738
While you sleep
Good morning YaPovtsy.
I want to talk a little bit about your work in the London Underground (on the Russian -metro-).
While the majority of normal people sleep, we work under the ground, and not just as part of the 270 subway stations and 408 kilometers of tracks.
Here is a small excerpt from the Wiki - London Underground - a system of underground lines in London (UK), combining ground and underground lines. London Underground - the oldest and one of the largest in the world. Londoners called the metro the Underground («subway"), or more frequently Tube («pipe"), most in the form of deep tunnels.
London Underground Work began January 10, 1863, much of the original route is now included in the line Hammersmith & City.
As of the 2010 London Underground includes 270 stations, length of routes - more than 253 miles (408 kilometers). Some of the stations and tunnels are closed today. London Underground Passenger traffic in 2008 amounted to 1.09 billion people, or about 3 million people a day.
01 photo. Upon entering we were met by a sign informing about the requirements of workwear and protection and who can provide first aid

History
The underground passages were used for thousands of years in the mining, water supply, and for military purposes. At the beginning of the XIX-th century on the main streets of London it was overcrowded due to the diversified transport of those times, not to mention pedestrians. Thousands of people every day crossed the Thames - by ferry or London Bridge. Because of the constant traffic jams from the merchants disappeared in the sun fruits and vegetables, which they tried to take to the market.
Marc Brunel Izambard - French engineer who lived in England - an idea that makes London streets eventually could to unload. Once Brunel watched as the ship worm paves the way for solid oak sliver. Bruyneel said that only a small head covered with a rigid clam shell. With its jagged edges worm bored into the tree. Delving, he left on the walls of a smooth stroke protective layer of lime. Taking this principle as a basis, a large cast iron Brunel patented tunneling shield that pushed underground jacks. Workers were able to remove the shield from the ground, but he could not prevent the collapse of the breed. Shield deep into the rock, and other workers formed a tunnel reinforce brickwork.
Applying this shield, Bruyneel has successfully built the world's first underwater tunnel, padded in soft soil - under the Thames - in 1843. Thus Brunel demonstrated the possibility of building tunnels and paved the way for the development of the modern metro.
In 1863 she opened the world's first underground line of the road, connecting London's main railway stations, and in 1865 bought Brunel tunnel to extend the line. The tunnel now forms part of the London Overground Overground.
London Underground was the first subway in the world. At the time, the railroad has already enjoyed great success in this regard, the proposal of one of London's lawyer about the construction of the underground city rail found supporters. Four years later, he built the first subway station, he ran from the station of Bishop's Road to Farringdon Road. At the time, London Underground was able to carry on the day to 40 000 passengers, and by 1880 it transported 40 million passengers a year. We are expanding rapidly, and other lines, which led to the fact that in 1884 was crowded and Central Line.
The first tunnels were built using conventional construction methods, that is, open way. The streets are dug to a depth of 10 meters, laid rails, built stone arch, then the whole structure obkladyvali brick and paved street again. The main drawback of this method has been many months Stopping streets where construction works were carried out. Open pit was built "Orange Line", the construction of which has caused the destruction of several houses from Paddington Station Bayswater.
The first London subway trains were steam. They worked on coal and emitted an awful fumes. Initially, the cars were divided into three classes. Hand luggage strengthened between the cars. The first time cars were completely devoid of windows, as it was thought to look under the ground is still not what. However, this design caused passengers psychological discomfort, so it was soon arranged production cars of the modern type.
When the train came on electricity, ventilation ceased to be a problem as acute and tunnels started to make deeper. For its construction were used for the first time so-called "drilling shields' cylindrical shape (the shape of the tunnel). The system today is a major in the construction of underground tunnels.
During the construction of the Victoria line was first used jointed ring finishing tunnels, but the system has not received the recognition due to lack of stability of the structure. The main part of London Underground stations built decorated with iron tubing, on the principle of Brunel.
The first electrified line linked the district with the City South London Railway, thereby became a reliable transport links. Switching to electric traction began in 1890 and ended in 1906.
In the early XX century, the coexistence of the six independent lines caused certain inconvenience to passengers; in many places to go from one line to the other people had to go some distance above the ground. The costs to eliminate many of the problems were great, leaving many companies operating underground, turned to the financiers to allocate their money to eliminate a lot of inconvenience, as well as to fully electrify the Metro.
In the future, the construction of the underground were involved in the new company and the company, which led to a fragmentation of structures and diverse nature of the lines. In 1933, the London Underground system was transferred to a specially created "Directorate of Urban Transport." Due to the types of devices and structures subway have become more standard than they were before.
Also, work began on the construction of new lines and stations, but they were interrupted by World War II. During the war the metro was used as a bomb shelter. London authorities initially prevented this, but then still gave permission: at stations posted beds, toilets and clinics.
On December 23, 2007 the East London Line (orange) has been closed for renovation. During the reconstruction of the line has been completely remodeled and expanded. April 27, 2010 the line came in the elevated Overground, cruising through the new trains - they will be an important link to the Transport for London 2012 Olympics. (Wikipedia)
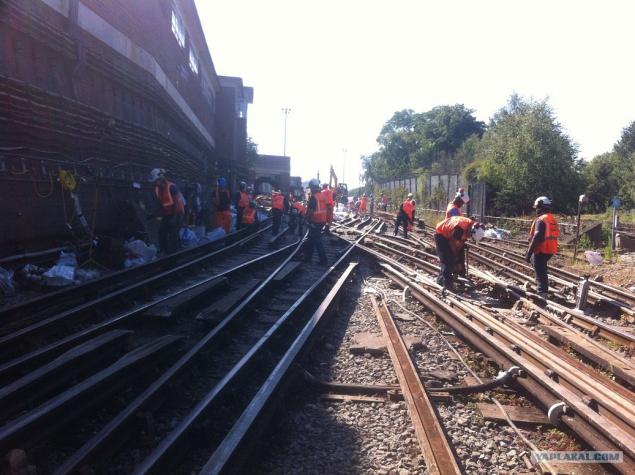
Work carried out after midnight and till the morning and close at the weekend 2-3 metro line and then there work crews being replaced every 12 hours until Monday morning vlot.
constantly and gradually upgrade all the systems, changing the rails, sleepers, cable system signals.
Each photo will sign individually to make it clear what is and what is used when finished will tell.
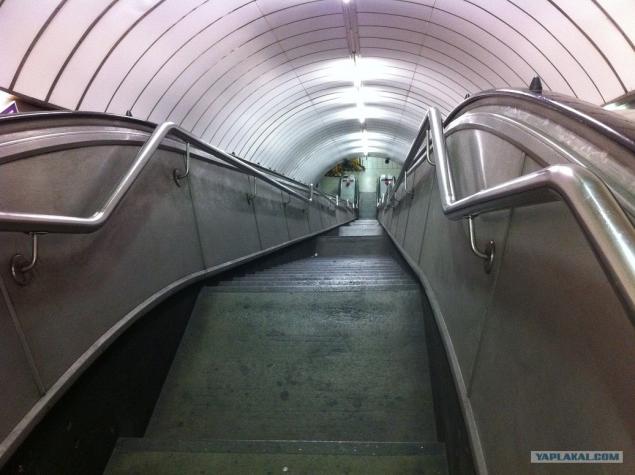
02. since the subway is not running and escalators, too. We have spuskatsya stairs

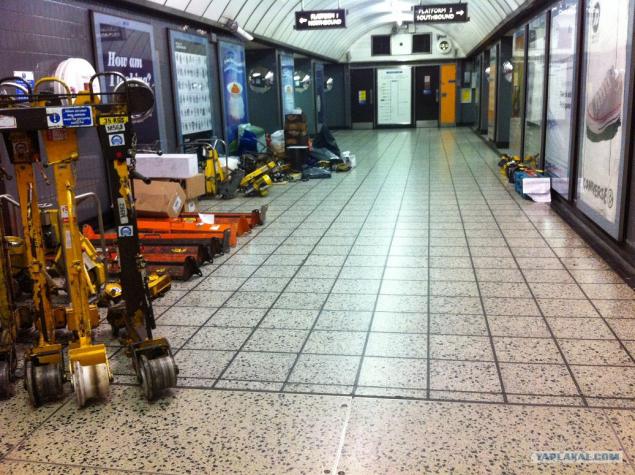
03.V bottom met us mountains of tools and materials. Orange pieces on the left are called Ironmen and are used for lifting and transporting rail at close range.

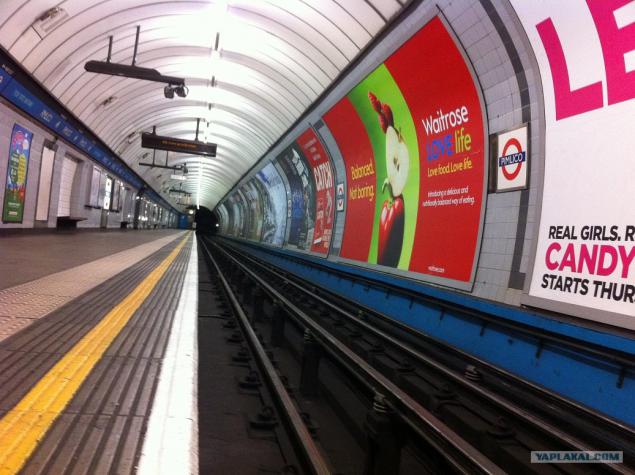
04. Just kind of platform free of crowds.

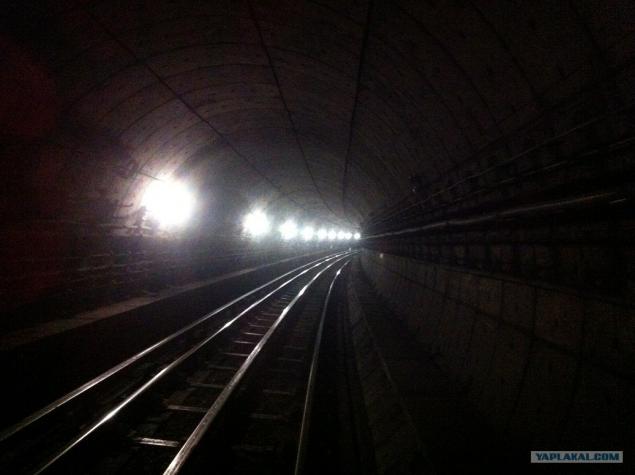
05.Vot we tunnel. One pair of rails for the train wheels and one for the current supply. In the middle of a negative voltage of 280 volts and 420 volts positive side, and the train of voltage is supplied to the 700 volts.

06. recently begun to change the current supply rails from steel to aluminum.
That is one of the new
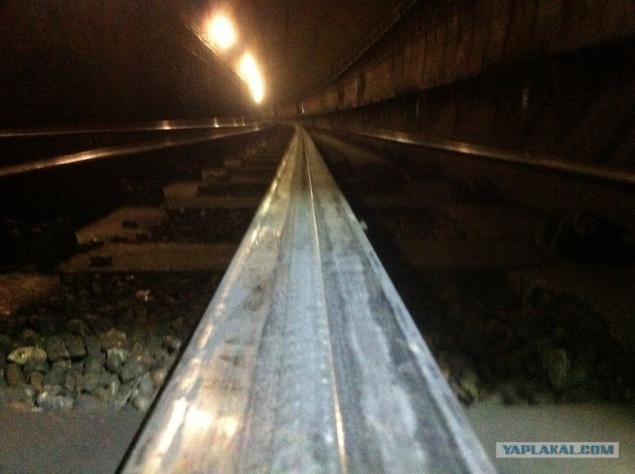

07. It is held here on such centers.
In English it is called POT.
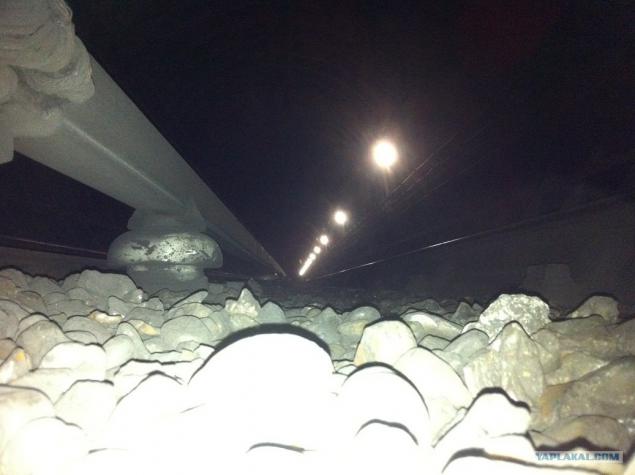

08. Type of mounting rails. Very convenient to be dismantled.
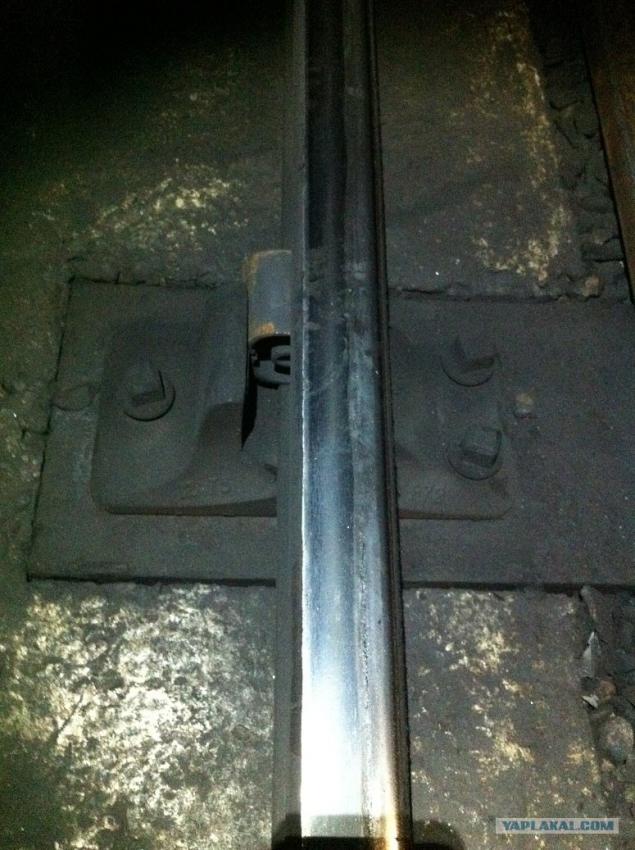

09.Passage. A small tunnel between the subject on which the trains are.
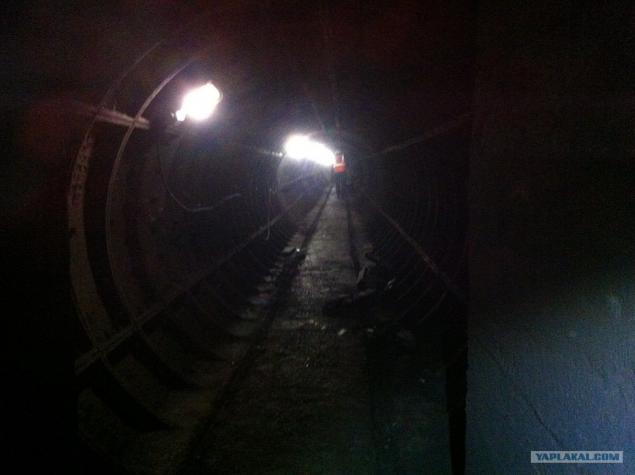

10. The entire tunnel consists of the following blocks of twisted metal bolts hell knows when
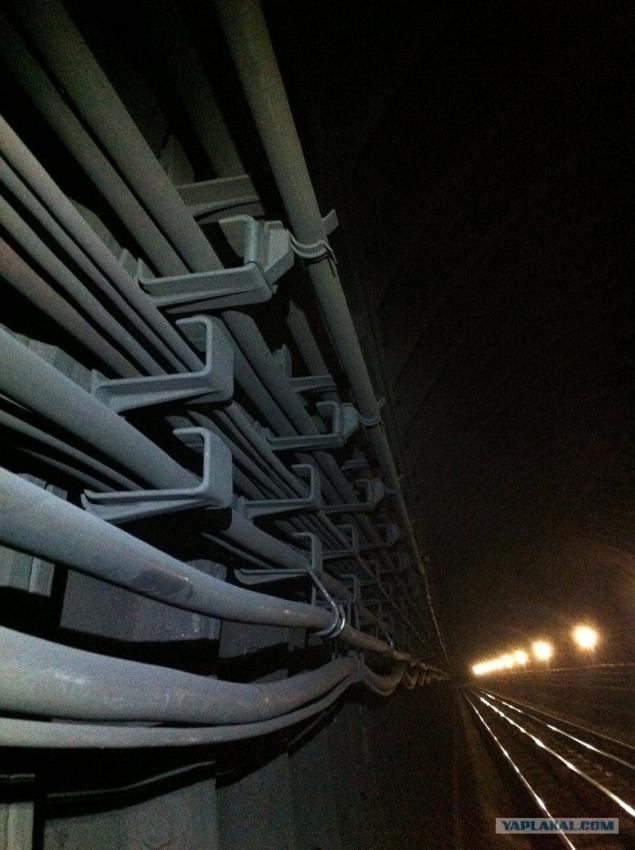
11. And of course, the cable in the tunnel binding

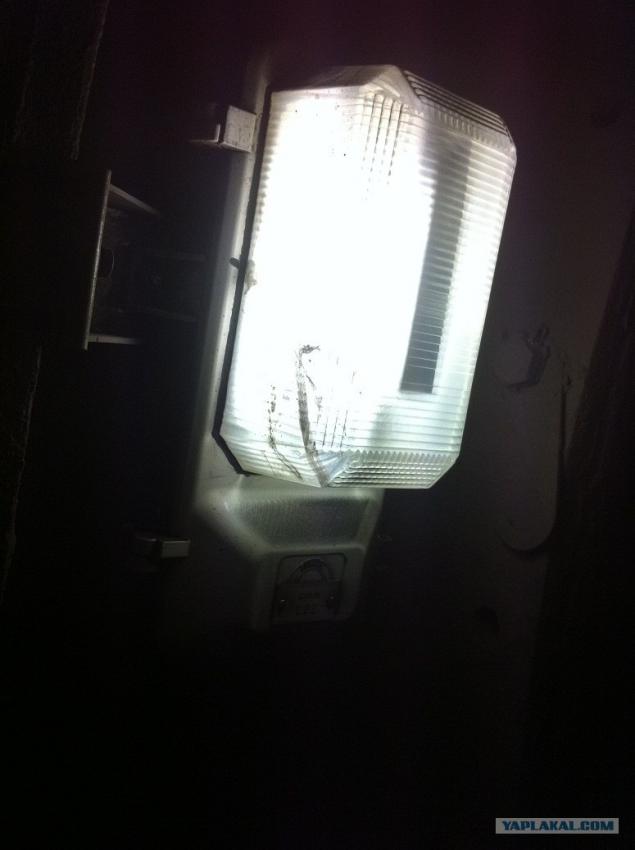
12. The light comes on automatically when the voltage is turned off on the tracks

13. All the tools are powered from the power outlets here such 120 volts. which are located every 50 meters

14.

15. A little talk about tools.
Ironmen - For lifting and transportation of rail.
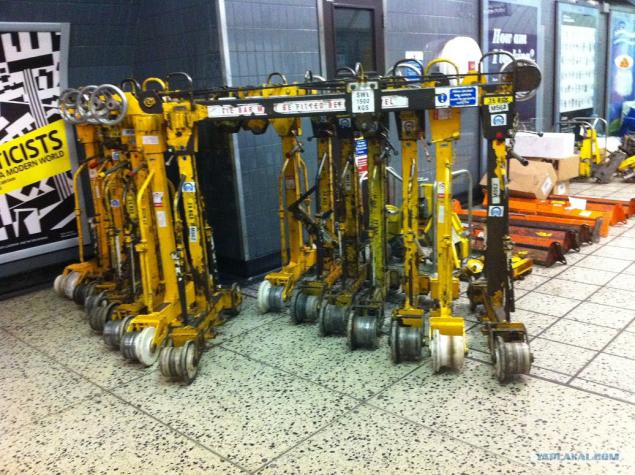

16. Saw Cutting rail
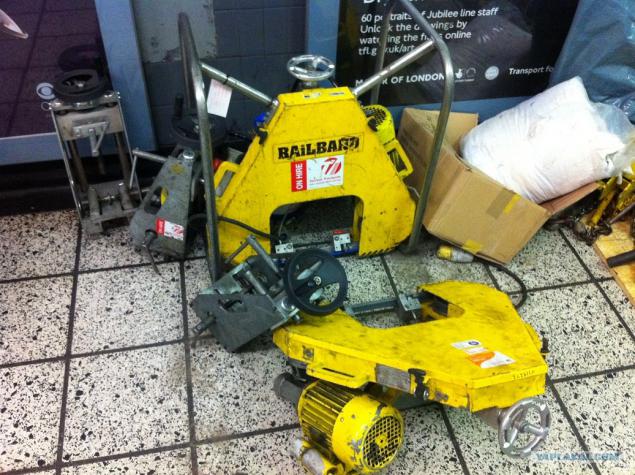

17. Pedestrian stacker for transporting tools and materials
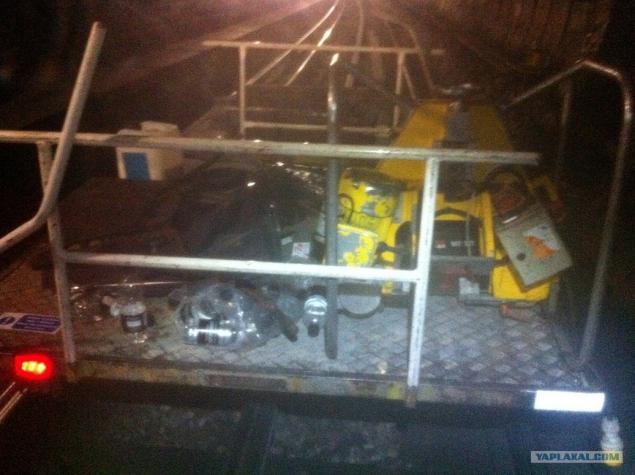

18. motorized four passengers Can be used with a trailer, working from 8 akamulyatorov.

19. A little closer
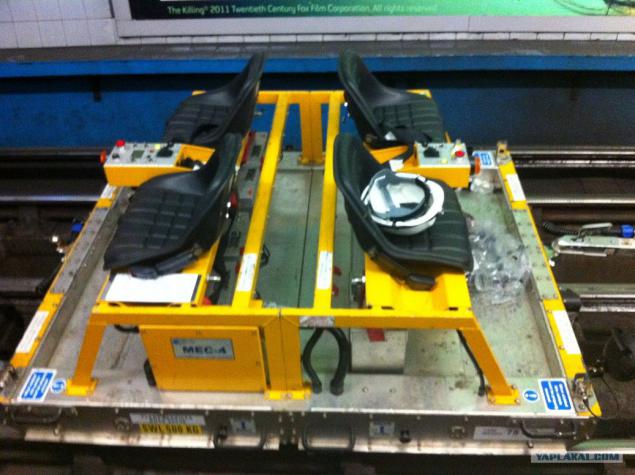

20. Also, in an open area that's very helpful to such machines. It arrives on the ground and then easily drives onto the track
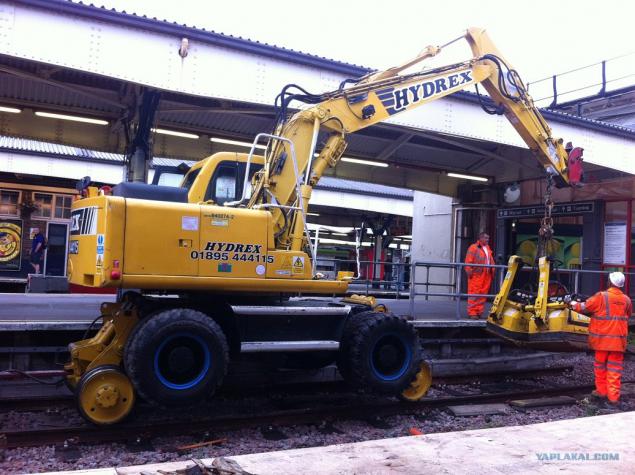

21
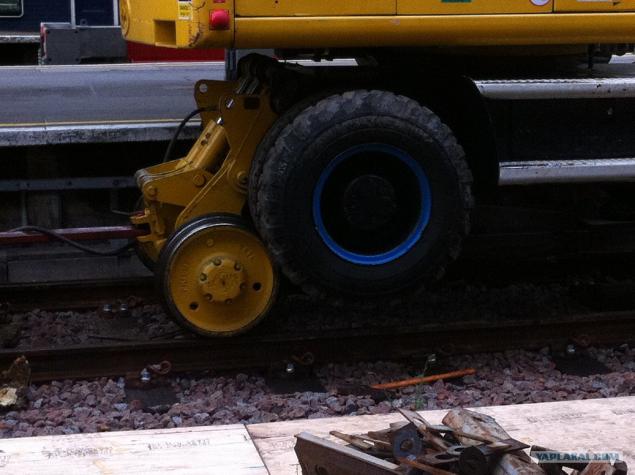

22.
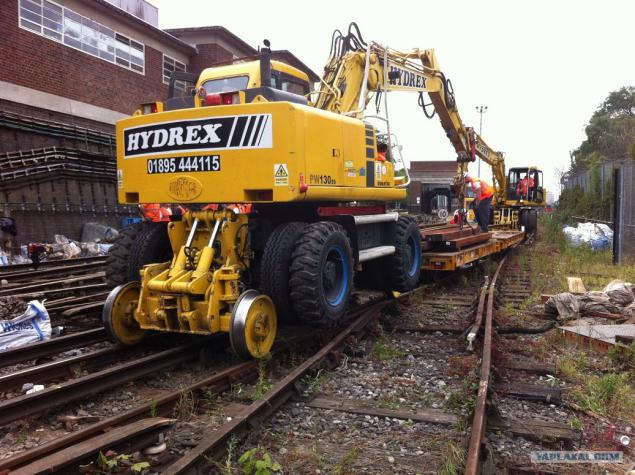

23. Well, they do not want to work!
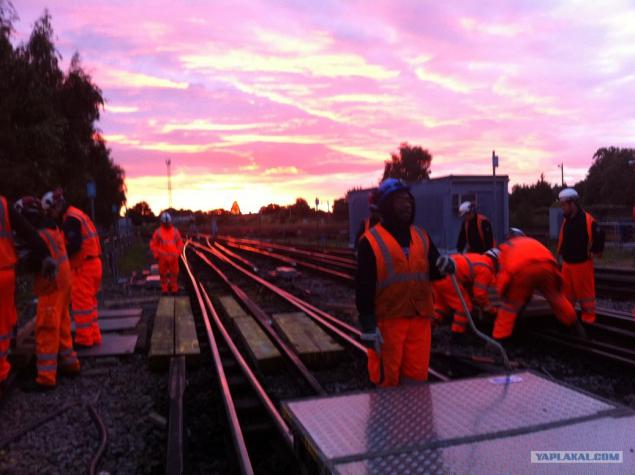

24. This I have seen the sunrise on Sunday morning.

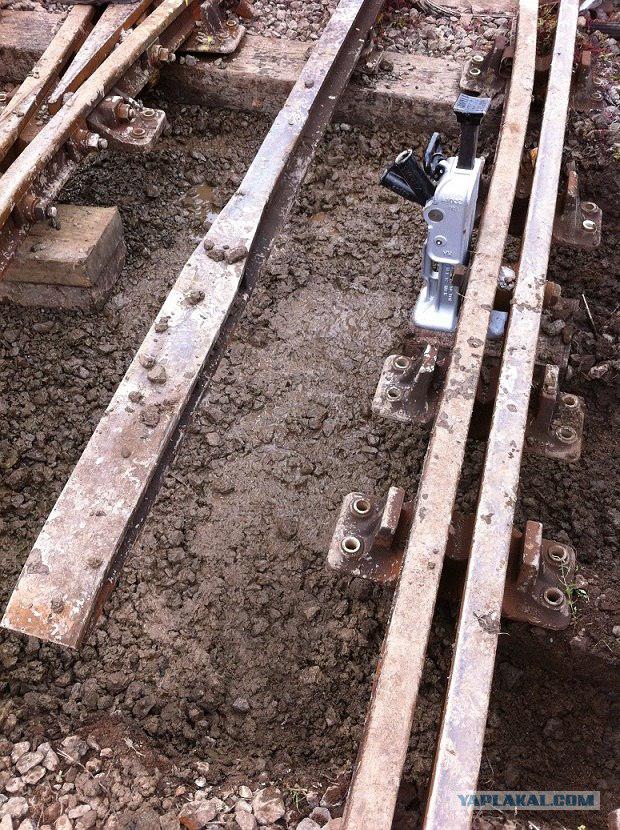
25. Here it is necessary to dig a hole to replace the sleepers. The old railway sleepers have pulled Though this had to lift the whole track.

26. casting sleepers
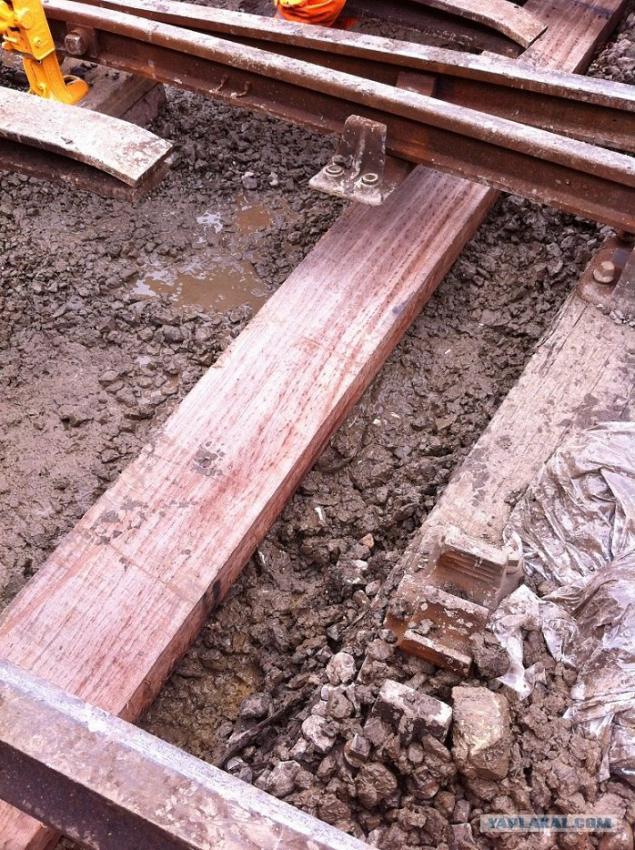

27. At night this place is finished.
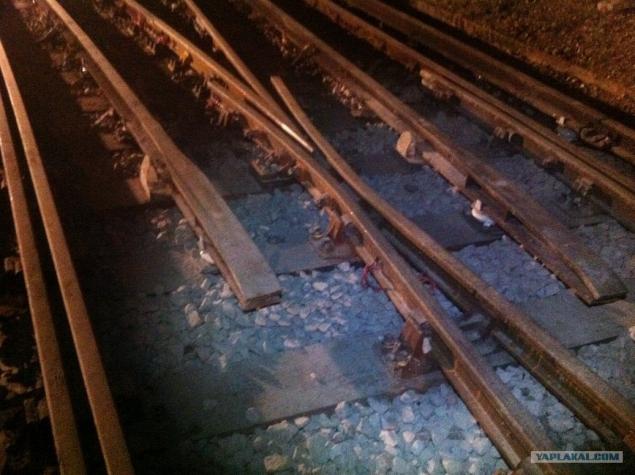

28. General view of the place of work. Day.

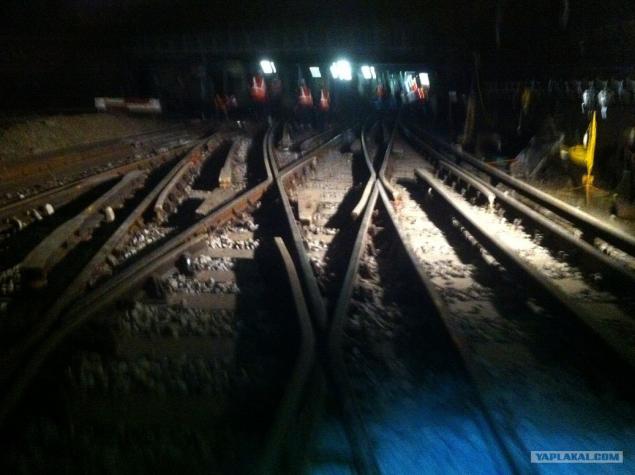
29. And at night. Almost everything is finished, we're leaving. But come is another change that will finish what we did not have time to prepare and track the movement of trains. After all, everyone will be on Monday morning rush to work.
That's all I wanted to say.

Source:
I want to talk a little bit about your work in the London Underground (on the Russian -metro-).
While the majority of normal people sleep, we work under the ground, and not just as part of the 270 subway stations and 408 kilometers of tracks.
Here is a small excerpt from the Wiki - London Underground - a system of underground lines in London (UK), combining ground and underground lines. London Underground - the oldest and one of the largest in the world. Londoners called the metro the Underground («subway"), or more frequently Tube («pipe"), most in the form of deep tunnels.
London Underground Work began January 10, 1863, much of the original route is now included in the line Hammersmith & City.
As of the 2010 London Underground includes 270 stations, length of routes - more than 253 miles (408 kilometers). Some of the stations and tunnels are closed today. London Underground Passenger traffic in 2008 amounted to 1.09 billion people, or about 3 million people a day.
01 photo. Upon entering we were met by a sign informing about the requirements of workwear and protection and who can provide first aid

History
The underground passages were used for thousands of years in the mining, water supply, and for military purposes. At the beginning of the XIX-th century on the main streets of London it was overcrowded due to the diversified transport of those times, not to mention pedestrians. Thousands of people every day crossed the Thames - by ferry or London Bridge. Because of the constant traffic jams from the merchants disappeared in the sun fruits and vegetables, which they tried to take to the market.
Marc Brunel Izambard - French engineer who lived in England - an idea that makes London streets eventually could to unload. Once Brunel watched as the ship worm paves the way for solid oak sliver. Bruyneel said that only a small head covered with a rigid clam shell. With its jagged edges worm bored into the tree. Delving, he left on the walls of a smooth stroke protective layer of lime. Taking this principle as a basis, a large cast iron Brunel patented tunneling shield that pushed underground jacks. Workers were able to remove the shield from the ground, but he could not prevent the collapse of the breed. Shield deep into the rock, and other workers formed a tunnel reinforce brickwork.
Applying this shield, Bruyneel has successfully built the world's first underwater tunnel, padded in soft soil - under the Thames - in 1843. Thus Brunel demonstrated the possibility of building tunnels and paved the way for the development of the modern metro.
In 1863 she opened the world's first underground line of the road, connecting London's main railway stations, and in 1865 bought Brunel tunnel to extend the line. The tunnel now forms part of the London Overground Overground.
London Underground was the first subway in the world. At the time, the railroad has already enjoyed great success in this regard, the proposal of one of London's lawyer about the construction of the underground city rail found supporters. Four years later, he built the first subway station, he ran from the station of Bishop's Road to Farringdon Road. At the time, London Underground was able to carry on the day to 40 000 passengers, and by 1880 it transported 40 million passengers a year. We are expanding rapidly, and other lines, which led to the fact that in 1884 was crowded and Central Line.
The first tunnels were built using conventional construction methods, that is, open way. The streets are dug to a depth of 10 meters, laid rails, built stone arch, then the whole structure obkladyvali brick and paved street again. The main drawback of this method has been many months Stopping streets where construction works were carried out. Open pit was built "Orange Line", the construction of which has caused the destruction of several houses from Paddington Station Bayswater.
The first London subway trains were steam. They worked on coal and emitted an awful fumes. Initially, the cars were divided into three classes. Hand luggage strengthened between the cars. The first time cars were completely devoid of windows, as it was thought to look under the ground is still not what. However, this design caused passengers psychological discomfort, so it was soon arranged production cars of the modern type.
When the train came on electricity, ventilation ceased to be a problem as acute and tunnels started to make deeper. For its construction were used for the first time so-called "drilling shields' cylindrical shape (the shape of the tunnel). The system today is a major in the construction of underground tunnels.
During the construction of the Victoria line was first used jointed ring finishing tunnels, but the system has not received the recognition due to lack of stability of the structure. The main part of London Underground stations built decorated with iron tubing, on the principle of Brunel.
The first electrified line linked the district with the City South London Railway, thereby became a reliable transport links. Switching to electric traction began in 1890 and ended in 1906.
In the early XX century, the coexistence of the six independent lines caused certain inconvenience to passengers; in many places to go from one line to the other people had to go some distance above the ground. The costs to eliminate many of the problems were great, leaving many companies operating underground, turned to the financiers to allocate their money to eliminate a lot of inconvenience, as well as to fully electrify the Metro.
In the future, the construction of the underground were involved in the new company and the company, which led to a fragmentation of structures and diverse nature of the lines. In 1933, the London Underground system was transferred to a specially created "Directorate of Urban Transport." Due to the types of devices and structures subway have become more standard than they were before.
Also, work began on the construction of new lines and stations, but they were interrupted by World War II. During the war the metro was used as a bomb shelter. London authorities initially prevented this, but then still gave permission: at stations posted beds, toilets and clinics.
On December 23, 2007 the East London Line (orange) has been closed for renovation. During the reconstruction of the line has been completely remodeled and expanded. April 27, 2010 the line came in the elevated Overground, cruising through the new trains - they will be an important link to the Transport for London 2012 Olympics. (Wikipedia)
Work carried out after midnight and till the morning and close at the weekend 2-3 metro line and then there work crews being replaced every 12 hours until Monday morning vlot.
constantly and gradually upgrade all the systems, changing the rails, sleepers, cable system signals.
Each photo will sign individually to make it clear what is and what is used when finished will tell.
02. since the subway is not running and escalators, too. We have spuskatsya stairs

03.V bottom met us mountains of tools and materials. Orange pieces on the left are called Ironmen and are used for lifting and transporting rail at close range.

04. Just kind of platform free of crowds.

05.Vot we tunnel. One pair of rails for the train wheels and one for the current supply. In the middle of a negative voltage of 280 volts and 420 volts positive side, and the train of voltage is supplied to the 700 volts.

06. recently begun to change the current supply rails from steel to aluminum.
That is one of the new

07. It is held here on such centers.
In English it is called POT.

08. Type of mounting rails. Very convenient to be dismantled.

09.Passage. A small tunnel between the subject on which the trains are.

10. The entire tunnel consists of the following blocks of twisted metal bolts hell knows when
11. And of course, the cable in the tunnel binding

12. The light comes on automatically when the voltage is turned off on the tracks

13. All the tools are powered from the power outlets here such 120 volts. which are located every 50 meters

14.

15. A little talk about tools.
Ironmen - For lifting and transportation of rail.

16. Saw Cutting rail

17. Pedestrian stacker for transporting tools and materials

18. motorized four passengers Can be used with a trailer, working from 8 akamulyatorov.

19. A little closer

20. Also, in an open area that's very helpful to such machines. It arrives on the ground and then easily drives onto the track

21

22.

23. Well, they do not want to work!

24. This I have seen the sunrise on Sunday morning.

25. Here it is necessary to dig a hole to replace the sleepers. The old railway sleepers have pulled Though this had to lift the whole track.

26. casting sleepers

27. At night this place is finished.

28. General view of the place of work. Day.

29. And at night. Almost everything is finished, we're leaving. But come is another change that will finish what we did not have time to prepare and track the movement of trains. After all, everyone will be on Monday morning rush to work.
That's all I wanted to say.

Source: