1015
A little bit of space.
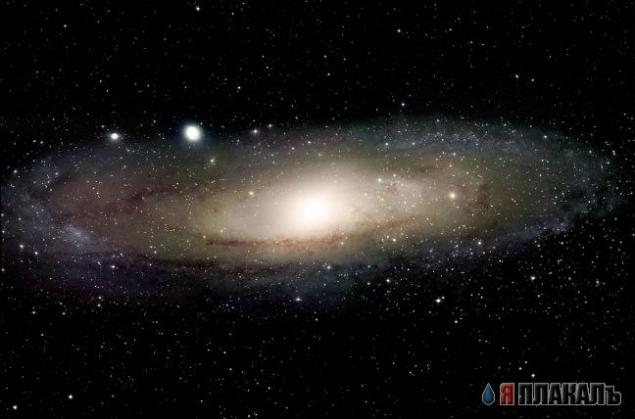
1. How far can you see? The most distant object visible to the naked eye - M31 is the great Andromeda Galaxy, which is from us at a distance of about two million light-years. But without a telescope, even this immense spiral galaxy appears as a faint, nebulous cloud in the constellation Andromeda. However, this stunning photos of one of the closest island universes, which is composed of obtained using digital imaging telescope, sealed a bright yellow nucleus, dark winding dust lanes, gorgeous blue spiral arms and star clusters.
Selection of materials www.astronet.ru/
Text lot. I read. And you can just see photos - beautiful!

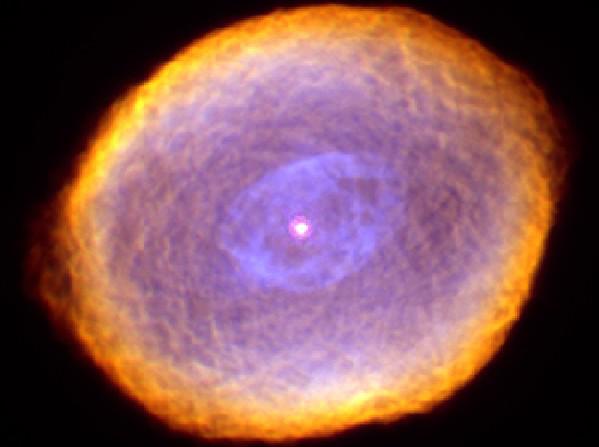
2. The planetary nebula IC 418, nicknamed the Spirograph Nebula for its resemblance with the same drawing tool, has a very unusual structure, the origin of which still remains largely unsolved. His bizarre form of the nebula may be obliged to chaotic winds emanating from the central variable stars whose luminosity varies in unpredictable ways over time intervals of a few hours. However, according to available data only a few million years ago, IC 418 was apparently just a star like our sun. What kind of a few thousand years ago, IC 418 was a common red giant. However, after the exhaustion of stocks of nuclear fuel, the outer shell of the star began to expand, leaving behind a hot core, that fate has prepared to become a white dwarf star, located in the center of the image. Radiation from the central core excites atoms in the nebula causing them to glow. IC 418 is from us at a distance of about 2,000 light-years, and its diameter is 0.3 light-years. In this image, false color, received recently the Hubble Space Telescope clearly visible details of the unusual structure of the nebula.
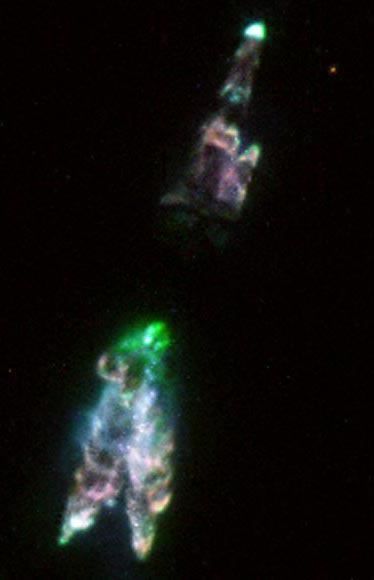
3. Just a few centuries ago, CRL 618 was rather unremarkable star - a red giant. Since then, the supply of nuclear fuel at its core has dried up and began the transformation of the stars in a planetary nebula. Currently, CRL 618 is a fast evolving protoplanetary nebula, which emits hot gas in the form of complex-shaped jets and rings moving away from the center at a speed of more than 700 000 kilometers per hour. After a few thousand years of cold-hot core of the red giant naked, revealing a white dwarf star world. In the formation of planetary nebulae, much remains unclear, including what exactly how structures arise like this. Perhaps one day a part of this planetary nebula can declare victory - CRL 618 different unusually high content of chain molecules of carbon compounds.
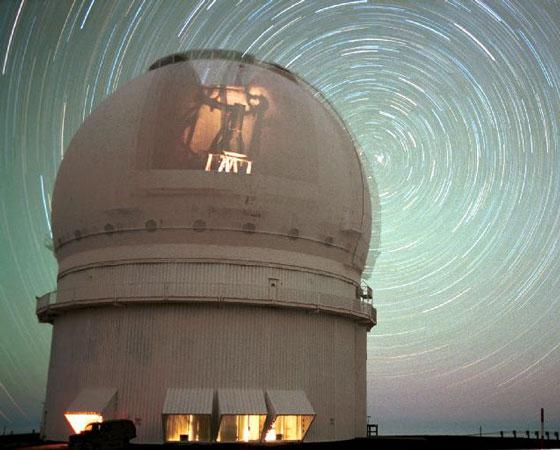
4. Unlike the human eye, which at one time collects light for only a small fraction of a second, like a telescope Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) can collect light for hours. Thus it is possible to detect faint objects, which previously could not even imagine. These careful observations usually take so much time that the Earth's rotation changes the position of the telescope on the sky background. In the above pictures are clearly visible manifestations of the Earth's rotation in the form of traces of the stars in the sky background. In order to maintain accurate guidance on the object under study, CFHT telescope must be rotated in the opposite direction. The car is photographed against the background of the telescope, it gives an idea of the huge size of the dome CFHT, and it is far not the largest telescope on Mauna Kea!

