1044
Soviet moon program
It is believed that the Soviet lunar program ended without result. That is, we lost the race to the Americans, wasted a lot of time and effort? Just today, when the "top secret" with these developments finally cleared, we can be sure that the opinion of the lunar program as a failure is false, because almost all of our achievements: the launch of the first satellite, the first cosmonaut, the first interplanetary probes - were somehow associated with it and worked on the main thing - the preparation of landing a man on the moon.
via Monotonik

PROJECT "NORTH»
January 2, 1959 in the Soviet Union conducted the first successful launch of a three-stage launch vehicle "Vostok", established under the family of R-7. The rocket launched to the flight path of the moon automatic station "Luna-1", which after 34 hours after the launch took place in six thousand kilometers away from the goal. Communication with the station support more than 60 hours.
In March of the same year, under the leadership of Sergei Korolev started preparations for the establishment of a new spacecraft designed for near-Earth flights and flights to the Moon. Initially, the project, called "North", did not include landing an astronaut on the surface of our natural satellite - it was only about a manned flight around the moon. By the summer of the construct developed parameters which formed the basis for the design of future spacecraft.

As a preliminary step was conceived program "Soyuz 7K-L1." The spacecraft in this program was designed for a manned flight around the moon lasting 6-7 days. Since it is not provided for access to the lunar orbit, the ship has not established a powerful propulsion system, and return to Earth ensured maneuver in the gravitational field of the moon. If accurate calculations and the correct engine start breeding for the return is not required at all. The spacecraft "Soyuz 7K-L1" weighed about 5,600 kilograms and was created on the basis of the "Union." Externally P1 resembled "Union", but there was a double and had a spherical orbital module.
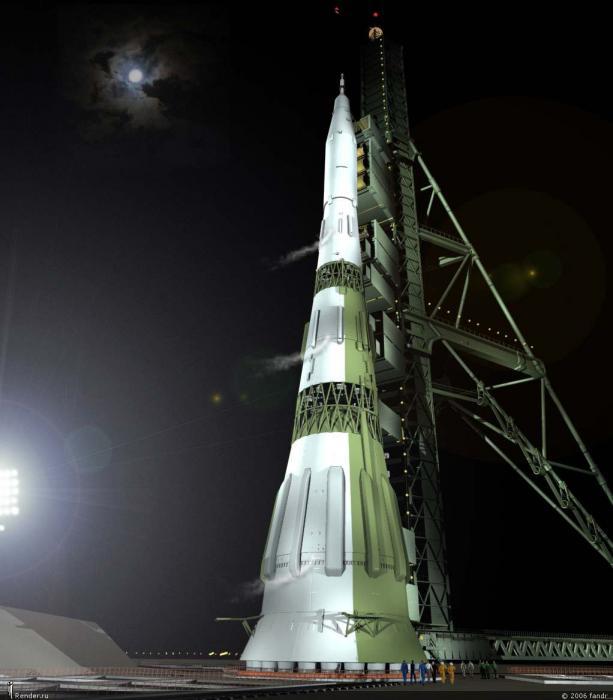
However, at the first stage of the work it became clear that the project is necessary to start serial production of a completely new type of launcher. Therefore, 23 July 1960, the Soviet Government has set the OKB-1 task of creating the new carrier rocket with a launch mass of more than 2000 tons to output in low orbit payload above 80 tons. The rocket was supposed to use conventional chemical fuel, and the whole development was given 7 years. The program is called H-1 (probably - from the word "carrier") and had spetsoboznachenie -11A52.

July 28 the same year in the United States was officially announced the beginning of the project Apollo, which provided for a manned flight around the moon and landing on its surface. Battle for the moon began. TO THE MOON royally
Almost immediately from the start of work on a new vehicle between the two leading Soviet designers Valentin Glushko (OKB-456) and Sergei Korolev (OKB-1) revealed serious differences on the issue of further development of the rocket. Glushko believed that the best fuel components are nitric acid and heptyl. Specifications during combustion of these compounds are quite high, but they are extremely toxic and dangerous to operate. Korolev's approach, according to which in the first stage could be used traditional kerosene, and for the second and third should develop engines on hydrogen.
American designer of Wernher von Braun in creating support for the Apollo program also followed the path of the use of kerosene and hydrogen. In the first stage of the rocket Saturn-V planned to place 5 engines an F-1 with a thrust of 690 tons. Work on an F-1 began in 1955, and in August 1961 passed the first test firing.
Because of such power in the Soviet Union could not be reached, Korolev decided to use engines with a thrust of 150 tons. These engines can be created in OKB-456 (Glushko) or OKB-276 (Nikolai Kuznetsov). Since Korolev and Glushko had different views on this issue, the development was entrusted Kuznetsov. In August 1964, in response to the US plan landing on the moon, it was decided to develop a similar program on the basis of the carrier rocket N-1 under the scheme provides for the orbital and lander. The program included the withdrawal of the lunar orbit double the space orbiter "Soyuz 7K-LOK" and the single of the lunar ship LK-T2K. For braking meant about the moon rocket unit D. In orbit one of the astronauts had to move through open space in the lunar craft and using the same block D start landing on the moon. Just before boarding the D block is discarded and the ship, using its own propulsion system (block €) gently down on four legs. Cosmonaut left the ship in a spacesuit, "Merlin" and about a day working on the lunar surface. After completing work on the surface of the moon ship was using the block E to go back into orbit and dock with the orbital module. Cosmonaut passed through the open space in the orbital module and transferred to a sample of lunar soil, after which the moon ship separated. To return to Earth was to be involved orbiter propulsion (unit). The landing was performed in the same way as in the project "Soyuz 7K-L1».
According to the calculations approximate weight fueled orbital module was 20 tonnes, landing module - about 6 tons. The total load is displayed on the trajectory to the Moon, it was 30 tons. In order to support the orbit accelerate to escape velocity, it required additional stage vesivshaya with 40-50 tons of fuel. Then, the carrier rocket was to deliver to low-Earth orbit 75-100 tons of cargo. In a short time this problem can be solved only N-1 rocket. October 12, 1964 the first flight of three-ship "Voskhod", piloted by astronauts Komarov, Feoktistov and Yegorov. The ship put into the orbit of a new rocket "Soyuz". The first three cosmonauts were on the ship without spacesuits. Flying under the "Sunrise" were conducted to practical working systems of the future orbital spacecraft for lunar expeditions. Due to the haste in the project was not a system for emergency rescue, and the risk of flight on the "Sunrise" was very high. Fortunately, the flight went smoothly, and the astronauts returned safely to Earth. VICTIMS space race
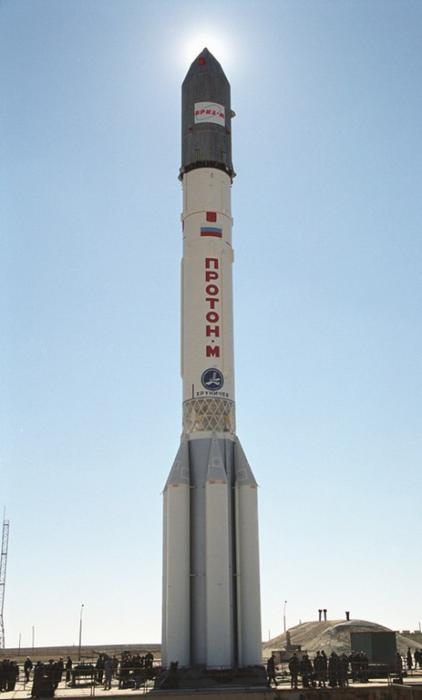
In December 1965, the project has been orbiting the Moon completely passed the OKB-1 to Sergei Korolev. New scenario involved the use of a single series of "Soyuz" for flying by the moon (modification "Soyuz 7K-LK1") and landing on the moon (modification "Soyuz 7K-LOK"), and for the flyby was used developed by a leading designer of OKB-52 Vladimir Chelomey rocket "Proton" and landing -korolёvskaya rocket H-1.

In both projects he was involved developed in OKB-1 booster D. 14 January 1966 during the surgery died Sergei Korolev. He was replaced by Vasily Mishin, who had less experience and personal connections. Nevertheless, the overall management of the lunar program left him.
In February, the project H-1 rocket has undergone processing. To increase the output of the program took into orbit the weight from 75 to 95 tons. The first launch was scheduled for March 1968. In November 1966, he entered a phase of flight test series of spacecraft "Soyuz" (modification 7K-OK for near-Earth missions). As the carrier used rocket "Soyuz". The first launch Nov. 28 revealed a large number of problems. Ship spontaneously run out of fuel for the engines of the orientation and rotate uncontrollably. There were failures in the system of automatic release. December 14 at the start of the next "Union" there was fire and explosion of the launch vehicle. It was badly damaged launch pad.
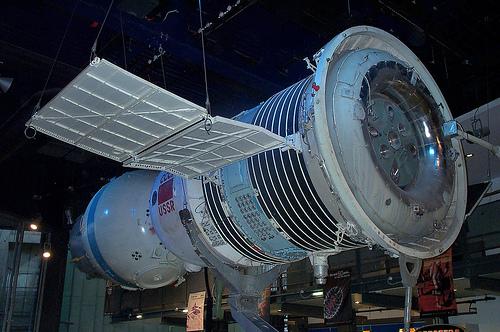
In January 1967 began test-launch rocket "Proton-K" series of spacecraft "Soyuz", able to make a flight around the Moon (double modification 7K-L1). After flying by the moon lander spacecraft had to make a two-stage entry into the atmosphere and a soft landing on the territory of the USSR. It was assumed that this complex manned mission will take place in June 1967, but the first unmanned launches revealed shortcomings of control systems of the ship and the upper stage D, as well as problems in the rocket "Proton-K».
At this time, the US lunar program received a heavy blow. On January 27, a result arising during prelaunch testing of fire killed the crew of the first ship series Apollo. The cause of the fire was a short circuit, which proved fatal in the oxygenated atmosphere of the ship. Less than a minute the fire is completely filled the space command module, and despite attempts by the crew to open the exit hatch, flames covered the astronauts. The investigation of the incident revealed the imperfection of many systems, and the subsequent completion of the ship led to a delay in the implementation of the US program for 18 months. The USSR had a chance to close the gap and win the race. For this was taken a risky step. April 23, 1967, despite the fact that none of the previous four flights of unmanned spacecraft "Soyuz 7K-OK" did not pass without a single accident, went into space, "Soyuz-1" Vladimir Komarov on board. The rocket "Soyuz" brought the ship into orbit, where it was supposed to dock with the start of the next day, "Soyuz-2" (crew: Bykovsky, Khrunov and Elisha). Two of the three members of the crew of "Soyuz-2" had to go to the "Soyuz-1", after which the two ships returned to Earth. Thus it was fulfilled the basic operations that had to be done in lunar orbit for the moon landing. However, immediately after the start on «Cora s e - 1" is not opened a solar cell, and to carry out operations on rendezvous and docking did not have enough energy. Start of "Soyuz-2" was canceled and it was decided to plant the "Soyuz-1" ahead of schedule. Because of the refusal of automation Komarov planted vehicle manually. During the descent in the atmosphere has not left the main drag chute did not open and spare, with the result that the rate of decline was about 600 km / h. Vladimir Komarov was killed when struck lander on the ground.
Nevertheless, work on the lunar program did not stop, and in October, the two unmanned spacecraft series "Soyuz 7K-OK" for the first time successfully completed the automatic docking in orbit. Shine and poverty lunar program
In March 1968, the launch complex "Proton-K" - "Soyuz 7K-L1." Upper Stage D worked without comment, unmanned spacecraft accomplished the flight path of HEO, but because of the failure of the two-step orientation instead of a smooth entry into the atmosphere lander made a ballistic descent to the point of unplanned and was destroyed by ground command. The newspapers reported about the successful flight vehicle "Zond-4". Subsequently probes were called and other unmanned vehicles in this series, is flying in the 1968-70 years. Although the accident occurred on April 22 carrier rocket "Proton", the first Soviet manned flight around the Moon was scheduled for November. Such haste was due to a desire to overtake the American ship Apollo-8, which launched to the moon scheduled for the end of December. CIA official has warned management NASA about the readiness of the USSR to the manned flight around the moon. In May new superheavy rocket H-1 was first established at the start. The test flight was scheduled for September, but because of the damage to the oxygen tank first stage of the rocket had to return to the assembly and testing facility. September 15 was successfully launched "Soyuz 7K-L1", named "Zond-5". After flying by the moon spacecraft could not carry out a two-stage entry into the atmosphere and made a landing on a ballistic trajectory away from the design point. October 26 launched an orbital ship "Soyuz-3", piloted by astronaut Shore.
In this first after the death of Vladimir Komarov flight was planned for docking with the unmanned spacecraft "Soyuz-2" kicked off the day before. Automatic docking ships moved close to 200 meters, after which the astronaut moved to manual control. However, because at the same time admitted mistakes and cost overruns arising from the fuel dock had to be abandoned. Planting both ships successfully.
November 10 went to the Moon "Zond-6". Upon successful completion of this flight the next ship would have to start with the crew on board. After flying by the moon, and a two-stage entry into the atmosphere the ship began to decline at the design point of the USSR, however, due to premature separation of the parachute crashed. Later it turned out that even in space occurred depressurization capsule. Despite the risks associated with the operation of ships of class "Union", the astronauts trained on the lunar program, sent a letter to the Politburo, which asked for permission to hold in December manned flight to the Moon. They are motivated by the fact that the presence on board the astronaut will increase the likelihood of success. A few days before the start of Saturn-V - Apollo-8 in Baikonur was prepared to launch complex "Proton-K" - "Soyuz 7K-L1" and 8 December astronauts were ready to fly, however, a high probability of the disaster did not allow the management to decide the launch before the Americans. December 21, 1968, astronauts Borman, Lovell and Anderson launched to the moon aboard the Apollo-8. For the first time people have left the near-Earth space. For the first time they did not observe sunrise and sunset for the first time with their own eyes saw the side of the moon. After a few turns in lunar orbit, the spacecraft successfully returned to Earth. The United States won the first stage of the battle for the moon. The last spurt
After the mission Apollo-8 relevance of manned flight around the moon as part of the program "Soyuz7K-L1" disappeared, and the next launch in January it was unmanned. At the stage of removing the accident occurred rocket "Proton-K" and has not worked emergency rescue system. This finally cooled interest in the program, which is relegated to second place. The Soviet Union was still a chance to get around the United States with the first human landing on the moon. February 21, 1969, the first launch of the rocket H-1. The purpose of the flight was the conclusion to the lunar orbit unmanned spacecraft "Soyuz 7K-L1A" (modification 7K-L1). However, due to high-frequency vibrations arising failure occurred in the first pipeline stage. After the start of a fire, damage to the system of management, the first stage engines were turned off after 69 seconds of flight, the rocket fell into the 52 kilometers from the start.

July 3 was the second launch of the rocket H-1. Changes to the design of the first stage of the changes have not helped. Immediately after starting the fuel pump is one of the engines was foreign metal objects, after which the pump was destroyed and there was a fire. Within 23 seconds after the start of a fully dressed with rocket struck the launch pad and almost destroyed it. It was slightly damaged nearby is the second launch pad. On the restoration of the destroyed and the introduction of new modifications to the rocket it took two years. July 13 last attempt at least something ahead of the Americans. With the carrier rocket "Proton-K" to the Moon launched a new generation of automatic station "Luna-15", which was supposed to deliver the first lunar samples to Earth pound. After entering lunar orbit experience trouble, however, it was decided to land. But by July 16 it began flying an American of Apollo-11 crew of astronauts Armstrong, Collins and Aldrin. The flight program so the first landing of man on the moon.
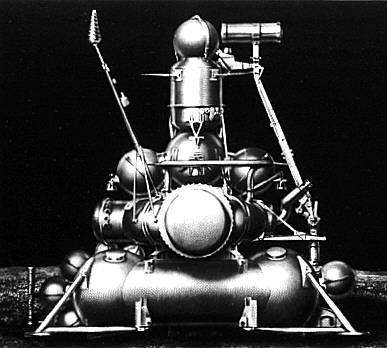
July 20, 1969, almost simultaneously began landing automatic station "Luna-15" and the lunar module, Armstrong and Aldrin manned. And here again, luck was on the side of the Americans, "Luna-15" crashed, and the lunar module made a successful landing. Astronaut Neil Armstrong became the first man to set foot on the lunar surface. Thus, the United States on all counts and won the eight-race regained its prestige. However, work on the Soviet lunar program did not stop there. August 7 was successfully launched and after 5 days, circled over and photographing the moon, landed near Kustanai drone "Zond-7." It was the first and only flight program "Soyuz 7K-L1" held without comment. Because after the July explosion implementation moon landing was delayed, it was decided in 1970, a manned flight around the moon aboard the "Soyuz 7K-L1" and carry out the test the "Soyuz 7K-LOK" and 7K-T2K unmanned near-Earth orbit. Changed and the objectives of the program N1-LZ.
All.
Source:
via Monotonik

PROJECT "NORTH»
January 2, 1959 in the Soviet Union conducted the first successful launch of a three-stage launch vehicle "Vostok", established under the family of R-7. The rocket launched to the flight path of the moon automatic station "Luna-1", which after 34 hours after the launch took place in six thousand kilometers away from the goal. Communication with the station support more than 60 hours.
In March of the same year, under the leadership of Sergei Korolev started preparations for the establishment of a new spacecraft designed for near-Earth flights and flights to the Moon. Initially, the project, called "North", did not include landing an astronaut on the surface of our natural satellite - it was only about a manned flight around the moon. By the summer of the construct developed parameters which formed the basis for the design of future spacecraft.

As a preliminary step was conceived program "Soyuz 7K-L1." The spacecraft in this program was designed for a manned flight around the moon lasting 6-7 days. Since it is not provided for access to the lunar orbit, the ship has not established a powerful propulsion system, and return to Earth ensured maneuver in the gravitational field of the moon. If accurate calculations and the correct engine start breeding for the return is not required at all. The spacecraft "Soyuz 7K-L1" weighed about 5,600 kilograms and was created on the basis of the "Union." Externally P1 resembled "Union", but there was a double and had a spherical orbital module.
However, at the first stage of the work it became clear that the project is necessary to start serial production of a completely new type of launcher. Therefore, 23 July 1960, the Soviet Government has set the OKB-1 task of creating the new carrier rocket with a launch mass of more than 2000 tons to output in low orbit payload above 80 tons. The rocket was supposed to use conventional chemical fuel, and the whole development was given 7 years. The program is called H-1 (probably - from the word "carrier") and had spetsoboznachenie -11A52.

July 28 the same year in the United States was officially announced the beginning of the project Apollo, which provided for a manned flight around the moon and landing on its surface. Battle for the moon began. TO THE MOON royally
Almost immediately from the start of work on a new vehicle between the two leading Soviet designers Valentin Glushko (OKB-456) and Sergei Korolev (OKB-1) revealed serious differences on the issue of further development of the rocket. Glushko believed that the best fuel components are nitric acid and heptyl. Specifications during combustion of these compounds are quite high, but they are extremely toxic and dangerous to operate. Korolev's approach, according to which in the first stage could be used traditional kerosene, and for the second and third should develop engines on hydrogen.
American designer of Wernher von Braun in creating support for the Apollo program also followed the path of the use of kerosene and hydrogen. In the first stage of the rocket Saturn-V planned to place 5 engines an F-1 with a thrust of 690 tons. Work on an F-1 began in 1955, and in August 1961 passed the first test firing.
Because of such power in the Soviet Union could not be reached, Korolev decided to use engines with a thrust of 150 tons. These engines can be created in OKB-456 (Glushko) or OKB-276 (Nikolai Kuznetsov). Since Korolev and Glushko had different views on this issue, the development was entrusted Kuznetsov. In August 1964, in response to the US plan landing on the moon, it was decided to develop a similar program on the basis of the carrier rocket N-1 under the scheme provides for the orbital and lander. The program included the withdrawal of the lunar orbit double the space orbiter "Soyuz 7K-LOK" and the single of the lunar ship LK-T2K. For braking meant about the moon rocket unit D. In orbit one of the astronauts had to move through open space in the lunar craft and using the same block D start landing on the moon. Just before boarding the D block is discarded and the ship, using its own propulsion system (block €) gently down on four legs. Cosmonaut left the ship in a spacesuit, "Merlin" and about a day working on the lunar surface. After completing work on the surface of the moon ship was using the block E to go back into orbit and dock with the orbital module. Cosmonaut passed through the open space in the orbital module and transferred to a sample of lunar soil, after which the moon ship separated. To return to Earth was to be involved orbiter propulsion (unit). The landing was performed in the same way as in the project "Soyuz 7K-L1».
According to the calculations approximate weight fueled orbital module was 20 tonnes, landing module - about 6 tons. The total load is displayed on the trajectory to the Moon, it was 30 tons. In order to support the orbit accelerate to escape velocity, it required additional stage vesivshaya with 40-50 tons of fuel. Then, the carrier rocket was to deliver to low-Earth orbit 75-100 tons of cargo. In a short time this problem can be solved only N-1 rocket. October 12, 1964 the first flight of three-ship "Voskhod", piloted by astronauts Komarov, Feoktistov and Yegorov. The ship put into the orbit of a new rocket "Soyuz". The first three cosmonauts were on the ship without spacesuits. Flying under the "Sunrise" were conducted to practical working systems of the future orbital spacecraft for lunar expeditions. Due to the haste in the project was not a system for emergency rescue, and the risk of flight on the "Sunrise" was very high. Fortunately, the flight went smoothly, and the astronauts returned safely to Earth. VICTIMS space race
In December 1965, the project has been orbiting the Moon completely passed the OKB-1 to Sergei Korolev. New scenario involved the use of a single series of "Soyuz" for flying by the moon (modification "Soyuz 7K-LK1") and landing on the moon (modification "Soyuz 7K-LOK"), and for the flyby was used developed by a leading designer of OKB-52 Vladimir Chelomey rocket "Proton" and landing -korolёvskaya rocket H-1.

In both projects he was involved developed in OKB-1 booster D. 14 January 1966 during the surgery died Sergei Korolev. He was replaced by Vasily Mishin, who had less experience and personal connections. Nevertheless, the overall management of the lunar program left him.
In February, the project H-1 rocket has undergone processing. To increase the output of the program took into orbit the weight from 75 to 95 tons. The first launch was scheduled for March 1968. In November 1966, he entered a phase of flight test series of spacecraft "Soyuz" (modification 7K-OK for near-Earth missions). As the carrier used rocket "Soyuz". The first launch Nov. 28 revealed a large number of problems. Ship spontaneously run out of fuel for the engines of the orientation and rotate uncontrollably. There were failures in the system of automatic release. December 14 at the start of the next "Union" there was fire and explosion of the launch vehicle. It was badly damaged launch pad.

In January 1967 began test-launch rocket "Proton-K" series of spacecraft "Soyuz", able to make a flight around the Moon (double modification 7K-L1). After flying by the moon lander spacecraft had to make a two-stage entry into the atmosphere and a soft landing on the territory of the USSR. It was assumed that this complex manned mission will take place in June 1967, but the first unmanned launches revealed shortcomings of control systems of the ship and the upper stage D, as well as problems in the rocket "Proton-K».
At this time, the US lunar program received a heavy blow. On January 27, a result arising during prelaunch testing of fire killed the crew of the first ship series Apollo. The cause of the fire was a short circuit, which proved fatal in the oxygenated atmosphere of the ship. Less than a minute the fire is completely filled the space command module, and despite attempts by the crew to open the exit hatch, flames covered the astronauts. The investigation of the incident revealed the imperfection of many systems, and the subsequent completion of the ship led to a delay in the implementation of the US program for 18 months. The USSR had a chance to close the gap and win the race. For this was taken a risky step. April 23, 1967, despite the fact that none of the previous four flights of unmanned spacecraft "Soyuz 7K-OK" did not pass without a single accident, went into space, "Soyuz-1" Vladimir Komarov on board. The rocket "Soyuz" brought the ship into orbit, where it was supposed to dock with the start of the next day, "Soyuz-2" (crew: Bykovsky, Khrunov and Elisha). Two of the three members of the crew of "Soyuz-2" had to go to the "Soyuz-1", after which the two ships returned to Earth. Thus it was fulfilled the basic operations that had to be done in lunar orbit for the moon landing. However, immediately after the start on «Cora s e - 1" is not opened a solar cell, and to carry out operations on rendezvous and docking did not have enough energy. Start of "Soyuz-2" was canceled and it was decided to plant the "Soyuz-1" ahead of schedule. Because of the refusal of automation Komarov planted vehicle manually. During the descent in the atmosphere has not left the main drag chute did not open and spare, with the result that the rate of decline was about 600 km / h. Vladimir Komarov was killed when struck lander on the ground.
Nevertheless, work on the lunar program did not stop, and in October, the two unmanned spacecraft series "Soyuz 7K-OK" for the first time successfully completed the automatic docking in orbit. Shine and poverty lunar program
In March 1968, the launch complex "Proton-K" - "Soyuz 7K-L1." Upper Stage D worked without comment, unmanned spacecraft accomplished the flight path of HEO, but because of the failure of the two-step orientation instead of a smooth entry into the atmosphere lander made a ballistic descent to the point of unplanned and was destroyed by ground command. The newspapers reported about the successful flight vehicle "Zond-4". Subsequently probes were called and other unmanned vehicles in this series, is flying in the 1968-70 years. Although the accident occurred on April 22 carrier rocket "Proton", the first Soviet manned flight around the Moon was scheduled for November. Such haste was due to a desire to overtake the American ship Apollo-8, which launched to the moon scheduled for the end of December. CIA official has warned management NASA about the readiness of the USSR to the manned flight around the moon. In May new superheavy rocket H-1 was first established at the start. The test flight was scheduled for September, but because of the damage to the oxygen tank first stage of the rocket had to return to the assembly and testing facility. September 15 was successfully launched "Soyuz 7K-L1", named "Zond-5". After flying by the moon spacecraft could not carry out a two-stage entry into the atmosphere and made a landing on a ballistic trajectory away from the design point. October 26 launched an orbital ship "Soyuz-3", piloted by astronaut Shore.
In this first after the death of Vladimir Komarov flight was planned for docking with the unmanned spacecraft "Soyuz-2" kicked off the day before. Automatic docking ships moved close to 200 meters, after which the astronaut moved to manual control. However, because at the same time admitted mistakes and cost overruns arising from the fuel dock had to be abandoned. Planting both ships successfully.
November 10 went to the Moon "Zond-6". Upon successful completion of this flight the next ship would have to start with the crew on board. After flying by the moon, and a two-stage entry into the atmosphere the ship began to decline at the design point of the USSR, however, due to premature separation of the parachute crashed. Later it turned out that even in space occurred depressurization capsule. Despite the risks associated with the operation of ships of class "Union", the astronauts trained on the lunar program, sent a letter to the Politburo, which asked for permission to hold in December manned flight to the Moon. They are motivated by the fact that the presence on board the astronaut will increase the likelihood of success. A few days before the start of Saturn-V - Apollo-8 in Baikonur was prepared to launch complex "Proton-K" - "Soyuz 7K-L1" and 8 December astronauts were ready to fly, however, a high probability of the disaster did not allow the management to decide the launch before the Americans. December 21, 1968, astronauts Borman, Lovell and Anderson launched to the moon aboard the Apollo-8. For the first time people have left the near-Earth space. For the first time they did not observe sunrise and sunset for the first time with their own eyes saw the side of the moon. After a few turns in lunar orbit, the spacecraft successfully returned to Earth. The United States won the first stage of the battle for the moon. The last spurt
After the mission Apollo-8 relevance of manned flight around the moon as part of the program "Soyuz7K-L1" disappeared, and the next launch in January it was unmanned. At the stage of removing the accident occurred rocket "Proton-K" and has not worked emergency rescue system. This finally cooled interest in the program, which is relegated to second place. The Soviet Union was still a chance to get around the United States with the first human landing on the moon. February 21, 1969, the first launch of the rocket H-1. The purpose of the flight was the conclusion to the lunar orbit unmanned spacecraft "Soyuz 7K-L1A" (modification 7K-L1). However, due to high-frequency vibrations arising failure occurred in the first pipeline stage. After the start of a fire, damage to the system of management, the first stage engines were turned off after 69 seconds of flight, the rocket fell into the 52 kilometers from the start.

July 3 was the second launch of the rocket H-1. Changes to the design of the first stage of the changes have not helped. Immediately after starting the fuel pump is one of the engines was foreign metal objects, after which the pump was destroyed and there was a fire. Within 23 seconds after the start of a fully dressed with rocket struck the launch pad and almost destroyed it. It was slightly damaged nearby is the second launch pad. On the restoration of the destroyed and the introduction of new modifications to the rocket it took two years. July 13 last attempt at least something ahead of the Americans. With the carrier rocket "Proton-K" to the Moon launched a new generation of automatic station "Luna-15", which was supposed to deliver the first lunar samples to Earth pound. After entering lunar orbit experience trouble, however, it was decided to land. But by July 16 it began flying an American of Apollo-11 crew of astronauts Armstrong, Collins and Aldrin. The flight program so the first landing of man on the moon.

July 20, 1969, almost simultaneously began landing automatic station "Luna-15" and the lunar module, Armstrong and Aldrin manned. And here again, luck was on the side of the Americans, "Luna-15" crashed, and the lunar module made a successful landing. Astronaut Neil Armstrong became the first man to set foot on the lunar surface. Thus, the United States on all counts and won the eight-race regained its prestige. However, work on the Soviet lunar program did not stop there. August 7 was successfully launched and after 5 days, circled over and photographing the moon, landed near Kustanai drone "Zond-7." It was the first and only flight program "Soyuz 7K-L1" held without comment. Because after the July explosion implementation moon landing was delayed, it was decided in 1970, a manned flight around the moon aboard the "Soyuz 7K-L1" and carry out the test the "Soyuz 7K-LOK" and 7K-T2K unmanned near-Earth orbit. Changed and the objectives of the program N1-LZ.
All.
Source: