Russian physicists have found two types of dust in the atmosphere of Mars

group of French and Russian scientists, including three experts from laboratory infrared spectroscopy of planetary atmospheres high permission MIPT (PhD Anna Fedorova, PhD Alexander Rodin and Dr. Sci Oleg Korablev), published in the journal Icarus scientific work with the results of large-scale studies, in which for the first time were simultaneously analyzed data of infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers SPICAM machine "Mars Express" in probing the atmosphere at the limb of the planet. As a result, the scientists were able to restore the radii and the concentration of particles in the Martian atmosphere at altitudes of 10 to 50 km. Measurements were carried out in the southern and northern hemispheres in the northern summer season.
The results are interesting. It turns out that the dust in the Martian atmosphere is composed of two fractions, and at an altitude of 40-50 km layer showed aerosol composition is not yet certain.
Press Release IKI
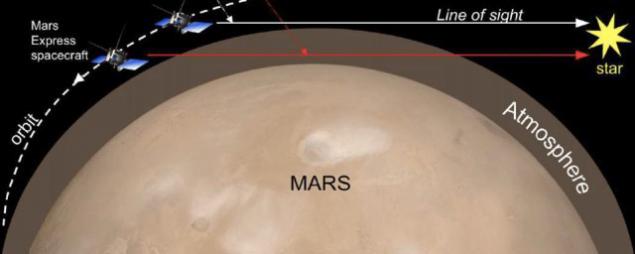
The illustration shows how SPICAM spectrometer receives data on the Martian atmosphere, comparing the spectrogram at different heights with a clear spectrogram of the Sun i>
As it turned out, in the Martian atmosphere contains two groups of particles. The first type consists of a spray of larger particles of water ice (average radius of 1 to 2 microns) and dust (0, 7 microns). They are not very much from 0, 01 to 10 particles per cubic centimeter. The second type - the dust particles within a few tenths and hundredths of a micrometer, which is much more: 1 to 1000 per cubic centimeter, depending on the altitude.
In the northern hemisphere at high latitudes (60 degrees), the level of "large" fraction of aerosol extends to an altitude of 30 km, the average - rises to 40-50 km, with over 20 km is mostly water ice, and below - dust. Particle radius is about 0, 76 microns (dust) and 1, 2 microns (water ice), and the concentration ranges, respectively, in the range 0, 4-2 and 0, 01-0, 3 particles per cubic cm.
"Small" dust much more: At 10 km the number comes to 10,000 particles per cubic centimeter, and only 30-35 km - 100 particles in the same volume. Its average size coarsens from the pole to the equator: 0, 039 mm at latitudes above 60 degrees and 0, 048 - lower (mean value 0 and 044 microns).
In the southern hemisphere, as is known from other observations, the atmosphere is generally quite clean. The average size of the large particles of dust at latitudes above 50 degrees was 0, 75 m, and the number per cubic centimeter varies from 0, 1 and 2. The water ice particles are larger - radius approximately equal to 0, 86 m, the concentration is changed from 0, 005 0 to 05 per cubic cm. The average radius of the fine dust is greater than the north: 0, 07 micrometers - and the concentration decreases with height from 100 (35 km) to 0, 6 particles (70 miles) per cubic cm. low latitudes, the sky is almost clean, and the aerosol concentration is low.
Interestingly, however, that in this area at altitudes of 40-50 km in the ultraviolet range showed a layer of mist until a certain composition. If this dust, particles having very small (0, 06 microns), and their number per cubic centimeter very large - from 100 to 3000. In the case of water ice particles size becomes slightly larger, and the concentration, by contrast, is less. Its existence, this layer may be required to global flows of warm air masses from the northern (summer) hemisphere to the southern, where they cool and sink (called Hadley cell). This circulation is typical for the season, a close solstice in both hemispheres.
From the press release of Sciences i> blockquote> The concentration of particles in the Martian atmosphere is not high. By earthly standards, it is pure atmosphere. Even in the "dusty" areas of Mars concentration of particles smaller than usual in the air of the room until the dust storm begins.
Interestingly, the role played by aerosols in the climate system of Mars. The fact that the above described composition of the particles in the atmosphere can not exist for a long time. Obviously, it is replenished from outside. A source of new particles can be dust from the surface of the planet.
The modern climate of Mars is interesting in itself, because it is unique among the terrestrial planet with a condensing atmosphere and climate system is largely controlled by the spray. In addition, the planet may have experienced catastrophic climate change and save the following past climates, suggest scientists from MIPT.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/227471/