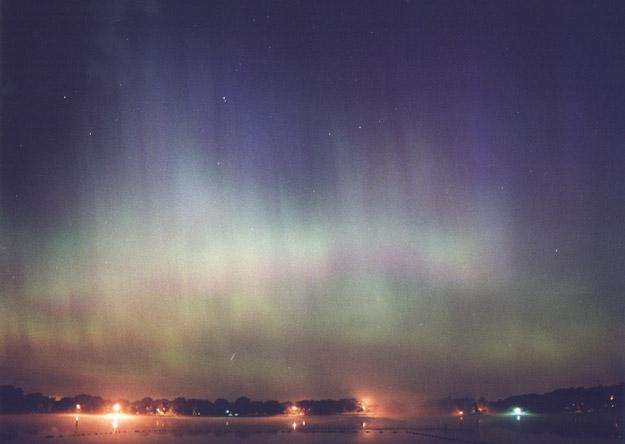
5. The diagram here photograph shows a faint Perseid meteor stream in the background fantastic aurora over Lake Cross Lake in Wisconsin, USA. In the near future it will be possible to observe how other auroras and more spectacular meteor showers. Auroras are becoming more commonplace as being their root cause - our Sun - close to the peak of its activity in the framework of an eleven-year cycle. In mid-November it will be possible to watch quirky Leonid meteor shower. Despite the fact that this is one of the most studied meteor showers, the Leonids has repeatedly surprised the astronomers, and many observers, intends to spend time in the year under the open sky, hoping to see an unforgettable show.

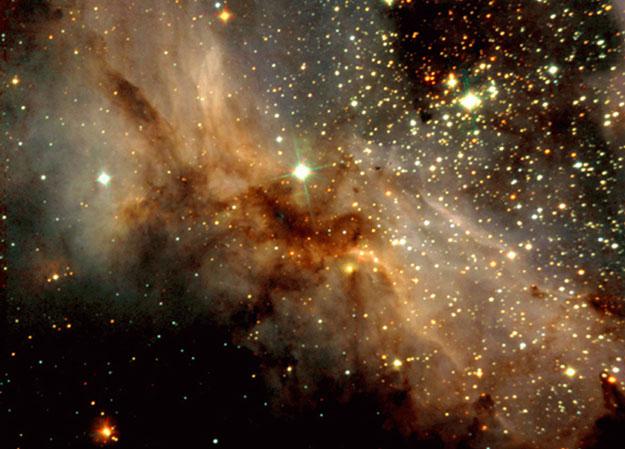
6. At the very back of the field dark clouds of dust and molecular gas known as the nebula M17, stars continue to be born. Clouds on this recently published photos of M17, resulting in the New Technology Telescope, so dark as to appear almost black in infrared light. His blackness of these molecular clouds are obliged to absorb starlight thick layer of dust consisting of particles the size of smoke particles. During his birthday massive stars are sources of high luminosity intense and hard radiation, which leads to the evaporation of the dark shell. Because of its unusual appearance M17 had names like The Omega Nebula, the Horseshoe Nebula, and the Swan Nebula. Nebula M17, which can be seen with binoculars in the constellation of Sagittarius, lies 5000 light-years away and has a diameter of about 20 light-years.

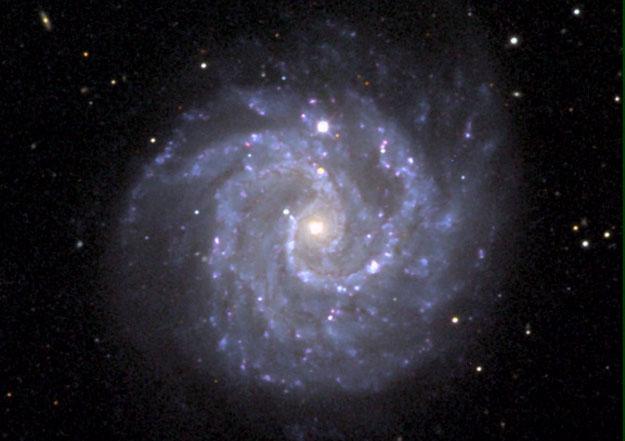
7. NGC 3184 - a large spiral galaxy with a small nucleus and long sprawl spiral arms. Although the stars in NGC 3184 several hundred billion, its blue spiral arms she owes relatively few bright blue stars. The space between the spiral arms are not filled with emptiness - bright blue stars that define the outlines of arms, born in huge density waves, which move around the galactic center. The light emitted by the galaxy NGC 3184, which is visible with a small telescope towards the constellation of Ursa Major, it takes about 25 million years to reach the Earth and about 50 thousand years to just cross the galaxy from one end to the other. Galaxy NGC 3184 (according to the classification type Sbc Hubble) is remarkable for its high content of heavy elements and the fact that it recently broke supernova.

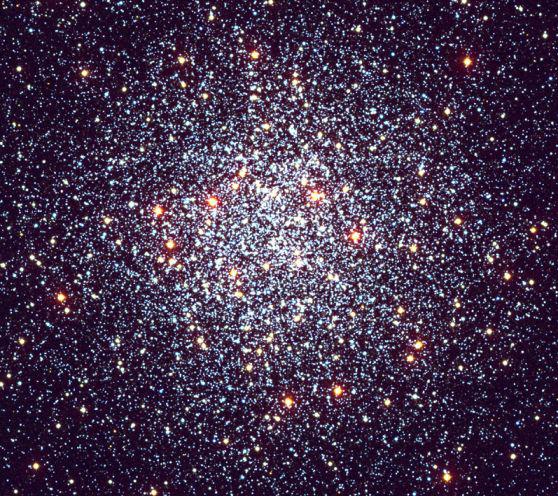
8. Fifty-fifth object in Messier - M55 - is a pretty globular cluster, numbering about 100 000 stars. Located in the constellation of Sagittarius at a distance of just 20 000 light-years from the Sun Cluster M55 looks like a circle about 2/3 the size of the disk of the full moon. Globular clusters like M55 is gravitationally bound populations of stars that roam the halo of our Milky Way while older stars of the galactic disk. Astronomers who conduct detailed studies of the stars in these objects, learn to accurately determine the age and distance of clusters. Their findings limit the possible age of the Universe (... it must be older than there are stars!), And are a fundamental element of the astronomical distance scale. In this gorgeous three-color image taken with astronomical (BVI) filters, shows an area the size of about 100 light-years away in the center of the globular cluster M55.

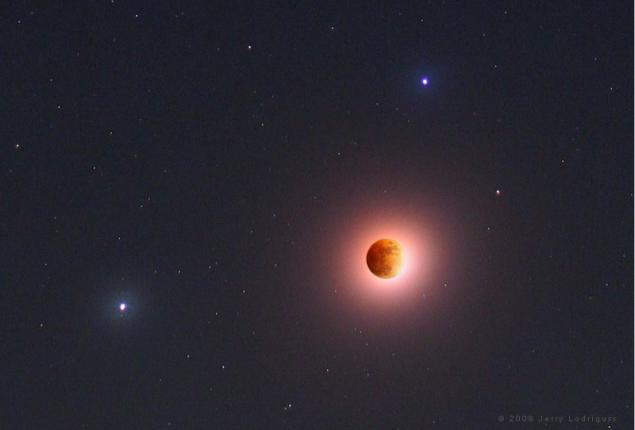
9. Observers of the Moon in the Americas, Europe, Africa and western Asia, who were lucky with clear skies this week could enjoy the view of a total lunar eclipse. Putting the eclipse moonlight astrophotographer Jerry Lodrigass created this kind of inspiring celestial phenomena, which immersed in the shadow of the moon accompanied by wandering planet Saturn (left) and Regulus - the brightest star in the constellation Leo (on the Moon). Attractive composite image was assembled from images of the Moon and the surrounding star field produced by a filter and a telephoto lens, and the telescopic image. This photomontage allows brighter reveal reddened moonlight, and at the same time shows the change in brightness and colors on the lunar surface, immersed in a not so dark shadow of the Earth.

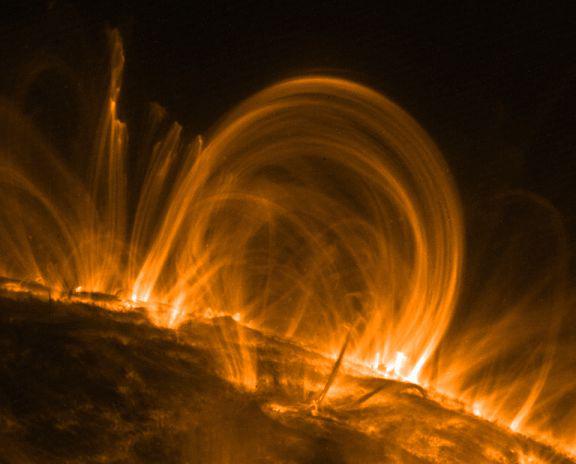
10. When viewed from the surface of the Earth solar corona, which extends over the Sun's visible surface - the photosphere - looks like a barely perceptible sparse pale education, which, however, as measured in the hundreds of times hotter than the photosphere itself. What is the source of its heat? Astronomers have long believed the cause of the high temperature of the corona, magnetic field, which raise monstrous loops of solar plasma above the photosphere. However, the new incredibly detailed observations of coronal loops made by the satellite TRACE, point to a different source of energy of unknown nature. This and other pictures sdelennye satellite TRACE in the vacuum ultraviolet range, indicate that the heating process takes place in the lower part of the crown near the bottom of the loop where they connect with the surface of the sun. The new findings refute the generally accepted theory, assuming uniform heating of its hinges. In this fantastic image with the TRACE satellite visible beams majestic hot coronal loops in the sizes of 30 or more times the diameter of Earth.

11. In this spectacular image from the Hubble Space Telescope captures the process of the birth of a cluster of massive stars. We see newborn stars at the moment of their birth from the parent nebula. The very size of the nebula is only 12 light-years known as N81 and lies about 200 000 light-years in our neighboring galaxy, the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). Dimensions nebulae surrounding other massive star clusters can reach a thousand or more light-years. Only thanks to observations with the Hubble telescope were the first to establish that in the N81 and similar compact emission nebulae are born single stars or star clusters. In the case of the N81 in the Hubble data clearly shows a lot of hot stars, the luminosity of some of them almost 300 000 times greater than the sun. In this colorful picture clearly visible graceful arcs of dark interstellar dust, as well as the structure of glowing gas, owe their origin to the action of high-energy wind and radiation from young stars.
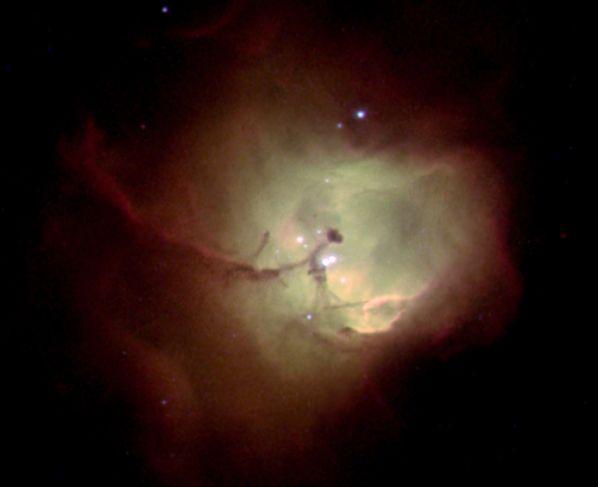
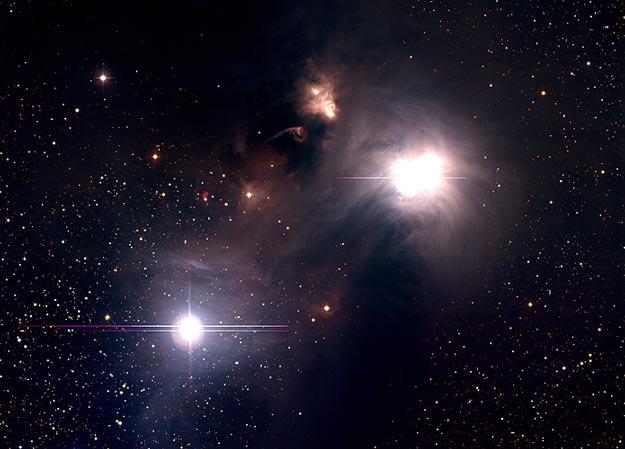
12. The young star R Corona Australis House dusty. A layer of dust in the upper left of the picture is so tight, that through him almost invisible star background. Less dense dust near the stars reflects light R Corona Australis (upper right) and an adjacent star TY South Crown, smoothing the visible form the surrounding area. Whether these stars more massive, the energy of their radiation would be sufficient to ionize a significant portion of the surrounding hydrogen gas - which is now almost invisible - causing it to glow bright red. Unusual formation of the central part of the picture - a Herbig-Haro object, that is a star cluster ejected gas, faced with the surrounding gas envelope. Distance to R Corona Australis about 500 light-years, and the diameter of the area shown here about four light-years away.

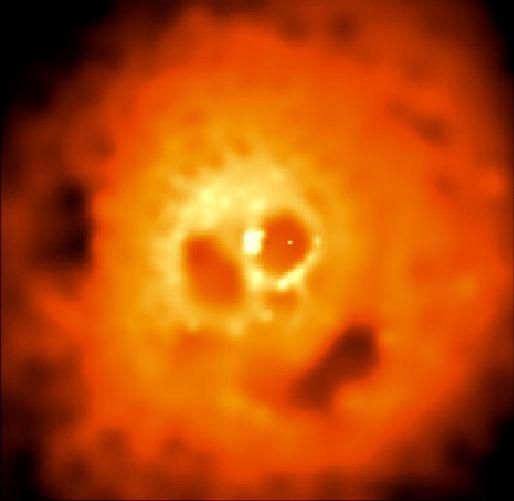
13. Against this ominous picture from the orbiting Chandra Observatory captures the kind of clusters of galaxies in the constellation Perseus X-ray photon energy of which a thousand or more times the energy of visible light photons. Located at a distance of three hundred and twenty million light years away in the Perseus cluster of galaxies thousands of galaxies, but here you will not see any of them. The main character in this X-ray photograph - is not just galaxies, and red-hot to fifty million degree cloud of intergalactic gas, whose mass is greater than the mass of all the galaxies cluster together. Observed from this angle of emptiness and bright areas in the X-ray hot gas cloud is something resemble. Two dark bubble located on either side of the central X-ray source like the eye sockets of the skull. A third elongated bubble (in the direction of a five-hour division, when viewed from the center) shows a toothless mouth. The bright X-ray source is likely a supermassive black hole at the center of the cluster, and bubbles blown beams of high-energy particles that were thrown from the explosion of a black hole and expanding into a huge cloud of gas. By the way, dark spot, forming a "nose" of the skull, it was an X-ray shadow ... from the giant galaxy, with the inexorability of fate that attracts the center of the cluster.

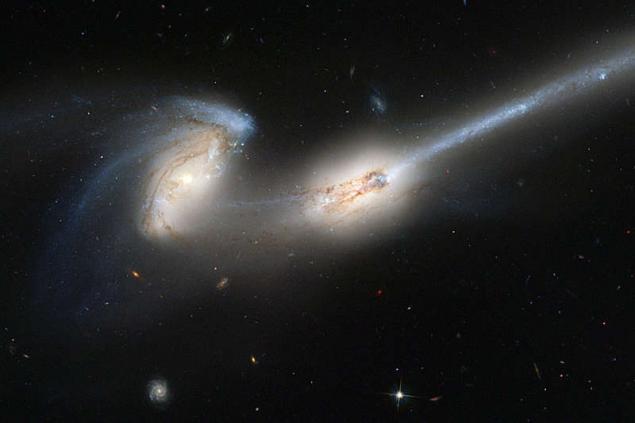
14. These two huge galaxies take away each other. This spiral galaxy "Mice", so called because of their long tails, have already passed through each other. Most likely, they will face again and again, until the merge. Long tails are formed because they attract different proximal and distal portions to one another. Cooperation in space at such great distances is slow, with a time scale of hundreds of millions of years. Galaxy NGC 4676 located at a distance of 300 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. They probably are part of a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Coma Berenices. The picture obtained by the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installed on the Space Telescope. Hubble. It is more sensitive and covers a wider field of view than other cameras on the space telescope. Due to the high sensitivity of the camera in the picture randomly appeared as distant galaxies scattered within the image field.

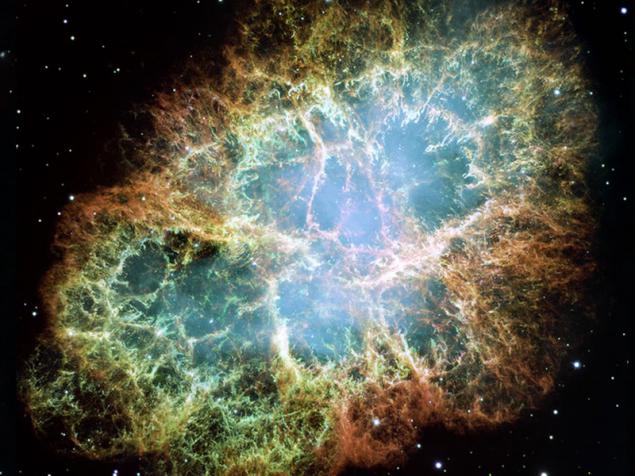
15. This confusion remained after the explosion of the star. The Crab Nebula is the result of a supernova explosion that was observed in 1054 AD. The supernova remnant is filled with mysterious filaments. The fibers are not only tremendously complex. According to experts, the mass contained therein is less than the amount of material ejected in the explosion of a supernova. In addition, the estimated speed is higher than the velocity of the material in a state of free expansion. The image that you see in the picture, get the camera Space Telescope. Hubble in three colors that were chosen for scientific interest. The Crab Nebula is ten light years. In the center of the nebula is a pulsar - a neutron star as massive as the Sun but only the size of a small town. The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times per second.

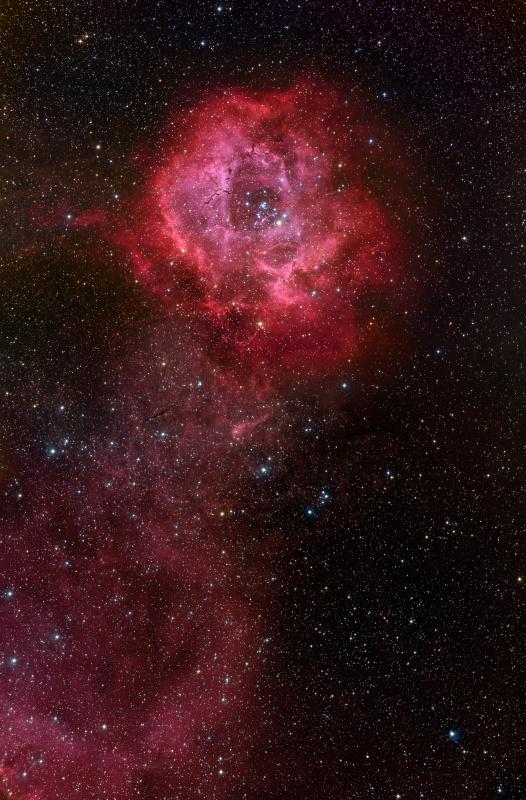
16. The Rosette Nebula (NGC 2237) - is not the only cosmic cloud of gas and dust, like a flower. However, it was her image often considered the most suitable for the Day of St. Valentine. Of the many excellent Rosette Nebula pictures submitted to APOD editors, this view seemed most appropriate, as to the composition and included a long "leg" of glowing hydrogen gas. The nebula is located on the edge of a large molecular cloud in Monoceros, a distance of about 5000 light-years. Petals of this rose are actually - stellar nursery whose lovely, symmetric shape is sculpted by winds and radiation from its central cluster of hot young stars. The stars in the cluster, cataloged as NGC 2244, are only a few million years, and the diameter of the central cavity of the Rosette Nebula - about 50 light-years.

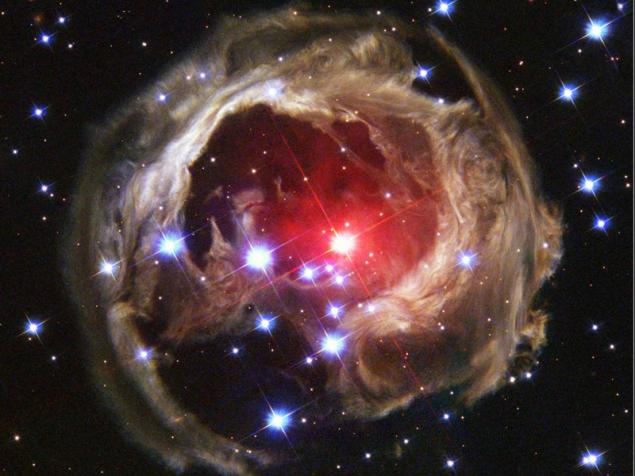
17. Why is an outbreak of V838 Mon? For reasons unknown, the outer layers of the star V838 Mon suddenly greatly expanded, so that became the brightest star in the galaxy in January 2002. And then, just as suddenly, it faded. Flash stars of this kind have not been observed. It is known that the explosion of a supernova or nova stellar material is ejected into the interstellar medium. Although the V838 Mon flash can be attributed to the release of the substance, as it can be interpreted by looking at the image of the Hubble Space Telescope. Hubble, in fact you see a star moving away from the light echo of the bright flash. A light echo is light from the flash reflecting off of distant stars by successive shells of interstellar dust that surrounds the star even before the outbreak. V838 Mon is located at a distance of 20,000 light-years away in the constellation Monoceros. Dust shell, create the phenomenon of the light echo, add up to a diameter of about six light-years away.

Source:
Selection of materials www.astronet.ru/
Text lot. I read. And you can just see photos - beautiful!

2. The planetary nebula IC 418, nicknamed the Spirograph Nebula for its resemblance with the same drawing tool, has a very unusual structure, the origin of which still remains largely unsolved. His bizarre form of the nebula may be obliged to chaotic winds emanating from the central variable stars whose luminosity varies in unpredictable ways over time intervals of a few hours. However, according to available data only a few million years ago, IC 418 was apparently just a star like our sun. What kind of a few thousand years ago, IC 418 was a common red giant. However, after the exhaustion of stocks of nuclear fuel, the outer shell of the star began to expand, leaving behind a hot core, that fate has prepared to become a white dwarf star, located in the center of the image. Radiation from the central core excites atoms in the nebula causing them to glow. IC 418 is from us at a distance of about 2,000 light-years, and its diameter is 0.3 light-years. In this image, false color, received recently the Hubble Space Telescope clearly visible details of the unusual structure of the nebula.

3. Just a few centuries ago, CRL 618 was rather unremarkable star - a red giant. Since then, the supply of nuclear fuel at its core has dried up and began the transformation of the stars in a planetary nebula. Currently, CRL 618 is a fast evolving protoplanetary nebula, which emits hot gas in the form of complex-shaped jets and rings moving away from the center at a speed of more than 700 000 kilometers per hour. After a few thousand years of cold-hot core of the red giant naked, revealing a white dwarf star world. In the formation of planetary nebulae, much remains unclear, including what exactly how structures arise like this. Perhaps one day a part of this planetary nebula can declare victory - CRL 618 different unusually high content of chain molecules of carbon compounds.

4. Unlike the human eye, which at one time collects light for only a small fraction of a second, like a telescope Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) can collect light for hours. Thus it is possible to detect faint objects, which previously could not even imagine. These careful observations usually take so much time that the Earth's rotation changes the position of the telescope on the sky background. In the above pictures are clearly visible manifestations of the Earth's rotation in the form of traces of the stars in the sky background. In order to maintain accurate guidance on the object under study, CFHT telescope must be rotated in the opposite direction. The car is photographed against the background of the telescope, it gives an idea of the huge size of the dome CFHT, and it is far not the largest telescope on Mauna Kea!

5. The diagram here photograph shows a faint Perseid meteor stream in the background fantastic aurora over Lake Cross Lake in Wisconsin, USA. In the near future it will be possible to observe how other auroras and more spectacular meteor showers. Auroras are becoming more commonplace as being their root cause - our Sun - close to the peak of its activity in the framework of an eleven-year cycle. In mid-November it will be possible to watch quirky Leonid meteor shower. Despite the fact that this is one of the most studied meteor showers, the Leonids has repeatedly surprised the astronomers, and many observers, intends to spend time in the year under the open sky, hoping to see an unforgettable show.

6. At the very back of the field dark clouds of dust and molecular gas known as the nebula M17, stars continue to be born. Clouds on this recently published photos of M17, resulting in the New Technology Telescope, so dark as to appear almost black in infrared light. His blackness of these molecular clouds are obliged to absorb starlight thick layer of dust consisting of particles the size of smoke particles. During his birthday massive stars are sources of high luminosity intense and hard radiation, which leads to the evaporation of the dark shell. Because of its unusual appearance M17 had names like The Omega Nebula, the Horseshoe Nebula, and the Swan Nebula. Nebula M17, which can be seen with binoculars in the constellation of Sagittarius, lies 5000 light-years away and has a diameter of about 20 light-years.

7. NGC 3184 - a large spiral galaxy with a small nucleus and long sprawl spiral arms. Although the stars in NGC 3184 several hundred billion, its blue spiral arms she owes relatively few bright blue stars. The space between the spiral arms are not filled with emptiness - bright blue stars that define the outlines of arms, born in huge density waves, which move around the galactic center. The light emitted by the galaxy NGC 3184, which is visible with a small telescope towards the constellation of Ursa Major, it takes about 25 million years to reach the Earth and about 50 thousand years to just cross the galaxy from one end to the other. Galaxy NGC 3184 (according to the classification type Sbc Hubble) is remarkable for its high content of heavy elements and the fact that it recently broke supernova.

8. Fifty-fifth object in Messier - M55 - is a pretty globular cluster, numbering about 100 000 stars. Located in the constellation of Sagittarius at a distance of just 20 000 light-years from the Sun Cluster M55 looks like a circle about 2/3 the size of the disk of the full moon. Globular clusters like M55 is gravitationally bound populations of stars that roam the halo of our Milky Way while older stars of the galactic disk. Astronomers who conduct detailed studies of the stars in these objects, learn to accurately determine the age and distance of clusters. Their findings limit the possible age of the Universe (... it must be older than there are stars!), And are a fundamental element of the astronomical distance scale. In this gorgeous three-color image taken with astronomical (BVI) filters, shows an area the size of about 100 light-years away in the center of the globular cluster M55.

9. Observers of the Moon in the Americas, Europe, Africa and western Asia, who were lucky with clear skies this week could enjoy the view of a total lunar eclipse. Putting the eclipse moonlight astrophotographer Jerry Lodrigass created this kind of inspiring celestial phenomena, which immersed in the shadow of the moon accompanied by wandering planet Saturn (left) and Regulus - the brightest star in the constellation Leo (on the Moon). Attractive composite image was assembled from images of the Moon and the surrounding star field produced by a filter and a telephoto lens, and the telescopic image. This photomontage allows brighter reveal reddened moonlight, and at the same time shows the change in brightness and colors on the lunar surface, immersed in a not so dark shadow of the Earth.

10. When viewed from the surface of the Earth solar corona, which extends over the Sun's visible surface - the photosphere - looks like a barely perceptible sparse pale education, which, however, as measured in the hundreds of times hotter than the photosphere itself. What is the source of its heat? Astronomers have long believed the cause of the high temperature of the corona, magnetic field, which raise monstrous loops of solar plasma above the photosphere. However, the new incredibly detailed observations of coronal loops made by the satellite TRACE, point to a different source of energy of unknown nature. This and other pictures sdelennye satellite TRACE in the vacuum ultraviolet range, indicate that the heating process takes place in the lower part of the crown near the bottom of the loop where they connect with the surface of the sun. The new findings refute the generally accepted theory, assuming uniform heating of its hinges. In this fantastic image with the TRACE satellite visible beams majestic hot coronal loops in the sizes of 30 or more times the diameter of Earth.

11. In this spectacular image from the Hubble Space Telescope captures the process of the birth of a cluster of massive stars. We see newborn stars at the moment of their birth from the parent nebula. The very size of the nebula is only 12 light-years known as N81 and lies about 200 000 light-years in our neighboring galaxy, the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). Dimensions nebulae surrounding other massive star clusters can reach a thousand or more light-years. Only thanks to observations with the Hubble telescope were the first to establish that in the N81 and similar compact emission nebulae are born single stars or star clusters. In the case of the N81 in the Hubble data clearly shows a lot of hot stars, the luminosity of some of them almost 300 000 times greater than the sun. In this colorful picture clearly visible graceful arcs of dark interstellar dust, as well as the structure of glowing gas, owe their origin to the action of high-energy wind and radiation from young stars.

12. The young star R Corona Australis House dusty. A layer of dust in the upper left of the picture is so tight, that through him almost invisible star background. Less dense dust near the stars reflects light R Corona Australis (upper right) and an adjacent star TY South Crown, smoothing the visible form the surrounding area. Whether these stars more massive, the energy of their radiation would be sufficient to ionize a significant portion of the surrounding hydrogen gas - which is now almost invisible - causing it to glow bright red. Unusual formation of the central part of the picture - a Herbig-Haro object, that is a star cluster ejected gas, faced with the surrounding gas envelope. Distance to R Corona Australis about 500 light-years, and the diameter of the area shown here about four light-years away.

13. Against this ominous picture from the orbiting Chandra Observatory captures the kind of clusters of galaxies in the constellation Perseus X-ray photon energy of which a thousand or more times the energy of visible light photons. Located at a distance of three hundred and twenty million light years away in the Perseus cluster of galaxies thousands of galaxies, but here you will not see any of them. The main character in this X-ray photograph - is not just galaxies, and red-hot to fifty million degree cloud of intergalactic gas, whose mass is greater than the mass of all the galaxies cluster together. Observed from this angle of emptiness and bright areas in the X-ray hot gas cloud is something resemble. Two dark bubble located on either side of the central X-ray source like the eye sockets of the skull. A third elongated bubble (in the direction of a five-hour division, when viewed from the center) shows a toothless mouth. The bright X-ray source is likely a supermassive black hole at the center of the cluster, and bubbles blown beams of high-energy particles that were thrown from the explosion of a black hole and expanding into a huge cloud of gas. By the way, dark spot, forming a "nose" of the skull, it was an X-ray shadow ... from the giant galaxy, with the inexorability of fate that attracts the center of the cluster.

14. These two huge galaxies take away each other. This spiral galaxy "Mice", so called because of their long tails, have already passed through each other. Most likely, they will face again and again, until the merge. Long tails are formed because they attract different proximal and distal portions to one another. Cooperation in space at such great distances is slow, with a time scale of hundreds of millions of years. Galaxy NGC 4676 located at a distance of 300 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. They probably are part of a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Coma Berenices. The picture obtained by the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installed on the Space Telescope. Hubble. It is more sensitive and covers a wider field of view than other cameras on the space telescope. Due to the high sensitivity of the camera in the picture randomly appeared as distant galaxies scattered within the image field.

15. This confusion remained after the explosion of the star. The Crab Nebula is the result of a supernova explosion that was observed in 1054 AD. The supernova remnant is filled with mysterious filaments. The fibers are not only tremendously complex. According to experts, the mass contained therein is less than the amount of material ejected in the explosion of a supernova. In addition, the estimated speed is higher than the velocity of the material in a state of free expansion. The image that you see in the picture, get the camera Space Telescope. Hubble in three colors that were chosen for scientific interest. The Crab Nebula is ten light years. In the center of the nebula is a pulsar - a neutron star as massive as the Sun but only the size of a small town. The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times per second.

16. The Rosette Nebula (NGC 2237) - is not the only cosmic cloud of gas and dust, like a flower. However, it was her image often considered the most suitable for the Day of St. Valentine. Of the many excellent Rosette Nebula pictures submitted to APOD editors, this view seemed most appropriate, as to the composition and included a long "leg" of glowing hydrogen gas. The nebula is located on the edge of a large molecular cloud in Monoceros, a distance of about 5000 light-years. Petals of this rose are actually - stellar nursery whose lovely, symmetric shape is sculpted by winds and radiation from its central cluster of hot young stars. The stars in the cluster, cataloged as NGC 2244, are only a few million years, and the diameter of the central cavity of the Rosette Nebula - about 50 light-years.

17. Why is an outbreak of V838 Mon? For reasons unknown, the outer layers of the star V838 Mon suddenly greatly expanded, so that became the brightest star in the galaxy in January 2002. And then, just as suddenly, it faded. Flash stars of this kind have not been observed. It is known that the explosion of a supernova or nova stellar material is ejected into the interstellar medium. Although the V838 Mon flash can be attributed to the release of the substance, as it can be interpreted by looking at the image of the Hubble Space Telescope. Hubble, in fact you see a star moving away from the light echo of the bright flash. A light echo is light from the flash reflecting off of distant stars by successive shells of interstellar dust that surrounds the star even before the outbreak. V838 Mon is located at a distance of 20,000 light-years away in the constellation Monoceros. Dust shell, create the phenomenon of the light echo, add up to a diameter of about six light-years away.

Source: