720
Six years in the Martian dust
In each of the six wheels of Martian automatic Scout Spirit is the engine that runs independently of the other five. But now that all six wheels stuck in the Martian sand rover nothing will. Photo: NASA / JPL-Caltech
January 26, 2010 NASA decided to stop trying to pull the mars rover Spirit from a sand trap in which he landed nearly nine months ago. However, this device will not end a career. Since he is able to communicate with the Earth, it will still stationary research laboratory. In addition, Spirit - not the only one, is not the first and not the last explorer Mars. The history of planetary reconnaissance goes back forty years. However, first things first.
Number one
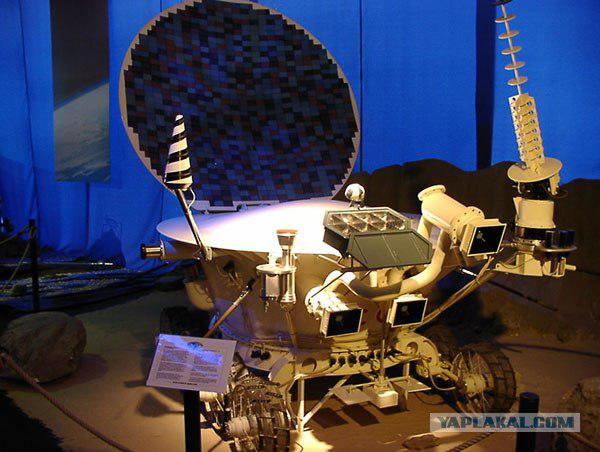
In the early 60-ies of the last century, the famous OKB-1, which was led by Sergei Korolev (1907-1966), was born ambitious and rather unusual idea of creating a self-propelled vehicles intended for the study of various cosmic objects (planets and moons). The primary goal for scientists began as the moon is closest to Earth and most-studied celestial body. In the autumn of 1966 it was approved the preliminary design of the first "Lunokhod", and by the end of 1967 prepared all design documentation. Thus, the design has been completed in record time, and in fact scientists and designers had to solve a complex of complex and unusual tasks. [Next]
Firstly, it was necessary to develop a chassis. Among the options are walking, jumping, and rolling machines and even "lunoplavy", as there is a hypothesis that the Moon's surface is covered with a thick layer of dust, which will sink any lander. By the way, scientists debate about the lunar soil lasted more than a year, until the king decided to issue an order, imposing his famous resolution "Luna hard!».
Exotic movers and were not considered, and to focus on more conventional wheeled, tracked or screw systems. This raises the second problem - severe restrictions on the weight of the chassis, combined with the highest requirements for durability and reliability. Initially, the development of propulsion had engaged employees of the Research Institute of the State Committee of Automobile and Tractor and agricultural machinery (NATI). However, they considered the requirements put forward by the OKB-1, is too rigid and refused to develop.
As a result, moonwalker do at the Institute of Transport Engineering (VNIITransmash), specialized in the design of armored equipment. By the end of 1967 under the leadership of Alexander Leonovich Kemurdzhiana (1921-2003), self-propelled chassis was completed. Propulsion consisted of eight motor-wheels, firmer suspension, electro-mechanical transmission with an individual drive wheel brake, switch box and a set of information and measurement equipment, designed for the control of the chassis.
With its wide application in the design of titanium alloys VNIITransmash still "fit" in the strict requirements of OKB-1, the total mass of the self-propelled chassis was only 84 kg.
Room temperature
In parallel with the development of the chassis engineers have solved the problem of thermoregulation system. The Moon has no atmosphere, there is no protection from the sun, the light is not scattered, and every body is heated from one side only - where the sun. The unit had to operate in conditions of appalling temperature difference: the sun lit the board is heated to +150 ° C, and the opposite - nearly three hundred degrees colder. At the same time inside the "Lunokhod", for the normal functioning of all systems must be supported by "normal conditions" - that is, the room temperature (actually a little lower - 17 ° C), humidity and pressure (that ensure the integrity of the body and constant temperature inside).
For this purpose, the upper part of the body "Lunokhod" placed radiator cooling system, which was closed for the night kind of cover to keep warm. On the same "cap" on the inside were mounted solar panels, supplied the day "Lunokhod" electricity. Well, during the lunar night, until the "Lunokhod" stood for heating instrument compartment used radioisotope heat source, and a system of heaters operating on battery power.
Finally, it was necessary to resolve the issue of the control system. Initially, projects were considered fully automatic planetary rovers, but then stopped for a radio-controlled version. Eighteen "seating astronauts' missile officers, were to be the crew" Lunokhod ". Interestingly, the candidates pilots (who are always willing to take on the position of "ordinary astronauts) were not even considered. Among the main requirements for the candidates, in addition to discipline, efficiency, good health, and other stressouystoychivosti quite normal quality, was "a complete lack of any previous experience in the management of vehicles." Even avid cyclists wrapped pending personal file. Scientists thought that the "earth" experience in the management of vehicles will only interfere.
At the second attempt
The first "moonwalker" went to the moon February 19, 1969. After 51 seconds of flight there was a destruction fairing ship, causing splinters flying safely along the third and the second stage, crashed into the fuel tanks, triggering a spectacular explosion.
The second launch took place only 10 November 1970. During this time the moon had visited the crew of the American "Apollo 11". This time everything went without pads: interplanetary station "Luna-17" safely prilunilas Mare Imbrium on November 17 and "Lunokhod-1" has started to fulfill its mission. The program was completed by 20 February 1971, but "Lunokhod-1", even was not going to die. It was necessary to develop a new research program for the following lunar day, and then another one, and then another one ...
Total Planetary worked 301 days. 6 hours 37 minutes, more than three times the design life. During this time the "Lunokhod-1" surveyed about 80 thousand. M2 surface of the moon, the earth passed more than 20 thousand. Images of the surface, more than 200 panoramas. The 25 points was carried out a chemical analysis of the surface layer of lunar soil and in more than 500 locations identified by physical and mechanical properties of the surface.
September 15, 1971, upon the occurrence of the 11th lunar night equipment recorded a drop in temperature inside the instrument compartment, probably due to resource development isotope heat source. Sept. 30, at the dawn of the next lunar day, "Lunokhod-1" on the connection is not released.
The second expedition
January 16, 1973 automatic interplanetary station "Luna-21" delivered on Earth's natural satellite precious cargo - "Lunokhod-2". This unit was, in fact, only slightly improved copy of the first planetary rovers.
First of all, it was rebuilt by the TV system, allowing the transmission rate of one frame was reduced to three seconds, regardless of the complexity of the terrain (at the "Lunokhod-1", this process took up to twenty seconds, which significantly complicates the process control). Secondly, to improve the survey added a third chamber located at the eye level of a standing person. Third, the system was modified automatic locks, triggered in the event of danger to the device (large roll, motor overload wheels and so on. D.). Fourth, the system was changed to the power supply. On the "Lunokhod-2" were two batteries modified total capacity 250 Ah (against 200 Ah first model), as well as enhanced solar cells.
Nevertheless career "Lunokhod-2" did not start too well. First lander nearly fell into the crater, landing just three meters away from him. Then it turned out that the navigation system is refused. Well, finally, dangerous crater, which landed near the descent module was so close that at the initial examination areas did not notice him, and "Lunokhod-2" drove right into it. Fortunately the machine not only turned, but was able to successfully get out of the crater and proceed to carry out the program.
Despite the failure of the navigation system (because of which the navigators had to rely on the sun and the environment), "Lunokhod-2" was much more productive than its predecessor. He conveyed to the Earth more than 80 thousand. Images of the lunar surface, 86 panoramas with a lot of data on-board instrumentation, and passed, a total of about 40 km. Unfortunately, the mission of the "Lunokhod-2" ended a little earlier than planned. May 9, 1973 "Lunokhod-2" examined a large crater on the eastern boundary fault "Direct". When you exit from it emerged emergency situation which led to the premature death of the machine. May 10, 1973 "Lunokhod-2" silent forever.
Entrance to Mars
In May 1971, until the "Lunokhod-1" meets the dawn of its seventh lunar day, the side of Mars from Earth sent two carrier rocket "Proton-K" automatic interplanetary station "Mars-2" and "Mars-3". Both stations were equipped with descent module landing on the surface. And neither one of them was unable to fulfill its mission, "Mars-2" crash-landed, and "Mars-3" has worked a total of 20 seconds. But that's not it - both stations carried on board the world's first rovers with the mysterious name "Device patency assessment - Mars", for short - propyl-M.
It was very simple and extremely compact scouts. The weight of the device was only 4, 5 kg of scientific instruments on board were the only dynamic penetrometer and gamma-ray densitometer to measure the density and structure of the soil. Move prop-M was walking with the help of the chassis are two "ski", located on the sides of the body. Power and control was carried out using a 15-meter cable connecting the rover with a landing stage, which, in turn, also serve as a receiving station, radio transmission from Earth.
In front of the prop-M was located simple sensors detect obstacles. Every 1, 5 m (or a collision with an obstacle) rover should automatically stop and wait for confirmation of the course. Such a system was required to maintain control over the apparatus, because the signal from the Earth and Mars goes from 4 to 20 minutes, depending on their distance from each other.
After the failure of the rovers was followed by an attempt to improve the Lunar Prospector. "Lunokhod-3" can transmit stereoscopic images from two cameras that were placed in a rotary HDA mounted on the external bar. Now to explore the area "Lunokhod" did not have to turn his whole body, just "shook his head." This arrangement later borrowed rovers Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity. New planetary rovers was fully staffed and all onboard scientific instruments, passed the whole cycle of ground tests and ... will forever remain in the museum NPO. Lavochkin. The launch, planned for 1977, did not take place.
The work continued. Russian rover, created by the Institute of Space Research, in 1992 even experience even in Death Valley (California), but to get to Mars, he was not fated. Planetary scout reappeared in the history of space exploration only after more than twenty years.
"Martian tractor»
December 4, 1996 from Cape Canaveral launch vehicle "Delta-2." After exactly 7 months, 4 July 1997 automatic interplanetary station «Mars Pathfinder» made a soft landing on the Martian surface. In addition to scientific instruments and communications systems on board the landing module was a small rover Sojourner. July 5, he began to perform scientific tasks. Its chassis was a six wheels individually driven by DC motors. The rover was equipped with three video cameras (front stereo pair and one rear camera) and mobile spectrometer for studying the chemical composition of Martian rocks and soil. Inside it, there were three radioisotope element, used to maintain the required temperature in the instrument compartment. Management carried out by a microprocessor. Himself rover exchange signals only from the lander, which, in turn, kept in touch with the Earth.
Total Sojourner worked for a little less than three months. September 27, 1997 was the last regular session with the station, and then (until October 7) unit sent only meaningless information indecipherable. Attempts were made to revive the unit until March 1998, but they were not crowned with success. During his short career Mars Pathfinder managed to pass 16, 5 thousand. Pictures Taken cameras lander and 550 images from the rover's cameras. In addition, joint efforts are fifteen times analyzed the various rocks of Mars.
Rovers did not find traction for miniaturization: the smallest of all was Sojourner (center) - the size of a microwave. It is still not lost their connection with the Earth Spirit and Opportunity (left) overtaken and outstripped the children's pedal cars. The device of the next generation Curiosity, whose mission will begin in the coming year, similar in size to a small SUV. Photo: NASA / JPL-Caltech
Opportunity and Spirit
After the untimely death of Sojourner, in the XXI century it was running two identical rovers with a very pretentious title "The Spirit» - Spirit (June 10, 2003) and "Opportunity» - Opportunity (7 July 2003). Their propeller has six wheels driven by DC motors. The source of electric energy are solar panels, and the "eyes" - two high-resolution video camera, located on the remote bar with swivel mechanism. In addition, Spirit and Opportunity thoroughly equipped for scientific research. Then there are the microscope to study the structure of soil and rocks, and three spectrometer and a miniature drill. Communication with Earth is carried out using a repeater, the role played by apparatus «Mars Odyssey», hanging orbiting Mars since October 2001.
4 and 25 January 2004 phones made a successful landing on the surface of the "red planet." But without troubles still not done. Firstly, even when both devices were in flight during a routine test revealed that "Spirit" is one of the spectrometer operates correctly. Then, after landing one of the inflatable shock landing stage I am not blown away after landing and blocked the main rover descent from the platform. As a result, "Spiritu" had a few days to maneuver, to still get down from the descent stage. January 21 zasboila flash-memory rover, because of what began on-board computer continuously restarts. Fortunately, this problem is also solved successfully. Initially, the Spirit was given to the team to use the volatile memory instead of flash-modules, and then drives a reformat, then the work of the unit included in the normal mode.
Meanwhile, Mars came Opportunity. With him, too, not everything went smoothly. During system testing revealed that because of the broken thermostat one of the heaters periodically turn on spontaneously at night. Additional power consumption reduces the number of working rover on battery, but this issue is not critical.
Spirit and Opportunity were designed for 90 days of operation. To date, the two rovers six years later (!) Are still functioning, and communicate with Earth. During this time, the machine sends an enormous amount of scientific information, thousands of images of Mars have found evidence for the existence of liquid water in the past to the "red planet", studied the traces of volcanic activity. Opportunity even found a piece of rock, with a high degree of probability is an ancient meteorite.
Spirit is now officially received the status of "stationary research platform." April 23, 2009 rover stuck in sand sulfate. By this time, the device is already out of service two wheels of the six may therefore attempt to rescue Spirit from the sand trap, which lasted nearly nine months, have been unsuccessful.
With regard to Opportunity, it is still quite cheerfully creeps on Mars and may have time to make some sensational finds before his death.
It is now built another rover, also speaking in the name of "Curiosity» - Curiosity. Its launch, as part of the interplanetary station Mars Science Laboratory, scheduled for October 2009. However, NASA announced the postponement of the mission in 2011. Perhaps this is due to the fact that immobilized the Opportunity and Spirit, despite his more than respectable age, is retain the ability to explore the Red Planet.
Yuri Popov, 10.02.2010 www.vokrugsveta.ru/telegraph/cosmos/1100/

Source:
January 26, 2010 NASA decided to stop trying to pull the mars rover Spirit from a sand trap in which he landed nearly nine months ago. However, this device will not end a career. Since he is able to communicate with the Earth, it will still stationary research laboratory. In addition, Spirit - not the only one, is not the first and not the last explorer Mars. The history of planetary reconnaissance goes back forty years. However, first things first.
Number one
In the early 60-ies of the last century, the famous OKB-1, which was led by Sergei Korolev (1907-1966), was born ambitious and rather unusual idea of creating a self-propelled vehicles intended for the study of various cosmic objects (planets and moons). The primary goal for scientists began as the moon is closest to Earth and most-studied celestial body. In the autumn of 1966 it was approved the preliminary design of the first "Lunokhod", and by the end of 1967 prepared all design documentation. Thus, the design has been completed in record time, and in fact scientists and designers had to solve a complex of complex and unusual tasks. [Next]
Firstly, it was necessary to develop a chassis. Among the options are walking, jumping, and rolling machines and even "lunoplavy", as there is a hypothesis that the Moon's surface is covered with a thick layer of dust, which will sink any lander. By the way, scientists debate about the lunar soil lasted more than a year, until the king decided to issue an order, imposing his famous resolution "Luna hard!».
Exotic movers and were not considered, and to focus on more conventional wheeled, tracked or screw systems. This raises the second problem - severe restrictions on the weight of the chassis, combined with the highest requirements for durability and reliability. Initially, the development of propulsion had engaged employees of the Research Institute of the State Committee of Automobile and Tractor and agricultural machinery (NATI). However, they considered the requirements put forward by the OKB-1, is too rigid and refused to develop.
As a result, moonwalker do at the Institute of Transport Engineering (VNIITransmash), specialized in the design of armored equipment. By the end of 1967 under the leadership of Alexander Leonovich Kemurdzhiana (1921-2003), self-propelled chassis was completed. Propulsion consisted of eight motor-wheels, firmer suspension, electro-mechanical transmission with an individual drive wheel brake, switch box and a set of information and measurement equipment, designed for the control of the chassis.
With its wide application in the design of titanium alloys VNIITransmash still "fit" in the strict requirements of OKB-1, the total mass of the self-propelled chassis was only 84 kg.
Room temperature
In parallel with the development of the chassis engineers have solved the problem of thermoregulation system. The Moon has no atmosphere, there is no protection from the sun, the light is not scattered, and every body is heated from one side only - where the sun. The unit had to operate in conditions of appalling temperature difference: the sun lit the board is heated to +150 ° C, and the opposite - nearly three hundred degrees colder. At the same time inside the "Lunokhod", for the normal functioning of all systems must be supported by "normal conditions" - that is, the room temperature (actually a little lower - 17 ° C), humidity and pressure (that ensure the integrity of the body and constant temperature inside).
For this purpose, the upper part of the body "Lunokhod" placed radiator cooling system, which was closed for the night kind of cover to keep warm. On the same "cap" on the inside were mounted solar panels, supplied the day "Lunokhod" electricity. Well, during the lunar night, until the "Lunokhod" stood for heating instrument compartment used radioisotope heat source, and a system of heaters operating on battery power.
Finally, it was necessary to resolve the issue of the control system. Initially, projects were considered fully automatic planetary rovers, but then stopped for a radio-controlled version. Eighteen "seating astronauts' missile officers, were to be the crew" Lunokhod ". Interestingly, the candidates pilots (who are always willing to take on the position of "ordinary astronauts) were not even considered. Among the main requirements for the candidates, in addition to discipline, efficiency, good health, and other stressouystoychivosti quite normal quality, was "a complete lack of any previous experience in the management of vehicles." Even avid cyclists wrapped pending personal file. Scientists thought that the "earth" experience in the management of vehicles will only interfere.
At the second attempt
The first "moonwalker" went to the moon February 19, 1969. After 51 seconds of flight there was a destruction fairing ship, causing splinters flying safely along the third and the second stage, crashed into the fuel tanks, triggering a spectacular explosion.
The second launch took place only 10 November 1970. During this time the moon had visited the crew of the American "Apollo 11". This time everything went without pads: interplanetary station "Luna-17" safely prilunilas Mare Imbrium on November 17 and "Lunokhod-1" has started to fulfill its mission. The program was completed by 20 February 1971, but "Lunokhod-1", even was not going to die. It was necessary to develop a new research program for the following lunar day, and then another one, and then another one ...
Total Planetary worked 301 days. 6 hours 37 minutes, more than three times the design life. During this time the "Lunokhod-1" surveyed about 80 thousand. M2 surface of the moon, the earth passed more than 20 thousand. Images of the surface, more than 200 panoramas. The 25 points was carried out a chemical analysis of the surface layer of lunar soil and in more than 500 locations identified by physical and mechanical properties of the surface.
September 15, 1971, upon the occurrence of the 11th lunar night equipment recorded a drop in temperature inside the instrument compartment, probably due to resource development isotope heat source. Sept. 30, at the dawn of the next lunar day, "Lunokhod-1" on the connection is not released.
The second expedition
January 16, 1973 automatic interplanetary station "Luna-21" delivered on Earth's natural satellite precious cargo - "Lunokhod-2". This unit was, in fact, only slightly improved copy of the first planetary rovers.
First of all, it was rebuilt by the TV system, allowing the transmission rate of one frame was reduced to three seconds, regardless of the complexity of the terrain (at the "Lunokhod-1", this process took up to twenty seconds, which significantly complicates the process control). Secondly, to improve the survey added a third chamber located at the eye level of a standing person. Third, the system was modified automatic locks, triggered in the event of danger to the device (large roll, motor overload wheels and so on. D.). Fourth, the system was changed to the power supply. On the "Lunokhod-2" were two batteries modified total capacity 250 Ah (against 200 Ah first model), as well as enhanced solar cells.
Nevertheless career "Lunokhod-2" did not start too well. First lander nearly fell into the crater, landing just three meters away from him. Then it turned out that the navigation system is refused. Well, finally, dangerous crater, which landed near the descent module was so close that at the initial examination areas did not notice him, and "Lunokhod-2" drove right into it. Fortunately the machine not only turned, but was able to successfully get out of the crater and proceed to carry out the program.
Despite the failure of the navigation system (because of which the navigators had to rely on the sun and the environment), "Lunokhod-2" was much more productive than its predecessor. He conveyed to the Earth more than 80 thousand. Images of the lunar surface, 86 panoramas with a lot of data on-board instrumentation, and passed, a total of about 40 km. Unfortunately, the mission of the "Lunokhod-2" ended a little earlier than planned. May 9, 1973 "Lunokhod-2" examined a large crater on the eastern boundary fault "Direct". When you exit from it emerged emergency situation which led to the premature death of the machine. May 10, 1973 "Lunokhod-2" silent forever.
Entrance to Mars
In May 1971, until the "Lunokhod-1" meets the dawn of its seventh lunar day, the side of Mars from Earth sent two carrier rocket "Proton-K" automatic interplanetary station "Mars-2" and "Mars-3". Both stations were equipped with descent module landing on the surface. And neither one of them was unable to fulfill its mission, "Mars-2" crash-landed, and "Mars-3" has worked a total of 20 seconds. But that's not it - both stations carried on board the world's first rovers with the mysterious name "Device patency assessment - Mars", for short - propyl-M.
It was very simple and extremely compact scouts. The weight of the device was only 4, 5 kg of scientific instruments on board were the only dynamic penetrometer and gamma-ray densitometer to measure the density and structure of the soil. Move prop-M was walking with the help of the chassis are two "ski", located on the sides of the body. Power and control was carried out using a 15-meter cable connecting the rover with a landing stage, which, in turn, also serve as a receiving station, radio transmission from Earth.
In front of the prop-M was located simple sensors detect obstacles. Every 1, 5 m (or a collision with an obstacle) rover should automatically stop and wait for confirmation of the course. Such a system was required to maintain control over the apparatus, because the signal from the Earth and Mars goes from 4 to 20 minutes, depending on their distance from each other.
After the failure of the rovers was followed by an attempt to improve the Lunar Prospector. "Lunokhod-3" can transmit stereoscopic images from two cameras that were placed in a rotary HDA mounted on the external bar. Now to explore the area "Lunokhod" did not have to turn his whole body, just "shook his head." This arrangement later borrowed rovers Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity. New planetary rovers was fully staffed and all onboard scientific instruments, passed the whole cycle of ground tests and ... will forever remain in the museum NPO. Lavochkin. The launch, planned for 1977, did not take place.
The work continued. Russian rover, created by the Institute of Space Research, in 1992 even experience even in Death Valley (California), but to get to Mars, he was not fated. Planetary scout reappeared in the history of space exploration only after more than twenty years.
"Martian tractor»
December 4, 1996 from Cape Canaveral launch vehicle "Delta-2." After exactly 7 months, 4 July 1997 automatic interplanetary station «Mars Pathfinder» made a soft landing on the Martian surface. In addition to scientific instruments and communications systems on board the landing module was a small rover Sojourner. July 5, he began to perform scientific tasks. Its chassis was a six wheels individually driven by DC motors. The rover was equipped with three video cameras (front stereo pair and one rear camera) and mobile spectrometer for studying the chemical composition of Martian rocks and soil. Inside it, there were three radioisotope element, used to maintain the required temperature in the instrument compartment. Management carried out by a microprocessor. Himself rover exchange signals only from the lander, which, in turn, kept in touch with the Earth.
Total Sojourner worked for a little less than three months. September 27, 1997 was the last regular session with the station, and then (until October 7) unit sent only meaningless information indecipherable. Attempts were made to revive the unit until March 1998, but they were not crowned with success. During his short career Mars Pathfinder managed to pass 16, 5 thousand. Pictures Taken cameras lander and 550 images from the rover's cameras. In addition, joint efforts are fifteen times analyzed the various rocks of Mars.
Rovers did not find traction for miniaturization: the smallest of all was Sojourner (center) - the size of a microwave. It is still not lost their connection with the Earth Spirit and Opportunity (left) overtaken and outstripped the children's pedal cars. The device of the next generation Curiosity, whose mission will begin in the coming year, similar in size to a small SUV. Photo: NASA / JPL-Caltech
Opportunity and Spirit
After the untimely death of Sojourner, in the XXI century it was running two identical rovers with a very pretentious title "The Spirit» - Spirit (June 10, 2003) and "Opportunity» - Opportunity (7 July 2003). Their propeller has six wheels driven by DC motors. The source of electric energy are solar panels, and the "eyes" - two high-resolution video camera, located on the remote bar with swivel mechanism. In addition, Spirit and Opportunity thoroughly equipped for scientific research. Then there are the microscope to study the structure of soil and rocks, and three spectrometer and a miniature drill. Communication with Earth is carried out using a repeater, the role played by apparatus «Mars Odyssey», hanging orbiting Mars since October 2001.
4 and 25 January 2004 phones made a successful landing on the surface of the "red planet." But without troubles still not done. Firstly, even when both devices were in flight during a routine test revealed that "Spirit" is one of the spectrometer operates correctly. Then, after landing one of the inflatable shock landing stage I am not blown away after landing and blocked the main rover descent from the platform. As a result, "Spiritu" had a few days to maneuver, to still get down from the descent stage. January 21 zasboila flash-memory rover, because of what began on-board computer continuously restarts. Fortunately, this problem is also solved successfully. Initially, the Spirit was given to the team to use the volatile memory instead of flash-modules, and then drives a reformat, then the work of the unit included in the normal mode.
Meanwhile, Mars came Opportunity. With him, too, not everything went smoothly. During system testing revealed that because of the broken thermostat one of the heaters periodically turn on spontaneously at night. Additional power consumption reduces the number of working rover on battery, but this issue is not critical.
Spirit and Opportunity were designed for 90 days of operation. To date, the two rovers six years later (!) Are still functioning, and communicate with Earth. During this time, the machine sends an enormous amount of scientific information, thousands of images of Mars have found evidence for the existence of liquid water in the past to the "red planet", studied the traces of volcanic activity. Opportunity even found a piece of rock, with a high degree of probability is an ancient meteorite.
Spirit is now officially received the status of "stationary research platform." April 23, 2009 rover stuck in sand sulfate. By this time, the device is already out of service two wheels of the six may therefore attempt to rescue Spirit from the sand trap, which lasted nearly nine months, have been unsuccessful.
With regard to Opportunity, it is still quite cheerfully creeps on Mars and may have time to make some sensational finds before his death.
It is now built another rover, also speaking in the name of "Curiosity» - Curiosity. Its launch, as part of the interplanetary station Mars Science Laboratory, scheduled for October 2009. However, NASA announced the postponement of the mission in 2011. Perhaps this is due to the fact that immobilized the Opportunity and Spirit, despite his more than respectable age, is retain the ability to explore the Red Planet.
Yuri Popov, 10.02.2010 www.vokrugsveta.ru/telegraph/cosmos/1100/

Source: