535
Gyro - yesterday, today and tomorrow.
More recently, the gyro was the instrument that was used in a rather exotic for the average person areas, such as the aerospace, aviation, weapons systems. But now it is already firmly entrenched in the life of any person, together with mobile and gaming devices, becoming a common thing as a camera phone.
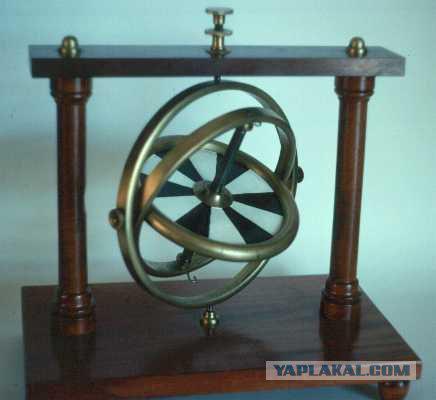

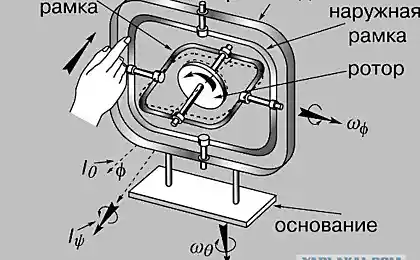
Probably everyone knows the design, which is freely rotatable within the drive in three planes that can respond to changes in the angles of orientation relative to the housing. That's the way the classic rotary gyroscope, whose use in small devices were previously impossible because of technical constraints associated with the manufacture of such devices is small size. Make way for the use of gyroscopes in modern mobile devices have opened the so-called vibrating gyroscopes. They use the same physical principles as the rotor, i.e. the effect of the Coriolis force, but are based on MEMS technology that combines microelectronic and micromechanical components on a silicon substrate. In essence, they are combined with piezoelectric sensors, vibrating in different planes.
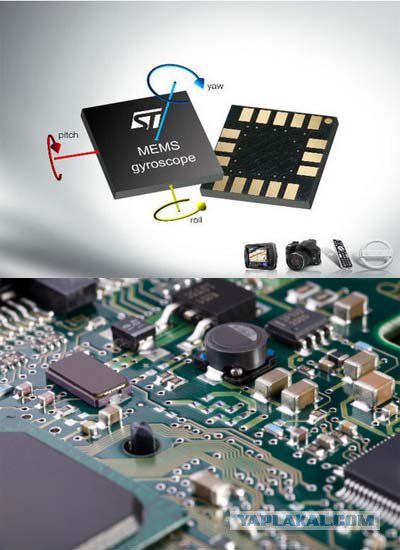

The next and the most promising generation of these devices will become asynchronous rotary gyroscopes that combine many of the advantages of modern technology. But most importantly - they are very small, are able to provide precision accuracy, and relatively inexpensive to mass produce. In general, rotary asynchronous gyroscopes used the principles of the design of multi-phase asynchronous motors.

The stator is formed by using a gyroscope MEMS technology on a silicon substrate and consists of a core and disposed around the electromagnetic coils that generate a rotating magnetic field, and simultaneously used as inductive sensors.

Gyroscope rotor diameter comparable to the diameter of a human hair (!). In the idle state, it is parked on the stator core. Magnetic field coils lifts and spins the rotor above the surface of the stator core, and the effect of scheduling not permit it to come into contact with the surface.
If you change the position of the body in space gyro it happens, respectively, the change in potential induction sensor stator, which is calculated on the testimony of a change of orientation angles.
Rotary-asynchronous gyroscopes in consumer devices available to all open just fantastic prospects for their use in everyday life and set the stage for a new qualitative leap in the use of high technology.

Source:

Probably everyone knows the design, which is freely rotatable within the drive in three planes that can respond to changes in the angles of orientation relative to the housing. That's the way the classic rotary gyroscope, whose use in small devices were previously impossible because of technical constraints associated with the manufacture of such devices is small size. Make way for the use of gyroscopes in modern mobile devices have opened the so-called vibrating gyroscopes. They use the same physical principles as the rotor, i.e. the effect of the Coriolis force, but are based on MEMS technology that combines microelectronic and micromechanical components on a silicon substrate. In essence, they are combined with piezoelectric sensors, vibrating in different planes.

The next and the most promising generation of these devices will become asynchronous rotary gyroscopes that combine many of the advantages of modern technology. But most importantly - they are very small, are able to provide precision accuracy, and relatively inexpensive to mass produce. In general, rotary asynchronous gyroscopes used the principles of the design of multi-phase asynchronous motors.

The stator is formed by using a gyroscope MEMS technology on a silicon substrate and consists of a core and disposed around the electromagnetic coils that generate a rotating magnetic field, and simultaneously used as inductive sensors.

Gyroscope rotor diameter comparable to the diameter of a human hair (!). In the idle state, it is parked on the stator core. Magnetic field coils lifts and spins the rotor above the surface of the stator core, and the effect of scheduling not permit it to come into contact with the surface.
If you change the position of the body in space gyro it happens, respectively, the change in potential induction sensor stator, which is calculated on the testimony of a change of orientation angles.
Rotary-asynchronous gyroscopes in consumer devices available to all open just fantastic prospects for their use in everyday life and set the stage for a new qualitative leap in the use of high technology.

Source: