468
"Curiosity" confirmed the presence of methane in the Martian atmosphere
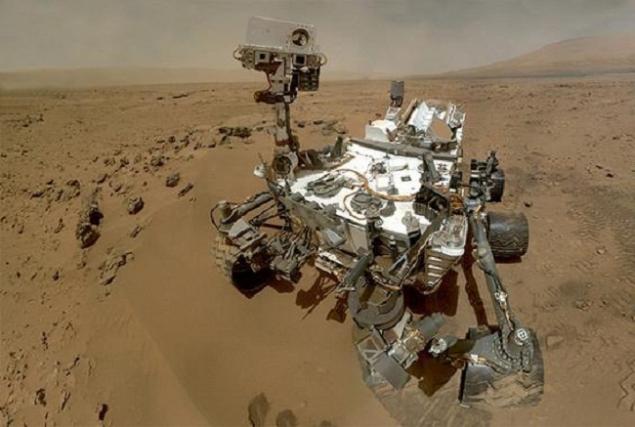

Custom laser spectrometer instrument SAM ("sample analysis at Mars") on the Curiosity Rover confirmed the discovery of episodic growth of methane concentration in the atmosphere of Mars, analyzing the data obtained during 605 Sol, or Martian days. The results were published recently in the journal Science.
These findings put the long debate about the presence of methane on Mars, which began over ten years ago when this gas was first discovered by ground-based telescopes. The flames were fanned dispute the measurements made by orbiting satellites, some of them were quite contradictory. New and irrefutable data open the way for new research that will be able to identify gas sources — among them there may be some biological activities and mechanisms that remove gas from such an inexplicable rate.
Since the telescope is a Canadian-French-Hawaiian Observatory on the Mauno Kea for the first time announced the discovery of methane in the Martian atmosphere, the study gas was carried out using several other tools from the Ground and from satellites Mars Express and Mars Global Surveyor.
Since methane can be a product of biological activity — virtually all of the existing methane in Earth's atmosphere is born thus, has high hopes that the Martian methane has the same origin.
Methane on Arsenalotti were contradictory. Some of them suggested a pattern of distribution that was limited in space (with the source in the Northern hemisphere) and time (with a peak concentration during the summer in the Northern hemisphere and a gradual descent for a few months). Both facts unexplained attracting available photochemical and General circulation models, which are used to define our understanding of the Martian atmosphere.
According to these models, if Mars really had existed methane, he would have remained there for 300 years and during this period would be distributed evenly in the atmosphere. But since we have no model which would explain its appearance, localization, and the rapid disappearance, all findings were deemed questionable, and the results attributed to the error of the tools that were at the limit of their possibilities.
"In this context, when we all were pretty sure that the collected data needs to be at least not completely accurate, take action on them would help only a more accurate measurement using SAM", — says the researcher of the Andalusian Institute of earth Sciences.
Using the TLS block, SAM found basal levels of methane concentration in the range from 0.7 parts per billion by volume and confirmed that growth of this magnitude occurs within six Sol in the tenfold volume, up to 7 ppb.
The new data are based on observations made during almost one Martian year (nearly equal to two of the earth), including the part of the mission (nominal), during which Only explored about 8 miles in the basin of the Gale crater.
Martian times Godan during this period, which covered the full cycle of Martian seasons, the environmental data collected by the meteorological station REMS (Rover Environmental Monitoring Station), has allowed to establish possible correlations between environmental parameters: relative humidity, temperature and atmospheric transparency.
REMS is a tool that was developed and supported by the Spanish scientists, members of the team studying this question. The assumption of the existence of seasonal fluctuations in methane concentration in correlation with certain environmental variables in any case be confirmed in further studies in the future. With regard to spatial locations of plumes of methane, the scientists came to the conclusion that those born in the course of a very short and weak events in very specific areas.
TLS is a configurable two-channel laser spectrometer that analyzes infrared light — more specifically, a wavelength of 2.7 µm on the first channel, and 3.27 µm on the second. The last channel specially prepared for the detection of methane. It is able to detect spectrographic fingerprint of the methane at three certain lines during "a simple and sensitive non-invasive" procedures.
Possible posledstviya to the scientists, new issues that rise in connection with the detected results exceed the answers. The fact of the presence of methane in the atmosphere of Mars causes other, more complex and far-reaching questions related to the nature of his sources, which may include one or two additional sources, not considered in the model so far. Should not be excluded from biological methanogenesis. Other questions relate to the strange evolution of methane in the Martian atmosphere after its emission. Both sides of the issue will be examined in further studies.
Newcomer machine MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution) from NASA will provide continuity of study of this issue, and in the near future, the TGO apparatus developed jointly by the European space Agency and Roscosmos, also will participate in the ExoMars mission, will measure the concentration of methane on a large scale.published
Source: hi-news.ru