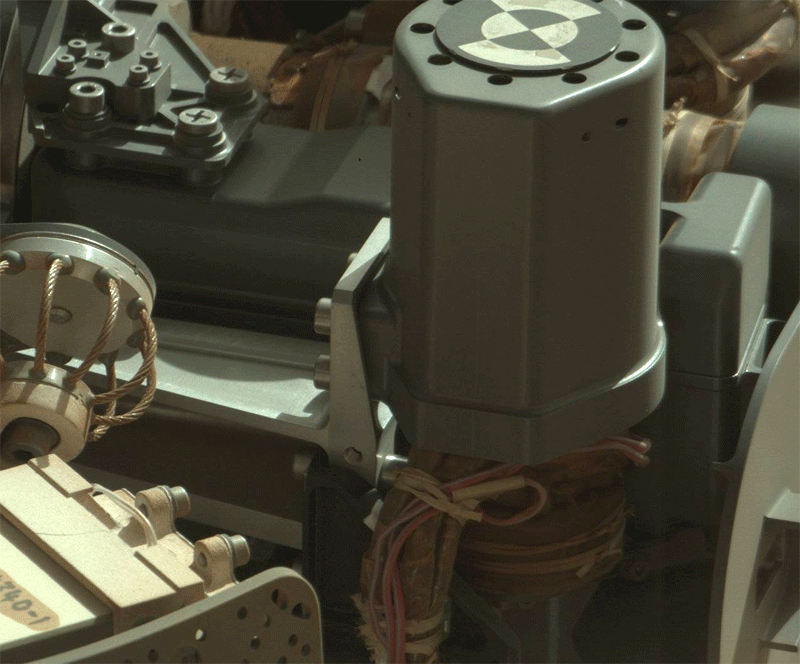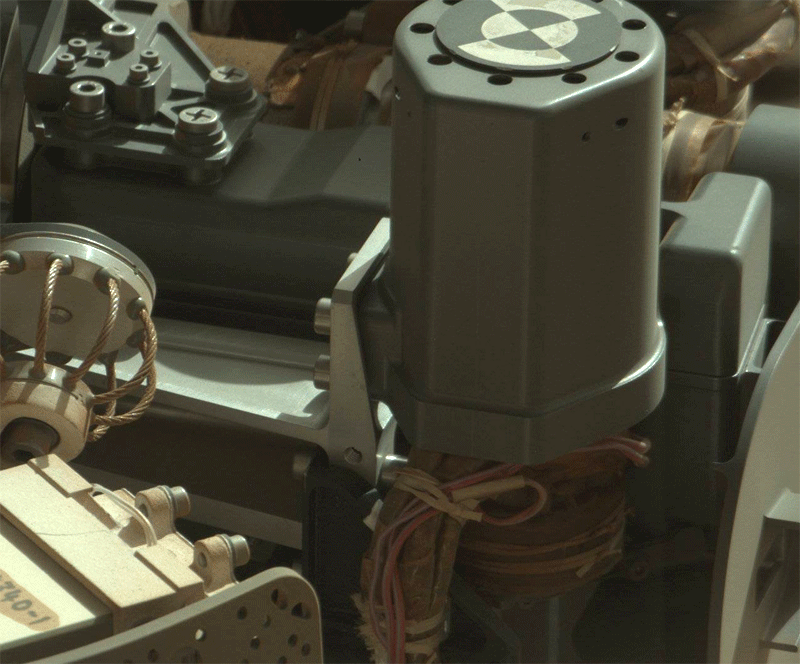
Problem arose after Curiosity third time scooped bucket dark sand and was about to prepare it for research. Because of the "anomalies» Chimra rover stopped the study of dark sand dunes and continued to explore the area using the spectrometer APXS and ChemCam.
It is too early to say how the problem is likely to harm the rover's science mission and when to be able to cope with it. Previous experience shows that engineers are creative ways to overcome these difficulties, but it is not yet known, even the cause of failure, so it remains but wait, and hope for the best.
To learn what the results of the study of dark sand, its composition and possible origins, we also find out later, when geologists will finish processing the results.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/270696/
Why major corporations are hoarding trillions of dollars?
Can artificial intelligence to become US president