691
NASA scientists have identified the root cause of changes in the Martian atmosphere

Photo: NASA / GSFC i>
NASA has announced that its experts working in the project Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN), were able to identify a process that plays a major role in climate change Mars warm and humid (by the way, there is speculation that warm and humid Mars as the just never had) on the dry and cold.
Data provided MAVEN , allowed the researchers to determine the rate of loss of the atmosphere under the influence of the Red planet of the solar wind. The researchers also found that the rate increases very much during solar storms. The research results are published in the journal Science and Geophysical Research Letters for November 5.
"Mars was formerly quite thick and warm atmosphere to exist there liquid water, a key element of life, we believe now," - says John Gransfeld (John Grunsfeld), an astronaut and a representative of NASA Science Mission Directorate. "Understanding what happened to the Martian atmosphere will allow us to understand the dynamics and evolution of the gaseous envelope of the Red Planet. Understanding what can cause changes to the environment such that they can keep up such a life that is not in a position to do so, is a key issue, "- continued Gransfeld.
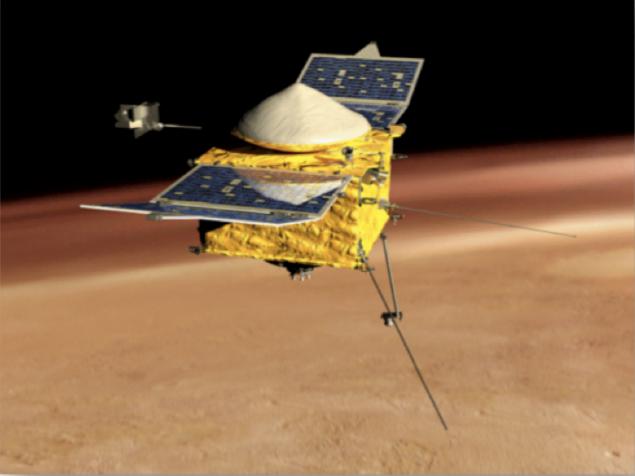

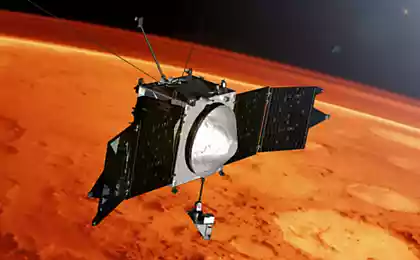
Spacecraft MAVEN
MAVEN data show that the solar wind blows into space about 100 grams of gas atmosphere every second. Over time, the changes are very significant. At the same time during solar storms rate of escape of the atmosphere into space is greatly increased. On this basis, the scientists concluded that when the Sun was more active (billions of years), the rate of loss of the planet's atmosphere was much higher than now.
Conclusion on the acceleration of the loss of Mars' atmosphere is made after analyzing the data MAVEN, relating to March 2015. Then the Sun happened several storms, and the unit recorded a significant increase in the rate of withdrawal of gases into space.
Со́лнечный wind (Eng. Solar wind) - megaionizirovannyh stream of particles (mostly helium-hydrogen plasma), flowing from the solar corona at speeds of 300-1200 km / s into the surrounding space. He is one of the main components of the interplanetary medium.
MAVEN could determine how the solar wind and ultraviolet radiation endured dioxide from the Martian upper atmosphere into space. New results show that losses are mainly in three different regions of the red planet: in the "tail" behind Mars over Martian poles and increased gas cloud surrounding Mars. About 75% of outgoing ions lose the "tail", about 25% - Pole and just a little bit (of a percent) lost a third region.
In some regions of Mars, there are clear signs existed here once liquid water. This allowed the scientists to make a conclusion that water once flowed on the surface is really a planet, and this is possible only if the warm climate and a thick atmosphere.
Interestingly, at NASA, there are a group of scientists who believe that Mars never been particularly warm and humid . These experts argue that even if the atmosphere of Mars was indeed much denser than it is now, most of it was lost at the time of the formation of a network of valleys and rivers. At this time, the atmosphere was still dense enough to sustain liquid water, but warm this era can not be called. Most likely, most of Mars was covered not lakes and ice, with occasional snowfalls the rain. And with a little raise the temperature of the ice melted, followed by the appearance of large amounts of liquid water, forming a valley. After a while it all over again would freeze.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/265354/