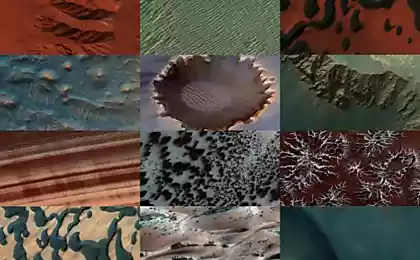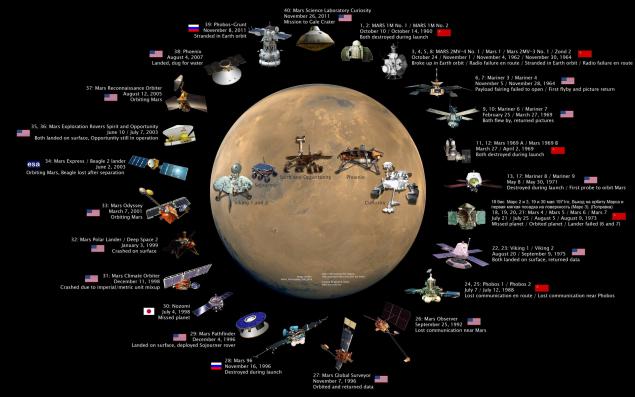
Since the time of flight of the Soviet station 1 Mars in 1963, in the vicinity of the red planet was visited by four dozen artificial messengers Earth, more than 10 vehicles reached the planet's surface. In sum was received a huge amount of information that changed forever our understanding of the red planet. Of the possible cradle of higher forms of life, Mars appeared dry and cold world.
However, this world was not always so. Geological past of Mars is divided into three periods:
Noyskaya era h5> begins with the formation of the Martian surface more than 4 billion years ago. For regions that were formed in those days peculiar huge impact craters on the surface of Mars in the hundreds and thousands of kilometers. These zones occupy the main part of the southern hemisphere of the planet, where the first is landing aids, reached the surface of Mars - Mars 2, 3 and 6. The same regions were the first that were removed during the first successful flight of the apparatus Mariner 4 in 1964.

In the era of Mars had a very thick atmosphere and hydrosphere impressive - the global oceans. And the Mars rover Opportunity, working on Mars for 10 years, not far from the ancient primarsivshiysya Erebus crater and Endeavour, discovered in them is strong evidence of the existence of fresh water billions of years ago. Then Mars possessed a full magnetic field, the remains of which are fixed for the first time the Soviet probe Mars 2, 3 and 5 (which is 500 times weaker than the Earth), as well as plate tectonics on Earth (the device Mars Global Surveyor).
Hypothetical oceans of Mars by the end of the era noyskoy:
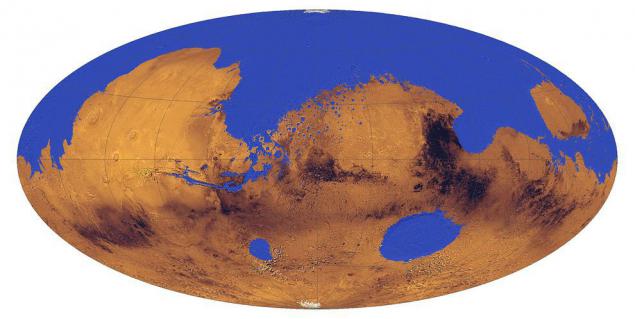
End noyskoy era marked by the cessation of heavy bombardment 3, 5 - 3, 7 billion years ago, during which and formed a majority of the above mentioned regions kraterizirovanyh. The surface of our Moon also took its modern form in that era. At the same time educated and 154 km crater Gale, who in the next era as Gusev Crater, is filled with water.
Hesperian h5> Geology of Mars is determined not by a meteorite impact, but the beginning of volcanic activity. This era was the interim, during which began to form large Tharsis volcanoes - Olympus mountain Arsiya, peacocks and Askriyskaya, a similarly Highlands Elysium. According to the most popular among scientists conjecture, this activity could be an echo of a collision with a large planetoid Mars diameter of 2000km in the early days of its existence. This would explain the appearance of the giant North pools on Mars.
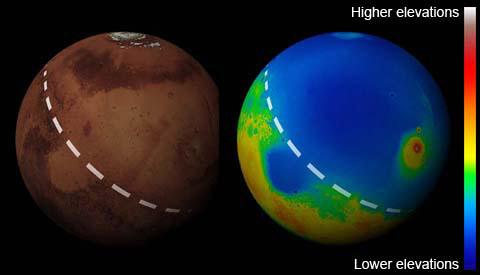
Already gesperiyskuyu era Mars has a permanent hydrosphere - Ocean occupies the northern plains by volume was comparable with the current Arctic Ocean on Earth. This circumpolar region, Odyssey orbiter discovered huge deposits of ice beneath the surface, which was confirmed by the successful operation of the apparatus here primarsivshegosya Phoenix. Another ocean occupied lowland Utopia (Utopia planitia), in the northern hemisphere, selected for jobs Viking 2. In the low and middle latitudes were many rivers and lakes (crater Gale crater Gusev) .Obrazovanie Tharsis (Tarsis) probably led to giant canyon known as Valles Marineris. Canyon was discovered the first artificial satellite of Mars - Mariner 9 in 1971.
Tharsis volcanoes region (Tharsis), left the largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus. Right largest canyon in the solar system, Valles Marineris.
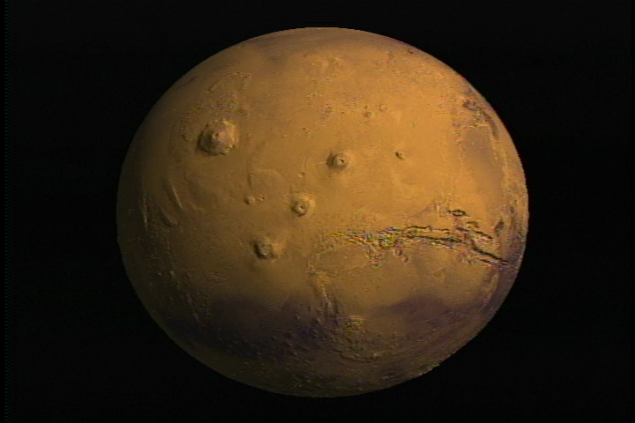

Mars gesperiyskoy era:

Huge glaciers on the high plateau to the south of this region, podtaplivayas flowed through Valles Marineris in the northern Chryse Planitia, provoking a huge flood. On this plain, yet scientists have long been interested (due to the Mariner 9), in the 70th working machine Viking 1.
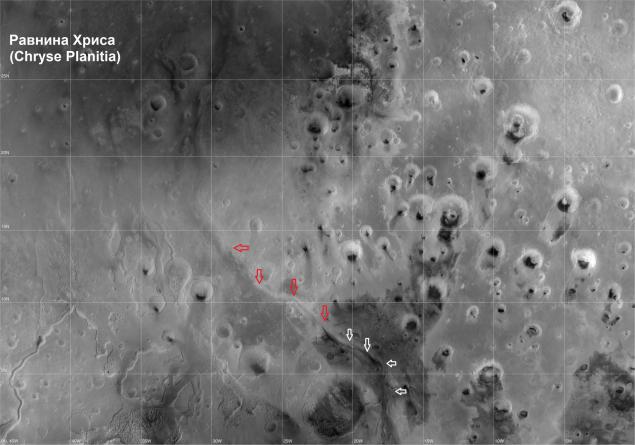
Amazoniyskaya era h5> To the top of the next, Amazoniyskoy age 2, 5 billion years ago, Mars possessed a dense atmosphere similar to Earth, with high temperatures (up to 30) and pressure up to 1 bar (about 100 000 Pa). Then formed Ares Vallis (south of Chryse Planitia), through which the Arctic Ocean from the southern highlands flow down stream of the Amazon is larger. In this valley in the 97th year working Mars Pathfinder.
Ares Vallis (indicated by arrows), "flowing" in the Chryse Planitia:

Amazoniyskaya era is characterized by a slow process of catastrophic climate change Mars. Form a large volcanic Tharsis and Elysium regions, appeared and disappeared seas and oceans. Approximately 1 billion years ago, Mars received a modern look. Most likely, the reason for the gradual cooling of the subsurface of Mars, scattering its atmosphere due to low gravity and huge temperature differences in geological time scales, the instability caused by the daily rotation of the planet's axis (the axis of the Earth's stability is maintained by the Moon).
Modern Mars:

The most interesting is the possibility of the existence of life on the planet in the wet and warm days, it is possible that it could exist at the junction and gesperiyskoy amazoniyskoy eras (and maybe today). Refinement of the geological past of Mars could shed light on this question. From this perspective, the sediments covering the mountain Aeolis (ex. Mountain Sharpe) in the center of the crater Gale, are of exceptional interest. Presumably they accumulate over 2 billion years and can tell a lot about the past of the planet and the process takes place in the lake, the ancient crater fills.
Gale Crater landing site and Curiosity / Original video rover landing in Gale Crater:
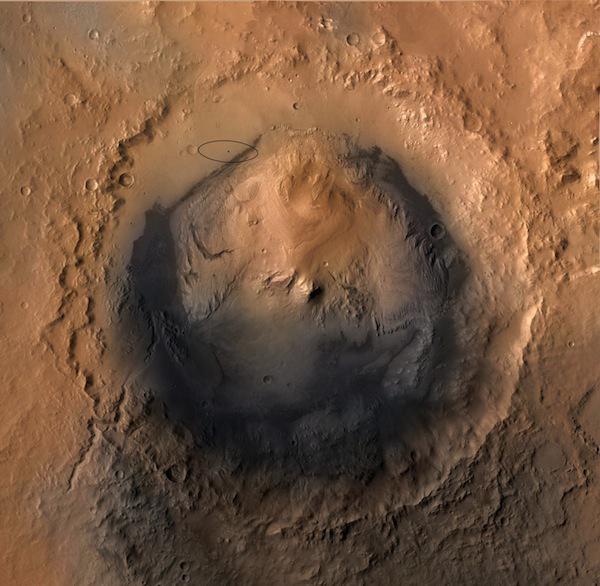

Originally the crater Gale had to go down the rover Spirit, but because of the lack of perfect technology of the time, the choice was changed to Gusev Crater. Today mountain Aeolis main goal of the rover Curiosity.
According orbiters Mars Global Surveyor, Mars Odyssey, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, and thanks largely to the work of the European unit Mars Express, the water reserves of northern and southern polar caps of Mars is estimated at 2, 4 million km3 (four times the reserves of the Black Sea). And given the recorded reserves beneath the surface of Mars - 52 million km3 of water, which is almost three times greater than the volume of the Arctic Ocean.
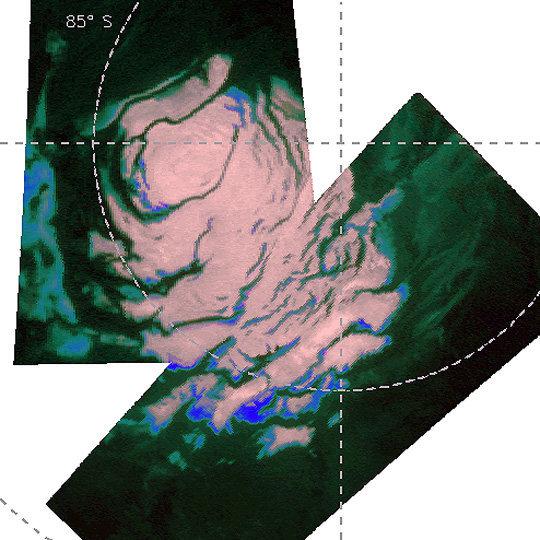
South polar cap of Mars Spectrometer Mars Express. Light pink color marked "dry" ice (CO2) from green to blue predominantly water ice:
Video of the orbital motion Mars Express:
The atmospheric pressure on Mars is about 700 Pa, strongly dependent on the height. Under such conditions, the existence of liquid water on the surface is not possible. Except for the bottom area of Valles Marineris and Hellas (Hellas Planitia) in the southern hemisphere of the planet. Since they are on average less than 7 kilometers Mars level atmospheric pressure there is twice higher than usual - 1400 Pa, which allows the existence of liquid water on the surface at temperatures of from 0 to 10 ° C (normal summer temperatures in these latitudes). Extremely low pressure is able to make people above 30 times - 35 000 Pa.
However, conditions on Mars do not reject the possibility of the existence of primitive life adapted to extreme conditions (as extremophiles on Earth). Especially that climate change on the Red Planet is slow enough that living organisms could be to adapt to them. In any case, tests for the presence of live organic conducted a series of Viking vehicles in 70th, was not allowed to make definitive conclusions on this matter.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/221833/