1405
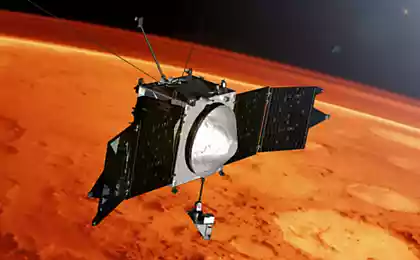
Spacecraft Maven successfully arrived in orbit of Mars

A few days ago, to publish information about that device Maven should soon come into the orbit of the Red Planet, and in order to "catch" for the gravity of Mars, the machine had to make a rather complex series of maneuvers. If the maneuver was unsuccessful, Maven could just pass by, in this case, the unit cost many tens of millions of dollars (and invaluable for science) would be lost. Over the 10 months since the launch of the device was 442 million kilometers.
But everything went well. As a result, a 33-minute maneuver, during which the fuel burned 6 main engines of the machine, the speed was dropped to the desired. During the 33 minutes was burned over half of all available on board the vehicle fuel. This enabled the machine to reach the orbit of Mars without any problems.
Now Maven was on 35-hour orbit, and a few weeks a team of operators, by performing another series of maneuvers to move the machine by 4 to 5 hours operating orbit. This orbit is quite extended, and the closest approach to the planet will be 150 km and a maximum - 6200 km.
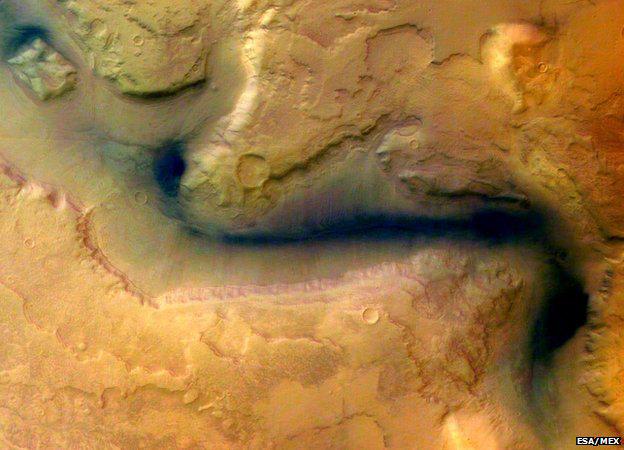

Once on the surface of Mars water flowed i>
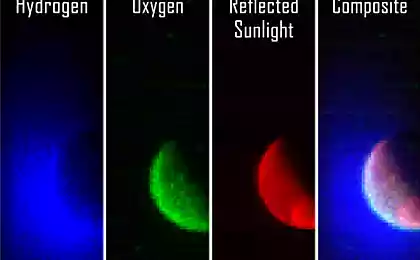
In the first few weeks of its presence on Mars orbit satellite Maven will check the performance of its scientific instruments (a total of nine).
The main task of Maven - study of the Martian atmosphere, to highlight the stages of its evolution. Thanks to the information received, scientists will be able to understand how Mars from quite hospitable planet turned into a dry desert. Perhaps the satellite will let you know when it began to change the atmosphere of Mars, and the experts will be able to know the reason. Perhaps this is the reason for the constant action of the solar wind - Mars has no magnetic field, like Earth's, so the "solar wind" has a strong impact on the planet and its atmosphere.
The main tasks of the unit the following:
Determine the effect of external factors on the change in the atmosphere of Mars; Determine the current state of the upper atmosphere of the planet, and inonosfery atmosphere interaction with the solar wind; Determine the current amount of "leakage "neutral gases and ions in outer space, as well as to study the processes that influence the leak; Determine the ratio of stable isotopes in the atmosphere of Mars.
For the current work will use three tools, including Particles and Fields Package (PFP), Remote Sensing Package (RSP), Neutral Gas and Ion Mass Spectrometer (NGIMS). I>
The other six instruments will study the solar wind and the ionosphere of Mars. This Solar Energetic Particle (SEP), Solar Wind Ion Analyzer (SWIA), Solar Wind Electron Analyzer (SWEA), SupraThermal and Thermal Ion Composition (STATIC), Langmuir Probe and Waves (LPW) experiment, Magnetometer (MAG). I >
Help in the study of the Martian atmosphere and has rover Curiosity, having on board a number of tools for analyzing air of Mars.
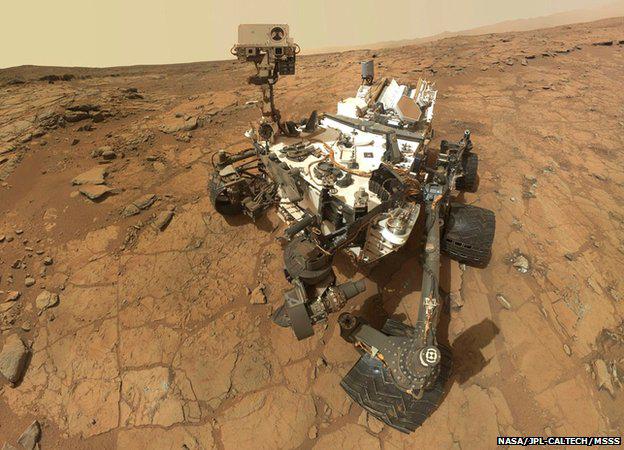

I>
Data with Maven, when combined with data Curiosity, will help identify the main stages in the evolution of the atmosphere of the Red Planet.
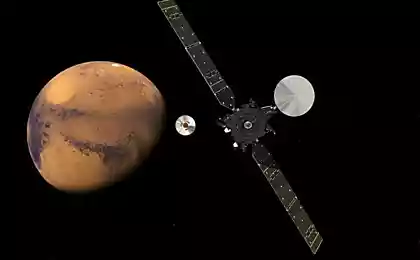
By the way, a couple of days to join his fellow Indian satellite Mangalyaan. This unit will also study the atmosphere of Mars, only will focus on the identification of methane - a potential indicator of biological activity on the planet (of course, the methane can be formed without the participation of living organisms - example is the Titan, where methane in the truest sense of the word, though a shovel oars).
bbc + nasaspaceflight
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/237651/