423
Gyro
Gyroscopes, navigational instrument, the main element of which is a rapidly rotating rotor, mounted so that its axis of rotation can be rotated. Three degrees of freedom (the axis of rotation possible) gyroscope rotor provided with two frames gimbal. If this device is not acted upon by external disturbance, then the proper rotation axis of the rotor maintains a constant orientation in space. If it works the moment external force tends to turn the axis of rotation of its own, then it starts to turn around the direction is not the time, and about an axis perpendicular to it (precession).
In a well-balanced (astatic) and quickly rotating gyroscope mounted on bearings of highly negligible friction moment there is practically no external forces, the gyroscope so long keeps almost unchanged its orientation in space. Therefore, it can indicate the angle of rotation of the base, which is fixed. That's Zh.Fuko French physicist (1819-1868) for the first time demonstrated the Earth's rotation. If the axis of rotation of the gyroscope to limit the spring, when the respective setting it, say, on an aircraft, to perform a U-turn, the gyro will deform the spring, until the moment of external force is balanced. In this case, the force of compression or tension spring is proportional to the angular velocity of the aircraft. This is the principle of action Indicator aviation and many other gyroscopic instruments. Since the bearing friction is very small, in order to maintain the rotation of the gyro rotor does not require a lot of energy. To bring it in rotation and to maintain rotation usually sufficient low-power motor or an air blast
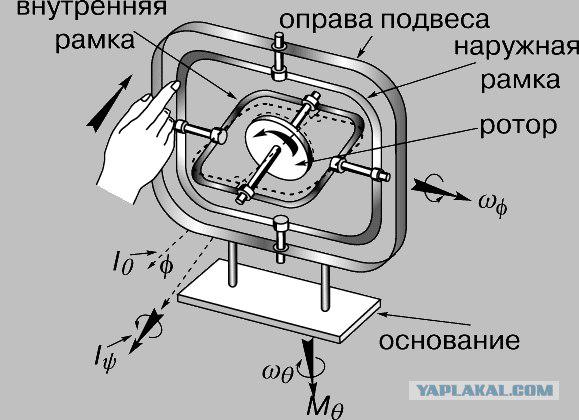
Fig. 1. gyroscope with three degrees of freedom (with two frames gimbal), kinematics. I & lt; sub & gt; y & lt; / sub & gt; - its own axis of rotation of the rotor, along which sent its kinetic moment; I & lt; sub & gt; 0 & lt; / sub & gt; - The reference direction of the angular momentum; j - the deflection angle of the inner frame gimbal; w & lt; sub & gt; j & lt; / sub & gt; - The angular velocity of rotation of the inner frame of the suspension (precession); M & lt; sub & gt; q & lt; / sub & gt; - The time of the disturbing external force; w & lt; sub & gt; q & lt; / sub & gt; - The angular velocity of rotation of the outer frame of the suspension (nutation) .Ris. 1. gyroscope with three degrees of freedom (with two frames gimbal), kinematics. Iy - own axis of rotation of the rotor, along which sent its kinetic moment; I0 - the reference direction of the angular momentum; j - the deflection angle of the inner frame gimbal; wj - the angular velocity of rotation of the inner frame of the suspension (precession); Mq - time disturbing external force; wq - the angular velocity of rotation of the outer frame of the suspension (nutation). © krugosvet.ru
Source:
In a well-balanced (astatic) and quickly rotating gyroscope mounted on bearings of highly negligible friction moment there is practically no external forces, the gyroscope so long keeps almost unchanged its orientation in space. Therefore, it can indicate the angle of rotation of the base, which is fixed. That's Zh.Fuko French physicist (1819-1868) for the first time demonstrated the Earth's rotation. If the axis of rotation of the gyroscope to limit the spring, when the respective setting it, say, on an aircraft, to perform a U-turn, the gyro will deform the spring, until the moment of external force is balanced. In this case, the force of compression or tension spring is proportional to the angular velocity of the aircraft. This is the principle of action Indicator aviation and many other gyroscopic instruments. Since the bearing friction is very small, in order to maintain the rotation of the gyro rotor does not require a lot of energy. To bring it in rotation and to maintain rotation usually sufficient low-power motor or an air blast
Fig. 1. gyroscope with three degrees of freedom (with two frames gimbal), kinematics. I & lt; sub & gt; y & lt; / sub & gt; - its own axis of rotation of the rotor, along which sent its kinetic moment; I & lt; sub & gt; 0 & lt; / sub & gt; - The reference direction of the angular momentum; j - the deflection angle of the inner frame gimbal; w & lt; sub & gt; j & lt; / sub & gt; - The angular velocity of rotation of the inner frame of the suspension (precession); M & lt; sub & gt; q & lt; / sub & gt; - The time of the disturbing external force; w & lt; sub & gt; q & lt; / sub & gt; - The angular velocity of rotation of the outer frame of the suspension (nutation) .Ris. 1. gyroscope with three degrees of freedom (with two frames gimbal), kinematics. Iy - own axis of rotation of the rotor, along which sent its kinetic moment; I0 - the reference direction of the angular momentum; j - the deflection angle of the inner frame gimbal; wj - the angular velocity of rotation of the inner frame of the suspension (precession); Mq - time disturbing external force; wq - the angular velocity of rotation of the outer frame of the suspension (nutation). © krugosvet.ru

Source: