1561
Non-rocket spacelaunch

Introduction h4> Good day dear habrazhiteli! Production and operation of launch vehicles is quite expensive and dangerous occupation. In this regard, the cost is high and the launch of a payload into orbit. In this article we will look at alternative (rocket-free) methods for removing spacecraft into space. If I you are interested, welcome under the cut.
Space elevator h4>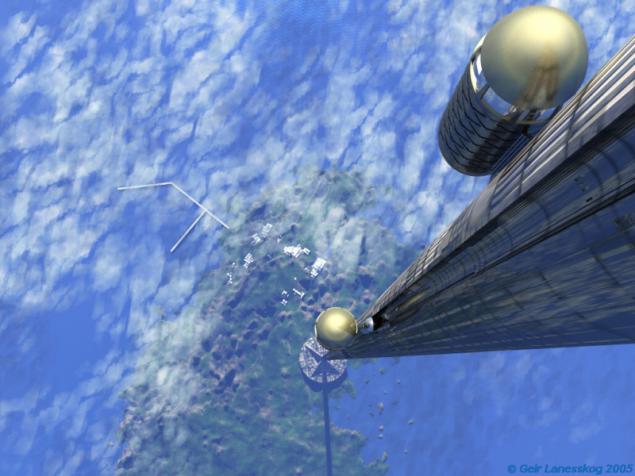 
This can be called a classic of the genre - such a concept is not described in the same sci-fi film. For the first time this idea was expressed in 1895 by Konstantin Tsiolkovsky. Space elevator is composed of three main parts: the base, cable and counterweight.
Base is a place on the surface of the planet, where the cable is attached, and begins the ascent cargo. It can be mobile (for example be placed on the ocean vessel), and is not movable. The advantage of the mobile base is quite clear - there is an opportunity to move away from hurricanes and storms that can damage the cable.
cable is a very thin thread (relative to its length, of course) of superalloy material, carried out during the geostationary orbit and held in this position by centrifugal force. Currently it is not possible to provide such material, but according to the theory, such a material may be carbon nanotubes. Alas, to produce them on an industrial scale is still very far. Durability Space tether must be of the order of 65-120 GPa, depending on the height (for comparison, the strength of steel is less than 1 GPa).
Counter is used to ensure that the cable is always in a state of tension. They can be any massive object, whether it is an asteroid or a space base (more attractive). The counterweight is well above the geostationary orbit, hence Breaking rope he might fly into a solar orbit. So if they will serve the space station, it must provide its own propulsion.
Loads lifted into orbit special lifts (and maybe not even one), and according to scientists, the path from end to end should take about 7 days. Not fast course, but very cheap. In the end, it is much faster than starting with missiles whose training takes many months. Needless project of this magnitude should be international, because no country will overcome it alone. And this in turn raises a number of problems and issues. Firstly, the territory in which to place such a construction? Indeed, because of its gigantic size, not avoid violating the airspace of several States. Secondly, the space elevator is necessary to protect against acts of terrorism and military conflicts.
Pros: h5>
The relative cheapness of delivery into geostationary orbit Significant cost savings when running interplanetary spacecraft Ability to implement low-cost space excursions < / Unlike rockets, the atmosphere is not thrown any toxic substancesCons: h5>
The complexity of implementation High construction costs The need to address the many legal and regulatory issues The orbital plane h4> Less fantastic and already feasible idea rocket-free space launch. Under the orbital plane, I mean exactly spaceship into orbit solely by its own engines. The peculiarity of such devices is that they can take off and land like conventional aircraft.
Generally, the idea of space is not new aircraft and has its roots in the middle of the XX century. The first detailed draft of automatic spacecraft was an unrealized project Zenger, to create suborbital combat bomber "Zilberfogel" in Nazi Germany. Theoretical flight altitude was 260 kilometers, certainly above the pocket (100 km), the official boundaries of the cosmos.

Model Silbervogel
Due to the high complexity of the propulsion and structural technologies, none of the projects of the orbital planes have not been realized. Currently, the company Reaction Engines is developing a reusable single-stage automatic spacecraft Skylon. I note that it will initially take off like a normal plane and reaching speeds in 5 Mach 5 and a height of 26 km, the transition to the power of their own oxygen tanks. According to experts, Skylon should reduce the cost of shipping goods by 15-20 times.
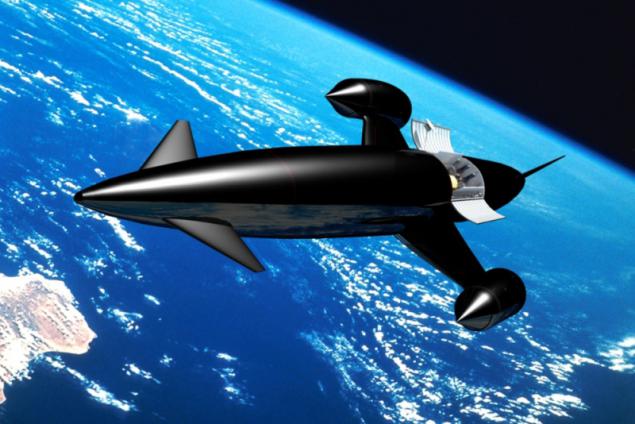

Spaceship Skylon. At an early stage of development.
Pros: h5>
No need for a special launch facility, suitable conventional airfields In contrast to the space elevator, there is a choice of orbit height Feasibility in the coming decadesCons: h5>
The need for a more sophisticated reusable engines Large fuel consumptionP.S. If someone liked the article, I will write about the continuation of other concepts of space launch rocket-free.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/221809/
Linus Torvalds received the IEEE Computer Pioneer Award
Mars today and yesterday. Brief Chronicle of robotic geologists